Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
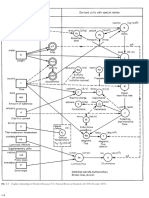
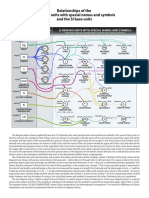
Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary Units
Transféré par
Rajkumar ATitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary Units
Transféré par
Rajkumar ADroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
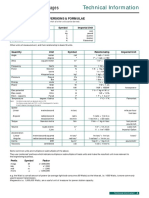
UNITS AND CONSTANT
Base and Supplementary Units
Quantity Unit Symbol
Length meter m
Mass kilogram kg
Time second s
Electric current ampere A
Thermodynamic temperature Kelvin K
Luminous intensity candela cd
Molecular substance mole mol
Plane angle radian rad
Solid angle steradian sr
Derived Units
Quantity Unit Symbol
Space and Time
Area square meter m²
Volume cubic meter m³
Velocity meter per second m/s
Acceleration meter per second per second m/s²
Angular velocity radian per second rad/s
Angular acceleration radian per second per second rad/s²
Frequency hertz Hz (cycle/s)
Rotational speed revolution per second r/s
revolution per minute r/m
Solid angle steradian sr
Mechanics
Density kilogram per cubic meter kg/m³
Momentum kilogram meter per second kg·m/s
Moment of inertia kilogram meter squared kg·m³
Force newton N (kg·m/s²)
Torque, moment of force newton meter N·m
Energy, work, heat quantity joule J (N·m)
Power watt W (J/s)
Pressure, stress pascal Pa (N/m²)
Solid angle steradian sr
Heat
Customary temperature degree Celsius °C
Thermal conductivity watt per meter Kelvin W/(m·K)
Entropy joule per Kelvin J/K
Specific heat joule per kilogram Kelvin J/(kg·K)
Electricity and Magnetism
Electric charge coulomb C (A·s)
Electric potential, voltage, electromotive V (W/A)
volt
force
Electric field strength volt per meter V/m
Capacitance farad F (A·s/V)
Current daily ampere per square meter A/m²
Magnetic field strength ampere per meter A/m
Magnetic flux weber Wb (V·s)
Magnetic flux density tesla T (Wb/m²)
Inductance henry H=V·s/A
Permeability henry per meter H/m
Resistance ohm =V/A
Conductance siemens S=A/V
Magnetomotive force ampere A
Light
Luminous flux lumen lm (cd·sr)
Illumination lux lx (lm/m²)
Luminance candela per square meter cd/m²
Viscosity
Kinematic viscosity square meter per second m²/s
Dynamic (absolute) viscosity pascal second Pa·s
Quantity Equivalent Dimensions S.I. units
Kilogram
Mass M
(kg)
Length L Metre (m)
Time T Second (s)
Frequency cycles/unit time T-1 Hertz (Hz)
Area length x width L2 m2
Volume length x height x width L3 m3
Density Mass/unit volume ML-3 kg/m3
Velocity Distance/unit time LT-1 m/s
Acceleration Velocity/unit time LT-2 m/s2
Force mass x acceleration MLT-2 Newton
mass x gravitational acceleration
Kilogram
Weight (terrestrial surface acceleration = 9.81 MLT-2
(?)
m/s2 = g)
Pressure or
force/unit area ML-1T-2 Pascal (Pa)
Stress
Moment of
mass x length2 ML2 kg m2
Inertia
Work force x distance ML2T-2 Joule (J)
Energy Work capacity ML2T-2 Joule (J)
Potential mass x gravitational acceleration x height
ML2T-2 Joule (J)
Energy raised
Kinetic Energy 1/2 mass x velocity2 ML2T-2 Joule (J)
Power Work/unit time ML2T-3 Watt (W)
Momentum Mass x velocity MLT-1
CONVERSIONS
Millibar (mb): 1 mb = 100 Pa; 1 Pa = 0.01 mb
Celsius: oC = K – 273.15; K = oC + 273.15
Fahrenheit: oF = 9/5(oC) + 32; oC = 5/9(oF-32)
USEFUL NUMERICAL CONSTANTS
Universal Gas Constant (R) 8.3143 J K-1 mol-1
Stefan-Boltzmann constant (s) 56.696 x 10-9 W m-2 K-4
Planck constant (h) 0.66262 x 10-33 J s
Velocity of light (c) 299.8 x 106 m s-1
Solar constant 1.38 x 103 W m-2
Wien’s constant 2897 mm
Acceleration due to gravity 9.80665 m s-2
Molecular weight of dry air 28.97 g mol-1
Density of dry air 1.209 kg m-3
Specific heat of air at constant pressure (Cp) 1004 J K-1 kg-1
Gas constant for dry air (Rd) 287 J kg-1 K-1
Standard atmospheric pressure 101.3 kPa
Molecular weight of water 18.016 g mol-1
Gas constant for water vapor (Rv) 461 J kg-1 K-1
Specific heat of water vapor at constant pressure 1952 J K-1 kg-1
Latent heat of vaporization (L) 2.50 x 106 J kg-1
Name Symbol Value
· atomic mass constant mu 1.660539x10-27 kg
· Avogadro constant NA 6.022142x1023 /mol
· Bohr magneton mB 9.274009x10-24 J/T
· Bohr radius a0 5.291772x10-11 m
· Boltzmann constant k 1.380650x10-23 J/K
· conductance quantum G0 7.748092x10-5 S
· electric permittivity constant 0 1/(m0·c2) = 8.85418781...x10-12 F/m
· electron Compton wavelength c 2.426310x10-12 m
· electron magnetic moment me 9.284764x10-24
· electron radius (classical) re 2.817940x10-15 m
· electron rest mass me 9.109382x10-31 kg
· electron volt eV 1.602176x10-19 J
· elementary charge e 1.602176x10-19 C
· Euler's constant 0.577215664901532...
· Faraday constant F 9.648524x104 C/mol
· fine-structure constant 7.297353x10-3
· first radiation constant c1 3.741771x10-16 W/m2
· golden ratio 1.618033988749894...
· gravitational constant G 6.6732x10-11 N-m2/kg2
· Josephson constant KJ 4.835979x1014 Hz/V
· magnetic flux quantum 0 2.067834x10-15 Wb
· magnetic permeability constant m0 4 x10-7 = 1.2566370614...x10-6 H/m
· natural log base e 2.718281828459045...
· neutron magnetic moment mn 9.662364x10-27 J/T
· neutron rest mass mn 1.674927x10-27 kg
· nuclear magneton mN 5.050783x10-27 J/T
· pi 3.14159265358979323846264...
· Planck constant h 6.626069x10-34 J-s
· proton Compton wavelength c,p 1.321410x10-15 m
· proton magnetic moment mp 1.410607x10-26 J/T
· proton rest mass mp 1.672622x10-27 kg
· Rydberg constant 1.097373x107 /m
· second radiation constant c2 1.438775x10-2 m-K
· speed of light in vacuum c 2.99792458x108 m/s
· standard volume of ideal gas V0 2.24136x10-2 m3/mol
· Stefan-Boltzmann constant s 5.670400x10-8 W/m2-K4
· universal gas constant R 8.314472 J/mol-K
· Wien displacement law constant b 2.897769x10-3 m-K
Lastly updated on ,
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- UnitsDocument16 pagesUnitsVinayChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Std11 Nutr EMDocument234 pagesStd11 Nutr EMkalaikalai360Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sugar Industry PrimerDocument38 pagesSugar Industry PrimerDody IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Saes-L-109, 1.29.2018Document16 pagesSaes-L-109, 1.29.2018Rami ELLOUMI100% (1)
- SI Units and Symbols Used in The Guide: Subject Physical Quantity Symbol Name UnitDocument5 pagesSI Units and Symbols Used in The Guide: Subject Physical Quantity Symbol Name UnitbalaramankrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping & Piping ComponentsDocument37 pagesPiping & Piping ComponentsRavindra S. JivaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm 02Document623 pagesAstm 02Bilel RebaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping S1Document44 pagesPiping S1Rajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview Of: Plant Layout AND PipingDocument21 pagesAn Overview Of: Plant Layout AND PipingRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview Of: Plant Layout AND PipingDocument21 pagesAn Overview Of: Plant Layout AND PipingRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Overview 01Document18 pagesPiping Overview 01Rajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Aramco Welding Inspector InterviewDocument18 pagesAramco Welding Inspector InterviewTurbo Snail R100% (5)
- SI Units Color Diagram PDFDocument1 pageSI Units Color Diagram PDFX800XLPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Assurance QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesQuality Assurance QuestionnaireAbdelkader FattouchePas encore d'évaluation
- SI Base UnitsDocument11 pagesSI Base UnitsHasan BashoriPas encore d'évaluation
- PICKLING HANDBOOK Surface Treatment of Stainless SteelsDocument26 pagesPICKLING HANDBOOK Surface Treatment of Stainless SteelsSuryaprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Source:: S.I. Units of MeasurementDocument2 pagesSource:: S.I. Units of Measurementnripen kalitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Noise Control in BuildingsDocument12 pagesPassive Noise Control in BuildingsANJUSREE B.S. MBT18CE025Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pid Legend PDFDocument1 pagePid Legend PDFSocMed Dtk UI0% (1)
- Protective Coatings Manual 1Document52 pagesProtective Coatings Manual 1Rajkumar A100% (2)
- Rocess LOW Iagram: An OverviewDocument20 pagesRocess LOW Iagram: An OverviewRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Math FormulasDocument173 pagesMath Formulasrajkumar.manjuPas encore d'évaluation
- 2004-D-Piping SpecialitiesDocument24 pages2004-D-Piping Specialitiessids82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Welding RodDocument368 pagesWelding Rodjrod91586% (29)
- Welding RodDocument368 pagesWelding Rodjrod91586% (29)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- SI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDocument6 pagesSI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolHazem SobhiPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM Grades in PipingDocument1 pageASTM Grades in PipingRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Units: 3. U.S. Units of Measurement 4. Tables of EquivalentsDocument8 pagesUnits: 3. U.S. Units of Measurement 4. Tables of EquivalentsAndré OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Standard and SpecificationDocument27 pagesPiping Standard and SpecificationSunil Kumar100% (2)
- API 570 ReviewDocument1 pageAPI 570 ReviewRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1Document8 pagesLesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1GM ShioriPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)Document18 pagesGraphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)annisa putriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Document5 pagesThe Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Sama UmatePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic and Derived Si UnitsDocument2 pagesBasic and Derived Si UnitsJey KPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion Factors PDFDocument3 pagesConversion Factors PDFArbenson CPas encore d'évaluation
- Si Units PDFDocument4 pagesSi Units PDFசெல்வ குமார்Pas encore d'évaluation
- AppendixDocument4 pagesAppendixResham ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix A: SI Units: Rules About Writing UnitsDocument3 pagesAppendix A: SI Units: Rules About Writing UnitsLuis SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Latin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of MeasureDocument5 pagesLatin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of MeasureChase CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- V. Dimensions and Units For Physical Quantities Mechanical UnitsDocument4 pagesV. Dimensions and Units For Physical Quantities Mechanical UnitsLei TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix 1 Units of Measures and SymbolsDocument1 pageAppendix 1 Units of Measures and SymbolsRam kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- UNITSDocument9 pagesUNITSDhayane RedoquerioPas encore d'évaluation
- SI UNITS (Physics 5054)Document2 pagesSI UNITS (Physics 5054)Haris ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Information: Back To Contents PagesDocument8 pagesTechnical Information: Back To Contents PagesAditya PrasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unidades para Formato ApaDocument4 pagesUnidades para Formato ApaJanePas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix A: The International System of UnitsDocument8 pagesAppendix A: The International System of UnitsIvan gheorghePas encore d'évaluation
- Si UnitsDocument2 pagesSi Unitsmaharshi DaddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Information: Engineering Units, Conversions & FormulaeDocument8 pagesTechnical Information: Engineering Units, Conversions & FormulaePeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Internatsystem UnitDocument1 pageInternatsystem Unitdobridorin2023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Scalar and Units ReviewDocument43 pagesVector Scalar and Units ReviewGumball DumballPas encore d'évaluation
- Leo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesDocument12 pagesLeo Betis Morales Thermodyanmics Reviewer NotesVynz JoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas 4Document1 pageFormulas 4Anavheoba Abraham100% (1)
- 48) Sistemul InternationalDocument5 pages48) Sistemul InternationalCosmin LTDAPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME Secc II D Si UnitsDocument3 pagesASME Secc II D Si UnitsCARLOS MARIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Power and Energy Measurement Units and Techniques: 2.1 The SI System and Conversion FactorsDocument19 pagesPower and Energy Measurement Units and Techniques: 2.1 The SI System and Conversion FactorsSatyam SankhuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Table 1. Si Derived Units Expressed in Terms of Si Base Units and Si Supplementary UnitsDocument6 pagesTable 1. Si Derived Units Expressed in Terms of Si Base Units and Si Supplementary Unitskevin_pajarinPas encore d'évaluation
- SI Mapa 17157Document1 pageSI Mapa 17157Yary GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Symbols2Document27 pagesPhysics Symbols2ClothoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unut Conversion 1Document1 pageUnut Conversion 1Vincent SangPas encore d'évaluation
- Base Si UnitsDocument10 pagesBase Si UnitsJehana NaolPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2Document10 pagesLecture 2am1998jedPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading 1Document11 pagesReading 1shafyvonommyPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFDocument6 pagesPhysical Quantities, Standards and Units PDFARAVINDPas encore d'évaluation
- The International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesThe International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsSamir ZaghloolPas encore d'évaluation
- Notebook 1: Lindsey ShrinerDocument3 pagesNotebook 1: Lindsey Shrinerapi-338662480Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper Anthe-2017Document4 pagesSample Paper Anthe-2017Bhumika DPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Electric Circuit Theory BTDocument18 pagesLecture 1 Electric Circuit Theory BTnjuraimelvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics SymbolsDocument2 pagesPhysics SymbolsAbdul SamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Units Table 2ttoDocument1 pageUnits Table 2ttoapi-457971404Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes-56395934Document34 pagesPhysics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes-56395934masairev8Pas encore d'évaluation
- FSK 2024 Practical Manual StudentsDocument64 pagesFSK 2024 Practical Manual Studentsnapnom22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Symbols1Document7 pagesPhysics Symbols1ClothoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Short History of MeasurementDocument12 pagesA Short History of MeasurementAsad SamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Named Units Derived FromDocument5 pagesNamed Units Derived FromYuunari LingPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Exam Quick Revision NotesDocument40 pagesPhysics Exam Quick Revision NotesPinky Ann DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves and Waveforms: Symbol Meaning SI Units of MeasureDocument5 pagesWaves and Waveforms: Symbol Meaning SI Units of MeasurePRincess ScarLetPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Document2 pagesBasic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Muhammad Noman Mughal0% (1)
- Physics Muster PDFDocument36 pagesPhysics Muster PDFMarlon FariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Mechanics o Level Notes 2023-24 SyllabusDocument19 pagesComplete Mechanics o Level Notes 2023-24 SyllabusAbsar KhaskheliPas encore d'évaluation
- Single-Phase Transformers and AC Machines: Electric Power / ControlsDocument134 pagesSingle-Phase Transformers and AC Machines: Electric Power / ControlsIsrael AriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping & Fittings Surface & Volume Information 2Document12 pagesPiping & Fittings Surface & Volume Information 2Rajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Hse Officer Approval Application: Plot No. HSE Officer's ID No. (If Any) Contractor NameDocument2 pagesHse Officer Approval Application: Plot No. HSE Officer's ID No. (If Any) Contractor Namejap marcellenPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Calculation & PaintDocument14 pagesSurface Calculation & PaintRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Jotun Top Coat ApplicationDocument5 pagesJotun Top Coat ApplicationRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Using SSPC Coating Material Standards 1 PDFDocument11 pagesUsing SSPC Coating Material Standards 1 PDFarbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hempelin Mastic 45889 Epoxy Primer Base For Multi Component Product MSDSDocument13 pagesHempelin Mastic 45889 Epoxy Primer Base For Multi Component Product MSDSRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- QC Engineer (Mechanical) - 2Document5 pagesQC Engineer (Mechanical) - 2Rajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- API 510 Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesAPI 510 Sample Questionsbichibtech1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ameron 2000m and 7000mDocument28 pagesAmeron 2000m and 7000mhadrijkPas encore d'évaluation
- PipingDocument8 pagesPipingRajkumar APas encore d'évaluation
- Pipng Questionnaire - 1Document32 pagesPipng Questionnaire - 1Bala MuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Tank Heating Log FormDocument7 pagesTank Heating Log FormGetting 1Million Subs Without Videos CHALLENGEPas encore d'évaluation
- Solenoid Valve 3V Series Air Valve 3A Series: Pneumatic PneumaticDocument8 pagesSolenoid Valve 3V Series Air Valve 3A Series: Pneumatic PneumaticVivin Welroy RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- RT30 Operate InstrukcjaDocument97 pagesRT30 Operate Instrukcjaallegro.ds.spinPas encore d'évaluation
- 35-3000RKA-LEL Sample Draw Combustible Gas Detector: SpecificationsDocument18 pages35-3000RKA-LEL Sample Draw Combustible Gas Detector: SpecificationspcatruongPas encore d'évaluation
- CAT4-2 Complete ENDocument264 pagesCAT4-2 Complete ENalltheloveintheworldPas encore d'évaluation
- LMP NodalBasics 2004jan14Document61 pagesLMP NodalBasics 2004jan14Dzikri HakamPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.4.1 INV5.4.1HessLawLab - Sem2 2017-HaleemMohamedAli EditDocument7 pages5.4.1 INV5.4.1HessLawLab - Sem2 2017-HaleemMohamedAli EditHaleem MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Vc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJDocument6 pagesVc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJGary IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit ConversionDocument21 pagesUnit ConversioninsidereaderPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4 Water Conservation: Water Monitoring and ManagementDocument3 pages1.4 Water Conservation: Water Monitoring and ManagementGaurav DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calefaccion Mazda 3 2006 - 2010Document2 pagesCalefaccion Mazda 3 2006 - 2010Jhon ConnorPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes 08Document25 pagesLecture Notes 08Abdul Hakeem Semar KamaluddinPas encore d'évaluation
- (Page113-134) GCSE Physics Mark Scheme Paper 1 Nov 18Document12 pages(Page113-134) GCSE Physics Mark Scheme Paper 1 Nov 18ShaguPas encore d'évaluation
- 80010046v01 15 7 2013 10 19 5 331Document2 pages80010046v01 15 7 2013 10 19 5 331Ricardo LoureiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Outotec: Managing Talent Globally With Successfactors® SolutionsDocument3 pagesOutotec: Managing Talent Globally With Successfactors® SolutionsxandaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Power Theft Monitering - 2Document22 pagesWireless Power Theft Monitering - 2chakri1327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sizing Phase-Change Energy Storage Units For Air-Based Solar Heating SystemsDocument5 pagesSizing Phase-Change Energy Storage Units For Air-Based Solar Heating Systemsfabio1199Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline & Gas Journal PDFDocument128 pagesPipeline & Gas Journal PDFcespinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preview 2006+ASHRAE+HANDBOOKDocument8 pagesPreview 2006+ASHRAE+HANDBOOKashraf haniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethylene Glycol Heat-Transfer FluidDocument4 pagesEthylene Glycol Heat-Transfer Fluidashif28Pas encore d'évaluation
- HYSYS Upstream GuideDocument188 pagesHYSYS Upstream GuideJahangir Malik100% (1)
- Manufacturing ProcessDocument42 pagesManufacturing ProcesssuganyaPas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual-Heated DryerDocument65 pagesUser Manual-Heated Dryersasa hhPas encore d'évaluation
- Omnik - Let Mankind Share and Enjoy Blue Sky and White Clouds Professional Inverter ManufacturerDocument18 pagesOmnik - Let Mankind Share and Enjoy Blue Sky and White Clouds Professional Inverter ManufactureromnikshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Omnicomm LLS 4 Fuel Level Sensors: User Manual 18.12.2018Document20 pagesOmnicomm LLS 4 Fuel Level Sensors: User Manual 18.12.2018Giovanni QuinteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Spare Parts List STORM 15 20180000 XDocument4 pagesSpare Parts List STORM 15 20180000 XFati ZoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Opgc Owners Engineer - CPPDocument18 pagesOpgc Owners Engineer - CPPwas00266Pas encore d'évaluation