Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ircle: Mathematics - Shishir Kant Singh
Transféré par
Shishir Kant SinghTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ircle: Mathematics - Shishir Kant Singh
Transféré par
Shishir Kant SinghDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MATH CIRCLE
Mathematics | Shishir Kant Singh
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
Brief Introduction
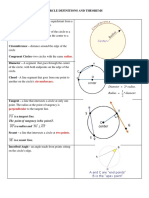
Circle is a set of all points in the plane which are equidistant from a given point ?, called the
center of circle.
Unit circle is a circle, whose radius is equal to one.
Disk is part of the plane bounded by circle.
Radius of circle R is the distance from the circle center ? to any point on the circle.
Diameter of circle D is a segment that connects two points on circle and passes through its
center.
Properties of a circle
1. Diameter of circle is equal two radiuses.
D = 2r
2. The shortest distance from the center circle to the secant (chord) is always smaller radius.
3. Three points that not placed on a straight line can hold only one circle.
4. Among all closed curves of equal length, circle has the largest area.
5. If two circle touch at one point, this point placed on the line that passes through the centers of
the circles.
The Pathshala Classes Page 1
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
Area and circumference of circle
Length of circumference
1. Formula of the circumference length in terms of the diameter:
C = 𝜋𝐷
2. Formula of the circumference length in terms of the radius:
C = 2πr
Formula of the circle area
1. Formula of the circle area in terms of the radius:
𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2
2. Formula of the circle area in terms of the diameter:
A = πD² / 4
The equation of circle
1. The equation of circle with radius r and center at the start of Cartesian coordinate:
r² = x² + y²
2. The equation of circle with radius r and center at point with coordinates (a, b) in the Cartesian
coordinate:
r² = (x - a)² + (y - b)²
3. Parametric equations of circle with a radius r and center at point with coordinates (a, b) in the
Cartesian coordinate:
x = a + r cos t
y = b + r sin t
Tangent of circle and its properties
Tangent is a coplanar straight line that touches the circle at a single point.
Tangent properties
1. Tangent is always perpendicular to the radius of the circle drawn at the point of contact.
2. The shortest distance from the center of circle to tangent is radius of the circle.
The Pathshala Classes Page 2
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
3. If two tangents from touch points B and C on the same circle are not parallel, they intersect at
point A and the point of contact between the segment and the point of intersection of a tangent is
the same segment on a different tangent:
AB = AC
Also, if you draw a line through the center O and the intersection point A of these tangents, the
angles between this line and tangents will be equal:
OAC = OAB
Secant of circle and its properties
Secant of a circle is a straight line, connecting two points of circle.
Properties of circle secant
1.If a point outside the circle (Q) obtained two secant, crossing the circle at two
points A and B for a first secant and C and D for another secant, the products of
two intersecting segments are equal:
AQ · BQ = CQ · DQ
2. If the point comes out of Q circle secant, crossing the circle at two points A and
B, and the tangent point of contact C, then product segments the secant lengths equal
to the square of the tangent:
AQ · BQ = CQ²
The Pathshala Classes Page 3
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
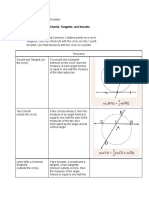
Chord of circle and its properties
Chord of a circle is a segment that connects two points of circle. Chord is a segment of
tangent.
Length of chord
Length of chord in terms of radius and central angle
1. Formula of the chord length in terms of the radius and central angle:
AB = 2r sin (α / 2)
2. Formula of the chord length in terms of the radius and inscribed angle:
AB =2r sin α
Chord properties
1. Two equal chords tightening two identical arc:
if chords AB = CD, then
arc ᵕAB = ᵕ CD
2. If the chord are parallel, the arcs between them will be the same:
if chords AB || CD, then
The Pathshala Classes Page 4
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
ᵕ AD = ᵕ BC
3. If radius of circle is perpendicular to the chord, it divides
chord in half at the point of intersection:
if OD | AB, then
AC = BC
4. If two chords AB and DE intersect at point Q, then the product segments,
formed at the intersection, one chord is the product of a different chord sections:
AQ · BQ = DQ · QC
5. Chords of equal length are equidistant from the center of circle.
if chords AB = CD, then
ON = OK
6. The greater chord the closer it is to the center.
if CD > AB, then
ON < OK
The Pathshala Classes Page 5
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
Central angle and inscribed angle of a circle and its properties
Central angle circle is the angle, the apex of which is the center of circle.
Inscribed angle is the angle inside the circle, the apex of which lies on the circle.
Angle properties
1. All inscribed angles, based on one arc is equal (one end of the chord).
2. Inscribed angle will be a straight (90°), if it is based on the diameter of the
circle.
3. Any inscribed angle is always equal to half the central angle, based on the
same arc
4. If two inscribed angles based on a chord and located on either side of her, the
sum of the angles is 180°.
α+β= 180
The Pathshala Classes Page 6
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Circle Shishir Kant Singh
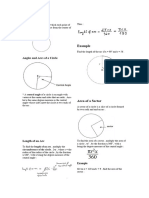
Arc of a circle (ᵕ) is part of the circle, connecting two points on the circle.
Subtending angle of an arc is angle between two radii which limit this arc. Subtending angle
arc is always equal the central angle between radii, which limits end points this arc.
arc length
Formula of the arc length in terms of the central angles (in degrees) and radius:
l = (π r / 180). α
Semicircle is arc whose ends are connected by diameter of a circle.
Semidisc is part of the disk, which is bounded by a semicircle and diameter.
Sector is part of the disk, which is bounded by two radii and an arc between the radii.
Formula of the sector area in terms of the radius and central angles (in degrees)
A = ( π r² / 360°) · α
Segment is part of the disk, which is bounded by the arc and the chord connecting the ends of
this arc.
Concentric circle is circle with different radii whish having a common center.
Annulus is part of the plane bounded by two concentric circles.
The Pathshala Classes Page 7
Saket Nagar | Kidwai Nagar
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesD'EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry CirclesDocument38 pagesGeometry Circlesmishi19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Module 2 - Circle2Document19 pagesFinal Module 2 - Circle2Noel S. De Juan Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Circles TheoryDocument4 pagesCircles TheoryJamal AliyevPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A CircleDocument33 pagesParts of A CircleMr. Rhumer LanojanPas encore d'évaluation
- Topik-2 Bulatan CircleDocument36 pagesTopik-2 Bulatan Circle许如楠Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics ReviewerDocument2 pagesMathematics Revieweremerlayn21Pas encore d'évaluation
- CIRCLES - Angles, ChordsDocument158 pagesCIRCLES - Angles, ChordsMika Pelagio100% (2)
- 6.1 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesDocument42 pages6.1 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesJV GamoPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of A ParallelogramDocument7 pagesProperties of A ParallelogramKristel Mae CaveroPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 10 Week 5 q2Document24 pagesMATH 10 Week 5 q2Jerald TungolPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-10 Maths NotesDocument7 pagesCh-10 Maths NotesJsjn NPas encore d'évaluation
- CirclesDocument19 pagesCirclesHari KrushnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle Definitions and TheoremsDocument8 pagesCircle Definitions and TheoremsGani Almeron100% (1)
- Definitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryDocument8 pagesDefinitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryPaula FanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet06dated16072021 PDFDocument1 pageWorksheet06dated16072021 PDFPushpendra KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10Document68 pagesChapter 10grace_16Pas encore d'évaluation
- G7 Math Q3 Week 7 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesDocument41 pagesG7 Math Q3 Week 7 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesROSEMARIE SANTOSPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles, Secants & TangentsDocument39 pagesCircles, Secants & TangentsKimmy Airam Ramos100% (1)
- CirclesDocument54 pagesCirclesNiggaerPas encore d'évaluation
- Math GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesMath GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerGab AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chord, Tangent and SecantDocument8 pagesChord, Tangent and SecantpraveenshridharPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Project - CirclesDocument41 pagesMaths Project - CirclesSatyan Mittal80% (10)
- Geometry of The Circle PDFDocument7 pagesGeometry of The Circle PDFGregory LewisPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles RevisionDocument31 pagesCircles RevisionTuition MastersPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles RebornDocument13 pagesCircles RebornAyush SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NepanagarDocument37 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya NepanagarSunny KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Las Mathematics 10 Week 2 Quarter 2 Jonathan D NunagDocument9 pagesLas Mathematics 10 Week 2 Quarter 2 Jonathan D NunagJONATHAN NUNAGPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Project For Class 10Document18 pagesMaths Project For Class 10John Nguyen57% (42)
- Day 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Document51 pagesDay 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Free student100% (1)
- CircleDocument11 pagesCircleKathleen Bermejo CatainPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 10 Q2W2Document69 pagesMath 10 Q2W2Leander Kelly Transporte MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles EnglishDocument12 pagesCircles EnglishSatya Prakash ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Math10 q2 Week 4 Act SheetDocument2 pagesMath10 q2 Week 4 Act Sheetzaile felinePas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Document3 pagesGeometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Tyler CosgrovePas encore d'évaluation
- CirclesDocument11 pagesCirclesSumit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 AcquireDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Acquirett NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of A Circle PresentationDocument14 pagesParts of A Circle Presentationromar.allen73Pas encore d'évaluation
- MELVINDocument16 pagesMELVINRosito BaragoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2.1 Mom1iDocument32 pagesChapter 2.1 Mom1iKarell Faye BatulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Math ScrapbookDocument13 pagesMath ScrapbookMark Danielle GeolagioPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles 1Document3 pagesCircles 1achraf najibPas encore d'évaluation
- CirclesDocument26 pagesCirclesNeha ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Circles Tangents and Intersecting ChordsDocument3 pagesCircles Tangents and Intersecting ChordsBinu Kumar SPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsDocument22 pagesImportant Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsStudy IQ92% (38)
- Geometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Document13 pagesGeometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Tapas SwainPas encore d'évaluation
- 24c60 Chapter 5 DoneDocument13 pages24c60 Chapter 5 DoneannabellPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7. CircleDocument18 pagesChapter 7. CirclealkristiyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 MATH13-1Document51 pagesLesson 2 MATH13-1akladffja100% (1)
- CirclesDocument27 pagesCirclesSkrt brrt brtPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Session 4 CircleDocument57 pagesGrade 10 Session 4 CirclemarlonPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts of A Circles and Its Related TermsDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts of A Circles and Its Related TermsAngelica MontezonPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 1-+Circle+Vocabulary+PPT+ (PDF+for+students)Document8 pages3 1-+Circle+Vocabulary+PPT+ (PDF+for+students)DANIEL FRANCO GOMEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle and TangentsDocument8 pagesCircle and Tangentssiddhartha khatuaPas encore d'évaluation
- G10 Math Q2 - Week 2 - 3 Angles-and-Arcs-of-Circles-PowerPointDocument64 pagesG10 Math Q2 - Week 2 - 3 Angles-and-Arcs-of-Circles-PowerPointOlive BotiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 3 Circle II by KelvinDocument7 pagesMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 3 Circle II by KelvinKelvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle and TheoremsDocument32 pagesCircle and Theoremsalexandradeleon080508Pas encore d'évaluation
- Circles PPTDocument69 pagesCircles PPTIfrah ZiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ikjeifjd: Male Shishir Kantsin 2446115 Moo 2 Y 10 M 19 DDocument1 pageIkjeifjd: Male Shishir Kantsin 2446115 Moo 2 Y 10 M 19 DShishir Kant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SBI Account Opening Form Without Cut Mark 02.08.2018Document20 pagesSBI Account Opening Form Without Cut Mark 02.08.2018Shishir Kant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SEED-Training PosterDocument1 pageSEED-Training PosterShishir Kant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Media Partners Profile 2015Document16 pagesMedia Partners Profile 2015Shishir Kant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Complex AnalysisDocument15 pagesMIT Complex AnalysisDheeraj Waghmare0% (1)
- Assignment AMS1110 2022-23Document2 pagesAssignment AMS1110 2022-23Sheikh SaifPas encore d'évaluation
- Compound Interest CalculationDocument2 pagesCompound Interest Calculationbilalak1990Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Practice - Coordinate GeometryDocument4 pagesMath Practice - Coordinate GeometryAvi DhallPas encore d'évaluation
- Matrix Square Root Computation AlgorithmDocument12 pagesMatrix Square Root Computation AlgorithmdoraemonminiPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Mathematics For Jee Main 2019 Ravi Prakash Full ChapterDocument51 pagesComplete Mathematics For Jee Main 2019 Ravi Prakash Full Chapterjoanne.howard1000100% (14)
- L32 PDFDocument12 pagesL32 PDFManchimsetty Sri NidhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Representations of Linear FunctionsDocument4 pagesMultiple Representations of Linear FunctionsDillon StarzlPas encore d'évaluation
- Errata Garling1Document4 pagesErrata Garling1Iskandar Agung AgungPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths p1 QP Gr12 Sept 2021 - EnglishDocument11 pagesMaths p1 QP Gr12 Sept 2021 - EnglishAnymore NdlovuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lucio Boccardo, Gisella Croce - Elliptic Partial Differential Equations-De Gruyter (2013)Document204 pagesLucio Boccardo, Gisella Croce - Elliptic Partial Differential Equations-De Gruyter (2013)Amanda Clara ArrudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge O Level Mathematics Coursebook 2nd EditionDocument727 pagesCambridge O Level Mathematics Coursebook 2nd EditionHoang 13 Dinh TienPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra by Prof. R. Vittal Rao: DiagonalizationDocument6 pagesLinear Algebra by Prof. R. Vittal Rao: Diagonalizationrahul nehraPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Seismology: A Practical Introduction: October 2016Document8 pagesComputational Seismology: A Practical Introduction: October 2016Jane GallowayPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujian 1 k2 Tg42016Document3 pagesUjian 1 k2 Tg42016Ralphieyxa RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuzzy Magic Labelling of Neutrosophic Path and Star GraphDocument12 pagesFuzzy Magic Labelling of Neutrosophic Path and Star GraphScience DirectPas encore d'évaluation
- Zijlema Lecturenotes ODE and SWEDocument136 pagesZijlema Lecturenotes ODE and SWERossy Dinda PratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- First Course in Algebra Part 1 StudentDocument258 pagesFirst Course in Algebra Part 1 Studentlouyant2218100% (1)
- More About Equations: y X y XDocument56 pagesMore About Equations: y X y XWinnie SitPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 Radix SortDocument51 pages18 Radix SortFabio FirminoPas encore d'évaluation
- EC2202-question BankDocument24 pagesEC2202-question BankAnirudhan RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Riemann Zeta Function, Nicely Visualised PDFDocument26 pagesRiemann Zeta Function, Nicely Visualised PDFLazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7, Second Ex First Term 2023-2024 LasDocument2 pagesGrade 7, Second Ex First Term 2023-2024 Lasbehzadjunaid702Pas encore d'évaluation
- DC Coding and Decoding With Convolutional CodesDocument28 pagesDC Coding and Decoding With Convolutional CodesARAVINDPas encore d'évaluation
- Preference RelationDocument68 pagesPreference RelationOmer KhayyamPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Specimen Paper Unit 1 Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument13 pages2013 Specimen Paper Unit 1 Paper 2 Mark SchemeLatoyaWatkinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Maths 6Document77 pagesSecondary Maths 6Dav Gua67% (3)
- Unit 4 Operations ResearchDocument23 pagesUnit 4 Operations Researchkeerthi_sm180% (1)
- D09 FEcp 1 Sem 1Document2 pagesD09 FEcp 1 Sem 1Bhanu SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 15 Solution of A Sequencing ProblemDocument8 pagesLesson 15 Solution of A Sequencing ProblemshivasharanaPas encore d'évaluation