Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Infertility PDF
Transféré par
dharshini0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
64 vues3 pagesTitre original
Infertility.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
64 vues3 pagesInfertility PDF
Transféré par
dharshiniDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Infertility For fertile Women
natural period of fertility
Topics
= just efore and during ovulation
-Definition (d-10 to d-18 in a 28 day cycle)
-Fertile Period (Ovulation on approx d-14)
-Primary vs. secondary infertility and women are
-Effects naturally infertile
Psychological impact during the rest of the menstrual cycle
Social impact + during 1st 6 months of Breast Feeding.
-Emotional stress and marital difficulties
-Leave from work MALE FERTILE PERIOD
-Maternal Leave (Puberty to death)
-Paternal leave - peak fertility period - 25 – 40yrs.
-Causes
Sexually transmitted infections Incidence : (in heterosexual couples)
Other Infections -MTB 3-7% of all couples suffer from infertility
Genetic
Other Causes Causes
Nutritional - Vit B12/ Vit D deficiency Many different causes (See Extra Notes).
20-30% - due to male infertility,
Unexplained infertility 20-35% due to female infertility, and
-Medical treatments 25-40% due to combined problems
10-20% - no cause is found.
Fertility Tourism
If conservative medical treatments fail
Infertility is the Assisted reproductive technology (ART)
inability of a person, techniques are used to achieve a pregnancy,
to reproduce by natural means.
1. in vitro fertilization (IVF)
World Health Organization 1a) In-vitro gamete fusion
The WHO defines infertility as follows: 1b) ICSI
Infertility is followed by
“a disease of the reproductive system 1a/b.1) ZIFT
defined by the 1a/b.2) ZIUT
failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy 2. In-vivo Fertilization
(unable to conceive / implant) 2a. GIFT
even after 12 months or more of 2b. Artificial Insemination
regular unprotected sexual co-habitation
Or (if she conceives), 1. In-vitro fertilization (IVF).
unable to carry a pregnancy to full term -most commonly used ART.
(male or female cause)
Principle
Primary infertility Fertilization of the
-infertility in a female/couple who have male and female gametes (sperm and egg)
never had a child before. outside the female body (in-vitro)
(in lab in appropriate medium in a test tube) .
Then,
Secondary infertility
Implant this externally fertilized ovum
-failure to conceive in lady’s reproductive tract
following a previous pregnancy for further development / pregnancy
(had a child before).
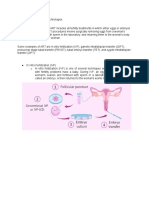
Basic IVF Method (Steps)
FEMALE FERTILE PERIOD 1a)
(menarche to menopause) 1. Ovum from Mother
Approx 12 to 45 yrs Transvaginal ovum collection
-peak fertility period - 24 to 30 yrs, -a small (ultrasound guided) needle is
inserted through the back of the vagina
into the ovarian follicles to collect the eggs / ova.
2. Sperms derived from father / Donor to establish a pregnancy.
(50,000 to 100,000 sperms required).
3. Sperms and ovum incubated in culture N.P. :
medium (Test tube) For ZIFT and IUET ,
4. Allowed to fuse /fertilize (IVF) Embryos can be derived by
IVF using both donor ova and sperms
1b) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection followed by development in mother
(ICSI)
Principle / Method OR
-a single sperm (from father/donor) parent ova and sperms
-injected into an egg followed by development in surrogate mother
(using a micro-pipette / needle).
Cytoplasmic transfer
TEST TUBE BABY (TTB) -contents of a fertile egg from a donor are
Defn : injected into the infertile egg of the patient
along with the sperm.
Baby produced by in-vitro fertilization
(in test tube)
& then transferred and 2. In-vivo Fertilization
nourished and developed in uterus
2a) Gamete intra-fallopian transfer (GIFT)
Uses of IVF/TTB Ovum from donor female
1. Maternal Causes of Infertility Transferred to uterus of infertile subject (female)
- inadequate / irregular / no ovulation, who cannot produce ova
- blocked or damaged tubes,
- endometriosis The subject must have normal uterus environment
for implantation & development
,
2. Paternal Causes of Infertility Ovum - derived trans-vaginaly from donor
- poor or low count (father’s sperms used ) lady
- nil count / low motility /abnormal sperms Sperms - from father / donor
(donor sperms used).
Utility
3. Unexplained infertility, Prospective mother who cannot conceive
Eg. Obesity, Vit D/B12 deficiency d/t
-no / abnormal ova or
-very irregular ovulation
After IVF (1a/1b),
product of fertilization / conception (zygote) 2b) Artificial Insemination
is transferred back into uterus / FT Principle
for Implantation and development Healthy ejaculated sperms
by 1 of following 2 (freshly collected/cryo-preserved) from
Healthy father / donor are
Methods of Developing TTB artificially introduced into vagina/uterus
1a/b.1) ZIFT of female subject
1a/b.2) ZIUT
Fertilization happens in-vivo (in female)
followed by In vivo Implantation and development in uterus of
1a/b.1) ZIFT (Zygote intra-fallopian transfer) recepient
after IVF, resulting zygote
(< 4 days / 8 cell / morula stage) N.P. : Also a mixture of sperms and eggs (gametes) can be
is then placed in fallopian tube. placed directly into a woman's fallopian tubes using laparoscopy
g.r.t. natural development of
artificially (in-vitro) fertilized TTB Utility
Impotency (no erections)
1a/b.2) ZIUT /Z IUET Difficult insemination IUI
(Zygote Intra Uterine Embryo transfer) / IUT Low counts IUI
(< 7 days, 32 cell / blastocyst stage) Or
After IVF resulting zygote is allowed to develop to
32 cell stage-Embryo) then placed Abnormal sperms then Donor sperms
into the uterus of the female
Legal adoption is best method for Managing
Diagnosis
Infertility
Treatment
Drugs used for both women and men
Fertility tourism -clomiphene citrate,
(
= traveling to another country for fertility treatments. (a -human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG),
-follicle-stimulating hormone(FSH),
form of medical tourism). -(GnRH) analogues,
-aromatase inhibitors, and metformin.
Extra Notes Genetic :Robertsonian translocation (in either partner) recurrent
spontaneous abortions or complete infertility
Common Female Causes of Infertility
-irregular / unable to ovulate.
Female Blamed in India
Eg. polycystic ovarian syndrome Infertility Clinics
(with sparse or absent menstrual periods.
-abnormal / partially developed eggs IVF followed by ET embryo transfer
(ovaries do not mature and release eggs).
-structural problems in the
Fallopian tube or uterus or
Eg. - blockage due to malformations,
- previous tubal ligation
EXERCISES
- adhesions d/t infection (TB) 1.What do you think is the significance of reproductive
- fibroids
health in a society?
-endometriosis 2.Suggest the aspects of reproductive health which need to
(growth of endometrial tissue in F tubes be given special attention in the present scenario.
/ extra uterine tissues)) 3.Is sex education necessary in schools? Why?
-Obesity or underweight 4.Do you think that reproductive health in our country has
-Infections improved in the past 50 years? If yes, mention some such
PID (pelvic inflammatory disease)
areas of improvement.
caused by -infections like
tuberculosis, Chlamydia,Gonorrhoea 5. What are the suggested reasons for population explosion?
6. Is the use of contraceptives justified? Give reasons.
-advanced maternal age (>35yrs) 7.Removal of gonads cannot be considered as a contraceptive
option. Why?
-Nutritional - Vit B12/ Vit D deficiency 8. Amniocentesis for sex determination is banned in our
-Dysperunia-painful intercourse (dry vagina)
country. Is this ban necessary? Comment.
Common Male Causes 9.Suggest some methods to assist infertile couples to have
children.
-low semen quality/motility.. 10.What are the measures one has to take to prevent from
-low sperm count contracting STDs?
(d/t primary ciliary dyskinesia, stress, endocrine problems, drugs, radiation, or infection).
-testicular malformations, 11.State True/False with explanation
-blockage of the man's duct system. A) Abortions could happen spontaneously too. (True/False)
-previous vas ligation B) Infertility is defined as the inability to produce a viable
-defect in sperm
offspring and is always due to abnormalities/defects in the
- DNA, centrioles, acrozomal enzymes (not be detected by semen analysis) female partner. (True/False)
C) Complete lactation could help as a natural method of
-folate pathway gene abnormalities contraception. (True/False)
-epigenetic modifications in sperm D) Creating awareness about sex related aspects is an
effective method to improve reproductive health of the
- Nutritional -Vit D / Vit B-12 deficiency
people. (True/False)
General / Common causes
(Male & Female Infertility) Correct the following statements :
A) Surgical methods of contraception prevent gamete
-Diabetes mellitus, formation.
-thyroid disorders (esp autoimmune), B) All sexually transmitted diseases are completely curable.
-Hypo-pituitarism (Abnormal GnRH/Gonadotropin release)
C) Oral pills are very popular contraceptives among the rural
Environmental factors women.
Toxins D) In E. T. techniques, embryos are always transferred into
Tobacco smokers the uterus.
glues, volatile organic solvents or silicones, pesticides.
Factors that can cause
DNA damage in sperms / ova
- smoking,
-radiation or chemotherapy for cancer
-other mutagens (DNA damaging agents)
-Unexplained infertility (no Known cause)
-20% couples have unexplained infertility.
(abnormalities are likely to be present but not detected by current
methods).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12 - EditedDocument17 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Class 12 - Editedharveylenseena2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Last-minute Biology revision guide for Class XII students in Jaipur regionDocument18 pagesLast-minute Biology revision guide for Class XII students in Jaipur regionghjPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Document11 pagesChapter:4 Reproductive Health: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)Nikhil BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled Document-17Document2 pagesUntitled Document-17izellalegendz140708Pas encore d'évaluation
- Techniques For Assisted Human ReproductionDocument51 pagesTechniques For Assisted Human ReproductionArina ChifulescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical Issues On Artificial Reproduction 2Document62 pagesEthical Issues On Artificial Reproduction 2Michaela ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- BioprojectDocument15 pagesBioprojectMohit NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Issues On ArtifDocument7 pagesIssues On ArtifRegene SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of The Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Reproductive SystemRose Kathreen Quintans AuxteroPas encore d'évaluation
- IVF BabiesDocument20 pagesIVF BabiesMaica GeePas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial ReproductionDocument9 pagesArtificial ReproductionSagar HanamasagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive Health Problems and StrategiesDocument12 pagesReproductive Health Problems and StrategiesNirmal ChakravarthyPas encore d'évaluation
- IRJP 2 (7) 2011 22-25: Review of In Vitro Fertilization TechniquesDocument4 pagesIRJP 2 (7) 2011 22-25: Review of In Vitro Fertilization TechniquesAditya VirayudhaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 108 Transes No. 1 PrelimDocument15 pagesNCM 108 Transes No. 1 PrelimAaron De DiosPas encore d'évaluation
- ScienceDocument8 pagesSciencePurplePas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument14 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technologyarchana jainPas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument16 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologyQilaPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument17 pagesBiologyharveylenseena2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test Tube Baby1Document4 pagesTest Tube Baby1kakoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Surrogacy: in This Technique, Fertilization Is BroughtDocument7 pagesSurrogacy: in This Technique, Fertilization Is BroughtdesehPas encore d'évaluation
- An Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezDocument11 pagesAn Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezMica BongalaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahPas encore d'évaluation
- In-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterDocument20 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilisation: Shruti Samal ROLL NUMBER - 1120096 B.Sc. Life Science Second SemesterSHRUTI SAMALPas encore d'évaluation
- (L7) - Reproductive Health - Aug 23, 2019 - FridayDocument49 pages(L7) - Reproductive Health - Aug 23, 2019 - Fridaysarthak kedariPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Tube Baby 1Document16 pagesTest Tube Baby 1nitesh.th15005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted ReproductionDocument3 pagesAssisted Reproductionapi-190806285Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive and Other New Technologies Lecture 2022Document36 pagesReproductive and Other New Technologies Lecture 2022Pavan chowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem VI IVFDocument5 pagesSem VI IVFFAYYAZ KHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Contribution of Science and Technology to Human ReproductionDocument24 pagesContribution of Science and Technology to Human ReproductionteahockPas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologiesDocument19 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologiesGURU ROHIIT KPas encore d'évaluation
- WHAT IS INFERTILITY Final - Docx 1Document16 pagesWHAT IS INFERTILITY Final - Docx 1guntamukkalaparinikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Reproduction Technology ARTDocument15 pagesAssisted Reproduction Technology ARTSimran Singh100% (2)
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument25 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationKaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project Report: Submitted By:-Preeti SinghDocument11 pagesA Project Report: Submitted By:-Preeti Singhkhushboo_khannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) ExplainedDocument4 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) ExplainedNadiya RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- In Vitro FertilisationDocument5 pagesIn Vitro FertilisationVikram VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- EN Tech. J., vol. 1, 1984, pp. 161–166 Ethics of IVFDocument6 pagesEN Tech. J., vol. 1, 1984, pp. 161–166 Ethics of IVFAnonymous Bol3JqKUygPas encore d'évaluation
- ExplainerDocument11 pagesExplainerabdallahehaab2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ivf ENTER - Final FinalDocument15 pagesIvf ENTER - Final FinalsumanavijitPas encore d'évaluation
- HEALTH EDUCATION LIBRARY FOR PEOPLE IVFDocument2 pagesHEALTH EDUCATION LIBRARY FOR PEOPLE IVFAryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assited Reproductive TechnologyDocument40 pagesAssited Reproductive TechnologySanthosh.S.UPas encore d'évaluation
- Amplify The Learning (Ob) Week #17: Vidon, Aubrey Rose A. April 18, 2020 BSN 2Y2-2Document2 pagesAmplify The Learning (Ob) Week #17: Vidon, Aubrey Rose A. April 18, 2020 BSN 2Y2-2AriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Infertility and New Reproductive Technologies: Marriage As A VacationDocument5 pagesInfertility and New Reproductive Technologies: Marriage As A VacationGisselle Mildred PauloPas encore d'évaluation
- General Embryology 1Document34 pagesGeneral Embryology 1asenathderlene27Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINEDDocument34 pagesASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINEDBhawna JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Shelina Elora LiewPas encore d'évaluation
- ART Regulation in IndiaDocument15 pagesART Regulation in IndiaSHREYAPas encore d'évaluation
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument21 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationRahul shyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Care at the Beginning of Life: Bioethical Issues in Reproductive TechnologiesDocument8 pagesCare at the Beginning of Life: Bioethical Issues in Reproductive TechnologiesJayricDepalobosPas encore d'évaluation
- Art Bio Project PDFDocument13 pagesArt Bio Project PDFKriti SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Art Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesArt Bio ProjectKriti Sharma86% (7)
- Assisted Reproduction Technology (ART)Document15 pagesAssisted Reproduction Technology (ART)RPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit100% (1)
- Assisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboDocument19 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboRosemaryPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is in Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Its ProcessDocument4 pagesWhat Is in Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Its ProcessPlanet womenPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioethics Education: Lifestyle, Fertility and The Assisted Reproductive TechnologiesDocument18 pagesBioethics Education: Lifestyle, Fertility and The Assisted Reproductive Technologies7260678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Why and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?Document2 pagesWhy and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?gbrclinicPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 atDocument4 pages4 atKawaii NekoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Investigatory Reproductive HealthDocument12 pagesBiology Investigatory Reproductive HealthSubath KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Insemination, or AI, Is The Process by Which: Citation NeededDocument3 pagesArtificial Insemination, or AI, Is The Process by Which: Citation NeededKathleen Palencia NunezPas encore d'évaluation
- Selecting Male Or Female Child Here's How It Works - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Guide To Gender SelectionD'EverandSelecting Male Or Female Child Here's How It Works - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Guide To Gender SelectionPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE AIPMT 2005 Prelims Question Paper PhysicsDocument36 pagesCBSE AIPMT 2005 Prelims Question Paper PhysicsKiran Raj RPas encore d'évaluation
- (40MB) Arihant Bio 27 Yrs PDFDocument383 pages(40MB) Arihant Bio 27 Yrs PDFdharshiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitrogen CycleDocument17 pagesNitrogen CycledharshiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ix XDocument17 pagesIx Xskj6272Pas encore d'évaluation
- Controversies in IuiDocument19 pagesControversies in IuiSuryakant HayatnagarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal LaborDocument8 pagesNormal LaborNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Fallacy of The Fundal HeightDocument3 pagesFallacy of The Fundal Heightمحمد النويجمPas encore d'évaluation
- Week Wise Pregnancy & Fetus DevelopmentDocument22 pagesWeek Wise Pregnancy & Fetus DevelopmentVirtue BabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Permanent ContraceptionDocument8 pagesPermanent ContraceptionJean Mae DesquitadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelims Exam - (NCM 107)Document4 pagesPrelims Exam - (NCM 107)conahs nasugbu100% (1)
- Is Sex During Pregnancy Safe?Document3 pagesIs Sex During Pregnancy Safe?mirrawahabPas encore d'évaluation
- OG Informing Abortion Debate DR Christine BaileyDocument2 pagesOG Informing Abortion Debate DR Christine BaileyYwagar YwagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion Law and Medical Ethics AnalysisDocument4 pagesAbortion Law and Medical Ethics AnalysislvohPas encore d'évaluation
- AG3 TraitsDocument7 pagesAG3 TraitsMini MannPas encore d'évaluation
- M.2..Abortion REPORTING (SC 109 - Mr. Aganan)Document14 pagesM.2..Abortion REPORTING (SC 109 - Mr. Aganan)Rekkusu MakeinuPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Kontap InternasionalDocument5 pagesJurnal Kontap InternasionalNGADIRAHPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of ReproductionDocument5 pagesThe Process of ReproductionNamie DagPas encore d'évaluation
- PIIS0015028219324847Document18 pagesPIIS0015028219324847Maged BedeawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Contraceptive Pills: Medical and Service Delivery GuidanceDocument24 pagesEmergency Contraceptive Pills: Medical and Service Delivery GuidanceAdityaWijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fertility Awareness MethodDocument15 pagesFertility Awareness MethoddivyamuthyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- YearDocument95 pagesYearBasil KuriakosePas encore d'évaluation
- ContraceptionDocument1 pageContraceptionSibel ErtuğrulPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine RuptureDocument5 pagesUterine RuptureMaria De Los A MejiaPas encore d'évaluation
- An Improved Technique of The Artificial Insemination in DucksDocument29 pagesAn Improved Technique of The Artificial Insemination in DucksMuahamad MusaPas encore d'évaluation
- THW Legalize AbortionDocument3 pagesTHW Legalize AbortionRaymond ArifiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion ProceduresDocument23 pagesAbortion ProceduresAnastasia Widha SylvianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFDocument3 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFgooodePas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Contraceptives in Nigeria: Benefits, Challenges and Probable SolutionsDocument13 pagesThe Use of Contraceptives in Nigeria: Benefits, Challenges and Probable SolutionsShaguolo O. JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioethics session key pointsDocument3 pagesBioethics session key pointsBernadeth Barrientos ZamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chari. - For MergeDocument6 pagesChari. - For MergeMark ElbenPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormonal and Reproductive Factors...Document11 pagesHormonal and Reproductive Factors...Saverio CainiPas encore d'évaluation
- AnilingusDocument5 pagesAnilingusGregor SamsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioethical Issues On Current Reproductive Technology Artificial Insemination (Ai)Document8 pagesBioethical Issues On Current Reproductive Technology Artificial Insemination (Ai)Dred Gementiza AlidonPas encore d'évaluation
- English Pil KBDocument4 pagesEnglish Pil KBNINING ARIESTIPas encore d'évaluation