Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lung Ca
Transféré par
Aqila Mumtaz0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
33 vues1 pagelung ca notes during study group . prepared by kenny
Titre original
Lung-Ca
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentlung ca notes during study group . prepared by kenny
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
33 vues1 pageLung Ca
Transféré par
Aqila Mumtazlung ca notes during study group . prepared by kenny
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
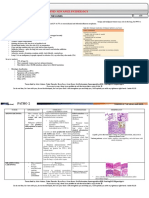
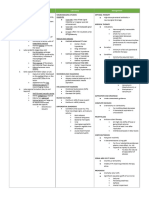
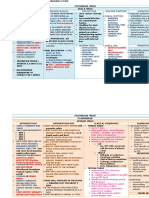
Lung carcinoma
Definition Classification – small cell VS non small cell, metastatic, Complication
carcinoid tumour
- Malignancy of lung arising from Local
epithelium of bronchial tree Small cell lung carcinoma
- 2nd place in men after prostate ca - Massive hemoptysis
- 2nd place in women after breast ca
- Approx. 20% of lung ca - Acute SOB
Etiology - Rapid growing - Pleural effusion
- Metastasize rapidly - SVCO
- Smoking - Central lesion - Chest pain by tumour
- Asbestos exposure infiltration of chest wall
- Familial predisposition Non small cell lung ca – commonest approx. 85%. - Nerve palsy phrenic &
- Air pollution Types: recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Horner’s syndrome
Adenocarcinoma - Pericarditis & Atrial Fib
Symptoms/history
- Arises from bronchial musical gland Metastasize
- Non productive cough - Most common
- Productive cough (blood or non blood). If - Arises in peripheral of the lung - Brain
blood - Subtypes: broncholoaveolar ca - Bone pian, anemia, increase
o Bright red active bleeding o From type II pneumocytes Ca+
o Dark red earlier bleed o Along alveolar septa - Liver
- Progressive breathlessness o Solitary peripheral nodule - Adrenal Addison’s
- Chest pain : o Voluminous watery sputum
o Persistent Endocrine
o Severe Squamous cell ca
o Boring - Small cell
o Disturbing sleep - Centrally located o SIADH
o Tenderness - Presented ad cavitary lesion o ACTH Cushing
- Fever high grade2o bacterial - Histo keratin pearl synd
infection - Squamous
- LOW, LOA Large cell ca o PTH increase
Calcium
- Large peripheral mass on CXR
Physical examination - Histofocal necrosis & no keratinization or Non metastasize CNS complication
gland
General - Confusion
Metastasize - Fits
- Increased JVP SVCO in Pancoasts - Cerebellar syndrome
tumour - Male from colon ca - Proximal myopathy
- Cyanosis - Female from breast ca - Neuropathy
- Clubbing - CXR cannon ball appearance - Polymyositis
- Hypertrophic Pulm osteoarthropathy - Lambert – Eaton syndrome
(wrist swollen & pain) Carcinoid tumours
- Lymph node (hard, discreet, non-tender, Others
- Slow grower
adherent to underlying structure)
- Resectable at diagnosis
- Flap CO2 retention - HPOA
- Facial swelling SVCO - Dermatomyositis
- Pemberton sign +ve - Acanthosis nigrican
Investigation
- Palloranemia in chronic dz - Thrombophlebitis migran
- FBC increase WBC in 2o infection
Respi exam
- ESR >100ml/1hr in malignancy Treatment
- ABG hypoxia & CO2 retention
- Decrease chest movement
- Sputum cytrology, culture, sensitivity Non-small cell excision if early detection
- Trachea deviation
- Pleural fluid cytology, culture, sensitivity
- Dullness on percussion
- Ultrasound diff between cystic or solid Small cell chemotherapy
- Bronchial breath sound and crepitation
- Bronchoscopy
- Pleural effusion sign – stony dullness,
- Chest x-ray - Cyclophosphamide
no/reduced air entry
- Doxorubicin
Possible differential diagnosis - Vincristine
- etoposide
- Pulmonary TB
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Foreign body aspiration
- Lung abscess
- bronchiectasis
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Respiratory 03 – Bronchiogenic CA Pathogenesis: Lung Cancer Types & FeaturesDocument2 pagesRespiratory 03 – Bronchiogenic CA Pathogenesis: Lung Cancer Types & Featureskamil malikPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-Bronchogenic Carcinoma & ParamalignantDocument20 pages5-Bronchogenic Carcinoma & ParamalignantMayar JaradPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenDocument3 pagesRed Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenMaryam FadahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung Tumour Types and CausesDocument7 pagesLung Tumour Types and CausesNestley TiongsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung Cancer Risk Factors and StagesDocument5 pagesLung Cancer Risk Factors and StagesGeraldinePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Small Cell Lung CancerDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Small Cell Lung CancerChristine Pialan SalimbagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Onco ImDocument2 pagesOnco ImAlexandra BascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsDocument2 pagesSurgical Pathology - Major and Minor Salivary GlandsIsabel CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung CancerDocument12 pagesLung CancerАнастасия ОстапенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Facts/Problems Hypotheses Need To Know Li'S: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFDocument3 pagesFacts/Problems Hypotheses Need To Know Li'S: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFDarrah KFPas encore d'évaluation
- MC Tumors and Cancers of Various OrgansDocument12 pagesMC Tumors and Cancers of Various OrgansRyan TurnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Oncologic EmergenciesDocument4 pagesOncologic EmergenciesJoharaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsChristine Pialan SalimbagatPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Infection: VIRAL Meningitis Tetanus Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesCNS Infection: VIRAL Meningitis Tetanus Nursing ManagementYuri G. FelipePas encore d'évaluation
- Subspec Urology: GU TumorsDocument5 pagesSubspec Urology: GU TumorsThakoon TtsPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.2 Renal Masses and Congenital AnomaliesDocument9 pages5.2 Renal Masses and Congenital AnomaliesMaria roxanne HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Neoplasm Types, Causes, Symptoms & DiagnosisDocument2 pagesBrain Neoplasm Types, Causes, Symptoms & DiagnosisVin TagenPas encore d'évaluation
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 pagesIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgPas encore d'évaluation
- IM Part 1Document48 pagesIM Part 1sasghfdgPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Paranasal Sinus VariantsDocument6 pages5 Paranasal Sinus VariantsMatheusDorigattiSoldatelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Nkeeveepuff - Pediatric Cardio Part 1Document5 pagesNkeeveepuff - Pediatric Cardio Part 1Tricia Kaye IblanPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal TumorsDocument1 pageRenal TumorsMohammad Moufaq El-BashabshehPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaDocument5 pagesGroup 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaZazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast Cancer (Aka BR CA) : - Routine Screening For Genetic Abnormalities of A Strong Family HX of BR CA Is NOT NeededDocument6 pagesBreast Cancer (Aka BR CA) : - Routine Screening For Genetic Abnormalities of A Strong Family HX of BR CA Is NOT NeededChanthorn SokPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitology Mid Term AssignmentDocument21 pagesParasitology Mid Term AssignmentYogita SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intrahepatic Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument1 pageIntrahepatic Biliary Tract DiseaseMaryam FadahPas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasms of The ThyroidDocument5 pagesNeoplasms of The ThyroidMahmoud AbouelsoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho Robbins Sumary Pereira MDDocument22 pagesPatho Robbins Sumary Pereira MDNicole SarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Respi - PathDocument19 pagesRespi - PathKimberly KanemitsuPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathway Tumor GinjalDocument1 pagePathway Tumor GinjalElizabeth VickiPas encore d'évaluation
- C HPB (blue keyword pyq)Document5 pagesC HPB (blue keyword pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Vasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OtherDocument3 pagesVasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OthermcwnotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Types and Functions in the Stomach and Small IntestineDocument2 pagesCell Types and Functions in the Stomach and Small IntestineKelly YeowPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 3 Raised Intracranial PressureDocument9 pagesLec 3 Raised Intracranial PressureEmily MurrayPas encore d'évaluation
- PATH - Lung Cancer (7p)Document7 pagesPATH - Lung Cancer (7p)Cristopher NivelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Chest Pain and DyspneaDocument1 pageCase Chest Pain and DyspneaVineePas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress Seizures Patent Ductus ArteriosusDocument1 pageRespiratory Distress Seizures Patent Ductus ArteriosusReno Jun NagasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatrics: Acyanotic Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesPaediatrics: Acyanotic Heart Diseasecgao30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology: Sean Keenan 2021Document23 pagesPathology: Sean Keenan 2021Sean KeenanPas encore d'évaluation
- (OHNS) Epistaxis (Dr. Joman Laxamana, 2021)Document3 pages(OHNS) Epistaxis (Dr. Joman Laxamana, 2021)Noreen Hannah GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Intravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc SerumDocument2 pagesIntravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc Serumazhar hussinPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Medicine Cheat Sheet Ebook PDFDocument18 pagesClinical Medicine Cheat Sheet Ebook PDFMokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medgeeks Clinical Cheat SheetsDocument18 pagesMedgeeks Clinical Cheat SheetsRishikesh AsthanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardio 3B - VHDDocument8 pagesCardio 3B - VHDAndrassy Twinkle AlineaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain TumorsDocument3 pagesBrain TumorsDrashty DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Salivary Gland TumorsDocument16 pagesSalivary Gland Tumorsmaria del mar RoblesPas encore d'évaluation
- (Type The Documen T Title) : Jeffrey ConnorDocument50 pages(Type The Documen T Title) : Jeffrey ConnorJeffrey HingPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Nervous system (自动保存的)Document36 pagesCentral Nervous system (自动保存的)Wai Kwong ChiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitology Notes on Phasmids and AphasmidsDocument4 pagesParasitology Notes on Phasmids and AphasmidsOrhan AsdfghjklPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumors of External and Middle EarDocument43 pagesTumors of External and Middle EarNupur GargPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Tumors - Types, Grades and Key Imaging FeaturesDocument2 pagesCNS Tumors - Types, Grades and Key Imaging FeaturesIsabel CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Wilm's Tumour Nephroblastoma Renal Cell Ca Adenocarcima Grawitz's Carcioma of Urinary BladderDocument2 pagesWilm's Tumour Nephroblastoma Renal Cell Ca Adenocarcima Grawitz's Carcioma of Urinary BladderAhmed ALiPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map LeukemiaDocument7 pagesConcept Map LeukemiaDiane AbanillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain AbscessDocument3 pagesBrain AbscessAndrew JavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Tables NurologyDocument5 pagesTables NurologyRazan AlayedPas encore d'évaluation
- MBBS Differential ListDocument58 pagesMBBS Differential Listsmoore1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Spleen and Some of Its Diseases: Being the Bradshaw Lecture of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, 1920D'EverandThe Spleen and Some of Its Diseases: Being the Bradshaw Lecture of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, 1920Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4.5. How To Test - Testing Strategy HBV Decision-Making Tables - PICO 3Document10 pages4.5. How To Test - Testing Strategy HBV Decision-Making Tables - PICO 3Aqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Hev Easl CPGDocument45 pagesHev Easl CPGRaluca-Elena AlexaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) ManagementDocument48 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) ManagementAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach of TraumaDocument45 pagesApproach of TraumaAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing Dehydration Chart Msword 485697997Document2 pagesAssessing Dehydration Chart Msword 485697997Aqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Palsnewpacket PDFDocument29 pagesPalsnewpacket PDFAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Weight Percentiles CalculatorDocument1 pageWeight Percentiles CalculatorAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Bdb06ff135c7ccb File 2Document29 pagesBdb06ff135c7ccb File 2Mary ThaherPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide Public Health Chapter 6Document2 pagesStudy Guide Public Health Chapter 6Aqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual CBC 1 3: - Wbcs - Platelets Count - PCV or HCT - Retics Count - HB Estimation 3 3 4 5 6Document25 pagesManual CBC 1 3: - Wbcs - Platelets Count - PCV or HCT - Retics Count - HB Estimation 3 3 4 5 6Aqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- DKA Study GroupDocument24 pagesDKA Study GroupAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar StateDocument17 pagesHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar StateAqila Mumtaz50% (2)
- BST Notes GRRRRDocument5 pagesBST Notes GRRRRAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Weight Percentiles CalculatorDocument1 pageWeight Percentiles CalculatorAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue Fever TutorialDocument3 pagesDengue Fever TutorialAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument3 pagesDiabetic Foot UlcerAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- BirdbrainDocument1 pageBirdbrainplastonePas encore d'évaluation
- ParkinsonDocument5 pagesParkinsonAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Traumatic Brain Injury LectureDocument12 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury LectureAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Approval2013 - NewDocument8 pagesEthics Approval2013 - NewAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- BED SITE NOTE - Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument2 pagesBED SITE NOTE - Guillain Barre SyndromeAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments 2016: M T W T F S SDocument12 pagesAssignments 2016: M T W T F S SAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychiatry MnemonicsDocument7 pagesPsychiatry MnemonicsFahad Almalki93% (15)
- Psychiatry MnemonicsDocument7 pagesPsychiatry MnemonicsFahad Almalki93% (15)
- Ac LeukemiaDocument10 pagesAc LeukemiaAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments 2016: M T W T F S SDocument12 pagesAssignments 2016: M T W T F S SAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment and Management of AstrocytomaDocument2 pagesTreatment and Management of AstrocytomaAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue and Other Viral Hemorrhagic FeverDocument6 pagesDengue and Other Viral Hemorrhagic FeverAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- HO OnG NotesDocument38 pagesHO OnG NotesAqila MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmed Mohamed Abdel Rahim Rammah: Senior Registrar Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Al - Adan Hospital, KuwaitDocument32 pagesAhmed Mohamed Abdel Rahim Rammah: Senior Registrar Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Al - Adan Hospital, Kuwaithossam626Pas encore d'évaluation
- "A Nursing Process On Ovarian Cancer": Pres. Diosdado Macapagal Blvd. Metropolitan Park, Pasay CityDocument21 pages"A Nursing Process On Ovarian Cancer": Pres. Diosdado Macapagal Blvd. Metropolitan Park, Pasay Citysaint_ronald8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fcps SurgeryDocument75 pagesFcps SurgeryLANKAPATRUDU6772Pas encore d'évaluation
- COURSE PLAN Child Health NursingDocument11 pagesCOURSE PLAN Child Health NursingSanthosh.S.U33% (3)
- Dr. J.P. Jose Merlin Curriculum Vitae - Cancer Research Nanobiotechnology EducationDocument7 pagesDr. J.P. Jose Merlin Curriculum Vitae - Cancer Research Nanobiotechnology EducationramPas encore d'évaluation
- HE in Your Text: Thesis StatementDocument1 pageHE in Your Text: Thesis StatementRence EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Essay - Aiden PsczulkoskiDocument14 pagesResearch Essay - Aiden Psczulkoskiapi-608831675Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study On Breast Cancer (2003)Document58 pagesA Case Study On Breast Cancer (2003)Katty Rine100% (6)
- Urinalisis MikroskopisDocument26 pagesUrinalisis MikroskopisShandy Bethan100% (1)
- Surgery Paper 1 Viva QDocument46 pagesSurgery Paper 1 Viva QMusabbirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan On Alternative System of MedicineDocument37 pagesLesson Plan On Alternative System of MedicineArchana Sahu100% (1)
- PATH - Acute Kidney InjuryDocument12 pagesPATH - Acute Kidney InjuryAyyaz HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigations of Respiratory SystemDocument20 pagesInvestigations of Respiratory SystemSubhada GosaviPas encore d'évaluation
- The Histological Aspects of Fillers Complications: Ute S. Zimmermann, MD, and Thierry J. Clerici, MDDocument10 pagesThe Histological Aspects of Fillers Complications: Ute S. Zimmermann, MD, and Thierry J. Clerici, MDMichele CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Zeoreport - ZeolitaDocument17 pagesZeoreport - ZeolitageofloPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Pathology PDFDocument7 pagesLiver Pathology PDFjohn smithPas encore d'évaluation
- SANOV18 DikonversiDocument93 pagesSANOV18 DikonversiIc-tika Siee ChuabbiePas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Plan: Awareness Prevention TreatmentDocument16 pagesStrategic Plan: Awareness Prevention TreatmentAoy RangsimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Homeo TipsDocument146 pagesHomeo TipsBalaji Siddhu100% (2)
- Tobacco Advertising and Sports: Why Did Cigarette Companies Move Into Sport in The First Place?Document41 pagesTobacco Advertising and Sports: Why Did Cigarette Companies Move Into Sport in The First Place?Dody FirstMedPas encore d'évaluation
- RT244 Study Guide Radiation Protection NotesDocument6 pagesRT244 Study Guide Radiation Protection NotesAsha6842100% (1)
- Esophageal Varices and Body Habitus Contrast StudiesDocument7 pagesEsophageal Varices and Body Habitus Contrast StudiesJo CuisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Radiology Notes GIT PDFDocument115 pagesMaster Radiology Notes GIT PDFuroshkgPas encore d'évaluation
- Incident vs. Prevalent Cases and Measures of OccurrenceDocument3 pagesIncident vs. Prevalent Cases and Measures of OccurrenceRenzo FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Induced Skin Reaction ManagementDocument7 pagesRadiation Induced Skin Reaction ManagementLokesh ViswanathPas encore d'évaluation
- LiliDocument7 pagesLilialan azizPas encore d'évaluation
- Byol Meridians - Body MeridiansDocument31 pagesByol Meridians - Body MeridiansAbhijitGhosh100% (6)
- Aluminium SmelterDocument9 pagesAluminium SmelterAnup Dalal100% (1)
- Uveitis WorkupDocument75 pagesUveitis WorkupGopal RaoPas encore d'évaluation