Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
X-Ray Interpretation PDF
Transféré par
Naveen KovalDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
X-Ray Interpretation PDF
Transféré par
Naveen KovalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
X-RAY
INTERPRETATION
1 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
X- RAYS
Definition: They are a Form of Ionizing Radiation That Can Penetrate the Body to
Form an Image On Film.
Types of Chest X- Ray:
* Plain X-Ray (Without Contrast)
* Contrast X-Ray (With Contrast).
--------------------------------------------------------------
CHEST X- RAY
It is the Most Common X-Ray Used in Medicine Field.
It Can Help Us to Diagnose Many Respiratory and Cardiovascular Problems.
View of Chest X- Ray:
1- Postero-Anterior View (P-A View):
It Means Source of Radiation From Behind of Patient, and the Film From Front.
This View is the Most Common View Used in Chest X-Ray.
and Done For the Patient Who Can Walk and Stand.
2- Antero-Posterior View (A-P View):
It Means Source of Radiation From Front of Patient, and the Film From Behind.
This View Done For the Patient Who Can’t Walk OR Stand OR Patient with Coma
OR in ICU OR Emergency Patients.
This View Show Us False Cardiomegaly.
3- Lateral View:
It Means Source of Radiation From Side of Patient, and the Film From Other Side.
How to Differentiate Between P-A View and A-P View:
P-A Chest X-Ray: A-P Chest X-Ray:
1. The Clavicles Appears Like V- Shape. 1. The Clavicles Appears Horizontal Shape.
2. The Scapula Appears in the Periphery of the 2. The Scapula Appears in the Center of the
Chest. Chest.
2 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Detection of Right and Left Lung of Chest X- Ray:
Left Lung Characters: Right Lung Characters:
1. Presence of Aortic Knuckle. Normally the Base of Right Lung is Elevated
2. Presence of Apex (Left Ventricle) of the Heart. More than Left Lung; Because of Right Dome
3. Presence of Gases of the Stomach. Diaphragm is Higher than Left Dome of
Diaphragm.
3 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Centralization of Chest X- Ray:
Well Centralized Chest X-Ray: Not Centralized Chest X-Ray:
Means Distance From Vertebral Spine to Medial Also Called Rotated Chest X Ray.
End of Right Clavicle is Equal to Distance From Means Distance From Vertebral Spine to Medial
Vertebral Spine to Medial End of Left Clavicle. End of Right Clavicle is Not Equal to Distance
From Vertebral Spine to Medial End of Left
Clavicle.
Quality of Chest X- Ray:
Poor Exposure: Vertebral Spines Behind the Heart Can NOT Be Seen.
Good Exposure: Vertebral Spines Behind the Heart Slightly Seen.
Over Exposure: Vertebral Spines Behind the Heart Clear and Visible.
Intensity of Chest X- Ray:
*Air: Appear Black.
*Soft Tissue: Appear Gray.
*Fluid and Bone: Appear White.
4 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Degree of Inspiration of Chest X- Ray:
Full Inspiration.
Usually Chest X Ray Taken During
Number of Anterior Ribs in X-Ray During Full Inspiration are 6 Ribs.
& Number of Posterior Ribs in X-Ray During Full Inspiration are 10 Ribs
So;
If You Count 6 Anterior Ribs; That Means Chest X-Ray Taken In Full Inspiration.
If You Less than 6 Anterior Ribs; That Means X-Ray Not Take In Full Inspiration.
If You More than 6 Anterior Ribs; That Means Hyper-Inflated Chest X-Ray.
Note:
Chest X-Ray Can Be Taken During Expiration in Case of:
1. Small Pneumonia.
2. Foreign Body Aspiration.
Zones of Lung in Chest X- Ray:
Upper Zone: Above 2nd Anterior Rib.
Middle Zone: Between 2nd and 4th Anterior Rib.
Lower Zone: Below 4th Anterior Rib.
5 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
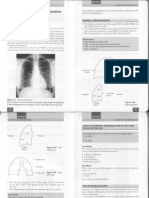
Features of Normal Chest X-Ray:
6 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Abnormalities of Chest X-Ray:
Abnormalities of Pleura:
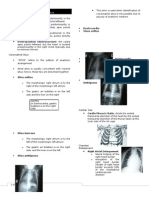
1. Pleural Effusion:Pathological Accumulation of Fluid in Pleural Space (>50ml)
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
1. Obliteration of Costo-Phrenic Angle.
2. Homogenous Opacity.
3. Crescent Shape of Lower Border (Meniscus Sign).
7 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Massive Pleural Effusion:
1. Homogenous Opacity All Over the Hemi-Thorax (White Lung).
2. Deviation of Mediastinum to the Opposite Side.
8 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
2. Pneumothorax: Accumulation of Air in Pleural Space.
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
1. Jet Black Lung Field (Loss of Lung Marking).
2. Lung is Deflated (Collapsed Lung).
9 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Tension Pneumothorax:
1. Jet Black Lung Field All Over The Hemi-Thorax.
2. Shifting of Mediastinum to the Opposite Side.
10 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
3. Hydro-Pneumothorax: Could Be Pyo-Pneumothorax (Air + Pus) OR
Heamo-Pneumothorax (Air + Blood).
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
Air Fluid Level of Lung Field (Upper Half Black & Lower Half White).
11 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Abnormalities of Lung Tissue (Lung Parenchyma):
1. Hyper-Inflated Chest: Commonly Presented with COPD Patients.
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
1. More Darkness of Lung. 2. Number of Anterior Ribs More than 6 Ribs.
3. Horizontal Anterior Ribs. 4. Wide Inter-Costal Space.
5. Tubular Shape Heart. 6. Flat Diaphragm.
12 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
2. Lung Cavity: Could Be Complete Black Cavity OR Air Fluid Level Cavity.
Complete Black Cavity: Air Fluid Level Cavity:
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:- In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
Single, Black, Rounded OR Oval Lesion Surrounded Single, Rounded OR Oval Lesion with Black Upper
By White Wall. Half & White Lower Half, Surrounded By
White Wall.
Differential Diagnosis of Complete Black Cavity: Differential Diagnosis of Air Fluid Level Cavity:
1. Pulmonary TB. 1. Lung Abscess (Regular Wall).
2. Broncogenic Carcinoma (Squamous Cell Type). 2. Rupture Hydatid Cyst.
3. Chronic Abscess. 3. Cavitatory Carcinoma.
4. Wegener’s Granulomatosis (Multiple Cavitation). 4. Aspergilloma.
5. Emphysematous Bullae (Multiple Cavitation
Small & Surrounded By Thin Wall).
13 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
3. Lung Mass (>3cm): Could Be Single Mass OR Multiple Masses.
Single Lung Mass: Multiple Lung Masses:
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:- In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
Single, White to Gray, Rounded OR Oval Lesion. Multiple, White to Gray, Rounded OR Oval Lesion.
Differential Diagnosis of Single Lung Mass: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Lung Masses:
1. Bronchogenic Carcinoma (Irregular Border). 1. Secondary Lung Metastasis OR Cannon Ball
2. Single Lung Metastasis. (From Renal Cell Carcinoma, Testicular Carcinoma,
3. Hydatid Cyst (Regular Border). Choriocarcinoma).
4. Lymphoma. 2. Septic Emboli.
5. Aspergilloma. 3. Wegener’s Granulomatosis.
6. Others: Hamartoma, Lipoma. 4. Caplan’s Syndrome of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
14 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
4. Reticulo-Nodular Shadow (Lung Nodules <3cm):
Indicate Pulmonary Fibrosis.
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
Multiple, White to Gray, Small, Nodules with Reticular Infiltration Starting From
Periphery Up to Center of the Lung.
Differential Diagnosis of Reticulo-Nodular Shadow:
1. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Most Common 50% (Apical Lung Fibrosis).
2. Silicosis (Apical Lung Fibrosis).
3. Asbestosis (Basal Lung Fibrosis).
4. Sarcoidosis.
5. Connective Tissue Diseases (Rheumatoid Arthritis, SLE).
15 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Note:
Miliary TB in X-Ray Characterized By Formation of Multiple, White to Gray, Very Small,
Tiny Nodules (Millimeters in Size).
16 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
5. Reticular Shadow (Trabecular Shadow): Indicate Pulmonary Edema.
In Chest X Ray Characterized By:-
Reticular Infiltration Starting From Center to Periphery of Lung;
Characterized By ABCD:
A Alveolar Edema (Butterfly Edema OR Bath Swing Sign).
B B- Line Due to Interstitial Edema (Reticular Infiltration).
C Cardiomegaly.
D Dilated Upper Lobe Vessels.
17 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Abnormalities of Trachea & Mediastinum:
1. Deviation of Trachea & Mediastinum: Could Be Pushed OR Pulled;
Pushed Trachea & Mediastinum:
Deviation to the Opposite Side.
Causes:
1. Massive Pleural Effusion.
2. Tension Pneumothorax.
18 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Pulled Trachea & Mediastnum:
Deviation to the Same Side.
Causes:
1. Lung Collapse.
2. Post Pneumonectomy.
19 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
2. Widening of Mediastinum:
Differential Diagnosis of Wide Mediastinum:
1. Para Tracheal Lymphadenopathy ( Due to; Pulmonary TB, Lymphoma, CA Lung).
2. Aortic Aneurysm. 3. Retro-Sternal Goiter.
4. Achalesia. 5. Thymoma.
20 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Abnormalities of Hilum:
1. Enlargement of Hilar Shadow:
Normally the Hilum Lies Between 2nd & 4th Rib,
It Contains: Lymph Nodes, Bronchus, and Blood Vessels.
Differential Diagnosis of Enlarged Hilar Shadow:
1. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis.
2. Lymphoma.
3. Cancer Lung (Bronchogenic Carcinoma).
4. Pulmonary TB.
5. Mycoplasma Pneumonia.
21 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Abnormalities of Cardiac Shadow:
1. Cardiomegaly: Measured From P-A View Chest X Ray.
Cardiomegaly Detected in Chest X Ray By Cardio-Thoracic Ratio.
Cardio-Thoracic Ratio Cardiac Shadow Less than 50% of Thoracic Diameter.
In Case of Cardiomegaly; Cardiac Shadow More than 50% of Thoracic Diameter.
2. Flask Shape Heart: Indicate Pericardial Effusion.
3. Tubular Shape Heart: Indicate COPD.
22 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Abnormalities of Diaphragm:
1. Elevation of Diaphragm Dome: Indicate Phrenic Nerve Palsy, Lung
Collapse, Pneumonectomy OR Lower Lobectomy, Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly.
2. Air Under Diaphragm: Indicate Perforated Viscous
(Ex Perforated Peptic Ulcer).
Differential Diagnosis of Differential Diagnosis of
Homogenous Opacity of the Lung: Hometrogenous Opacity of the Lung:
1. Pleural Effusion. 1. Interstitial Lung Disease.
2. Lung Collpase. 2. Pulmonary Edema.
3. Lobar Pneumonia. 3. Broncho Pneumonia
23 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
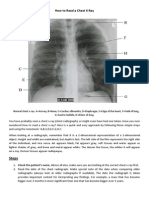
How to Read X-Ray Film:
1. Check From Name, Age, Date.
2. Make Sure If the X-Ray was Plain OR with Contrast
3. Make Sure From View of X-Ray P-A View OR A-P View.
P-A View (Postero-Antero View) (Common View) Clavicles Appears V- Shape.
A-P View (Antero-Postero View) Clavicles Appears Horizontal Shape.
4. Make Sure If the X-Ray was Well Centralized OR NOT.
Distance From Vertebral Spine to Medial End of Right Clavicle is Equal to
Distance From Vertebral Spine to Medial End of Left Clavicle.
24 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
5. Check From Quality of X-Ray.
Poor Exposure: Vertebral Spines Behind the Heart Can NOT Be Seen.
Good Exposure: Vertebral Spines Behind the Heart Slightly Seen.
6. Now Look For Any Abnormalities in Pleural Space:
Look For Any Obliteration of Costo-Phrenic Angle;
Obliteration of Costo-Phrenic Angle, Homogenous Opacity, Crescent Shape
Lower Border (Meniscus Sign) Indicate Pleural Effusion.
Pleural
Effusion
25 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Note:
Obliteration of Costo-Phrenic Angle + Homogenous Opacity All Over the Hemi-Thorax with
Deviation of Mediastinum to the Opposite Side Indicate Massive Pleural Effusion.
Look For Any Jet Black Lung Field;
Jet Black Lung Field with Collapsed Lung Indicate Pneumothorax.
Pneumothorax
26 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Note:
Jet Black Lung Field All Over the Hemi-Thorax with Shifting of Mediastinum to the Opposite Side
Indicate Tension Pneumothorax.
Look For Any Air Fluid Lung Field;
Air Fluid Level of Lung Field (Upper Half Air & Lower Half Fluid) Indicate
Hydro-Pneumothorax (Heamo-Pneumothorax OR Pyo-Pneumothorax).
Hydro-
Pneumothorax
27 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
7. Now Look For Any Abnormalities in Lung Tissue
(Lung Parenchyma Abnormalities):
Look For Any Hyper-Inflated Chest;
More Darkness of Lung, Number of Anterior Ribs More than 6 Ribs, Horizontal
Anterior Ribs with Wide Inter-Costal Space, Tubular Heart & Flat Diaphragm
Indicate Obstructive Airway Disease (Mainly COPD).
Hyper-Inflated Chest:
28 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Look For Any Lung Cavity;
Could Be Complete Black Cavity OR Air Fluid Cavity;
If Complete Black Cavity Indicate Pulmonary TB, Squamous Cell
Type of Bronchogenic Carcinoma, Chronic Abscess.
If Air Fluid Level Cavity Indicate Lung Abscess, Cavitatory
Carcinoma, Rupture Hydatid Cyst, Aspergilloma.
Complete Black Cavity:
Air Fluid Level Cavity:
29 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Look For Any Lung Mass;
Could Be Single OR Multiple;
If Single Mass Indicate Bronchogenic Carcinoma, Single Lung
Metastasis, Hydatid Cyst, Aspergilloma.
If Multiple Masses Indicate Secondary Lung Metastasis, Septic
Emboli, Wegener’s Granulomatosis.
Single Lung Mass:
Multiple Lung Masses (Cannon Ball):
30 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Look For Any Reticulo-Nodular Shadow;
Multiple, White to Gray, Small, Nodules with Reticular Infiltration Starting
From Periphery Up to Center of the Lung Indicate Pulmonary Fibrosis.
31 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Look For Any Reticular Shadow (Trabecular Shadow);
Reticular Infiltration Starting From Center Up to Periphery of the Lung
Indicate Pulmonary Edema.
*Pulmonary Edema* Characterized By:
A Alveolar Edema (Butterfly Edema OR Bath Swing Sign).
B B- Line Due to Interstitial Edema (Reticular Infiltration).
C Cardiomegaly.
D Dilated Upper Lobe Vessels.
32 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
8. Now Look For Any Abnormalities in Mediastinum:
Look For Any Widening of Mediastinum;
IndicatePara Tracheal Lymphadenopathy (Pulmonary TB, Lymphoma, CA Lung),
Aortic Aneurysm, Retro-Sternal Goiter, Achalesia, Thymoma.
33 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
9. Now Look For Any Abnormalities in Hilum:
Look For Any Enlargement of Hilar Shadow;
Indicate Pulmonary Sarcoidosis, Lymphoma, Bronchogenic
Carcinoma (CA Lung), Pulmonary TB, Mycoplasma Pneumonia.
Note:
Normally the Hilum Lies Between 2nd & 4th Rib,
It Contains: Lymph Nodes, Bronchus, and Blood Vessels.
34 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
10. Now Look For Any Abnormalities in Cardiac Shadow:
Look For Any Cardiomegaly;
Cardiac Shadow More than 50% of Thoracic Diameter.
Look For Any Flask Shape Heart;
Indicate Pericardial Effusion.
35 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
11. Now Look For Any Abnormalities in Diaphragm:
Look For Any Elevation of Diaphragm Dome;
Indicate Phrenic Nerve Palsy, Lung Collapse, Pneumonectomy
OR Lower Lobectomy, Hepatomegaly, Splenomegaly.
Look For Any Air Under Diaphragm;
Indicate Perforated Viscous (Ex Perforated Peptic Ulcer).
36 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
37 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
38 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
39 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
40 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
41 DR. MOHCEN AL. HAJ
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basics of Chest X-RayDocument23 pagesBasics of Chest X-RayRabi Dhakal100% (1)
- Chest X-ray Interpretation for Radiographers, Nurses and Allied Health ProfessionalsD'EverandChest X-ray Interpretation for Radiographers, Nurses and Allied Health ProfessionalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chest X-Ray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology OSCEDocument1 pageChest X-Ray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology OSCEValentina SepúlvedaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Read A Chest X RayDocument11 pagesHow To Read A Chest X RayHilmia Fahma100% (2)
- Chest X-RayDocument125 pagesChest X-RayRusda Syawie100% (1)
- Eustachian Tube: Structure, Function, and Role in Middle-Ear Disease, 2eD'EverandEustachian Tube: Structure, Function, and Role in Middle-Ear Disease, 2ePas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Xray Interpretation and Cases For FinalsDocument39 pagesAbdominal Xray Interpretation and Cases For Finalsfahadrock2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cases RadiologyDocument22 pagesCases RadiologyPri Shents100% (1)
- Ultrasound Physics II Fill in The Blank QuestionsDocument5 pagesUltrasound Physics II Fill in The Blank QuestionsAngie MelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chest X Ray Made SimpleDocument103 pagesChest X Ray Made SimpleMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- Clinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenDocument8 pagesClinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenPreeti Joan Buxani100% (1)
- List of Iranian English Journals Indexed in Scopus PDFDocument4 pagesList of Iranian English Journals Indexed in Scopus PDFhusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- USG ImagingDocument26 pagesUSG ImagingskPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Chest X Ray Solutions 2013Document281 pages101 Chest X Ray Solutions 2013Mohamed Saeed El Khayat100% (4)
- Paediatric Radiology QuizDocument11 pagesPaediatric Radiology QuizManju ManjunathPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Chest X-Ray InterpretationDocument11 pages05 Chest X-Ray InterpretationChirayu DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pocket Tutor Chest X-Ray Interpretation 1st PDFDocument233 pagesPocket Tutor Chest X-Ray Interpretation 1st PDFKarthik S100% (1)
- Chest Radiology: Alex Nguyen FSU College of Medicine MS4Document62 pagesChest Radiology: Alex Nguyen FSU College of Medicine MS4First Last100% (1)
- OSCE - Chest PainDocument2 pagesOSCE - Chest PaincgalongPas encore d'évaluation
- RadiologyDocument27 pagesRadiologyGmoa Branchunion Diyathalawasrilanka50% (2)
- O2 - BasketDocument4 pagesO2 - BasketShekky007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hariqbal Singh - Radiology For Undergraduates and General PractitionersDocument250 pagesHariqbal Singh - Radiology For Undergraduates and General PractitionersJeshil ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Navni Garg MBBS, DNB (Radiology)Document79 pagesDR Navni Garg MBBS, DNB (Radiology)Manikandan PerumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasound Physics and Instrumentation Content OutlineDocument19 pagesUltrasound Physics and Instrumentation Content OutlineSherif H. Mohamed100% (1)
- Emergency Radiology MAHMUOD PDFDocument134 pagesEmergency Radiology MAHMUOD PDFCut Nonda MaraciluPas encore d'évaluation
- Chesneys Equipment For Student Radiographers by P H Carter PDFDocument5 pagesChesneys Equipment For Student Radiographers by P H Carter PDFAwadhPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Pages of RadiologyDocument17 pagesSample Pages of RadiologyskPas encore d'évaluation
- Zlib - Pub Radiography Essentials For Limited PracticeDocument657 pagesZlib - Pub Radiography Essentials For Limited PracticeLucjan KrawczyszynPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Pass FCPS Part One in Radiology by KSBDocument5 pagesHow To Pass FCPS Part One in Radiology by KSBksbabar0% (1)
- Vertebral Column Skull Projection MethodDocument8 pagesVertebral Column Skull Projection MethodLaFranz CabotajePas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To PoisoningDocument107 pagesApproach To PoisoningAlex beharuPas encore d'évaluation
- PaediatricDocument172 pagesPaediatricMPas encore d'évaluation
- Mark Rodriguez - Philips Trainee For Excellence - Unofficial Guide To Radiology PDFDocument90 pagesMark Rodriguez - Philips Trainee For Excellence - Unofficial Guide To Radiology PDFdsekulic_1100% (1)
- Cardiology - CVS OSCE ChecklistDocument5 pagesCardiology - CVS OSCE ChecklistPraveenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Xray Kub My Prep FinalDocument109 pagesXray Kub My Prep FinalphoenixibexPas encore d'évaluation
- Basis Chest X-RayDocument59 pagesBasis Chest X-RayadistyPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiology NotesDocument34 pagesRadiology Notesliweiss100% (2)
- Principles of SpectDocument31 pagesPrinciples of Spectinvaap100% (1)
- RADIOLOGY IMAGING MODALITIES OF THE SPINE. Cervical Spine ImagesDocument38 pagesRADIOLOGY IMAGING MODALITIES OF THE SPINE. Cervical Spine Imagesramon100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC IMAGINGaDocument77 pagesINTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC IMAGINGaStudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Medicine A Guide To Clinical Therapeutics by Rebecca L Attridge Monica L Miller Rebecca Moote Laurajo Ryan 0071745807Document5 pagesInternal Medicine A Guide To Clinical Therapeutics by Rebecca L Attridge Monica L Miller Rebecca Moote Laurajo Ryan 0071745807Hesbon MomanyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Limb Neurological Assessment: EquipmentDocument15 pagesLower Limb Neurological Assessment: EquipmentShalini RavPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac ImagingDocument7 pagesCardiac Imagingsarguss14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chest X Ray Diagnostic AlgorithmDocument10 pagesChest X Ray Diagnostic AlgorithmCalin Popa100% (1)
- Phys-FRCR Vol 1Document113 pagesPhys-FRCR Vol 1Anonymous oQtve4o100% (1)
- Basics of Chest Radiology - New Edition - DR H. Davies (Contributing Author)Document493 pagesBasics of Chest Radiology - New Edition - DR H. Davies (Contributing Author)komang86% (7)
- Rotation in RadiologyDocument6 pagesRotation in Radiologyminci sensei100% (3)
- Radiod MasterDocument149 pagesRadiod MasterAhmeid Eid0% (1)
- Aim4aiims - In: Ophthalmology Mnemonics For Medical ExamsDocument7 pagesAim4aiims - In: Ophthalmology Mnemonics For Medical ExamsRakib FoysalPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of Skeletal Radiology (2 Vol. Set)Document4 pagesEssentials of Skeletal Radiology (2 Vol. Set)gufaxite0% (1)
- Nishs Guide To Final YearDocument36 pagesNishs Guide To Final YearehtshmPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasound Measurement Cheat SheetDocument1 pageUltrasound Measurement Cheat SheetDr. MLKPas encore d'évaluation
- @medical - MCQ Chest Radiology MCQsDocument20 pages@medical - MCQ Chest Radiology MCQsKhalid Refaey100% (1)
- Preview PDFDocument21 pagesPreview PDFazehboPas encore d'évaluation
- Pakrat 10Document67 pagesPakrat 10towexpertPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart Manual: Post Myocardial Infarction (Post MI) EditionDocument18 pagesThe Heart Manual: Post Myocardial Infarction (Post MI) EditionPablo L RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Pediatrics PDFDocument32 pagesDrugs Pediatrics PDFNaveen KovalPas encore d'évaluation
- GIT Examination - Clinical Skills With DRDocument8 pagesGIT Examination - Clinical Skills With DRNaveen KovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Table 10.1 Causes of Splenomegaly.: HaematologicalDocument2 pagesTable 10.1 Causes of Splenomegaly.: HaematologicalNaveen KovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological Exam Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesNeurological Exam Lecture NotesNaveen KovalPas encore d'évaluation
- PARASITOLOGYDocument3 pagesPARASITOLOGYNaveen KovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Iecex Bas 13.0069XDocument4 pagesIecex Bas 13.0069XFrancesco_CPas encore d'évaluation
- Euronext Derivatives How The Market Works-V2 PDFDocument106 pagesEuronext Derivatives How The Market Works-V2 PDFTomPas encore d'évaluation
- Gr. 7 Math LM (Q1 To 4)Document260 pagesGr. 7 Math LM (Q1 To 4)Billy Ray C. Castro67% (3)
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Document49 pagesCpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Jasmine LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Prishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLDocument12 pagesPrishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLsudharaj86038Pas encore d'évaluation
- Safe Use of Power Tools Rev0Document92 pagesSafe Use of Power Tools Rev0mohapatrarajPas encore d'évaluation
- EASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanesDocument120 pagesEASA CS-22 Certification of SailplanessnorrigPas encore d'évaluation
- InflammationDocument44 pagesInflammationramsiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- UX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlineDocument7 pagesUX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlinemuhammadsabirinhadisPas encore d'évaluation
- Webinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018Document62 pagesWebinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- PapernathazDocument26 pagesPapernathazAbelardo LapathaPas encore d'évaluation
- V3 Tool Installation GuideDocument13 pagesV3 Tool Installation GuideLeonardo Floresta NascimentoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ponce vs. Court of AppealsDocument7 pagesPonce vs. Court of AppealsMp CasPas encore d'évaluation
- Banana Stem Patty Pre Finale 1Document16 pagesBanana Stem Patty Pre Finale 1Armel Barayuga86% (7)
- 02b. POS Learn ModuleDocument7 pages02b. POS Learn ModuleKUHINJAPas encore d'évaluation
- International Standard: Iso/Iec 7816-2Document16 pagesInternational Standard: Iso/Iec 7816-2Anwar MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- EVC AC Charger CatalogDocument2 pagesEVC AC Charger CatalogRaison AutomationPas encore d'évaluation
- Hitachi VSP Pricelist PeppmDocument57 pagesHitachi VSP Pricelist PeppmBahman MirPas encore d'évaluation
- 1349122940100212diggerDocument24 pages1349122940100212diggerCoolerAdsPas encore d'évaluation
- The London SchoolDocument3 pagesThe London SchoolKhawla Adnan100% (5)
- A Hack For The Yoga PoseDocument3 pagesA Hack For The Yoga PoseAlex NPas encore d'évaluation
- Punctuation WorksheetsDocument10 pagesPunctuation WorksheetsRehan Sadiq100% (2)
- Hortee OromooDocument48 pagesHortee OromooAsnaafii BantiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Y2V7 Full With SSDocument294 pagesY2V7 Full With SSAyanokoji KyotakaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)Document6 pages3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)hsem Al EimaraPas encore d'évaluation
- RHEL 9.0 - Configuring Device Mapper MultipathDocument59 pagesRHEL 9.0 - Configuring Device Mapper MultipathITTeamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ricoh Aficio SP C420DN PARTS CATALOGDocument82 pagesRicoh Aficio SP C420DN PARTS CATALOGYury Kobzar100% (2)
- Triangular Short Crested Weir. Local Geometry ? Discharge CoefficientsDocument7 pagesTriangular Short Crested Weir. Local Geometry ? Discharge CoefficientsTI Journals PublishingPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Product Innovation PDFDocument35 pagesFood Product Innovation PDFDidik HariadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailJay MPas encore d'évaluation
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionD'EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (34)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDD'EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)D'EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (82)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeD'EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (170)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsD'EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsPas encore d'évaluation
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (44)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesD'EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1412)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeD'EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceD'EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (51)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsD'EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBID'EverandHearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (20)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryD'EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (46)