Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Gsat Lasko Mulakso
Transféré par
ShhsTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Gsat Lasko Mulakso
Transféré par
ShhsDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Special Issue - 2016 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ICIDB - 2015 Conference Proceedings
Multiple-Antenna Techniques in Wireless
Communication-Technical Aspects
Jibendu Sekhar Roy
School of Electronics Engineering
KIIT University
Bhubaneswar 751024, Odisha, India
Abstract—Performance of wireless mobile communication operate at two or more frequency bands of relatively narrow
can be improved by using multiple antenna techniques. For frequency bands, multiple beam antennas which generate
different applications different types of multiple antenna simultaneous multiple beams. Also types of antennas may
techniques are used. This paper describes the technical details be omnidirectional antennas or directional antennas. Delay
of multiple antenna techniques for various types of wireless
spread in mobile environment is more for omnidirectional
communications. A comparison of all types of multiple
antenna techniques (MTA), described in this paper, is also antennas than directional antennas. A typical comparison of
reported. delay spreads for omnidirectional antenna and directional
antenna shown in Fig. 1.
Index Terms—Multiple antenna; antenna array; broadband
communication; mobility
I. INTRODUCTION
During last two decades, there was exceptional
technological development of wireless communication.
From earlier voice communication only, people demands
communication services for internet, laptop, FM radio,
mobile handset television, movie on demand, live sport
telecast and other various multimedia data transmission
with high mobility. To provide these services research work
progressed towards novel networking protocols, new
adaptive coding techniques, high speed data transmission, Fig. 1. Delay spread for omnidirectional and directional antennas
interference and fading mitigation techniques [1]. In
addition to above research areas, development of antenna Multiple-antenna techniques can provide high speed
techniques can solve many such problems in wireless broadband multimedia communication with reduced
mobile communication [2-5]. interference and fading [5-6]. Multiple antenna system, in
This paper describes the technical aspects of antenna wireless communication, may be an antenna array or may
techniques which may be used for next generation mobile not be an antenna array.
communication. Here technical details of multiple antenna
techniques for high speed wireless mobile communication III. MULTIPLE-ANTENNA TECHNIQUES
are explained. Multiple antenna techniques, like, sector USING ANTENNA ARRAY
antennas[1], beam steering/scanning antennas[1-3],
diversity antennas[1], smart antenna[2,3,7], space division Multiple-antenna system using antenna arrays is beam
multiple access (SDMA) antennas [8], multiple input steering/scanning antenna, smart antenna, SDMA antenna
multiple output (MIMO) antennas [9] are described. At last, etc.
application of multiple antenna technique in distributed A. Beam Steering/Scanning Antenna
antenna system [10] is reported.
This type of antenna is phased array antenna (Fig. 2)
where by changing phases of individual antenna elements
II. WIRELESS MOBILE ENVIRONMENT
electronically, beam can be tilted at any desired directions
[4]. The array factor of an n-element uniform linear array is
Wireless mobile communication is affected by
propagation path loss, long-term fading, short-term fading, 𝑛𝜓
𝑆𝑖𝑛( 2 )
co-channel interference, adjacent channel interference and 𝐴𝐹 = (1)
𝜓
inter-symbol interference (ISI) [1]. In order to mitigate these 𝑆𝑖𝑛( )
2
fading and interference in mobile environment, antenna
techniques can take part a major role. Depending on where, ψ = βdCos(ø) + α, d is the inter-element spacing
applications various types of antennas are necessary. Types in the array, α is the progressive phase shift and β=2π/λ.
of antennas may be broadband antennas which operate over Now, if the main beam is to be tilted at an angle ø0, then the
a wide frequency band, multi-frequency antennas which
Volume 4, Issue 01 Published by, www.ijert.org 1
Special Issue - 2016 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ICIDB - 2015 Conference Proceedings
progressive phase shift is to be adjusted in such a way so
that
𝜓 = 𝛽𝑑𝐶𝑜𝑠(ø) + 𝛼
That is, 𝛼 = −𝛽𝑑𝐶𝑜𝑠(ø) (2)
This MAT using scanned array is useful for vehicular
applications (Fig. 3).
Fig. 4. Beam steering/scanning antenna for intelligent transport system
B. Smart Antenna and SDMA antenna
Smart antenna reduces wastage of power by providing
point-to-point communication based on direction-of arrival
(DOA) of the signal [7, 8]. Beam is adapted by adjusting the
amplitudes and phases of signals for a desirable pattern
using antenna array. This adaptive antenna produces nulls
towards undesired (receiving) users and highly directive
beam towards desired direction (Fig. 5). SNR for the other
Fig. 2. Beam steering/scanning antenna array
co-channel users is improved as well as the SNR at the
desired receiver.
Fig. 3. Beam steering/scanning antenna for vehicular application
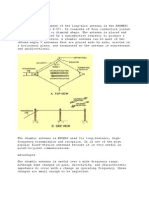
Beam scanning antennas are supposed to be very useful Fig. 5. Smart antenna
in wireless communication using millimeter wave band [11,
12], as suggested in IEEE 802.16. Architecture of intelligent In SDMA technique, multiple beams at same frequency
transport system using millimeter wave technology [11] is are generated with spatial angular separation (Fig. 6) to
shown in Fig. 4, where beam scanning antenna is used. communicate with multiple co-channel users within the
Intelligent transport system provides wireless personal area same frequency band [13]. SDMA is mainly MIMO-based
network (WPAN) communication, inter-vehicular or smart antenna-based wireless communication system and
communication (IVC) for the prevention of accident, road- suitable for mobile ad hoc network (MANET). In this case,
side to vehicle communication (RVC) etc. using millimeter network capacity in terms of users per cell is high.
wave technology.
Volume 4, Issue 01 Published by, www.ijert.org 2
Special Issue - 2016 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ICIDB - 2015 Conference Proceedings
Fig. 8. Comparison of call drop probability
IV. MULTIPLE-ANTENNA TECHNIQUES
USING INDEPENDENT MULTIPLE
ANTENNAS
Multiple-antenna techniques without using antenna
arrays include diversity antennas, MIMO antennas, sector
Fig. 6. SDMA antenna antennas etc.
Multiple antennas in SDMA protect quality of radio A. Diversity Antenna System
signal, safeguard against interference and also save power. Diversity antenna uses multiple antennas to improve
Spatial multiplexing in SDMA is accomplished by sending system performance in fading environment. Antennas are
several bit streams through multiple antennas increases data located to receive high cross correlation signals. Properties
rate. Typical performance graphs of SDMA are compared of antenna array elements are combined at the RF level
below in Fig.7 and Fig. 8 with performances of fixed (broadside, end-fire, any desired direction) but in diversity
channel allocation (FCA) and hierarchical SDMA with scheme signals from diversity antennas are combined at
dynamic channel allocation (HSDCA). either in IF level (Maximal-ratio combining) or in Baseband
level (Equal-gain combining) [1]. The basic diversity
system is shown in Fig. 9.
Fig. 7. Comparison of blocking probability
Fig. 9. Diversity system
There are various types of diversity schemes, used to
achieve best quality signal at different applications. In space
diversity, antennas are separated more than coherence
distance. In frequency diversity, antennas are used to
receive different frequencies. In pattern diversity, different
antennas have different radiation patterns and system
receives incoming signals, almost with 1800 coverage. In
Volume 4, Issue 01 Published by, www.ijert.org 3
Special Issue - 2016 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ICIDB - 2015 Conference Proceedings
polarization diversity scheme, a number of antennas are on antenna height, spacing and nature of scatterer. Antenna
used to receive vertical polarized signal and for horizontal separation is kept more than coherent distance. MIMO is
polarized signal or to receive right handed circularly most suitable technique for WiFi, WiMAX, IEEE 802.11,
polarized (RHCP) signal or left handed circularly polarized 802.16, 4G and long term evolution (LTE) system.
(LHCP) signal. In Fig. 10, diversity system in a mobile
handset uses two planar inverted-F antennas (PIFAs).
Fig. 12. MIMO system
Fig. 10. Diversity system used in mobile handset Within a next few years millions of people will try to
transmit and receive holographic video in all directions
B. Sector Antennas continuously and then the present MIMO system will fail
Sector antennas (Fig. 11) are directional antennas having to provide good quality service. A new system, called
radiation pattern like a sector, covering a portion of a massive MIMO is coming up using multiple antenna
cellular area [1, 4]. Sectors of 1200, 900, 600, 300 are known system which will be a large-scale antenna system [14, 15].
as 3-sector, 4-sector, 6-sector and 12-sector antennas
D. Distributed Antenna System
respectively. 3-sector antennas are widely used. Antenna
beam is tilted downward. In distributed antenna system, multiple antennas are
used to provide good quality secured wireless
communication in the urban and suburban areas where
signal quality is relatively poor. In DAS (Fig. 13) the main
processing antenna module is centralized at a location
which is central unit (CU) and is connected with distributed
antenna modules (DAM) [10]. Optimization of antenna
location in DAS based on signal-to-noise ratio and power
consumption is important.
Fig. 11. Sector antenna
Antenna gain of sector antennas decreases as the number
of sector increases. Multiple antenna technique used in
sector antenna reduces co-channel interference, increases
spectral efficiency in cellular communication, minimizes
delay spread and therefore, reduces bit error rate (BER).
Application of sector antennas in a cell provides efficient
frequency re-use. Fig. 13. Distributed antenna system
C. MIMO Antennas In future high data rate multimedia communication, like,
MIMO Wireless Systems is a spatial multiplexing to 4G, 5G and LTE, this technique might be very effective.
increase spectral efficiency or transmit diversity (space-time
coding) techniques [1, 9] to improve link reliability using
multiple antennas (Fig. 12). MIMO performance depends
Volume 4, Issue 01 Published by, www.ijert.org 4
Special Issue - 2016 International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181
ICIDB - 2015 Conference Proceedings
V. COMPARISON OF MULTIPLE-ANTENNA REFERENCES
TECHNIQUES [1] T. S. Rappaport, Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice’
2nd Edition, Prentice-Hall, 2002.
The performances of multiple antenna techniques, [2] L. C. Godara, “Application of antenna arrays to mobile
explained above, are tabulated in Table I. communications, Part II: beam-forming and direction-of-arrival
considerations”, Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 85, no. 8, Aug 1997,
pp. 1195–1245.
TABLE I. COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MULTIPLE ANTENNA
TECHNIQUES [3] J. B. Andersen, “Role of antennas and propagation for the wireless
systems beyond 2000”, Wireless Personal Communications, vol. 17,
Multiple Antenna Performances in Mobile Communication 2001, pp. 303–310.
Techniques [4] S. Saunders & A. A-Zavala, Antennas and Propagation for Wireless
Communication Systems, 2nd Edition, Wiley, 2007.
Beam Steering Reduces multipath effect, low delay spread, less [5] J. Mietzner, R. Schober, L. Lampe, W. H. Gerstacker, and P. A.
Antennas inter-symbol interference Hoeher, “Multiple-antenna techniques for wireless communications–
a comprehensive literature survey,” IEEE Communications Surveys
Diversity Reduces effect of multipath fading and reduces & Tutorials, vol. 11, no. 2, 2009, pp. 87-105.
Techniques polarization mismatch at the receiving end
[6] Boccardi, B. Clerckx, A. Ghosh, E. Hardouin, G. Jöngren, K.
Sector Antennas Enhances spectral efficiency and frequency re-use, Kusume, E. Onggosanusi, T. Yang, “Multiple-antenna techniques in
reduces interferences , minimizes delay spread and LTE-advanced”, IEEE Communication Magazine, Vol. 50, pp. 114-
reduces bit error rate (BER) 121, March 2012.
[7] T. K. Sarkar, M. C. Wicks, M. Salazar-Palma, Robert J. Bonneau,
MIMO Antennas Increases channel capacity, Improves signal quality Smart Antennas, Wiley-IEEE Press, 2003.
Smart Antenna Power saving, increases signal detection capability by [8] S. Bellofiore, J. Foutz, R. Govindaradjula, I. Bahceci, C.A. Balanis,
estimating DOA, nulling out co-channel interference A.S. Spanias, J.M. Capone, and T.M. Duman, “Smart antenna
and noise, jamming suppression is possible system analysis, integration and performance for mobile ad hoc
networks (MANETs)," IEEE Trans. on Antennas and Propagat, vol.
SDMA Antennas Efficient frequency re-use & high bit rate data, 50, no. 5, 2002, pp. 571-581.
enhanced network capacity in terms of users per cell [9] A. Paulraj, D. A. Gore, R. U. Nabar, and H. Boelcskei, “An
overview of MIMO communications–A key to gigabit wireless,”
Distributed Effective in poor signal condition, more power Proc. IEEE, vol. 92, no. 2, 2004, pp. 198–218.
Antenna System consumption, hardware implementation is expensive [10] S. Zhou, M. Zhao, X. Xu, and Y. Yao, “Distributed wireless
(DAS) communication systems: A new architecture for future public
wireless access,” IEEE Comm. Mag., vol. 41, no. 3, 2003, pp. 108-
113.
VI. CONCLUSION
[11] J. S. Roy, T. Mondal and D. Sainath Reddy, “design of antenna array
The reason behind the use of different multiple antenna for intelligent transport systems”, International Conf. on Intelligent
System and Control (EISCO-2005), Coimbatore, India, 7-9 Jan.,
techniques for different applications are presented here. In 2005, pp. 704-709.
spite of several advantages in wireless mobile [12] T. Mondal, J. S. Roy and S. R. Bhadra Chaudhuri, “Taylor line
communication of multiple antenna techniques in wireless source powered phased array antenna design for intelligent transport
applications, it has some drawbacks also. In multiple systems”, Proc. of International Symposium of Microwaves and
Millimeterwaves: Basics & Technologies (IsoMM – 09), Calcutta,
antenna technique, multiple parallel transmitter/receiver India, Jan. 14 – 16, 2009, pp. 60-62.
chains are required, leading to increased hardware costs. [13] P. Vandenameele, “A combined OFDM/SDMA approach,” IEEE
This technique may increase power consumptions and real- Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 18, no.11, 2000,
time implementations of near-optimum multiple-antenna pp. 795-825.
techniques can be challenging, specially, for massive [14] F. Rusek, D. Persson, B. K. Lau, E. G. Larsson, T. L. Marzetta, O.
MIMO. Edfors, and F. Tufvesson, “Scaling up MIMO: opportunities and
challenges with very large arrays,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag., vol.
30, no. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 40–60.
[15] E. G. Larsson, F. Tufvesson, O. Edfors, and T. L. Marzetta,
“Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems,” IEEE
Comm. Mag., vol. 52, no. 2, Feb. 2014, pp. 186–195.
Volume 4, Issue 01 Published by, www.ijert.org 5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Eng TELE-satellite 1007Document132 pagesEng TELE-satellite 1007Alexander WiesePas encore d'évaluation
- DVB RCS2 FactsheetDocument2 pagesDVB RCS2 Factsheetvsharma26Pas encore d'évaluation
- AERO March 2016 EuropeDocument2 pagesAERO March 2016 EuropeLeon LellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Materi PLCDocument33 pagesMateri PLCFauzan AuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- MicrowavesDocument29 pagesMicrowavesChristian NeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Communications Equipment IIDocument16 pagesCommunications Equipment IIWesley HansenPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhombic Antenna InfoDocument6 pagesRhombic Antenna InfovoidscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Ils or Loc Rwy 17L: Radar RequiredDocument1 pageIls or Loc Rwy 17L: Radar RequiredAnonymous PJwr26RFWnPas encore d'évaluation
- Document20 1st15rdDocument757 pagesDocument20 1st15rdPcnhs SalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mil Module 3 Lesson 1 New John AninoDocument13 pagesMil Module 3 Lesson 1 New John AninoJabsTheKnightPas encore d'évaluation
- TV 1&2Document48 pagesTV 1&2Zeeo Zia100% (1)
- Spectrum For 4g and 5gDocument34 pagesSpectrum For 4g and 5gSergio SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Communication Unit2 VtuDocument76 pagesAnalog Communication Unit2 Vturaghudathesh100% (2)
- Reference Signal Power Boosting in LTEDocument6 pagesReference Signal Power Boosting in LTEDiego AriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Reset All ReceiverDocument12 pagesMaster Reset All Receiverbaharhida100% (1)
- Ground - Based Navigation AidsDocument22 pagesGround - Based Navigation Aidsjei liPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable TV Networks and FTTX: U.K.P. Mihiranga (Mba in Mot, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), Pmp-Pmi (Usa), Amiesl)Document24 pagesCable TV Networks and FTTX: U.K.P. Mihiranga (Mba in Mot, B.Sc. Eng. (Hons), Pmp-Pmi (Usa), Amiesl)Pathum MihirangaPas encore d'évaluation
- LAN4Document103 pagesLAN4Raitei NdutPas encore d'évaluation
- RCC Oct 2006 WB7ESV The Tree AntennaDocument2 pagesRCC Oct 2006 WB7ESV The Tree AntennaADBKNOPas encore d'évaluation
- All BUC AND LNBDocument4 pagesAll BUC AND LNBSenan AlkaabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Media Family Tree INDIADocument1 pageMedia Family Tree INDIAKushagra AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Radio in SocietyDocument2 pagesRole of Radio in Societyamjad kham100% (1)
- Channel Estimation For Lte DownlinkDocument89 pagesChannel Estimation For Lte DownlinkAttila KovácsPas encore d'évaluation
- FinalExam MobileComDocument2 pagesFinalExam MobileComqassimPas encore d'évaluation
- Frequency Shift-Keying: Also Known As FSKDocument33 pagesFrequency Shift-Keying: Also Known As FSKCristel BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uniden Bearcat BC898T (Manual)Document64 pagesUniden Bearcat BC898T (Manual)Theodor EikePas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of The Design and Optimization of A Yagi Antenna With High Gain in Meteorological CommunicationDocument4 pagesAnalysis of The Design and Optimization of A Yagi Antenna With High Gain in Meteorological CommunicationSreto JankicPas encore d'évaluation
- Madda Walabu University Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument61 pagesMadda Walabu University Institute of Engineering and TechnologyTolera Tamiru67% (9)
- Communications Manual: For Frs and Ham RadiosDocument16 pagesCommunications Manual: For Frs and Ham Radiosclaudio andres contreras sanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Frequency Bands: System Band Uplink (MHZ) Downlink (MHZ) Channel NumberDocument4 pagesGSM Frequency Bands: System Band Uplink (MHZ) Downlink (MHZ) Channel NumberVarun PrakashPas encore d'évaluation