Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ALP
Transféré par
Rastu KaryanaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ALP
Transféré par
Rastu KaryanaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
0003333752190c501V11.
ALP2
Alkaline Phosphatase acc. to IFCC Gen.2
Order information
Analyzer(s) on which cobas c pack(s) can be used
03333752 190 Alkaline Phosphatase acc. to IFCC Gen.2 ALP2S 200 tests System‑ID 07 6761 1 Roche/Hitachi cobas c 311, cobas c 501/502
03333701 190 Alkaline Phosphatase acc. to IFCC Gen.2 ALP2L 400 tests System‑ID 07 6760 3 Roche/Hitachi cobas c 311, cobas c 501/502
10759350 190 Calibrator f.a.s. (12 x 3 mL) Code 401
10759350 360 Calibrator f.a.s. (12 x 3 mL, for USA) Code 401
12149435 122 Precinorm U plus (10 x 3 mL) Code 300
12149435 160 Precinorm U plus (10 x 3 mL, for USA) Code 300
12149443 122 Precipath U plus (10 x 3 mL) Code 301
12149443 160 Precipath U plus (10 x 3 mL, for USA) Code 301
10171743 122 Precinorm U (20 x 5 mL) Code 300
10171735 122 Precinorm U (4 x 5 mL) Code 300
10171778 122 Precipath U (20 x 5 mL) Code 301
10171760 122 Precipath U (4 x 5 mL) Code 301
05117003 190 PreciControl ClinChem Multi 1 (20 x 5 mL) Code 391
05947626 190 PreciControl ClinChem Multi 1 (4 x 5 mL) Code 391
05947626 160 PreciControl ClinChem Multi 1 (4 x 5 mL, for USA) Code 391
05117216 190 PreciControl ClinChem Multi 2 (20 x 5 mL) Code 392
05947774 190 PreciControl ClinChem Multi 2 (4 x 5 mL) Code 392
05947774 160 PreciControl ClinChem Multi 2 (4 x 5 mL, for USA) Code 392
04489357 190 Diluent NaCl 9 % (50 mL) System‑ID 07 6869 3
English ALP
System information p‑nitrophenyl phosphate + H2O phosphate + p‑nitrophenol
For cobas c 311/501 analyzers: The p‑nitrophenol released is directly proportional to the catalytic ALP
ALP2S: ACN 158 activity. It is determined by measuring the increase in absorbance.
ALP2L: ACN 683 Reagents - working solutions
For cobas c 502 analyzer:
R1 2‑amino‑2‑methyl‑1‑propanol: 1.724 mol/L, pH 10.44 (30 °C);
ALP2S: ACN 8158
magnesium acetate: 3.83 mmol/L; zinc sulfate: 0.766 mmol/L;
ALP2L: ACN 8683 N‑(2‑hydroxyethyl)‑ethylenediamine triacetic acid: 3.83 mmol/L
Intended use R2 p‑nitrophenyl phosphate: 132.8 mmol/L, pH 8.50 (25 °C);
In vitro test for the quantitative determination of alkaline phosphatase in preservatives
human serum and plasma on Roche/Hitachi cobas c systems.
Summary1,2,3,4,5,6 R1 is in position B and R2 is in position C.
Alkaline phosphatase in serum consists of four structural genotypes: the Precautions and warnings
liver‑bone‑kidney type, the intestinal type, the placental type and the variant For in vitro diagnostic use.
from the germ cells. It occurs in osteoblasts, hepatocytes, leukocytes, the Exercise the normal precautions required for handling all laboratory
kidneys, spleen, placenta, prostate and the small intestine. The reagents.
liver‑bone‑kidney type is particularly important. Disposal of all waste material should be in accordance with local guidelines.
A rise in the alkaline phosphatase occurs with all forms of cholestasis, Safety data sheet available for professional user on request.
particularly with obstructive jaundice. It is also elevated in diseases of the For USA: Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the
skeletal system, such as Paget’s disease, hyperparathyroidism, rickets and order of a physician.
osteomalacia, as well as with fractures and malignant tumors. A This kit contains components classified as follows in accordance with the
considerable rise in the alkaline phosphatase activity is sometimes seen in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008:
children and juveniles. It is caused by increased osteoblast activity following
accelerated bone growth.
The assay method was first described by King and Armstrong, modified by
Ohmori, Bessey, Lowry and Brock and later improved by Hausamen et al.
In 2011 the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory
Medicine (IFCC) Scientific Division, Committee on Reference Systems of
Enzymes (C‑RSE) recommended a reference procedure for the Warning
determination of alkaline phosphatase using an optimized substrate
concentration and 2‑amino‑2‑methyl‑1‑propanol as buffer plus the cations H315 Causes skin irritation.
magnesium and zinc at 37 °C. This assay follows the recommendations of
the IFCC, but was optimized for performance and stability. H319 Causes serious eye irritation.
Test principle6
Colorimetric assay in accordance with a standardized method. H412 Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
In the presence of magnesium and zinc ions, p‑nitrophenyl phosphate is Prevention:
cleaved by phosphatases into phosphate and p‑nitrophenol.
P264 Wash skin thoroughly after handling.
2017-08, V 11.0 English 1/4
0003333752190c501V11.0
ALP2
Alkaline Phosphatase acc. to IFCC Gen.2
P273 Avoid release to the environment. Reaction time / Assay points 10 / 13‑31
Wavelength (sub/main) 480/450 nm
P280 Wear protective gloves/ eye protection/ face protection.
Reaction direction Increase
Response:
Units U/L (µkat/L)
P332 + P313 If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Reagent pipetting Diluent (H2O)
P337 + P313 If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. R1 75 µL 25 µL
Disposal: R2 17 µL 21 µL
P501 Dispose of contents/container to an approved waste Sample volumes Sample Sample dilution
disposal plant. Sample Diluent (NaCl)
Product safety labeling follows EU GHS guidance. Normal 2.8 µL – –
Contact phone: all countries: +49-621-7590, USA: 1-800-428-2336 Decreased 2.8 µL 20 µL 80 µL
Reagent handling Increased 2.8 µL – –
Ready for use
Storage and stability cobas c 501 test definition
Assay type Rate A
ALP2S, ALP2L
Reaction time / Assay points 10 / 19‑48
Shelf life at 2‑8 °C: See expiration date
on cobas c pack Wavelength (sub/main) 480/450 nm
label. Reaction direction Increase
On‑board in use and refrigerated on the analyzer: 8 weeks Units U/L (µkat/L)
Diluent NaCl 9 % Reagent pipetting Diluent (H2O)
Shelf life at 2‑8 °C: See expiration date R1 75 µL 25 µL
on cobas c pack
R2 17 µL 21 µL
label.
Sample volumes Sample Sample dilution
On‑board in use and refrigerated on the analyzer: 12 weeks
Sample Diluent (NaCl)
Specimen collection and preparation
Normal 2.8 µL – –
For specimen collection and preparation only use suitable tubes or
collection containers. Decreased 2.8 µL 20 µL 80 µL
Only the specimens listed below were tested and found acceptable. Increased 2.8 µL – –
Serum.
Plasma: Li‑heparin plasma. cobas c 502 test definition
The sample types listed were tested with a selection of sample collection
tubes that were commercially available at the time of testing, i.e. not all Assay type Rate A
available tubes of all manufacturers were tested. Sample collection systems Reaction time / Assay points 10 / 19‑48
from various manufacturers may contain differing materials which could
affect the test results in some cases. When processing samples in primary Wavelength (sub/main) 480/450 nm
tubes (sample collection systems), follow the instructions of the tube Reaction direction Increase
manufacturer.
Units U/L (µkat/L)
Centrifuge samples containing precipitates before performing the assay.
Reagent pipetting Diluent (H2O)
Stability:7 7 days at 20‑25 °C
R1 75 µL 25 µL
7 days at 4‑8 °C
R2 17 µL 21 µL
2 months at -20 °C
Sample volumes Sample Sample dilution
Materials provided Sample Diluent (NaCl)
See “Reagents – working solutions” section for reagents.
Normal 2.8 µL – –
Materials required (but not provided)
Decreased 2.8 µL 20 µL 80 µL
▪ See “Order information” section
Increased 5.6 µL – –
▪ General laboratory equipment
Assay Calibration
For optimum performance of the assay follow the directions given in this Calibrators S1: H2O
document for the analyzer concerned. Refer to the appropriate operator’s
manual for analyzer‑specific assay instructions. S2: C.f.a.s.
The performance of applications not validated by Roche is not warranted Calibration mode Linear
and must be defined by the user.
Calibration frequency 2‑point calibration
Applications for serum and plasma • after reagent lot change
cobas c 311 test definition • as required following quality control
procedures
Assay type Rate A
2/4 2017-08, V 11.0 English
0003333752190c501V11.0
ALP2
Alkaline Phosphatase acc. to IFCC Gen.2
Calibration interval may be extended based on acceptable verification of Children13
calibration by the laboratory.
Males
Traceability: This method has been standardized against the IFCC
procedure (2011).6 Age
Quality control 0 – 14 days 83‑248 U/L (1.39‑4.14 µkat/L)
For quality control, use control materials as listed in the "Order information" 15 days – < 1 year 122‑469 U/L (2.04‑7.83 µkat/L)
section.
1 – < 10 years 142‑335 U/L (2.37‑5.59 µkat/L)
In addition, other suitable control material can be used.
The control intervals and limits should be adapted to each laboratory’s 10 – < 13 years 129‑417 U/L (2.15‑6.96 µkat/L)
individual requirements. Values obtained should fall within the defined 13 – < 15 years 116‑468 U/L (1.94‑7.82 µkat/L)
limits. Each laboratory should establish corrective measures to be taken if
values fall outside the defined limits. 15 – < 17 years 82‑331 U/L (1.37‑5.53 µkat/L)
Follow the applicable government regulations and local guidelines for 17 – < 19 years 55‑149 U/L (0.92‑2.49 µkat/L)
quality control. Females
Calculation Age
Roche/Hitachi cobas c systems automatically calculate the analyte activity
of each sample. 0 – 14 days 83‑248 U/L (1.39‑4.14 µkat/L)
Conversion factor: U/L x 0.0167 = µkat/L 15 days – < 1 year 122‑469 U/L (2.04‑7.83 µkat/L)
Limitations - interference 1 – < 10 years 142‑335 U/L (2.37‑5.59 µkat/L)
Criterion: Recovery within ± 10 % of initial value at an alkaline phophatase 10 – < 13 years 129‑417 U/L (2.15‑6.96 µkat/L)
activity of 100 U/L (1.67 µkat/L).
Icterus:8 No significant interference up to an I index of 60 for conjugated 13 – < 15 years 57‑254 U/L (0.95‑4.24 µkat/L)
and unconjugated bilirubin (approximate conjugated and unconjugated 15 – < 17 years 50‑117 U/L (0.84‑1.95 µkat/L)
bilirubin concentration: 1026 µmol/L or 60 mg/dL).
17 – < 19 years 45‑87 U/L (0.75‑1.45 µkat/L)
Hemolysis:8 No significant interference up to an H index of 200
(approximate hemoglobin concentration: 124 µmol/L or 200 mg/dL). Roche has not evaluated reference ranges in a pediatric population.
Lipemia (Intralipid):8 No significant interference up to an L index of 2000. Each laboratory should investigate the transferability of the expected values
There is poor correlation between the L index (corresponds to turbidity) and to its own patient population and if necessary determine its own reference
triglycerides concentration. ranges.
Drugs: No interference was found at therapeutic concentrations using Specific performance data
common drug panels.9,10 Representative performance data on the analyzers are given below.
In very rare cases, gammopathy, in particular type IgM (Waldenström’s Results obtained in individual laboratories may differ.
macroglobulinemia), may cause unreliable results.11
Precision
For diagnostic purposes, the results should always be assessed in Precision was determined using human samples and controls in an internal
conjunction with the patient’s medical history, clinical examination and other protocol with repeatability (n = 21) and intermediate precision (3 aliquots
findings. per run, 1 run per day, 21 days). The following results were obtained:
ACTION REQUIRED
Special Wash Programming: The use of special wash steps is mandatory Repeatability Mean SD CV
when certain test combinations are run together on Roche/Hitachi
cobas c systems. The latest version of the carry‑over evasion list can be U/L (µkat/L) U/L (µkat/L) %
found with the NaOHD-SMS-SmpCln1+2-SCCS Method Sheets. For further
instructions refer to the operator’s manual. cobas c 502 analyzer: All Precinorm U 99.2 (1.65) 0.7 (0.01) 0.7
special wash programming necessary for avoiding carry‑over is available Precipath U 241 (4.02) 1 (0.02) 0.6
via the cobas link, manual input is not required.
Human serum 1 54.6 (0.912) 0.5 (0.008) 0.9
Where required, special wash/carry‑over evasion programming must
be implemented prior to reporting results with this test. Human serum 2 648 (10.8) 4 (0.1) 0.7
Limits and ranges Intermediate precision Mean SD CV
Measuring range
5‑1200 U/L (0.084‑20.0 µkat/L) U/L (µkat/L) U/L (µkat/L) %
Determine samples having higher activities via the rerun function. Dilution Precinorm U 92.8 (1.56) 2.2 (0.04) 2.4
of samples via the rerun function is a 1:5 dilution. Results from samples
diluted using the rerun function are automatically multiplied by a factor of 5. Precipath U 224 (3.74) 4 (0.06) 1.7
Lower limits of measurement Human serum 3 82.2 (1.37) 1.8 (0.03) 2.1
Lower detection limit of the test Human serum 4 1025 (17.1) 9 (0.2) 0.9
5 U/L (0.084 µkat/L)
Method comparison
The lower detection limit represents the lowest measurable analyte level
that can be distinguished from zero. It is calculated as the value lying Alkaline phosphatase values for human serum and plasma samples
3 standard deviations above that of the lowest standard (standard 1 + 3 SD, obtained on a Roche/Hitachi cobas c 501 analyzer with the ALP IFCC
repeatability, n = 21). Gen.2 (ALP2) traceable to IFCC6 method (y), were compared with those
determined on the same analyzer with the same ALP2 reagent traceable to
Expected values IFCC14 method (x).
(measured at 37 °C) Sample size (n) = 106
Adults12 Passing/Bablok15 Linear regression
Males (n = 221) 40‑129 U/L (0.67‑2.15 µkat/L) y = 0.957x - 0.056 U/L y = 0.958x - 0.357 U/L
Females (n = 229) 35‑104 U/L (0.58‑1.74 µkat/L) τ = 0.993 r = 1.00
2017-08, V 11.0 English 3/4
0003333752190c501V11.0
ALP2
Alkaline Phosphatase acc. to IFCC Gen.2
The sample activities were between 17.9 and 1187 U/L (0.299 and FOR US CUSTOMERS ONLY: LIMITED WARRANTY
19.8 µkat/L). Roche Diagnostics warrants that this product will meet the specifications
References stated in the labeling when used in accordance with such labeling and will
1 Greiling H, Gressner AM, eds. Lehrbuch der Klinischen Chemie und be free from defects in material and workmanship until the expiration date
Pathobiochemie, 3rd ed. Stuttgart/New York: Schattauer Verlag 1995. printed on the label. THIS LIMITED WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ANY
2 King EJ, Armstrong AR. Can Med Assoc J 1934;31:376 OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED
3 Ohmori Y. Uber die Phosphomomesterase. Enzymologia WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR
1937;4:217-231. PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS BE LIABLE
4 Bessey OA, Lowry OH, Brock MJ. A method for the rapid determination FOR INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
of alkaline phosphatase with five cubic millimeters of serum. J Biol DAMAGES.
Chem 1946;164:321-329. COBAS, COBAS C, PRECICONTROL, PRECINORM and PRECIPATH are trademarks of Roche.
All other product names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
5 Hausamen TU, Helger R, Rick W, et al. Optimal conditions for the
determination of serum alkaline phosphatase by a new kinetic method. Additions, deletions or changes are indicated by a change bar in the margin.
Clin Chim Acta 1967;15:241-245. © 2017, Roche Diagnostics
6 Schumann G, Klauke R, Canalias F, et al. IFCC primary reference
procedures for the measurement of catalytic activity concentrations of
enzymes at 37° C. - Part 9. Reference procedure for the measurement
of catalytic concentration of alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem Lab Med Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Sandhofer Strasse 116, D-68305 Mannheim
www.roche.com
2011 Sep;49 (9):1439-46.
Distribution in USA by:
7 Guder WG, Narayanan S, Wisser H, et al. List of Analytes; Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN
Preanalytical Variables. Brochure in: Samples: From the Patient to the US Customer Technical Support 1-800-428-2336
Laboratory. Darmstadt: GIT-Verlag 1996.
8 Glick MR, Ryder KW, Jackson SA. Graphical Comparisons of
Interferences in Clinical Chemistry Instrumentation. Clin Chem
1986;32:470-475.
9 Breuer J. Report on the Symposium “Drug effects in Clinical Chemistry
Methods”. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1996;34:385-386.
10 Sonntag O, Scholer A. Drug interference in clinical chemistry:
recommendation of drugs and their concentrations to be used in drug
interference studies. Ann Clin Biochem 2001;38:376-385.
11 Bakker AJ, Mücke M. Gammopathy interference in clinical chemistry
assays: mechanisms, detection and prevention.
Clin Chem Lab Med 2007;45(9):1240-1243.
12 Abicht K, El-Samalouti V, Junge W, et al. Multicenter evaluation of new
GGT and ALP reagents with new reference standardization and
determination of 37 °C reference intervals. Clin Chem Lab Med
2001;39:Special Supplement pp S 346.
13 Estey MP, Cohen AH, Colantonio DA, et al. CLSI-based transference of
the CALIPER database of pediatric reference intervals from Abbott to
Beckman, Ortho, Roche and Siemens Clinical Chemistry Assays:
Direct validation using reference samples from the CALIPER cohort.
Clin Biochem 2013;46:1197–1219.
14 Tietz NW, Rinker AD, Shaw LM. International Federation of Clinical
Chemistry. IFCC methods for the measurement of catalytic
concentration of enzymes, Part 5. IFCC method for alkaline
phosphatase (orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase, alkaline
optimum, EC 3.1.3.1). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1983;21:731-748.
15 Bablok W, Passing H, Bender R, et al. A general regression procedure
for method transformation. Application of linear regression procedures
for method comparison studies in clinical chemistry, Part III. J Clin
Chem Clin Biochem 1988 Nov;26(11):783-790.
A point (period/stop) is always used in this Method Sheet as the decimal
separator to mark the border between the integral and the fractional parts of
a decimal numeral. Separators for thousands are not used.
Symbols
Roche Diagnostics uses the following symbols and signs in addition to
those listed in the ISO 15223‑1 standard (for USA: see
https://usdiagnostics.roche.com for definition of symbols used):
Contents of kit
Volume after reconstitution or mixing
GTIN Global Trade Item Number
4/4 2017-08, V 11.0 English
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQsDocument467 pages1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQskibrom atsbha67% (3)
- Nicolas-Lewis vs. ComelecDocument3 pagesNicolas-Lewis vs. ComelecJessamine OrioquePas encore d'évaluation
- Richard Herrmann-Fractional Calculus - An Introduction For Physicists-World Scientific (2011)Document274 pagesRichard Herrmann-Fractional Calculus - An Introduction For Physicists-World Scientific (2011)Juan Manuel ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Expansion Analysis of Offshore PipelineDocument25 pagesExpansion Analysis of Offshore PipelineSAUGAT DUTTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2 SHS Intro To World Religion - Module 2Document19 pagesQ2 SHS Intro To World Religion - Module 2jan roiPas encore d'évaluation
- Audience AnalysisDocument7 pagesAudience AnalysisSHAHKOT GRIDPas encore d'évaluation
- Limitations For The Study: Celebrity ViewsDocument3 pagesLimitations For The Study: Celebrity ViewsPakaya100% (2)
- Insert ALP2 0003333752190c501 V8 enDocument4 pagesInsert ALP2 0003333752190c501 V8 enAnonymous F50PFE3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ua 702Document5 pagesUa 702hairiPas encore d'évaluation
- TP2 501Document4 pagesTP2 501hairiPas encore d'évaluation
- ALP2 0003333752190COIN V5 enDocument4 pagesALP2 0003333752190COIN V5 enMMCSTOREPas encore d'évaluation
- c311 ALP2 enDocument3 pagesc311 ALP2 endr. SheryarOrakzaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilt3 2017-08 v7Document4 pagesBilt3 2017-08 v7Kouame FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnesium CobasDocument5 pagesMagnesium CobasMarcellia AngelinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tpuc 501Document4 pagesTpuc 501hairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phos2 2019-07 v9 1Document5 pagesPhos2 2019-07 v9 1ammarhp23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ua 501Document5 pagesUa 501hairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Insert CK 07531389001 V1 enDocument4 pagesInsert CK 07531389001 V1 enGuneyden GuneydenPas encore d'évaluation
- Amyl2: A) PNP P Nitrophenol B) G GlucoseDocument5 pagesAmyl2: A) PNP P Nitrophenol B) G Glucosesinghranjanr5748Pas encore d'évaluation
- AU Instructions For Use Total Protein: PrincipleDocument6 pagesAU Instructions For Use Total Protein: PrincipleAnas TjPas encore d'évaluation
- APOAT enDocument3 pagesAPOAT enYunita RapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alat (GPT) Fs : Order Information Warnings and PrecautionsDocument3 pagesAlat (GPT) Fs : Order Information Warnings and Precautionssovi haswindhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaline Phosphatase FS : Order Information SpecimenDocument3 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase FS : Order Information SpecimenmnemonicsPas encore d'évaluation
- PI e AST 2Document3 pagesPI e AST 2Cindy Mae A. PogoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Insert PREA 0108252645190c503 V4 enDocument3 pagesInsert PREA 0108252645190c503 V4 enVegha NedyaPas encore d'évaluation
- At 82560Document2 pagesAt 82560nidhal amamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pi e AP Ifcc 2 (1)Document2 pagesPi e AP Ifcc 2 (1)muhammadsufyanfp12Pas encore d'évaluation
- AslotDocument4 pagesAslotDrAlaa ZidanPas encore d'évaluation
- TG 702Document4 pagesTG 702hairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alat (GPT) Fs : Order Information Warnings and PrecautionsDocument4 pagesAlat (GPT) Fs : Order Information Warnings and Precautionssovi haswindhaPas encore d'évaluation
- LIPASEDocument4 pagesLIPASEsyufriyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Asat (Got) Fs : Order Information Warnings and PrecautionsDocument6 pagesAsat (Got) Fs : Order Information Warnings and PrecautionsTesya PratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Protéines Totales Biuret - ENDocument2 pagesProtéines Totales Biuret - ENYousra NanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kit InsertDocument2 pagesKit InsertfaujranePas encore d'évaluation
- Ifu BX e Bil Total 1Document6 pagesIfu BX e Bil Total 1Aditya FerdyPas encore d'évaluation
- WesternblotDocument46 pagesWesternblotcaanietoclPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunoassay Premium Plus Level 3Document24 pagesImmunoassay Premium Plus Level 3concocdocPas encore d'évaluation
- CREJ2Document4 pagesCREJ2ARIF AHAMMED PPas encore d'évaluation
- Apobt: Nacl Diluent 9%Document3 pagesApobt: Nacl Diluent 9%Yunita RapaPas encore d'évaluation
- PI e ALT 1 PDFDocument3 pagesPI e ALT 1 PDFMuhammad DaffaPas encore d'évaluation
- FOLATEDocument5 pagesFOLATEhairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaline Phosphatase FS : Components and Concentrations R1: R2: Storage Instructions and Reagent StabilityDocument2 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase FS : Components and Concentrations R1: R2: Storage Instructions and Reagent StabilityLia AiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaline Phosphatase FS : Order Information Warnings and PrecautionsDocument2 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase FS : Order Information Warnings and PrecautionsDaffasyenaPas encore d'évaluation
- AAT2 enDocument3 pagesAAT2 enSyahdie FahlediePas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaline Phosphatase Stable LiquidDocument1 pageAlkaline Phosphatase Stable LiquidRakib Hossain 3A-159Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manuali PDF 414Document1 pageManuali PDF 414Rakib Hossain 3A-159Pas encore d'évaluation
- AU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Document8 pagesAU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Anas TjPas encore d'évaluation
- ALB2Document4 pagesALB2Jonalyn SalandoPas encore d'évaluation
- AlpDocument4 pagesAlpGregorio De Las CasasPas encore d'évaluation
- Coinv 12Document4 pagesCoinv 12Raj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium: Enzymatic MethodDocument2 pagesSodium: Enzymatic MethodFariz KasyidiPas encore d'évaluation
- IFU - BX e CK 2Document6 pagesIFU - BX e CK 2betsabevegaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejemplo Inserto Control Tercera OpiniónDocument83 pagesEjemplo Inserto Control Tercera OpiniónNilo EvanzPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunoassay ControlsDocument28 pagesImmunoassay ControlsvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sgot Roche c111Document4 pagesSgot Roche c111Harditya FirdhausPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Protein FS : Order InformationDocument2 pagesTotal Protein FS : Order InformationMikko DecolongonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrquinone: CAS N°: 123-31-9Document109 pagesHydrquinone: CAS N°: 123-31-9Maruf MominPas encore d'évaluation
- CreaDocument5 pagesCreaKouame Francis0% (1)
- BILT3 en V6Document4 pagesBILT3 en V6Fahrurrozi AdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lact2 2018-11 v12Document4 pagesLact2 2018-11 v12Kouame FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium P FSDocument2 pagesCalcium P FSKang SoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Test KitDocument2 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase Activity Test KitRury Darwa Ningrum100% (1)
- en-ap-liDocument1 pageen-ap-liNghi NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pglu-Pap GB-D 21 001Document4 pagesPglu-Pap GB-D 21 001akaweadePas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaline phosphatase FS IFCC 37°C testDocument2 pagesAlkaline phosphatase FS IFCC 37°C testFatma GemalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies Alkaline Phosphatase C311 Lab 8803Document4 pagesLab Policies Alkaline Phosphatase C311 Lab 8803Valdez Francis ZaccheauPas encore d'évaluation
- Nihms 564727 PDFDocument24 pagesNihms 564727 PDFRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural Level Capabilities Making The Effect of Budgetary Slack Budgetary ParticipationDocument8 pagesCultural Level Capabilities Making The Effect of Budgetary Slack Budgetary ParticipationRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas BakteriDocument63 pagesAtlas BakteriRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Pembelajaran Membaca Menulis Menghitung (Calistung) untuk Anak Usia DiniDocument18 pagesModel Pembelajaran Membaca Menulis Menghitung (Calistung) untuk Anak Usia DiniRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretasi LabDocument1 pageInterpretasi LabRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Insert - Cortisol II - Ms 06687733190.V4.EnDocument5 pagesInsert - Cortisol II - Ms 06687733190.V4.EnRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- ALPDocument4 pagesALPRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- TransfusionDocument11 pagesTransfusionWalter Espinoza CiertoPas encore d'évaluation
- EmergencyDocument8 pagesEmergencyRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
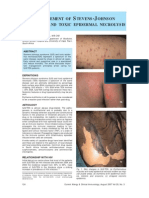
- Manajemen SJS Pada AnakDocument5 pagesManajemen SJS Pada AnaksylviasarahPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG InterpretationDocument8 pagesECG InterpretationRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chord CCRDocument3 pagesChord CCRRastu KaryanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Musicianship ChecklistDocument1 pageBasic Musicianship ChecklistStefanie MeijerPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 11 LeadershipDocument4 pagesUnit 11 LeadershipMarijana DragašPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Essay: Qualities of A Good Neighbour 1Document2 pagesSample Essay: Qualities of A Good Neighbour 1Simone Ng100% (1)
- Social Marketing PlanDocument25 pagesSocial Marketing PlanChristophorus HariyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Detect Organic Elements with Sodium FusionDocument10 pagesDetect Organic Elements with Sodium FusionMukundPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth-Song WorksheetDocument2 pagesEarth-Song WorksheetMuhammad FarizPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical CRM PracticesDocument21 pagesEthical CRM Practicesanon_522592057Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edu 510 Final ProjectDocument13 pagesEdu 510 Final Projectapi-324235159Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review Unit 10 Test CHP 17Document13 pagesReview Unit 10 Test CHP 17TechnoKittyKittyPas encore d'évaluation
- Commonlit The Cask of AmontilladoDocument10 pagesCommonlit The Cask of Amontilladoapi-506044294Pas encore d'évaluation
- Predict Y Scores Using Linear Regression EquationDocument6 pagesPredict Y Scores Using Linear Regression EquationreebenthomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid Cisterns & Cerebrospinal FluidDocument41 pagesSubarachnoid Cisterns & Cerebrospinal Fluidharjoth395Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 5 ADHAVANDocument29 pagesExperiment 5 ADHAVANManoj Raj RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Sta. Ignacia High School: Philosophy 101Document1 pageSta. Ignacia High School: Philosophy 101Mira VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bunga Refira - 1830104008 - Allophonic RulesDocument6 pagesBunga Refira - 1830104008 - Allophonic RulesBunga RefiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Chemical Bonding JH Sir-4163 PDFDocument70 pagesAssignment Chemical Bonding JH Sir-4163 PDFAkhilesh AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- De Broglie's Hypothesis: Wave-Particle DualityDocument4 pagesDe Broglie's Hypothesis: Wave-Particle DualityAvinash Singh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Legend of GuavaDocument4 pagesLegend of GuavaRoem LeymaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatics Formulas and Numerical ProblemsDocument11 pagesElectrostatics Formulas and Numerical ProblemsManish kumar100% (2)
- Tony Bates DepressionDocument7 pagesTony Bates DepressionNiamh WhiriskeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Case DurexDocument3 pagesCase DurexGia ChuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Title Iii 1 30Document3 pagesTitle Iii 1 30CheriferDahangCoPas encore d'évaluation
- Forum On Special Educational Needs: Phil Dexter Sharon Noseley Sophie FaragDocument14 pagesForum On Special Educational Needs: Phil Dexter Sharon Noseley Sophie Faragelena biancaPas encore d'évaluation