Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
4.6.2 Microgrinding Tools: 4.6.2.1 Abrasive Types
Transféré par
pkjhan13530 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6K vues1 pageMicrogrinding Toolss
Titre original
Microgrinding Toolss
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMicrogrinding Toolss
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
6K vues1 page4.6.2 Microgrinding Tools: 4.6.2.1 Abrasive Types
Transféré par
pkjhan1353Microgrinding Toolss
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Microgrinding 91
4.6.2 Microgrinding Tools
4.6.2.1 Abrasive Types
Diamond and cBN are the two most widely used abrasives in microgrinding operations.
There are two types of diamond—naturally occurring and synthetically manufactured.
Both have very high wear resistance, heat conductivity, hardness, and low coefficient of
friction. But the major drawback of diamond abrasives is their high chemical reactivity
with some metallic materials that results in the transformation of diamond into its graph-
ite form. Consequently, diamond abrasives are used only for grinding of brittle nonferrous
materials such as silicon, glass, and ceramics. Sometimes, diamond grains are coated with
suitable materials that prevent oxidation and thereby improve the grinding ratio during
the grinding process. Another approach to extend the life of the abrasive tool is to use
blocky, coarse-grained diamond grits that have higher abrasion resistance and better ther-
mal stability. Sometimes, ordinary grinding wheels are coated with polycrystalline dia-
mond films obtained by the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process. The sharp edges of
the microsized diamond crystallites are used for micropencil grinding tools. Further, cBN
has superior thermochemical stability compared to diamond. It can be used for grinding
those ferrous materials that react chemically with diamond.
4.6.2.2 Bonding of Abrasive Tools
The major bond systems used in grinding wheels are (i) metallic, (ii) resinoid, and
(iii) vitrified. Metal bonding can be separated into two different types: sintered metal bond-
ing and electroplating. In ultraprecision grinding, the sintered metal bond system is used
for thin wheels that cut brittle materials, for example, silicon wafers (slicing/dicing) [25], or
for micropencil grinding tools [26]. Often, electroplated metal bonding is applied to single-
layered grinding wheels with stochastically or well-defined positioning of the grains [27].
High heat conductivity and good wear resistance are the major benefits of metal-bonded
grinding tools.
Resin-bonded grinding wheels are normally used for rough grinding or abrasive
machining purposes. For ultraprecision grinding, epoxy or polyester resins are used to
generate high surface qualities by soft, smooth grinding or polishing, for example, in sili-
con wafer grinding.
Vitrified bonds have a glass-like structure and are fabricated at high temperatures from
mineral fluxes such as feldspars, firing clays, ground glass frits, and chemical fluxes [28].
Vitrified bonds have higher strength and are easier to dress. The elastic modulus is almost
four times higher than the resin bonding.
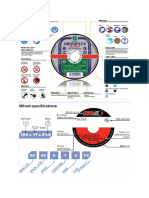
4.6.2.3 Geometry of the Grinding Wheels Used in Microgrinding Operations
Most grinding wheels applied in ultraprecision grinding are made with diverse design
concepts, for example, with undefined or defined grain settings, grooved wheels, or cup
wheels. Typically, the wheel diameter ranges from 50 to 400 mm and the grain sizes from
fine grained (∼0.125 mm) to coarse grained (∼200 mm). Such grinding wheels are used for
machining of materials such as silica, silicon, compound semiconductors, and materials
used in electronics components.
Grinding wheels with undefined grain settings are the most widely used type, and they
are applied with radial feed for surface grinding of optical products such as lenses and
mirrors. Cup wheels are a special type of grinding wheel in which the grains, instead of
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Self-healing Ceramic Matrix Composites: A MonographD'EverandSelf-healing Ceramic Matrix Composites: A MonographPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Production and Process3Document35 pagesAdvanced Production and Process3christo royPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2Document5 pagesCH 2alsltanyhasanPas encore d'évaluation
- MP Unit 4 GrindingDocument25 pagesMP Unit 4 GrindingJ S VAISHNAVPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling AbrasivesDocument78 pagesSterling AbrasivesITL200_UPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Process - Module5.0Document15 pagesManufacturing Process - Module5.0Fiza KamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To GrindingDocument8 pagesIntroduction To GrindingsreeshpsPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Metallography: Faculty of Production Engineering and ManagementDocument18 pagesPractical Metallography: Faculty of Production Engineering and ManagementMassimo FumarolaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12.solar Grinding MachineDocument43 pages12.solar Grinding Machinesathish33% (3)
- CA04 ParchamentoJVMDocument6 pagesCA04 ParchamentoJVMJohnrey ParchamentoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diamond Abrasive Based Cutting ToolDocument10 pagesDiamond Abrasive Based Cutting ToolCristian castroPas encore d'évaluation
- Abrasive Machining Processes: Grinding Lapping HoningDocument61 pagesAbrasive Machining Processes: Grinding Lapping HoningshivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Machining by AbrasionDocument7 pagesMachining by AbrasionSiddhi JainPas encore d'évaluation
- ,,knkjkjk1 s2.0 S0924013605004000 Main PDFDocument7 pages,,knkjkjk1 s2.0 S0924013605004000 Main PDFKarissa ElvinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Solar Grinding MachineDocument43 pages12 Solar Grinding MachineSaikumar GoliwadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Krishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesKrishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringVivek BajpaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Machining and Tools 9 PDFDocument15 pagesMachining and Tools 9 PDFAman KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceramics, Glass, Graphite, Diamond, and Nanomaterials: Structure, General Properties, and ApplicationsDocument26 pagesCeramics, Glass, Graphite, Diamond, and Nanomaterials: Structure, General Properties, and ApplicationsReal MePas encore d'évaluation
- Processing and Characterization of Impregnated Diamond Cutting Tools Using A Ferrous Metal MatrixDocument9 pagesProcessing and Characterization of Impregnated Diamond Cutting Tools Using A Ferrous Metal MatrixWinterstone W. DiamantPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Grinding and Realated OperationsDocument23 pages5 Grinding and Realated OperationsSaiful IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Finish ProcessesDocument7 pagesSurface Finish Processesapi-19790673Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mme203: Introduction To Metallurgical and Materials EngineeringDocument8 pagesMme203: Introduction To Metallurgical and Materials EngineeringKupoluyi VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Grinding PDFDocument106 pagesGrinding PDFvivekanand100% (2)
- Diamond Tool: History Advantages CategoriesDocument7 pagesDiamond Tool: History Advantages CategoriesRohmat DhoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceramics 1Document7 pagesCeramics 1Andrea DouglasPas encore d'évaluation
- Precision ManufacturingDocument18 pagesPrecision ManufacturingUrgie KuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2surjitPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Technology CAT 2 AnswersDocument4 pagesMachine Technology CAT 2 Answerskibwanajuma4956Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision On CeramicsDocument24 pagesRevision On Ceramicsnaz299971Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Iv Abrasive Processes and Gear Cutting: 4.1 GrindingDocument30 pagesUnit Iv Abrasive Processes and Gear Cutting: 4.1 Grindingrkscad11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-10 Grinding and FinishingDocument121 pagesCh-10 Grinding and FinishingMANJEET KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- MachiningDocument8 pagesMachiningBotstrap AWPas encore d'évaluation
- BTI1133 Ch26Document74 pagesBTI1133 Ch26ACC SHPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT V - Ceramics-Composites-Nano MaterialsDocument59 pagesUNIT V - Ceramics-Composites-Nano MaterialsHarsha MallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grinding Wheels Specification PDFDocument4 pagesGrinding Wheels Specification PDFPENONVVPas encore d'évaluation
- Deburring & Polishing Media and CompoundsDocument24 pagesDeburring & Polishing Media and CompoundsVivek GroverPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1 Grinding: ContentsDocument38 pages4.1 Grinding: Contentssh7shahidhaheelPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 - Abrasive Machining & Finishing OperationsDocument80 pages04 - Abrasive Machining & Finishing OperationsAbdul Moiz0% (1)
- CeramicDocument18 pagesCeramicIrfan DanialPas encore d'évaluation
- Diamond-Like Tools-1Document4 pagesDiamond-Like Tools-1Alberto VelazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Abrasion: Mineral PolishingDocument5 pagesMechanics of Abrasion: Mineral PolishingThulasi RamPas encore d'évaluation
- 5a AffDocument17 pages5a AffHARSHVARDHAN SINGH RATHOREPas encore d'évaluation
- Lubricants 11 00122Document52 pagesLubricants 11 00122Vivek Sriram R ed21d026Pas encore d'évaluation
- MMC 1Document16 pagesMMC 1Manjunath ShettarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ductile or Partial Ductile Mode Machining of Brittle MaterialsDocument7 pagesDuctile or Partial Ductile Mode Machining of Brittle MaterialsHangi TakimlisinPas encore d'évaluation
- Diamond PDFDocument6 pagesDiamond PDFPrashant ParshivnikarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceramic AmericaDocument9 pagesCeramic AmericaRoger Antonio Suarez SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectroceramicsDocument16 pagesElectroceramicsaisveryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Report CUMI - Correct.Document28 pagesReport CUMI - Correct.Dinesh guhan50% (2)
- RameshwarDocument6 pagesRameshwarBhawesh Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceramics: Presentation By: Sam-Bandawe Wesley A. Juma Mcdonald KDocument23 pagesCeramics: Presentation By: Sam-Bandawe Wesley A. Juma Mcdonald Kmcdonald jumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1Arun DegaonkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Session: 1: MetallographyDocument4 pagesLab Session: 1: MetallographyaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV GRINDING MACHINE 4 SEM MP GCOE S N GANDHAREDocument10 pagesUnit IV GRINDING MACHINE 4 SEM MP GCOE S N GANDHARE40 siddhesh petkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Metallic Materials Used For Machine Elements2Document42 pagesNon Metallic Materials Used For Machine Elements2RajanikantJadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Grinding and Grinding MachineDocument67 pagesGrinding and Grinding MachineTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHER100% (1)
- Lecture 4 (Read-Only)Document10 pagesLecture 4 (Read-Only)Md RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2000 - Metallic Binders For Diamond Tool ProductionDocument11 pages2000 - Metallic Binders For Diamond Tool ProductionWinterstone W. DiamantPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications and Processing of Ceramics Word FileDocument8 pagesApplications and Processing of Ceramics Word FileahmedkhalidhussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Abrasive Machining Processes: N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT KanpurDocument29 pagesAbrasive Machining Processes: N. Sinha, Mechanical Engineering Department, IIT KanpurRaghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engg.: Gurukul Institute of Engineering & Technology, KotaDocument18 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engg.: Gurukul Institute of Engineering & Technology, Kotapkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bainite Transformation An Intermediate TemperatureDocument3 pagesBainite Transformation An Intermediate Temperaturepkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- PCB Quick Quote: Total Amount For PCB PrototypingDocument3 pagesPCB Quick Quote: Total Amount For PCB Prototypingpkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer Location (2007)Document1 pageBuffer Location (2007)pkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Science of Lean Production (2007)Document1 pageThe Science of Lean Production (2007)pkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of StrategyDocument1 pageThe Role of Strategypkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer Flexibility (2007)Document1 pageBuffer Flexibility (2007)pkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water Quantity IndexDocument1 pageWater Quantity Indexpkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- BSH Bosch Und Siemens Hausgeräte GMBHDocument1 pageBSH Bosch Und Siemens Hausgeräte GMBHpkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Global Products - at The CoalfaceDocument1 pageGlobal Products - at The Coalfacepkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic TransmissionsDocument1 pageAutomatic Transmissionspkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Transmission CouplerDocument1 pageAutomatic Transmission Couplerpkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Low Temperature CombustionDocument1 pageLow Temperature Combustionpkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Transmission CouplerDocument1 pageManual Transmission Couplerpkjhan1353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Cu-Cr Alloy For Wear Resistance ApplicationDocument27 pagesDevelopment of Cu-Cr Alloy For Wear Resistance Applicationraghavendrajoshi87Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM C989 C989M 18aDocument3 pagesASTM C989 C989M 18amohaliaziz8Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Chemical KineticsDocument96 pages4 Chemical KineticsKenny Jay LabianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Pollution and Control EngineeringDocument10 pagesAir Pollution and Control EngineeringVINOTHKUMAR SAMPATHPas encore d'évaluation
- Biogenic Amines in Meat and Meat Products and Its Public Health Significance: A ReviewDocument15 pagesBiogenic Amines in Meat and Meat Products and Its Public Health Significance: A ReviewTrương Thị Thanh TuyếtPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Chemistry Module 1 Day 1 PDFDocument8 pagesConsumer Chemistry Module 1 Day 1 PDFPrincess Loraine Duyag100% (2)
- KNTE Patent ApplicationDocument32 pagesKNTE Patent ApplicationCharles GrossPas encore d'évaluation
- TDS TIS 331 Anti Drift AdjuvantDocument3 pagesTDS TIS 331 Anti Drift Adjuvantmuhammad imranPas encore d'évaluation
- ART Coumarins Thee Antimicrobial AgentsDocument9 pagesART Coumarins Thee Antimicrobial AgentsHECTORIBZAN ACERO SANDOVALPas encore d'évaluation
- "Toja" Shower Column Set Tx492Stn: Specifications Troubleshooting InstallationDocument1 page"Toja" Shower Column Set Tx492Stn: Specifications Troubleshooting InstallationAndrianus EffendyPas encore d'évaluation
- Act5 BATCH MANUFACTURING RECORDDocument4 pagesAct5 BATCH MANUFACTURING RECORDIsabel PeraltaPas encore d'évaluation
- Studi in Vitro Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kamboja (Plumeria Alba) Sebagai AntiDocument12 pagesStudi in Vitro Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kamboja (Plumeria Alba) Sebagai AntiingelitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment of Welded JointsDocument17 pagesHeat Treatment of Welded JointsErick HoganPas encore d'évaluation
- RESEARCHDocument2 pagesRESEARCHLorenzo CohenPas encore d'évaluation
- ALOHA ExamplesDocument57 pagesALOHA Examplesanwar318Pas encore d'évaluation
- Template - SAS Module 2 - Classification of Cosmetics and Its IngredientsDocument20 pagesTemplate - SAS Module 2 - Classification of Cosmetics and Its IngredientskatePas encore d'évaluation
- Fenrg-09-690725 LCA Palm HVODocument10 pagesFenrg-09-690725 LCA Palm HVOphimentPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaning Validation: Eun-Sook Gi April 12, 2004Document35 pagesCleaning Validation: Eun-Sook Gi April 12, 2004wkm782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Promatect-H SDSDocument6 pagesPromatect-H SDSjeffPas encore d'évaluation
- Ferolite Nam 32 Steel PDFDocument2 pagesFerolite Nam 32 Steel PDFMittapelly praveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy351 Case Study: CopperDocument18 pagesPhy351 Case Study: CopperDayini FarhanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Fibre Fishing Pole Repair Kit InstructionsDocument4 pagesCarbon Fibre Fishing Pole Repair Kit InstructionsdaveagriffPas encore d'évaluation
- The List by INDITEX. III Edition - 2017 PDFDocument722 pagesThe List by INDITEX. III Edition - 2017 PDFxuân ba caoPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome My Presentation ToDocument15 pagesWelcome My Presentation ToMay Hnin WaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MTT - Sigma AldrichDocument2 pagesMTT - Sigma AldrichFellicia RachmadianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Technology of Edible Coating Production - A ReviewDocument7 pagesRecent Technology of Edible Coating Production - A ReviewalvinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phillips 13 Cap 7Document27 pagesPhillips 13 Cap 7Alejandra CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Book of Abstracts - Prosciba 2023Document304 pagesBook of Abstracts - Prosciba 2023Jonatas LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Hardening of SteelDocument50 pagesSurface Hardening of SteelTeptep GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Stabilised Mud Blocks Reinforced With Treated With Coconut FibersDocument4 pagesSoil Stabilised Mud Blocks Reinforced With Treated With Coconut FibersKi KiethPas encore d'évaluation
- The Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneD'EverandThe Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelD'EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemD'EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureD'EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tD'EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (27)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70ED'EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (6)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesD'EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (9)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisD'EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesD'Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (28)
- The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsD'EverandThe Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Thinking and Innovation Metrics: Powerful Tools to Manage Creativity, OKRs, Product, and Business SuccessD'EverandDesign Thinking and Innovation Metrics: Powerful Tools to Manage Creativity, OKRs, Product, and Business SuccessPas encore d'évaluation
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesD'EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsD'EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersD'EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesD'EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsD'EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- The Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableD'EverandThe Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginablePas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsD'EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersD'EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Articulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceD'EverandArticulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (19)