Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ejerciciosturbinavapor PDF
Transféré par
fernando sanchez0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
90 vues1 pageTitre original
ejerciciosTurbinavapor.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
90 vues1 pageEjerciciosturbinavapor PDF
Transféré par
fernando sanchezDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
MACHINES AND THERMAL EQUIPMENT I
1. Steam enters a steady-flow turbine
with a mass flow rate of 13 kg/s at 600°C,
8 MPa, and a negligible velocity. The
steam expands in the turbine to a
saturated vapor at 300 kPa where 10
percent of the steam is removed for some
other use. The remainder of the steam
continues to expand to the turbine exit
where the pressure is 10 kPa and quality is
85 percent. If the turbine is adiabatic,
determine the rate of work done by the
steam during this process.
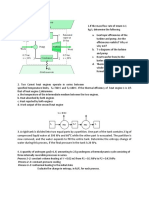
2. Separate streams of steam and air
flow through the turbine and heat
exchanger arrangement shown in
Fig. 2. Steady-state operating data
are provided on the figure. Heat
transfer with the surroundings can
be neglected, as can all kinetic and
potential energy effects.
Determine (a) T3, in K, and (b) the
power output of the second
turbine, in kW.
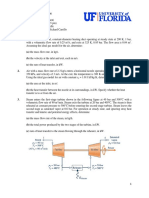
3. As shown in Fig. 3, hot
industrial waste water at 15 bar,
180°C with a mass flow rate of 5 kg/s
enters a flash chamber via a valve.
Saturated vapor and saturated liquid
streams, each at 4 bar, exit the flash
chamber. The saturated vapor
enters the turbine and expands to
0.08 bar, x = 90%. Stray heat transfer
and kinetic and potential energy
effectsare negligible. For operation
at steady state, determine the
power, in hp, developed by the
turbine.
Ing. Nicolás Ortega Miranda ITESI Electromecánica
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 633, February 18, 1888D'EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 633, February 18, 1888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Che198 Thermodynamics DrillsDocument8 pagesChe198 Thermodynamics DrillsTrebob GardayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reheat ProblemsDocument1 pageReheat ProblemsJohn paulo ulepPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo 2 - Quiz 1Document1 pageThermo 2 - Quiz 1Danielson CulanibanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics IndiabixDocument45 pagesThermodynamics Indiabixche.2ndyearPas encore d'évaluation
- U15met303 Etd Tutorial6,7Document3 pagesU15met303 Etd Tutorial6,7Kumaran RPas encore d'évaluation
- Kmem 2216 - Al2Document1 pageKmem 2216 - Al2Daniel WongPas encore d'évaluation
- ME267 Assignment01Document1 pageME267 Assignment01InsanePas encore d'évaluation
- Vapor Power CyclesDocument27 pagesVapor Power Cycleshrithik khannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetHannah TugononPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemario MFCDocument31 pagesProblemario MFCPonce MrlnPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem-Set 2Document20 pagesProblem-Set 2ERROLL ZANDRE NACAYA ANOBARPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicR SuyaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller EficienciasDocument2 pagesTaller EficienciasJohan Maldonado100% (1)
- Problemario MFCDocument80 pagesProblemario MFCBassaldua AlfreedPas encore d'évaluation
- Termodinámica taller análisis 1ra ley sistemas abiertosDocument2 pagesTermodinámica taller análisis 1ra ley sistemas abiertosSteven Gonzalez CardonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelims - PPEDocument1 pagePrelims - PPENathanielle AlvaradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Efficiency of Steam Power Plant CyclesDocument4 pagesThermal Efficiency of Steam Power Plant CyclesQue LanPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Ciclos de Potencia de Vapor 2019 IIDocument1 pageTaller Ciclos de Potencia de Vapor 2019 IIJalverAndresPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine Cycle Efficiency and ParametersDocument12 pagesRankine Cycle Efficiency and ParametersMario GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas Sugeridos EntropíaDocument1 pageProblemas Sugeridos EntropíaMercedes VidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleDocument24 pagesAssignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleMatthias100% (1)
- Thermodynamics II Assignment ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics II Assignment Problemsmihreteab ghebregzabherPas encore d'évaluation
- WhatsApp Image 2020-08-22 at 10.27.25 AMDocument2 pagesWhatsApp Image 2020-08-22 at 10.27.25 AMOmar PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine Cycle ProblemsDocument30 pagesRankine Cycle ProblemsAriel GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Iv - Primera Ley Sistemas Abiertos Primera ParteDocument2 pagesTaller Iv - Primera Ley Sistemas Abiertos Primera ParteJorge Gomez0% (1)
- Sheet (3) Regenerative Rankine Cycle A. Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesSheet (3) Regenerative Rankine Cycle A. Review QuestionsHamadaMohassabPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 1Document12 pages1 1Miguel Dominic BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Week7 Vapor Power Cycles PDFDocument34 pagesWeek7 Vapor Power Cycles PDFDavid Fernando Nieto Gomez100% (1)
- Module 1Document3 pagesModule 1സാരംഗ്എസ്കുമാർPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam ProblemsDocument10 pagesSteam ProblemsCaro Kan LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Seatwork ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageSeatwork ThermodynamicsJr OlivarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet (2) Reheat Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesSheet (2) Reheat Rankine CycleHamadaMohassabPas encore d'évaluation
- #Lecture 2 - Review of Steam Power CyclesDocument27 pages#Lecture 2 - Review of Steam Power Cyclesmohamed EldesokyPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPRE EXAM Power and Industrial No ChoicesDocument8 pagesCOMPRE EXAM Power and Industrial No ChoicesDhey Ortega ManahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignemnt 3Document3 pagesAssignemnt 3Nabeel AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 306 Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1: Vapor Power CyclesDocument3 pagesME 306 Applied Thermodynamics Problem Set 1: Vapor Power CyclesAnagha ChimankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 10 TermodinamicaDocument5 pagesTarea 10 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermoAmrinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- PPE AssignmentDocument3 pagesPPE AssignmentAshish Kumar SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- 062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankDocument12 pages062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankAjay KaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo I Set of Questions 2022Document6 pagesThermo I Set of Questions 2022Paa Kwesi ArhinfulPas encore d'évaluation
- ATD RAnkin Assignment-2011Document3 pagesATD RAnkin Assignment-2011Mradul Yadav0% (2)
- Tutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesDocument3 pagesTutorial Vapor and Combined Power CyclesShariff Mohamad Fairuz0% (1)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Maria SarwatPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas 2 MS2230 Sem II 18-19 PDFDocument1 pageTugas 2 MS2230 Sem II 18-19 PDFHanif MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On Rankine Cycle - PDFDocument1 pageProblems On Rankine Cycle - PDFchristo_nitinPas encore d'évaluation
- Geothermal PowerDocument11 pagesGeothermal PowerDiether RigorPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilencePas encore d'évaluation
- EML3100 Exam2ReviewDocument3 pagesEML3100 Exam2ReviewMax MichaudPas encore d'évaluation
- HW3 (2) Thermo UEM Aerospace 2021Document1 pageHW3 (2) Thermo UEM Aerospace 2021Marina Gil JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- FME 421 Thermodynamics IV TutorialDocument3 pagesFME 421 Thermodynamics IV TutorialSebastian AnnanakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For Day 2Document7 pagesAssignment For Day 2Aldrin Marc DaquizPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Problems On Brayton Cycle and Geothermal Power Plant With AnswersDocument6 pagesReview Problems On Brayton Cycle and Geothermal Power Plant With AnswersMichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Latihan Termodinamika IIDocument5 pagesSoal Latihan Termodinamika IIPur NomoPas encore d'évaluation
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronD'EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Certificate N° 1452847 Project 908293-01: Mesured Voltage RatioDocument1 pageTest Certificate N° 1452847 Project 908293-01: Mesured Voltage RatioMardiansyah AtrimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calorimetry ProblemsDocument3 pagesCalorimetry ProblemsLeticia CarandangPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Project Automatic Night Lamp Using LDRDocument10 pagesCbse Project Automatic Night Lamp Using LDRAbhayPas encore d'évaluation
- CBHF2-D 36V 25A Technical Manual US Version1Document4 pagesCBHF2-D 36V 25A Technical Manual US Version1Stefan CorjucPas encore d'évaluation
- EME PPT (For 32 To 35) by DivyeshDocument24 pagesEME PPT (For 32 To 35) by DivyeshDivyesh ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental of Electronics Engineering Lab (EC-211)Document2 pagesFundamental of Electronics Engineering Lab (EC-211)ragvshahPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D445-17Document16 pagesAstm D445-17ridermatePas encore d'évaluation
- Emi Unit 4Document2 pagesEmi Unit 4Murali KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Problems on Integral Momentum Balance and Bernoulli EquationDocument2 pagesTutorial Problems on Integral Momentum Balance and Bernoulli EquationelizaroyPas encore d'évaluation
- Rfic Unit IIDocument36 pagesRfic Unit IIBlessina PreethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic LabDocument14 pagesHydraulic LabAbdallah AlhasanPas encore d'évaluation
- IkhideMA - PHD Thesis PDFDocument247 pagesIkhideMA - PHD Thesis PDFfsdgsgsPas encore d'évaluation
- Dtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39Document1 pageDtu, Department of Energy Engineering S in (KJ/ (KG K) ) - V in (M 3/Kg) - T in (ºc) M.J. Skovrup & H.J.H Knudsen. 19-01-21 Ref:Dupont Suva Mp39sebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix GDocument22 pagesAppendix Gqwrtp79100% (1)
- Ed & I Lab 18ecl37 ManualDocument29 pagesEd & I Lab 18ecl37 Manualcharan mPas encore d'évaluation
- AB1019 Supercapacitors in Smart MetersDocument2 pagesAB1019 Supercapacitors in Smart MeterseyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Geophysics: Emad Hassan R. Al-KhersanDocument19 pagesGeophysics: Emad Hassan R. Al-KhersanIbrahim Kareem100% (1)
- 2018 - Tutorial - Heat and Heat TransferDocument6 pages2018 - Tutorial - Heat and Heat TransferShanel100% (1)
- Effects of Harmonics On Power SystemsDocument6 pagesEffects of Harmonics On Power SystemsLammie Sing Yew LamPas encore d'évaluation
- Downterm ADocument2 pagesDownterm Awiyatmi0% (1)
- Physrevd.13.191 Hawking RadDocument7 pagesPhysrevd.13.191 Hawking RadSteven ChapmanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Phasor Transform and Impedance: 1. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesThe Phasor Transform and Impedance: 1. ObjectivejbusowiczPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet HiE SXXXKNDocument2 pagesDatasheet HiE SXXXKNpal rajPas encore d'évaluation
- D16.7 Relative Motion Analysis - AccelerationDocument5 pagesD16.7 Relative Motion Analysis - AccelerationAbdullah AlotaibiPas encore d'évaluation
- GeneralPhysics1 - Q2 - Mod8 - Properties of An Ideal Gas and Ideal Gas LawDocument24 pagesGeneralPhysics1 - Q2 - Mod8 - Properties of An Ideal Gas and Ideal Gas LawJose GulitiwPas encore d'évaluation
- Boles Lecture Notes Thermodynamics Chapter 10Document15 pagesBoles Lecture Notes Thermodynamics Chapter 10prince assiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotating Frames Simulate GravityDocument6 pagesRotating Frames Simulate GravityAyesha SajjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion Problems: Kinematic: A V R ADocument7 pagesCircular Motion Problems: Kinematic: A V R AAshley De Leon100% (1)
- 4 Standards For AC Motors PDFDocument37 pages4 Standards For AC Motors PDFEdú BrizuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Low-Cost Digital Bipolar Hall-Effect Sensor Ics, Ss41F, Ss41G 32312814Document4 pagesLow-Cost Digital Bipolar Hall-Effect Sensor Ics, Ss41F, Ss41G 32312814AlihanPas encore d'évaluation