Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Transport Mechanism
Transféré par
Stephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Transport Mechanism
Transféré par
Stephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
TRANSPORT MECHANISM
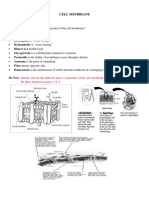
STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS OF THE CELL MEMBRANE
I. CELL MEMBRANE STRUCTURE
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on its
location and role in the body, lipids can make up to anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the
membrane, with the remainder being proteins. While lipids help to give membranes their
flexibility, proteins maintain and monitor the cell’s chemical climate and assist in the transfer of
molecules across the membrane.
CELL MEMBRANE LIPIDS
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
- A major component of cell membranes.
- They form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously
arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled
by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and the extracellular fluid.
- Phospholipids are considered amphipathic molecules since it has both hydrophilic and
hydrophobic parts.
CHOLESTEROL
- A lipid component of animal cell membrane
- Are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids
- This helps to keep cell membranes to become stiff by preventing phospholipids to become closely
packed together.
GLYCOLIPIDS
- Are located on cell membrane surfaces and have a carbohydrate sugar chain attached to them.
- They help the cell membrane to recognize other cells of the body.
CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS
STRUCTURAL PROTEINS
- Help to give the cell support and shape.
CELL MEMBRANE PROTEIN RECEPTORS
- Help cells communicate with the external environment through the use of hormones,
neurotransmitters and other signaling molecules.
TRANSPORT PROTEINS
- Transport molecules across cell membrane through facilitated diffusion
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE AND ITS FUNCTIONS
- The biological membrane is present in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell.
- It is called cell membrane as it works as a barrier between the inner and outer surface of a cell.
- In animal cells, the plasma membrane is present in the outer most layer of the cell and in
Plant cell it is present just beneath the cell wall.
PLASMA MEMBRANE
- It can be defined as a biological membrane or an outer membrane of a cell, which is composed of
two layers of phospholipids and embedded with proteins.
- It is a thin, semi-permeable membrane layer which surrounds the cytoplasm and other
constituents of the cell.
FUNCTIONS OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
1. It separates the contents of the cell from its outside environment and it regulates what enters and
exits the cell.
2. Plasma membrane plays a vital role in protecting the integrity of the interior of the cell by
allowing only selected substances into the cell and keeping other substances out.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 Page 1
3. It also serves as a base attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in
others. Thus the cell membrane supports the cell and helps in maintaining the shapes of the cell.
4. The cell membrane is primarily composed of proteins and lipids. While lipids help to give
membranes their flexibility and proteins monitor and maintain the cell’s chemical climate and
assist in the transfer of molecules across the membrane.
5. The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable membrane, which allows only selected molecules to diffuse
across membranes.
CHARACTERISTICS OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
1. The plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipids.
2. The plasma membrane has many proteins embedded in it.
3. The plasma membrane regulates the entry and exit of the cell.
4. The fundamental structure of the membrane is phospholipid bilayer and it forms a stable barrier
between two aqueous compartments.
5. The proteins present in the plasma membrane act as pumps, channels, receptors, enzymes or
structural components.
PLASMA MEMBRANE STRUCTURE
1. It is the boundary which separates the living and non living surroundings.
2. It is the phospholipids bilayer.
3. It is amphiphatic.
4. It is a fluid mosaic of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
5. It is a lipid bilayer which contains two layers of phospholipids, phosphate head is polar (water
loving), fatty acid tails non-polar (water fearing) and the proteins embedded in the membrane.
COMPONENTS OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
1. Proteins like glycoprotein which are used for cell recognition and act as receptors and antigens.
2. Proteins like glycolipids which are attached to phospholipids along with the sugar chains.
3. Lipids with short chain of carbohydrates which are attached to the extracellular side of the
membrane.
4. Phospholipid bilayer is made up of phosphate and lipids.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 Page 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Molecular Biology Open Exam Questions PART-IIDocument4 pagesMolecular Biology Open Exam Questions PART-IIeyoel0% (1)
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetEderlyn Zate100% (1)
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 4 Plasma MembraneDocument22 pages2 4 Plasma Membraneıamnıkolaı 4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amino Acids Peptides Protein StructuresDocument11 pagesAmino Acids Peptides Protein StructuresGabriel RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Cell Membrane and Lesson 3 HomeostasisAj MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT II Glycoproteins: (Chapter 46 - Harper's)Document6 pagesUNIT II Glycoproteins: (Chapter 46 - Harper's)Aine CebedoPas encore d'évaluation
- DiassDocument50 pagesDiassStephanie Cyrelle Jane Bacani100% (3)
- 11 Biosynthesis of RNADocument52 pages11 Biosynthesis of RNADayne Ocampo-SolimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry - ProteinsDocument6 pagesClinical Chemistry - Proteinsrosellae.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry MLT EXAMDocument8 pagesBiochemistry MLT EXAMLeonel NkwetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)Document5 pagesEnzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)Mrs Rehan100% (1)
- Effect of Extra Curricular Activities On The Academic Performance of The Shs Students - FinalDocument12 pagesEffect of Extra Curricular Activities On The Academic Performance of The Shs Students - FinalStephanie Cyrelle Jane Bacani100% (2)
- Solution Manual For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace MarshallDocument43 pagesSolution Manual For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace Marshallbrianpattersonanpyomzbed100% (41)
- Cell Membrane in Transport MechanismsDocument29 pagesCell Membrane in Transport MechanismsAnnie LouPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 5Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 5karyo eseymPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Document12 pagesStructural Components of Cell Membrane: Group 4Jeongyeonnie OppaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plasma MembraneDocument6 pagesPlasma Membraneparashakthi PRPas encore d'évaluation
- Genbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio Plasma Membrane ReviewerEleah MelchorPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport MechanismDocument1 pageTransport MechanismMari LouPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell MembraneDocument36 pagesThe Cell Membraneanulorance98Pas encore d'évaluation
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDocument10 pagesSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOWEEK5RANESDocument29 pagesBIOWEEK5RANESvrbatitangPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of LifeDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of Lifeochienganthony001Pas encore d'évaluation
- 16.plasma membr-WPS OfficeDocument4 pages16.plasma membr-WPS OfficeMohamed RizwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Plasma Membrane DeutschDocument5 pagesPlasma Membrane DeutschSafeer SefiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembraneDocument7 pagesCell MembraneRishikesh BhintadePas encore d'évaluation
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDocument13 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgRePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument3 pagesCell Membrane TransportHarry TeasdalePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Revieweraaleah moscaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesCell MembraneKhadija ShafiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular-Organization Part1Document7 pagesCellular-Organization Part1Nina IlaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology 2Document25 pagesMicrobiology 2Ba SitPas encore d'évaluation
- NSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer KeyDocument43 pagesNSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer Keygian leepsuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesThe Cell MembraneLalata, Bianca Nicole D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesCell MembranegrxcieePas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Aspects of CellDocument39 pagesBiochemical Aspects of CellHaroon BadarPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure and Function of CellsDocument93 pagesStructure and Function of CellsRonald BakangPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Document24 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell TransportDocument2 pagesCell TransportAshleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsDocument18 pagesBasic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsRikki Mae BuenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Document6 pagesCell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Rica NorcioPas encore d'évaluation
- Struct-Function Cell OrgaDocument30 pagesStruct-Function Cell OrgaSiaw Sing OngPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 B Cytology-Membrane StructuresDocument19 pages3 B Cytology-Membrane Structuresm.mansoor3377Pas encore d'évaluation
- This Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideDocument6 pagesThis Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideZuzuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues: Functional Compartments of The BodyDocument10 pagesChapter 3: Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues: Functional Compartments of The BodyShivani RailowalPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media2437312247486514219Document29 pagesLocal Media2437312247486514219Olive Vergara MuscaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell 1Document7 pagesThe Cell 1Eniola DaramolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell & Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesCell & Its Functionsamber tariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane ReportDocument30 pagesCell Membrane ReportRetchel Cadayong NavalesPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Cytology Membran JunctionDocument48 pages3 Cytology Membran JunctionSamPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument32 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryArbaan HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembraneDocument32 pagesCell Membraneour lecturePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Membrane (Cell Biology)Document10 pagesCell Membrane (Cell Biology)Muskan AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Bio ManuscriptDocument10 pagesGen Bio ManuscriptCheska Faith EstudilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Bio Module 7Document5 pagesGen Bio Module 7Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembraneDocument29 pagesCell Membranesyraregencia15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1doc 3Document4 pagesChapter 1doc 3Enju ChipepePas encore d'évaluation
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocument52 pagesMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3. Cellular Basis of Life-2Document13 pagesUnit 3. Cellular Basis of Life-2Kerala MekuriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- The CellDocument41 pagesThe CellDANIELLA LOMA CAPONPONPas encore d'évaluation
- Components of Plasma Membranes: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesComponents of Plasma Membranes: Learning ObjectivesAlthea Junsan BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Section 2 OutlineDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455051100% (1)
- CSIR Life Science Sample Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCSIR Life Science Sample Cell Biologygamer zonePas encore d'évaluation
- Explanation and Acceptable Reason YeahDocument3 pagesExplanation and Acceptable Reason YeahMj DeguzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Modelapi-2924390320% (1)
- LO Week 7Document22 pagesLO Week 7Matthew ChristopherPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell MembraneDocument45 pagesThe Cell MembraneKirito HatakuPas encore d'évaluation
- CMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadDocument24 pagesCMT 2021-22 by Mr. Adeel AhmadADEEL AHMADPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkynes: State University of New York at AlbanyDocument28 pagesAlkynes: State University of New York at AlbanyStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal BandagingDocument34 pagesAbdominal BandagingStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Enrile Vocational High School National Highway Barangay Ii, Enrile, CagayanDocument3 pagesEnrile Vocational High School National Highway Barangay Ii, Enrile, CagayanStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 2Document1 pageSheet 2Stephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Bio1Document1 pageGen Bio1Stephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis WholeDocument17 pagesThesis Wholeapi-431926146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hsslive XII 2 Chemistry BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesHsslive XII 2 Chemistry BiomoleculesRanit MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Levinthal 1968Document2 pagesLevinthal 1968lagares869Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science SHS 8.1 ProteinsDocument21 pagesPhysical Science SHS 8.1 ProteinsjouselleduayPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Whey Protein Isolate Vanilla 1Document1 pageLab Report Whey Protein Isolate Vanilla 1sounak SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Translation: Protein Biosynthesis Mrna Amino AcidsDocument4 pagesTranslation: Protein Biosynthesis Mrna Amino AcidsMalick AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein ArrayDocument21 pagesProtein Arrayryu rayPas encore d'évaluation
- DH - MethodDocument5 pagesDH - MethodlaviniakartikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug DesignDocument38 pagesDrug DesignPhArMaCyGrAdUaTeSPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomolecules Quick Review - BellringerDocument37 pagesBiomolecules Quick Review - Bellringerapi-261484540Pas encore d'évaluation
- Protein Signatures of Seminal Plasma From Bulls With Contrasting Frozen-Thawed Sperm ViabilityDocument14 pagesProtein Signatures of Seminal Plasma From Bulls With Contrasting Frozen-Thawed Sperm Viabilitysaifulmangopo123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hand Out-Biochemistry-2022Document3 pagesHand Out-Biochemistry-2022Rounak RajPas encore d'évaluation
- MutationActivity 1Document4 pagesMutationActivity 1Leo GordonPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are Enzymes?Document11 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?krishnarajagopal2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: DNA and The Genetic CodeDocument30 pagesChapter 3: DNA and The Genetic CodeRubén De Gracia SantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Biology of The Gene: Figures 10.1 - 10.5Document75 pagesMolecular Biology of The Gene: Figures 10.1 - 10.5Arif MulyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan in DNA and RNaDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in DNA and RNaGarilon Garcia TabadayPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Protein: Mia SrimiatiDocument66 pagesAnalisis Protein: Mia SrimiatiFarhan CFPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 8 Multiple Choice QuestionsDawlat SalamaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Structure and PropertiesDocument55 pagesDNA Structure and PropertiesSHARON MARIA SUNNYPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins 1Document131 pagesProteins 1EyaPas encore d'évaluation