Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
243.design and Analysis of Auto Disengagement Single Plate Clutch in Automatic Transmission and Its Performance Testing
Transféré par
Madhupriya KalahastiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
243.design and Analysis of Auto Disengagement Single Plate Clutch in Automatic Transmission and Its Performance Testing
Transféré par
Madhupriya KalahastiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
www.ierjournal.
org International Engineering Research Journal (IERJ) Special Issue 2 Page 1366-1371, 2015, ISSN 2395-1621
ISSN 2395-1621
Design and Analysis of Auto
Disengagement Single Plate Clutch In
Automatic Transmission and Its
Performance Testing
#1
Mr. Nilkanth G. Badhe, #2Prof. S. V. Patil
1
nilkanthbadhe@gmail.com
2
sukhivindar.patil@sinhgad.edu
1
PG student, Mechanical Design Engineering, RMD sinhgad school of engineering, Warje
2
Associate professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering RMD sinhgad school of
engineering, Pune,India
ABSTRACT ARTICLE INFO
Clutch plays fundamental role for engagement/disengagement in transmission system to Article History
transmit torque and power from driving to driven shaft. Disengage clutch Change gear, gradually
engage clutch thus three operations are to be performed while moving from one gear to another Received:30th September
as in conventional transmission system. Paper describes principle of operation of single plate 2015
automatic clutch is that of the ordinary friction plate clutch, with its friction and pressure plates
(and springs), but instead of using a foot pedal. So human effort to operate clutch will be reduced.
Received in revised form :
The auto-disengagement single plate automatic clutch employs only one set of compression 2ndOctober 2015
springs instead of the usual two sets, with this arrangement it is possible to reduce the weights of
the centrifugal member’s .When the clutch is disengaged and the engine is running at idling speed Accepted:6th October, 2015
the hinged bob-weights rest against the lower or inward sides of holes in the flywheel. upward
movement of bob weight is responsible to engagement of clutch and further torque and power Published online :
gets transmitted to driven shaft. ANSYS is used for the calculation of stresses, demo model built 9th October 2015
up for testing performance of clutch at various speed. This clutch may reduce jerk, transmission
losses and increase performace of automatic clutch.
Keywords:- Transmission, Single plate automatic clutch, Bob Weight, Jerk, ANSYS.
I. INTRODUCTION Automotive clutches are located between the engine and the
transmission. It provides mechanical coupling between the
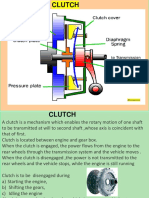
A clutch is a mechanical device for quickly and easily engine and transmission input shaft. Manual transmission
connecting or disconnecting a pair of rotating coaxial shafts. cars need a clutch to enable engaging and disengaging the
It is usually placed between the driving motor and the input transmission. The clutch engages the transmission gradually
shaft to a machine, permitting the engine to be started in an by allowing a certain amount of slippage between the
unloaded state. Single plate, dry clutch is among the popular flywheel and the transmission input shaft. Essential Features
type of clutches in use. A clutch is a mechanism designed to of Clutch: 1) Contact surfaces should develop a frictional
disconnect and reconnect driving and driven members. The force that may pickup and hold the load with reasonably low
need for the clutch seems mainly from the characteristics of pressure between contact surfaces, 2) Heat of friction should
the turning-effort developed by the engine over its lower be rapidly dissipated and tendency to grab should be
speed range. When idling, the engine develops insufficient minimum, 3) Surfaces should be backed by a material soft
torque for the transmission to be positively engaged. To enough to ensure reasonably uniform distribution of
obtain a smooth engagement, the clutch has to be pressure.
progressively engaged to take up the drive until the torque
transmitted from the engine equals that required to propel Types of Frictional Clutches- Disc or plate clutches, Single,
the vehicle. Also the clutch disconnects the engine from the plate or disc clutch, Multi plate or disc clutch, Cone clutches,
transmission to change the gear. The clutch, thus, takes up Centrifugal clutches.
the drive smoothly and also disengages the drive whenever a) Single Plate clutch:
necessary.
Single plate clutch consists of a clutch plate whose both
sides are lined or faced with friction material usually ferredo.
It is mounted on a hub which is free to move axially along
sp-lines or key way on the driven shaft. As shown in fig.1
© 2015, IERJ All Rights Reserved Page 1
www.ierjournal.org International Engineering Research Journal (IERJ) Special Issue 2 Page 1366-1371, 2015, ISSN 2395-1621
speed causes the shoe to press harder and enables more
torque to be transmitted thus centrifugal have jerk problem
during engagement and disengagement which causes
reducing clutch life also transmission losses present in
automatic clutches
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
Mamta G. Pawar stated in “Design and Analysis of Clutch
Using Sintered Iron as a Friction Material”, December 2013.
The clutch engages the transmission gradually by allowing a
certain amount of slippage between the flywheel and the
Fig.1 Components of Single plate Clutch
transmission input shaft. However, the slipping mechanism
of the clutch generates heat energy due to friction between
Pressure plate is mounted inside the clutch body which is the clutch disc and the flywheel. At high sliding velocity,
bolted to flywheel. Both pressure plate and flywheel rotate excessive frictional heat is generated which lead to high
with engine. Pressure plate pushes clutch plate towards temperature rise at the clutch disc surface, and this causes
flywheel by a set of strong springs arranged radially inside thermo-mechanical problems such as thermal deformations
body. Three levers called release levers or fingers are and thermo-elastic instability which can lead to thermal
carried on pivots suspended from the case of body. Levers cracking, wear and other mode of failure of the clutch disc
are arranged such that pressure plate moves away from component. FEM analysis can be done for sintered iron
flywheel by inward movement of thrust bearing. Thrust friction material. The stresses and deformation obtained for
bearing is mounted upon a forked shaft, moves forward this friction material is then compared to analysis software
when clutch pedal is pressed. result. The analysis is done for worn out friction disc. We
can design the clutch using sintered material and analysis
b) Centrifugal clutch: can be done using FEM software [1].
The centrifugal clutches are usually incorporated into motor According to K. Tripathi, the friction clutch must be
pulleys. It consists of a number of shoes on the inside of a designed for minimum axial force between the pressure
rim of the pulley, as shown in figure 2. plate and clutch plate. They suggested that for optimum
design of friction disc the ratio of inner radius to outer
radius should be kept 0.577.There basic design is based on
minimum axial force between pressure plate and clutch
plate. [2]
Ganesh Raut stated in“Analysis of Multidisc Clutch Using
FEA”, December 2013, A model of multi plate clutch has
been generated in CATIA V5 and then imported in ANSYS
workbench for Automobile Applications. He explained
structural analysis by varying the friction surfaces material
and keeping base material aluminum same. By seeing the
results, Comparison is done for both materials to validate
better lining material for multi plate clutch by doing analysis
Fig.2 Components of Centrifugal Clutch on clutch with help of ANSYS Workbench software for find
out which material is best for the lining of friction surfaces.
The outer surface of the shoes is covered up with a frictional We can design the clutch by applying various analysis for
material. These shoes which can move radially in guides, improving transmission performance [2].
are held against the boss (or spider) on the driving shaft by
means of springs. The springs exert a radially inward force Nitinchandra R. Patel stated in “Design Of Centrifugal
which is assumed constant. The mass of shoe, when Clutch By Alternative Approaches Used In Different
revolving, causes it to exert a radially outward force (i.e. Applications” , April 2013, Utilizing the centrifugal clutch
centrifugal force). The magnitude of this centrifugal force enables the selection of normal torque motors for running
depends upon the speed at which the shoe is revolving. A loads rather than the selection of high torque motors for
little consideration will show that when the centrifugal force starting loads. The torque carrying capacity can be
is less than the spring force, the shoe remains in the same calculated at different speed which is using in transmitting
position as when the driving shaft is stationary, but when the power. The entire work based on conventional design with
centrifugal force is equal to the spring force the shoe is just ferrodo lining, driving shaft, spring, shoe, spider, cover plate,
floating. When the centrifugal force exceeds the spring force, driven shaft. The detail design for various speed is made in
the shoe moves outward and comes into contact with the the centrifugal clutch to select an operating range of speed
driven member and presses against it. The force with which under which the application are designed for torque
the shoe presses against the driven member is the difference transmission. Also conventional clutch is expensive rather
of the centrifugal force and the spring force. The increase in
© 2015, IERJ All Rights Reserved Page 2
www.ierjournal.org International Engineering Research Journal (IERJ) Special Issue 2 Page 1366-1371, 2015, ISSN 2395-1621
than compliant clutch. We can use this design for designing When the clutch is disengaged and the engine is running at
of centrifugal clutch [3]. idling speed the hinged bob-weights rest against the lower
or inward sides of holes in the flywheel. When the engine is
Khamlichi, A and Bezzazi, M. stated in “Optimizing Friction accelerated above 700 to 800 rpm, the weights fly outwards
Behavior Of Clutch Facings Using Pin On Disk Test”, and in doing so their lever ends compress the springs as
January, 2008, A rational approach based on Taguchi shown in (fig.4), so as to engage the clutch plates. When the
technique and Pin-on-disk test is used in order to study the full engagement pressure between the clutch members has
friction coefficient behavior of clutch facings as function of been attained any further increase in engine speed brings the
material formulation. bob weights against the outsides of the flywheel holes, thus
limiting the pressure plate action.
They conducted experiments, according to the orthogonal
array L8 where the chosen factors are temperature and Working of Single Plate Automatic Clutch:
sliding speed. A complex interaction exists between the
surface texture of the produced clutch facings and the used There are three bob weights (A) are used in the three
manufacturing process parameters, particularly those flywheel holes (B). These weights are carried by levers(C)
associated to molding and grinding operations. They also which can rock on the pins mounted on the axis shown at
stated the friction coefficient behaviour of clutch facings (D). The ends of these levers engage the driving springs at
was mainly controlled by the sliding speed or by the the points (E). Situated between (E) & (D) is a fulcrum lever.
interaction between the sliding speed and temperature. A pin (F), carried by the pressure plate, carries a nut and
Important issue in the research and development process of washer which works over the fulcrum.
clutch facings consists in obtaining a sufficiently high and
stable friction coefficient during the whole product servicing
life. One should notice that the manufacturing process used
could also have a drastic influence on the final product
performances.
In case of important sensitivity to the manufacturing process,
the friction coefficient is expected to be irregular. It is
necessary therefore, that results of investigation on friction
behaviour should take into account both the actual material
composition and the manufacturing process parameters.
Friction coefficient must also be studied as function of the
general rubbing surface parameters which could be idealized
to include temperature, the sliding speed, the normal contact
pressure, surface roughness and surface state specifications
of the counter material. For common applications of clutch Fig.3 Out Side View of Single Plate Automatic Clutch
facings the last three parameters are likely to remain
constant, only behaviour of the friction coefficient as And spring load at (E), resisted by (F) operating around (D)
function of temperature and the sliding speed investigated will move weights against the inner stops thus releasing the
by means of the pin-on disk test system. pressure plate when the engine is stationary or idling. As the
engine accelerates (A) is thrown out, revolving around (D)
and loading up (E) against the pressure plate until the plate
III. EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
contacts the driven plate which then takes the load and
Single Plate Automatic Clutch: relieves this load at fulcrum (F). The clutch withdrawal
The Single plate automatic clutch employs only one set of levers are of orthodox design so that when clutch is
compression springs instead of the usual two sets, with this operating at speeds above its centrifugal engagement speed
arrangement it is possible to reduce the weights of the the clutch can be disengaged or reengaged for gear changing
centrifugal members. purpose as in normal hand gear change practice.
For automatic gear changing use is made of servo device to
perform clutch operations involved in gear changing.
Test Rig Set Up For Single plate Automatic Clutch:
Fig.4 Principle of Single Plate Automatic Clutch
© 2015, IERJ All Rights Reserved Page 3
www.ierjournal.org International Engineering Research Journal (IERJ) Special Issue 2 Page 1366-1371, 2015, ISSN 2395-1621
2xxN
= 60 x 93.25
2xxN
Assuming operation speed = 1500 rpm.
= 60 x 93.25
2 x x 1500
T = 0.59365 N-m
Assuming 25% overload.
T design = 1.25 x T
= 1.25 x 0.59365 x 103
= 0.742 x 103 N-mm.
Check For Torsional Shear Failure Of Shaft:
Assuming minimum section diameter on input shaft = 16
Fig.5 Test Rig Set Up mm
In order to demonstrate the functionality of the clutch the d = 16 mm
test rig set up has developed where in the input shaft or Td = /16 x fs act x d3
driver shaft of clutch is driven by a variable speed motor of fs act = 16 x Td
AC type, speed control achieved by means of an
x d3
continuously variable rheostat. = 16 x 0.742 x 103
x (16)3
The output shaft shall carry a dyno brake pulley if the brake
fs act = 0.9226 N/mm2
dynamometer testing is to be carried out in order analyze the
As fs act < fs all
torque transmitting capacity of clutch.
I/P shaft is safe under Torsional load.
IV. ANALYTICAL APPROACH
In this section, Design and analytical process has been
discussed,
Input Data,
a) Motor Details,
b) Single Phase AC Motor
c) 230 Volt, 50Hz
d) 0.5 Amps,
e) Power = 0.125Hp
= 93.25 watt
f) Speed = 1500 rpm
T = 0.59365 x 103 N-mm
T Design = 0.742 x 103 N-mm
Design of Input Shaft:
TABLE I
MATERIAL SELECTION FOR SHAFT
Fig.6 Input Shaft Model
Designation Ultimate Yeild strength
tensile strength N/mm2
N/mm2
EN 36C 900 700
According to ASME code permissible values of shear stress
may be calculated from various relations.
fs Max = 0.18 Sut
=162 N/mm2
fs Max = 0.3 Syt
=210 N/mm2
Calculate Input Torque
POWER = 2 NT
60
T = 60 x P
© 2015, IERJ All Rights Reserved Page 4
www.ierjournal.org International Engineering Research Journal (IERJ) Special Issue 2 Page 1366-1371, 2015, ISSN 2395-1621
Fig.7 Result after loading condition
Output Shaft:
Analysis of result after loading condition:
Meshing fig as shown in below after applying constraints to
output shaft.
Fig.10 Torque comparison with manual clutch.
Fig.11 Power comparison with manual clutch.
Above graph represent that power transmission capacity
is always better for single plate automatic clutch.
Fig.8 Meshing of Output shaft
V.CONCLUSION
The single plate automatic clutch is having smooth
engagement 95% during power transmission because of
using single plate for power and torque transmission so that
jerk during transmission is eliminated. It is having higher
torque/ power transmission capacity and it can be analysed
by testing performance of clutch. due to no jerk (only 5%)
there is less vibration and less wear during torque
transmission and these clutch has higher life as compare to
centrifugal / Single plate clutch.
Test rig is compact in size and easier to calculate Power
Vs Speed, Torque Vs speed, Brake Power Vs Speed
readings. We can conclude performance of clutch by
comparing reading with standards reading at various speeds.
So even it can be used for heavy vehicles for automatic
transmission due to high torque / power transmission
capacity.
Fig.9 Stress Distribution of output shaft
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
V.EXPERIMENTATION Authors are thankful to Dr. C. B. Bangal, Principal,
After conducting experiments, several trials have been taken RMD sinhgad school of Engineering, Pune (MH) India, for
at various speed or RPM of clutch and readings are noted his kind support.
also graph compared with graph of standard single plate
clutch REFERENCES
[1] Mamta G. Pawar, “Design and Analysis of Clutch Using
Sintered Iron as a Friction Material”, International Journal
of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering,
December 2013.
[2] Ganesh Raut, “Analysis of Multidisc Clutch Using FEA”,
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology,
December-2013.pp 23-47
© 2015, IERJ All Rights Reserved Page 5
www.ierjournal.org International Engineering Research Journal (IERJ) Special Issue 2 Page 1366-1371, 2015, ISSN 2395-1621
[3] Nitinchandra R. Patel, “Design of Centrifugal Clutch By
Alternative Approaches Used In Different Applications”,
International Journal of Innovative Research in Science,
April-2013.
[4] Khamlichi, A and Bezzazi, M, “Optimizing Friction
Behavior Of Clutch Facings Using Pin On Disk Test”,
International Journal of Physical Sciences Vol. 3 (2), pp.
065-070, January, 2008.
Report and Manual
[5] Altra Industrial Motion, Permanent Magnet and
Magnetic Particle Clutches and Brakes. Port Technology
International, Difference between dynamic and static
coefficient of friction
[6] Modern Transmission Systems, Arthur W Judge
[7] Engg. Mechanism, Erdman and Sandor
[8] Machine Design, R S Khurmi
[9] P S G Design data Book.
[10] Patent no-608,083, England, September. 5, 1956,
Centrifugal Friction Clutches, 1960.
[11] Patent no-178,666, England, December 8, 1937,
Centrifugal Clutch, 1937.
© 2015, IERJ All Rights Reserved Page 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ijert Ijert: Design and Structural Analysis of Single Plate Friction ClutchDocument7 pagesIjert Ijert: Design and Structural Analysis of Single Plate Friction ClutchBhanu Prakash Reddy GundreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Raghu Engineering College Dept. of Mech Engg Automobile Engg Unit - 2Document40 pagesRaghu Engineering College Dept. of Mech Engg Automobile Engg Unit - 2Avinash Sai KalyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Keshav Jangir Seminar-1Document33 pagesKeshav Jangir Seminar-1video songPas encore d'évaluation
- IJERT Designing and Validation of A SproDocument5 pagesIJERT Designing and Validation of A Spro20M155 - VENGATRAMANAN RPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Implementation of Cutting Brakes in ATV IJERTCONV7IS06024Document5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Cutting Brakes in ATV IJERTCONV7IS06024SarathPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabrication of Shaft Driven BicycleDocument6 pagesFabrication of Shaft Driven BicycleMANTECH PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- AENDocument10 pagesAENShaikh AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Malleshwar Rao 3 Sandhya Girish FinalDocument14 pages2 Malleshwar Rao 3 Sandhya Girish FinalPrateek DhamijaPas encore d'évaluation
- KSRTC Central Works Pappanamcode: Internship ReportDocument47 pagesKSRTC Central Works Pappanamcode: Internship ReportJayasuryaPas encore d'évaluation
- ClutchDocument25 pagesClutchRohit ChaubalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tom ImportantDocument87 pagesTom Importantaniket rautPas encore d'évaluation
- Irjet V6i5501Document4 pagesIrjet V6i5501Grezy MagnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Clutch Plate For Light Motor Vehicle NewDocument14 pagesDesign of Clutch Plate For Light Motor Vehicle NewKedar BardePas encore d'évaluation
- Parative Study On Flexible Type of ClutchesDocument6 pagesParative Study On Flexible Type of ClutchesSina ShourakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1: ObjectivesDocument27 pagesChapter - 1: ObjectivesjeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of An Intermediate Rear Axle Shaft Failure: January 2015Document4 pagesAnalysis of An Intermediate Rear Axle Shaft Failure: January 2015Ranjodh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- AT6501 QBDocument8 pagesAT6501 QBSahayaraj GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Train PDFDocument33 pagesPower Train PDFMohamed AbdelmagedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ijert Ijert: Engine Mounts and Its Design ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesIjert Ijert: Engine Mounts and Its Design ConsiderationsGulsan PratapPas encore d'évaluation
- Clutch - WikipediaDocument5 pagesClutch - WikipediaKrishanu ModakPas encore d'évaluation
- KSRTC ReportDocument32 pagesKSRTC ReportSumith raj0% (2)
- Ae Unit 2Document25 pagesAe Unit 2Iyyappan SivalingamPas encore d'évaluation
- Aim: - To Understand Construction, Working and Application of Clutches, Coupling and BrakesDocument6 pagesAim: - To Understand Construction, Working and Application of Clutches, Coupling and BrakesJyoti Ben PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity (Clutch Assembly)Document6 pagesActivity (Clutch Assembly)Ardelyn PaybanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity (Clutch Assembly)Document6 pagesActivity (Clutch Assembly)Ardelyn PaybanoPas encore d'évaluation
- KSRTC Final ReportDocument47 pagesKSRTC Final ReportBoby Thomas100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Clutches Upload Rev1Document11 pagesChapter 2 Clutches Upload Rev1Weekly ExposurePas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of A Shock Absorber: Conference PaperDocument16 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Shock Absorber: Conference PapercmuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions and Answers of CLUTCHDocument3 pagesQuestions and Answers of CLUTCHpriyankar75% (4)
- Keshav Jangir Seminar Front PageDocument39 pagesKeshav Jangir Seminar Front Pagevideo songPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchromesh MechanismDocument7 pagesSynchromesh MechanismZein ElserfyPas encore d'évaluation
- SynchromeshDocument7 pagesSynchromeshZein ElserfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element Analysis of The Oldham Coupling by Using ANSYSDocument6 pagesFinite Element Analysis of The Oldham Coupling by Using ANSYSTejas MirashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of A Shock AbsorberDocument15 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Shock Absorber9012Suchibrata MohantyPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of Single Plate Clutch by Mathematical Modelling and SimulationDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Single Plate Clutch by Mathematical Modelling and SimulationRaghav GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On CLUTCH VIJAY KALEDocument21 pagesReport On CLUTCH VIJAY KALEChinmay AlandkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - CouplingsDocument18 pagesModule 2 - CouplingsthandonksPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Textile Machinery ContentDocument59 pagesMechanics of Textile Machinery ContentPARAMASIVAM SPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 KelegaDocument48 pages1 KelegaSteven WassaakaPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 129283 - ExcitersDocument20 pages03 129283 - Exciterskara_25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Two Manual Transmission/TransaxleDocument13 pagesChapter Two Manual Transmission/TransaxleabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Microproject Plan B FormatDocument7 pagesMicroproject Plan B FormatKaustubh NaikPas encore d'évaluation
- AT6501 (R-13) Notes PDFDocument131 pagesAT6501 (R-13) Notes PDFAashiq NawinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter ThreeDocument29 pagesChapter ThreeAbel OmweriPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of Composite Drive ShaftDocument22 pagesDesign and Analysis of Composite Drive Shaft2129220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 8Document4 pagesExperiment 8Mohd ZakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimal Design of A Clutch Plate Using Ansys: V Mani Kiran Tipirineni, P. Punna RaoDocument5 pagesOptimal Design of A Clutch Plate Using Ansys: V Mani Kiran Tipirineni, P. Punna RaoInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationDocument24 pagesGear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationHada NanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Investigation of Safety Cross Stand For ScramblerDocument6 pagesDesign and Investigation of Safety Cross Stand For ScramblerFinger igPas encore d'évaluation
- Ijme V2i6p107Document5 pagesIjme V2i6p107Atthuru ManikantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modified Suspension of Motorcycle - A ReviewDocument4 pagesModified Suspension of Motorcycle - A ReviewMULYADIPas encore d'évaluation
- Cluch Disc Cover - enDocument4 pagesCluch Disc Cover - entika tokPas encore d'évaluation
- Friction Clutch: 1.single Plate Clutch (Disc Clutch)Document5 pagesFriction Clutch: 1.single Plate Clutch (Disc Clutch)Ashok PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Clutch Auto L.T.D.: Training ReportDocument53 pagesClutch Auto L.T.D.: Training ReportManoj PatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Clutches and Brakes: Prepared By: Solomon GDocument33 pagesClutches and Brakes: Prepared By: Solomon GToleraPas encore d'évaluation
- TugasDocument7 pagesTugasKanoe YoiePas encore d'évaluation
- 588-608 Syambabu NutalapatiDocument21 pages588-608 Syambabu NutalapatiSyam RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Systems: Module - IiDocument27 pagesTransmission Systems: Module - Iipesaru arjunPas encore d'évaluation
- Safari - Feb 4, 2024 at 11:37 PMDocument1 pageSafari - Feb 4, 2024 at 11:37 PMsyansyncPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Pumps - Api-610: Single Stage Volute Casing PumpsDocument5 pagesProcess Pumps - Api-610: Single Stage Volute Casing Pumpsmehrzad1373Pas encore d'évaluation
- Music: Teachers ManualDocument208 pagesMusic: Teachers Manualmydrina100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4chinnu rokzPas encore d'évaluation
- Re - Rockspace.local - Ap - SetupDocument6 pagesRe - Rockspace.local - Ap - SetuptrujillobresslerPas encore d'évaluation
- KeyViewFilterSDK 12.10 DotNetProgrammingDocument270 pagesKeyViewFilterSDK 12.10 DotNetProgrammingOswaldo JuradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Perception On MatrimonyDocument41 pagesConsumer Perception On Matrimonydeepak1818Pas encore d'évaluation
- A1 - Full Papers PS1 10834 2022Document18 pagesA1 - Full Papers PS1 10834 2022DmitryPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 460 Problems: SET 1, Statistics and Experimental DesignDocument69 pagesChemistry 460 Problems: SET 1, Statistics and Experimental DesignDwie Sekar Tyas PrawestryPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 - Using Modern Plant Trait Relationships Between Observed and Theoretical Maximum Stomatal Conductance and Vein Density To Examine Patterns of Plant MacroevolutionDocument10 pages2016 - Using Modern Plant Trait Relationships Between Observed and Theoretical Maximum Stomatal Conductance and Vein Density To Examine Patterns of Plant MacroevolutionJuan Torres CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample LT1 AnsDocument2 pagesSample LT1 AnsEirik LawPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment6 Multiplexer DemultiplexerDocument10 pagesExperiment6 Multiplexer DemultiplexerAj DevezaPas encore d'évaluation
- CuClad Laminates Data SheetDocument4 pagesCuClad Laminates Data SheetDenis CarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Data Management SoftwareDocument12 pagesTest Data Management SoftwareNNiveditaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pretvorbe Merskih EnotDocument4 pagesPretvorbe Merskih Enotpetrusa505Pas encore d'évaluation
- Christie Roadster S+20K Serial CommunicationsDocument87 pagesChristie Roadster S+20K Serial Communicationst_wexPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Investigations On The Causes of Road Failures Constructed AlongDocument8 pagesLaboratory Investigations On The Causes of Road Failures Constructed AlongMulugeta DessiePas encore d'évaluation
- Numpy For Matlab UserDocument17 pagesNumpy For Matlab Userreza khPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfred Sds ProjectDocument10 pagesAlfred Sds ProjectMr TuchelPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Spec Sheet PWM Controller ChipDocument16 pages04 Spec Sheet PWM Controller Chipxuanhiendk2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFDocument430 pages2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFBrianCook73% (11)
- UM0384Document35 pagesUM0384Pat 14HS1Pas encore d'évaluation
- MFTDocument63 pagesMFTvenkatwsPas encore d'évaluation
- iPLON ProfileDocument11 pagesiPLON Profilesudhirm16Pas encore d'évaluation
- GeaDocument17 pagesGeaEasy WritePas encore d'évaluation
- Vibration Absorbers: Scan This QR CodeDocument4 pagesVibration Absorbers: Scan This QR CodeMohamed RaafatPas encore d'évaluation
- PlaxisDocument6 pagesPlaxisRehan HakroPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 24Document8 pagesLecture 24gewaray536Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6.report Face RecognitionDocument45 pages6.report Face RecognitionSuresh MgPas encore d'évaluation
- TomatoDocument19 pagesTomatoaravind kishanPas encore d'évaluation
- Adr141c PDFDocument11 pagesAdr141c PDFNamrata Shetti100% (1)