Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
C1 Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Force
Transféré par
Abiha Marquez KazmiDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
C1 Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Force
Transféré par
Abiha Marquez KazmiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
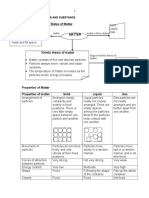
LESSON 1: KINETIC MOLECULAR MODELS OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
KEY WORDS:
OBJECTIVE/S:
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Explain the natre of liquid
Intramolecular forces and Intermolecular forces
and solid states using the
kinetic molecular theory; Ion-dipole force
and
Dipole-dipole force
describe the different
kinds of intermolecular London Dispersion
forces of attractiobn.
Hydorogen Bond
Described the states of
matter in terms of
SOLID LIQUID GAS
Arrangement of Closel Less closely Very far apart
Particles packed packed than Disorderly
Orderly in a solid
Disorderly
Kinetic Energy of Vibrate and Slide over Move abot at
particles rotate each other great speeds
about a
fixed
position
Particle Motion
Very low Low High
Attractive forces
between particles Very strong Strong Very weak
Ion-dipole
Intermolecular
Dipole-dipole
FOrces
London Dispersion
Hydrogen Bonding
CHAPTER 1-Compiled by : GUTIERREZ, Bernadeth F. Page 1
CHAPTER 1: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES OF SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS
1.1 The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Solids and Liquids
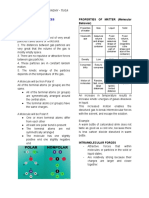
CRITERIA SOLID LIQUID ***LIQUIDS- due to its particle arrangements,
Particle they have:
Arrangement
- no strong attractive force (that is much as
strong as solids) thus, sufficient kinetic
energy can overcome their attractive forces.
- particles that can move at short distance and
Movement Held by very Held
collide with each other.
strong forces together by
of attraction strong forces - particles that does not move independently
Particle are of attraction thus, have fixed volume but does not have
not free to Particles fixed shape.
move are able - high diffusion rate and is slightly more
Particle to slide compressible than that of solid.
vibrate past one
about in another
fixed QUESTION TO PONDER:
positions
Density Very High High How about the Kinetic Molecular Theory of
Diffusibility Extremely Slow Slow Gas?
Compressibility Slightly Slightly
compressible compressible CRITERIA GAS
(more than solid) Particle Arrangement
Volume and Has fixed Indefinite shape
Shape volume and and has fixed
shape volume
Thermal Expands slightly Expands slightly Movement
Expansibility when heated when heated
(more than solid)
Density
***SOLIDS – due to its particle arrangement,
they have:
Diffusibility
- strong attractive force thus, the kinetic force
is not strong to overcome it.
- particles that are not free to move thus,
vibration is limited Compressibility
- fixed and volume
- slow diffusion rate and can be compressed
Volume and Shape
slightly.
Thermal Expansibility
CHAPTER 1-Compiled by : GUTIERREZ, Bernadeth F. Page 2
1.2 Intermolecular Forces
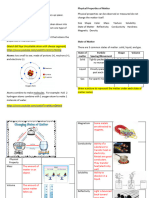
I. Intermolecular vs. Intramolecular *** Velcro- commonly used as a cloth fastener
Which is stronger intermolecular force or
intramolecular force?
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
A. Types of Intramolecular force of
attraction
Which is ionic and which is covalent?
CO2_______________ HCl_______________
CH4_______________ MgOH_______________
1. Ionic bond: METAL + NON-METAL
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
2. Covalent Bond: NON-METAL +
NON-METAL; formed between atoms
that have similar electronegativity (see
attachment of electronegativity table at the last page)
INTERMOLECULAR FORCE INTRAMOLECULAR FORCE
forces that exist forces that hold atoms
between molecules. together within a
molecule. __________________________________________
__________________________________________
CHAPTER 1-Compiled by : GUTIERREZ, Bernadeth F. Page 3
Nonpolar covalent bond vs. Which is polar and which is nonpolar?
Polar Covalent bond
C2H6__________________________
NH3___________________________
NONPOLAR CH3OH_________________________
POLAR
CF4____________________________
the difference in The difference in PCl5___________________________
electronegativity electronegativity
between bonded between bonded
atoms is less than atoms is between 0.5 b. Metallic Bond- This type of covalent
0.5. and 1.9. chloride bonding specifically occurs between atoms
of metals, in which the valence electrons are
POLAR free to move through the lattice.
a. Hydrogen directly
attached to F, O ,N
NONPOLAR
a. Monoatomic
b. Diatomic
The freely moving electrons in metals are
b. Lack symmetry responsible for their reflecting property—
Unidentical freely moving electrons oscillate and give off
c. Hydrocarbons elements outside photons of light—and their ability to effectively
the central element conduct heat and
electricity.
d. Symmetrical
*** Oscillate- move or swing back
Compound
and forth at a regular speed
With lone pair
Relative strength of the intramolecular forces
a. Nonpolar covalent bond
Which is stronger?
Au or NaCl ______________________________
CH4 or PCl5_______________________________________________
NH3 or H20 ______________________________
CHAPTER 1-Compiled by : GUTIERREZ, Bernadeth F. Page 4
B. Types of Intermolecular forces of 4. Hydrogen Bond : H+ F, O,N
attraction
1. Ion-Ion interaction: ION + ION
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________ 5. London Dispersion forces (Van der Waal)
__________________________________________ The more electrons a molecule has, the
stronger the London dispersion forces are.
2. Ion-dipole interaction: ION + DIPOLE
MOLECULE
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
Relative strength of intermolecular forces of
attraction
__________________________________________
Ion-dipole
__________________________________________ Hydrogen bond
__________________________________________ Dipole-dipole
London Dispersion
3. Dipole-dipole interactions: PARTIALLY ___________________________________________
POSITIVE CHARGE + PARTIALLY ___________________________________________
NEGATIVE CHARGE ___________________________________________
The rule of thumb
Intermolecular force= energy (to break the
force)
Boiling and melting points of
__________________________________________ compounds depend on the type and
__________________________________________ strength of the intermolecular forces
__________________________________________
present, as tabulated below:
CHAPTER 1-Compiled by : GUTIERREZ, Bernadeth F. Page 5
CHAPTER 1-Compiled by : GUTIERREZ, Bernadeth F. Page 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheets: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A General Chemistry 2Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A General Chemistry 2Ganilyn Ponciano0% (3)
- 2.1 Basic Concept of MatterDocument1 page2.1 Basic Concept of MatterIzzati AnuarPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids: 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument10 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids: 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterRusselle Therese DaitolPas encore d'évaluation
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument53 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryAaditya MKPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledAbigail OconPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheorymartynchekycPas encore d'évaluation
- The Kinetic Theory of Matter: Arrangement of Matter State of Matter Arrangement and Movement of ParticlesDocument1 pageThe Kinetic Theory of Matter: Arrangement of Matter State of Matter Arrangement and Movement of ParticlesnazatulfirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- GenChem2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGenChem2 ReviewerAshley TupasPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument15 pagesIntermolecular ForcesKrizthel RockwellPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022Document6 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022almafebe caselPas encore d'évaluation
- INTERMOLECULAR FORCES AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS - pdf0Document5 pagesINTERMOLECULAR FORCES AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS - pdf0Kutoo BayPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes (The Particulate Nature of Matter)Document5 pagesChemistry Notes (The Particulate Nature of Matter)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas100% (3)
- Kinetic Model NotesDocument4 pagesKinetic Model NotesAbdul rafay ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Chem Week 1 Properties of Matter and Its Various FormsDocument84 pagesGen Chem Week 1 Properties of Matter and Its Various FormsLeonard SalvacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Particle Nature of MatterDocument45 pagesParticle Nature of MatterDina RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)Document2 pagesMass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)hajra chatthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGPas encore d'évaluation
- LO1. Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and LiquidsDocument3 pagesLO1. Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquidsrandolf wassigPas encore d'évaluation
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Matter and Its Composition: Arrangement of Molecules: Comparative Study in Solid, Liquid and GasDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Matter and Its Composition: Arrangement of Molecules: Comparative Study in Solid, Liquid and GasAkshitaa PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Sajia Ehsani - Year 10-Winter Vacation HomeworkDocument11 pagesKami Export - Sajia Ehsani - Year 10-Winter Vacation HomeworkSajia EhsaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument4 pages04 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - The Particulate Nature of MatterEdric Teo Kai Feng (Msh)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Changes in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Document11 pagesChanges in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Jia JiaPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is MatterDocument1 pageWhat Is MatterkenenathPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Document21 pagesPhase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Jamilla KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Matters Chapter 1Document7 pagesChemistry Matters Chapter 1Ayan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Matters in Our SurroundingDocument48 pagesMatters in Our SurroundingXm PiratesPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic MolecularDocument5 pagesKinetic MolecularrenmarseyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Document28 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Fern Baldonaza100% (1)
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DemburePas encore d'évaluation
- KMT AND Intermolecular Forces 1Document17 pagesKMT AND Intermolecular Forces 1F. Andrea CieloPas encore d'évaluation
- Three States of MatterDocument36 pagesThree States of MatterFozia ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionDocument27 pagesThermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionSaad BBPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsRudra aminPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci P.5.5A Properties of Matter NotesDocument3 pagesSci P.5.5A Properties of Matter Notesnjuhatlast16Pas encore d'évaluation
- GenChem (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesGenChem (Lesson 1)abgolena5238valPas encore d'évaluation
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcusePas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 3-4 - KINETIC MOLECULAR AND PECHECKcdg Edited For PDFDocument72 pagesWEEK 3-4 - KINETIC MOLECULAR AND PECHECKcdg Edited For PDFMorissette GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Groups:: 1. Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034Document2 pagesGroups:: 1. Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034Dyvatyha ThyaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 3rd QuarterDocument36 pagesNotes 3rd QuarterKent DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Composition: Can Be Found Inside The EarthDocument3 pagesComposition: Can Be Found Inside The EarthGabPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle Theory)Document7 pagesChapter 1 (Kinetic Particle Theory)JiajunPas encore d'évaluation
- C07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)Document22 pagesC07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)a m i rPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in General Chemistry IiDocument3 pagesReviewer in General Chemistry IiGabrielle Anne OBOSPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen. Chemistry 2 - LAS NO.1 - E. Tamayao - VERSION 4Document4 pagesGen. Chemistry 2 - LAS NO.1 - E. Tamayao - VERSION 4Phia SamanePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 1Document7 pagesChemistry 1Kriezhel Kim TadlePas encore d'évaluation
- Genchem II Kinetic Theory I.F. of AttractionDocument2 pagesGenchem II Kinetic Theory I.F. of AttractionRosario Del PuertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap-2 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument23 pagesChap-2 - Kinetic Particle TheoryMin HanbyeolPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument3 pagesStates of MatterShivaani TekalePas encore d'évaluation
- NOTES, Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument2 pagesNOTES, Matter in Our Surroundingslogabi3459Pas encore d'évaluation
- College Notes Unit-1 Solid StateDocument24 pagesCollege Notes Unit-1 Solid StateRamanujam JPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure of The AtomDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The AtomGranville RegalarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeD'EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- CHAPTER - 2 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesCHAPTER - 2 - Acids, Bases and Saltsshuchi guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0950061820318560 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0950061820318560 MainElias SoaresPas encore d'évaluation
- CNG Cylinder Design and SafetyDocument53 pagesCNG Cylinder Design and SafetyMartha GamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of A Tapered Composite Leaf Spring K. Diwakar, N. Bhaskar, A. Surendra, Y. Uday Kumar & C. Srikar RaoDocument11 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Tapered Composite Leaf Spring K. Diwakar, N. Bhaskar, A. Surendra, Y. Uday Kumar & C. Srikar RaoRôpíp PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Box 1.5m 1.5mDocument22 pagesBox 1.5m 1.5mveevimalPas encore d'évaluation
- v91 247 PDFDocument6 pagesv91 247 PDFbariah al-bashirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 8Document4 pagesExperiment 8api-252952453100% (3)
- PCL BiomedicalDocument6 pagesPCL BiomedicalCynthia CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Moisture and Fire Resistant Gypsum Board (WRFR)Document3 pagesMoisture and Fire Resistant Gypsum Board (WRFR)burakPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science DLP Q1W3Document7 pagesPhysical Science DLP Q1W3junar asentistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphical Methods For Phase Equilibrium: Class 21Document3 pagesGraphical Methods For Phase Equilibrium: Class 21Aruna KumarasiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Techno-Economic Assessment About Propylene GlycolDocument4 pagesTechno-Economic Assessment About Propylene GlycolIntratec SolutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- ETHYLENEAMINE E-100 (E-100) : Technical BulletinDocument2 pagesETHYLENEAMINE E-100 (E-100) : Technical BulletinRAFAEL MIERESPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Determination of The Fiber Content of Peat Samples by Dry MassDocument2 pagesLaboratory Determination of The Fiber Content of Peat Samples by Dry MasssamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Discharge Through GasesDocument4 pagesElectrical Discharge Through GasessambhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoretical Framework: Compressive Strength TestDocument11 pagesTheoretical Framework: Compressive Strength TestqwertasdfgPas encore d'évaluation
- Resourceful Mock Ii Examinations 2017Document8 pagesResourceful Mock Ii Examinations 2017Baguma MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline SpecsDocument171 pagesOutline Specsmohamed fawzyPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia de Aditivos para Resolucao de ProblemasDocument20 pagesGuia de Aditivos para Resolucao de ProblemasFabiano DesangiacomoPas encore d'évaluation
- MANDA-TOWNHOUSE - Technical SpecificationsDocument10 pagesMANDA-TOWNHOUSE - Technical SpecificationsMark Nathan Sta. MonicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diamond Trainee Manual 901190 2 PDF FreeDocument242 pagesDiamond Trainee Manual 901190 2 PDF Freeswaters98Pas encore d'évaluation
- 496 GDJGGJGFDocument2 pages496 GDJGGJGFRaluca FarcasPas encore d'évaluation
- Base Oil Production IIDocument15 pagesBase Oil Production IIrvsinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMISTRY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Hemang Jain XI B)Document10 pagesCHEMISTRY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Hemang Jain XI B)Hemang JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages of ForgingDocument20 pagesAdvantages of ForgingPramod DhaigudePas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Geology and Rock Mechanics-3Document23 pagesStructural Geology and Rock Mechanics-3francessich0% (1)
- Technical Specifications Data Sheet For CCR Batteries: BattteryDocument4 pagesTechnical Specifications Data Sheet For CCR Batteries: BattterySubstationPas encore d'évaluation
- (Tom Schanz) Experimental Unsaturated Soil MechaniDocument490 pages(Tom Schanz) Experimental Unsaturated Soil MechaniChristopher CarrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic of Soil-Soil Formation (DR - Khalid Farooq)Document26 pagesBasic of Soil-Soil Formation (DR - Khalid Farooq)Haseeb Rehman100% (1)
- Solutions For Heat Transfer Quiz-II: D. Height of The CylinderDocument2 pagesSolutions For Heat Transfer Quiz-II: D. Height of The CylindermkvemulaPas encore d'évaluation