Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract - Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - Suprahyoid Region
Transféré par
jmccoyTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Abstract - Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - Suprahyoid Region
Transféré par
jmccoyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sonographic anatomy of the neck: The suprahyoid region - ScienceDirect Page 1 of 3
Journals & Books Create account Sign in
Get Access Share Export
Journal of Ultrasound
Volume 14, Issue 3, September 2011, Pages 130-135
Sonographic anatomy of the neck: The suprahyoid region
A. Gervasio , G. D’Orta, I. Mujahed, A. Biasio
Show more
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jus.2011.06.001 Get rights and content
Abstract
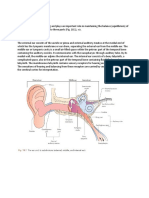
The suprahyoid region extends from the base of the skull to the hyoid bone and includes the
pharyngeal, parapharyngeal, parotid, carotid, masticator, retropharyngeal, and perivertebral
spaces, as well as the oral cavity. The areas that can be explored by ultrasound include the parotid,
carotid, and masticator spaces; the oral cavity; the submandibular and sublingual spaces; the floor
of the mouth; and the root of the tongue. The parotid space contains the parotid gland and the
excretory duct of Steno, the facial nerve, the external carotid artery, the retromandibular vein, and
the intraparotid lymph nodes. The carotid space in the suprahyoid region of the neck contains the
internal carotid artery, the internal jugular vein, cranial nerves IX to XII, and the sympathetic
plexus. Only some parts of the masticator space can be explored sonographically: these include the
masseter muscle, the zygomatic arch and the outer cortex of the ramus of the mandible, and the
suprazygomatic portion of the temporalis muscle. The submandibular space houses the
submandibular gland, the submental and submandibular lymph nodes, and the anterior belly of
digastric muscle. The facial artery and vein and the lower loop of the hypoglossal nerve all pass
through the submandibular space. The sublingual space includes the sublingual gland, the deep
portion of the submandibular gland and its main excretory duct, the hypoglossal nerve (cranial
nerve XII), the lingual nerve (branch of the mandibular branch of trigeminal), and the
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX cranial nerve), and the lingual artery and vein. The mylohyoid muscle
forms the floor of the mouth. The deepest portion of the oral tongue, the root, consists of the
genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles and includes the septum of the tongue. In this article we
present the ultrasound features of the structures located in the suprahyoid region of the neck.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S197134951100035X?via%3Dihub 5/14/19
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The TENS Electrode Placement AtlasDocument14 pagesThe TENS Electrode Placement AtlasSrce Za Srce89% (9)
- 683 Pares Biomagnetismo Engels PDFDocument23 pages683 Pares Biomagnetismo Engels PDFStellaEstel94% (16)
- QRS Jyotsna Rao 1st Year BDS (2) - Compressed - CompressedDocument537 pagesQRS Jyotsna Rao 1st Year BDS (2) - Compressed - CompressedJash Shah67% (12)
- Complete Assessment Script Print FormDocument6 pagesComplete Assessment Script Print Formkeirvyl0% (1)
- Matary Surgical Anatomy 2013Document320 pagesMatary Surgical Anatomy 2013Raouf Ra'fat Soliman96% (23)
- Cosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBDocument11 pagesCosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBcirugia plastica uisPas encore d'évaluation
- Sonographic Anatomy of The Neck - The Suprahyoid Region - AbstractDocument1 pageSonographic Anatomy of The Neck - The Suprahyoid Region - AbstractjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasound Anatomy of The Neck - The Infrahyoid Region - AbstractDocument1 pageUltrasound Anatomy of The Neck - The Infrahyoid Region - AbstractjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sushma 3rd Seminar Arterial Supply and Venous Drainage of HeadDocument63 pagesSushma 3rd Seminar Arterial Supply and Venous Drainage of HeadDrSushma NareshPas encore d'évaluation
- 210190Document6 pages210190meher chohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Neck and Oral CavityDocument41 pagesHead Neck and Oral Cavitymeharnigar123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles of The Head and NeckDocument176 pagesMuscles of The Head and Neckpianistgirl99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Salivary Gland AnatomyDocument38 pagesSalivary Gland AnatomyAlex HaileyesusPas encore d'évaluation
- Imaging The Oral Cavity - Key Concepts For The Radiologist - PMCDocument24 pagesImaging The Oral Cavity - Key Concepts For The Radiologist - PMCVilaseca224466Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oral CavityDocument82 pagesOral Cavitydavid100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of LarynxDocument37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Larynxsuci100% (1)
- Carlson 2000Document13 pagesCarlson 2000Mamadou DIENEPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharynx Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyDocument9 pagesPharynx Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyCarmen-BadeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocument34 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report CSOMDocument13 pagesCase Report CSOMNashria RusdhyPas encore d'évaluation
- Craneo Sobotta PDFDocument111 pagesCraneo Sobotta PDFMaria Teresa AlvaradoPas encore d'évaluation
- RADI AnatomyDocument37 pagesRADI AnatomyAmanda AmaroPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pharyngeal Arches - Clefts - Pouches - Embryology - TeachMeAnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Pharyngeal Arches - Clefts - Pouches - Embryology - TeachMeAnatomypinkrawpineapplePas encore d'évaluation
- The Infratemporal FossaDocument5 pagesThe Infratemporal FossaxxyumePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedDocument88 pagesLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomyofthe Auditory SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomyofthe Auditory System32. Nguyễn Tiến Thái SơnPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Submandibular Region-Dr - GosaiDocument14 pages7 Submandibular Region-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Regjionet 2Document105 pagesRegjionet 2Rijad Musli100% (1)
- Parotid Gland Anatomy and Clinical RelevanceDocument5 pagesParotid Gland Anatomy and Clinical RelevanceAndra BauerPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 RHINOLOGY NoseDocument116 pages1 RHINOLOGY NoseWai Kwong ChiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fascial Spaces of the Face and NeckDocument58 pagesFascial Spaces of the Face and Neckmuhamed sayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ve Summary ChartDocument10 pagesVe Summary ChartMoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigeminal NerveDocument2 pagesTrigeminal NerveVanshika JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter V - Human Anatomy: 7-Resources & Indexes Module 8-AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesChapter V - Human Anatomy: 7-Resources & Indexes Module 8-AbbreviationsIndranil SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- ანატომია ზეპირიDocument22 pagesანატომია ზეპირიmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sub Mandibular RegionDocument8 pagesThe Sub Mandibular RegionSugiarti YaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Oral Structures for Implant DentistryDocument61 pagesAnatomy of Oral Structures for Implant DentistryDeb SPas encore d'évaluation
- Head and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017Document53 pagesHead and Neck Anatomy: A. Arsalan, MD M. Martin MD, DMD October 4-5, 2017aaamirrrPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharynx NotesDocument8 pagesPharynx Notesm0rat0r1umPas encore d'évaluation
- ورق مذاكره PDFDocument100 pagesورق مذاكره PDFsalamred100% (1)
- PLASTIC SURGERY CRANIOFACIAL NOTESDocument69 pagesPLASTIC SURGERY CRANIOFACIAL NOTESseandarcy600100% (1)
- Skull 2Document34 pagesSkull 2saifPas encore d'évaluation
- US Anatomy of The Neck 2Document5 pagesUS Anatomy of The Neck 2Ignacio Navarrete LorenzonPas encore d'évaluation
- External Ear AnatomyDocument3 pagesExternal Ear AnatomybarbacumlaudePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The NeckDocument34 pagesAnatomy of The NeckAsma AlamoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocument12 pagesChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudiePas encore d'évaluation
- The Anatomical Record - ) SakamotoDocument9 pagesThe Anatomical Record - ) SakamotoIngridNatalyYomayuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Orbital Cavity & Oral Cavity AnatomyDocument3 pagesOrbital Cavity & Oral Cavity Anatomyحوراء عارف الموسويPas encore d'évaluation
- Found 903118732 4683Document2 pagesFound 903118732 4683Bogdan Robert CPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 AnatomyDocument14 pagesLecture 3 AnatomyZA IDPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefDocument88 pagesAnatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefGilbert Sterling OctaviusPas encore d'évaluation
- Skull Bones GuideDocument17 pagesSkull Bones Guideمدونة الأحترافPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Nose and Paranasal Sinusbayoe_pra100% (1)
- Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesParotid Glandneleh grayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharynx: DissectionDocument23 pagesPharynx: DissectionrajtanniruPas encore d'évaluation
- Head and Face: Dr. Muh. Iqbal Basri, M.Kes, SP.SDocument34 pagesHead and Face: Dr. Muh. Iqbal Basri, M.Kes, SP.SamiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 04 Upper Airways Larynx English 2014-2Document22 pages2 04 Upper Airways Larynx English 2014-2Mariam AlavidzePas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Anatomy 1Document4 pagesClinical Anatomy 1Oussama APas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of the Ear: External, Middle & Inner StructuresDocument63 pagesAnatomy of the Ear: External, Middle & Inner StructuresgabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Anat NotesDocument94 pagesAnat NotesCarineHugz (CarineHugz)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aa AnatomyDocument109 pagesAa AnatomyshailendraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)D'EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)Pas encore d'évaluation
- TBI-Integrated Approaches To Improve Prevention Clinical Care and ResearchDocument62 pagesTBI-Integrated Approaches To Improve Prevention Clinical Care and ResearchCarla PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Outcome Assessment After TBIDocument1 pageOutcome Assessment After TBIjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistema PrimovascularDocument2 pagesSistema PrimovascularDavid LeónPas encore d'évaluation
- When To Start Tongue Thrust TreatmentDocument6 pagesWhen To Start Tongue Thrust TreatmentjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dura - Sciatic Nerve TensionDocument5 pagesDura - Sciatic Nerve TensionjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension PDFDocument34 pagesIdiopathic Intracranial Hypertension PDFjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chiropractic and Energy Medicine A Shared HistoryDocument28 pagesChiropractic and Energy Medicine A Shared HistoryjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- gp09044 Boyd Mechanosensitivity PDFDocument11 pagesgp09044 Boyd Mechanosensitivity PDFjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension PDFDocument34 pagesIdiopathic Intracranial Hypertension PDFjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Carpal Tunnel PDFDocument7 pagesCarpal Tunnel PDFAnonymous hvOuCjPas encore d'évaluation
- Median Arcuate Ligament SyndromeDocument2 pagesMedian Arcuate Ligament SyndromejmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteopathic Fascia Treatment Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesOsteopathic Fascia Treatment Peripheral Nervous SystemjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Laparoscopic Umbilical Hernia RepairDocument5 pagesLaparoscopic Umbilical Hernia RepairjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteopathic Fascia Treatment Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesOsteopathic Fascia Treatment Peripheral Nervous SystemjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- JMDH 7 011 Skin Fascia and ScarsDocument14 pagesJMDH 7 011 Skin Fascia and ScarsjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Coupling of The Deep Abdominal and Paraspinal MmsDocument16 pagesFunctional Coupling of The Deep Abdominal and Paraspinal MmsjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Diastasis Recti 0038 1661380Document7 pagesDiastasis Recti 0038 1661380jmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Fibroblast Inorder To Comprehended The FasciaDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Fibroblast Inorder To Comprehended The FasciaSilvia Victoria SavaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Fibroblast Inorder To Comprehended The FasciaDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Fibroblast Inorder To Comprehended The FasciaSilvia Victoria SavaroPas encore d'évaluation
- The Thoracolumbar FasciaDocument30 pagesThe Thoracolumbar FasciaAlPas encore d'évaluation
- The Thoracolumbar FasciaDocument30 pagesThe Thoracolumbar FasciaAlPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological Manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome(s)Document14 pagesNeurological Manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome(s)jmccoy100% (2)
- Evaluación Manual Del DiafragmaDocument8 pagesEvaluación Manual Del DiafragmaSilvia Victoria SavaroPas encore d'évaluation
- JMDH 7 011 Skin Fascia and ScarsDocument14 pagesJMDH 7 011 Skin Fascia and ScarsjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Saliva Transit and GERDDocument6 pagesSaliva Transit and GERDjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cricopharyngeal DysfunctionDocument7 pagesCricopharyngeal Dysfunctionale5432Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Children With AerophagiaDocument7 pagesStudy of Children With AerophagiajmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- JMDH 6 281 PDFDocument11 pagesJMDH 6 281 PDFAmiliya EmilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lumbar Facet Pain ArticleDocument24 pagesLumbar Facet Pain ArticlejmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Maneuvers For BPPVDocument8 pagesComparison of Maneuvers For BPPVjmccoyPas encore d'évaluation
- General Principles of Physical ExaminationDocument6 pagesGeneral Principles of Physical ExaminationPhysiotherapist AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Radical Neck Dissection: (RND) Classification, Indication and TechniquesDocument42 pagesRadical Neck Dissection: (RND) Classification, Indication and TechniquesPatrycyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Massage Therapy School ProgramDocument270 pagesMassage Therapy School ProgramLimarOrravanPas encore d'évaluation
- Angiology: (LECTURE-3)Document6 pagesAngiology: (LECTURE-3)আহানাফ তাহমিদ শব্দPas encore d'évaluation
- The 7 Chakras What Are Chakras?Document42 pagesThe 7 Chakras What Are Chakras?Estefania LoaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPARATIVE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY CAT MUSCLESDocument10 pagesCOMPARATIVE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY CAT MUSCLESKenneth SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Rao's Guide to Hanging InjuriesDocument11 pagesDr. Rao's Guide to Hanging InjuriesNur Emmy Fizreena ShamsuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical assessment findings 55kg womanDocument5 pagesPhysical assessment findings 55kg womanMtch V. BumanlagPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3Document56 pagesQuiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3MedShare75% (4)
- Human Gross Anatomy Syllabus-Fall 2010-2011Document16 pagesHuman Gross Anatomy Syllabus-Fall 2010-2011Zeina Nazih Bou DiabPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigger Point FinderDocument160 pagesTrigger Point Finderec16043Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing BundleDocument107 pagesNursing BundleNina Klairea Padua75% (4)
- Korean Hand Therapy - Dan Lobash LAcDocument13 pagesKorean Hand Therapy - Dan Lobash LActvmedicine100% (6)
- Find A Comfortable Way of BreathingDocument4 pagesFind A Comfortable Way of Breathingarkaprava paulPas encore d'évaluation
- Affections of OesophagusDocument32 pagesAffections of OesophagusNaveen BasudePas encore d'évaluation
- Head and NeckkkkkkDocument7 pagesHead and NeckkkkkkJoey A. RumbaoaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Essential Guide to Neck Anatomy and DisordersDocument224 pagesThe Essential Guide to Neck Anatomy and DisordersDr SS ki VinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Trans SaVi Oto Lec 10 Head and Neck Anatomy and Benign Masses 1st SemDocument7 pagesTrans SaVi Oto Lec 10 Head and Neck Anatomy and Benign Masses 1st SemJoherPas encore d'évaluation
- @anesthesia Books 2015 Essentials PDFDocument406 pages@anesthesia Books 2015 Essentials PDFLuminița LumiPas encore d'évaluation
- College Nursing Allied Health SciencesDocument7 pagesCollege Nursing Allied Health SciencesSophia Sweet SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment: General AppearanceDocument2 pagesPhysical Assessment: General AppearanceSheryl Ann Barit PedinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drowning CaseDocument3 pagesDrowning CaseMiranda NasutionPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Tongue Root, Floor, Neck PhlegmonDocument30 pages5 Tongue Root, Floor, Neck PhlegmonАлександр ВолошанPas encore d'évaluation
- US Marines Close Combat HandbookDocument113 pagesUS Marines Close Combat Handbookbob76239100% (1)
- prb9916Document18 pagesprb9916api-330028659Pas encore d'évaluation