Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Transféré par
anon-579447Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Untitled
Transféré par
anon-579447Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Physical Geology
Chapter 8
Historical Geology/Geologic Time
Notes
Slide 2:
James Hutton was a Scottish _______________________ who lived in
the 1700’s.
He is considered by many people to be
______________________________________.
He believed the earth to be very ______________________ and talked
of it as being ______________________ of years old. He developed
the idea of ____________________________________________.
Slide 3:
________________________ is an idea that says the present
is the key to understanding the past. Natural processes at work today
also worked in the
past. These processes were also at work in the geologic
_______________________. Therefrore, what we see happening
_______________________ can be used to help us understand the
past.
_______________________ is more widely accepted.
_______________________says that processes today can be used to
help us interpret the past, however, we must keep in mind that
_______________________today may be much different than those
of processes in the past. Also, the _______________________ today
and in the past may not be exactly the same.
Slide 4:
In other words. . . If waves wash up on a shoreline today and create a
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 1
sandy beach with its associated features, environments, and life forms,
then we can assume that similar
_________________________happened in the past. When we see
features in rock that are like those formed in modern-
________________________ we can assume those rocks then formed
in a similar way as those today.
Sand moved by a current creates angled layers in a sand dune called
____________________________. If we see
___________________ in sand dunes today, and we see
___________________ in Sandstone of Zion’s Park, then in what
environment did the sandstone likely form?
__________________________________
What might similar cross-beds on Mars indicate?
Slide 5:
Geologists believe the earth to be very old
(_________________________ years old).
How much is a million? Billion? A billion is an unimaginable amount!
It would take you ________________ years and 7 months to count to
a billion if you counted one number
per second.
If you had a billion dollars it would take you _______________ years to
spend all the money if you spent 1000 dollars every hour.
Slide 6:
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 2
Name two methods used to date the age of the earth:
____________________________ and
____________________________
1) ____________________________ (numerical dating,
radiometric dating, or radioisotope dating)The use of radioactive
elements in minerals to give a specific number of years of a
geologic event.
2) ____________________________a method of dating geologic
events/features by putting them in a sequence or order in which
they occurred. It compares the
____________________________ of one event to other
events.
Slide 7:
State the law of superposition and make a drawing to represent it.
Slide 8:
State the law of original horizontality and make a sketch that shows it.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 3
Make a sketch that does not represent rocks with original horizontality.
Slide 9:
The law of __________________________ states that a disrupted
pattern is older than the cause of the disruption, or in other words, a
______________________________ that cuts another
_____________________________ is younger than the feature it
cuts.
Make a sketch that represents this principle.
Slide 10:
What are inclusions and what do they tell us?
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 4
Make a labeled sketch that shows two possible places we would find
inclusions.
Slide 12:
What is correlation?
Name three ways/process used in correlation
a)
b)
c)
Slide 13:
__________________________ describes how we are able to
physically trace a layer of rock. _____________________________ is
generally limited to a small geographic area, and does not extend to other
regions.
Slide 14:
Using ____________________________ types to correlate rocks
from one region to another can be very useful, however, it is best to use
a ______________________ of rock for such correlation.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 5
Make a simple sketch that shows how you could correlate rock layers
from two different places. Include no more than four layers in your
sketch.
Slides 16- 18
What is a problem with just using similar lithologies (rock types) for
correlation?
Slide 19:
________________________________ is comparing fossils from one
place to another.
As we study sedimentary rocks we notice that certain
_________________________ are found in certain layers of rock. We
also notice that ___________________________ found in layers of
rock occur in a certain patter at regular intervals in the rock record. We
can use this fossil pattern to correlate rocks from place to place.
The idea that fossil species follow each other in a definite and
recognizable pattern is called ____________________________.
_____________________________________ (several
different fossil species in a rock layer) are used by geologists in relative
dating. We correlate by comparing fossil assemblages from different
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 6
places.
Slide 22: Name a plant fossil used in correlation of Gondwanaland rocks.
___________________________________
Slide 23:
As we study layers of rocks we notice that there are
______________________ in the rock record. These gaps are created
by _________________ of previously existing layers or by
______________________________ of layers. A gap in the rock
record is called and _________________________________.
List the steps needed for the formation of an unconformity.
a)
b)
c)
Slide 24 :
Name three types of unconformities.
Slides 25:
In the space below define and draw a disconformity.
Name a place where you could see a disconformty.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 7
Slide 27:
In the space below define and draw and angular unconformity.
Name a place where you could see and angular unconformity.
Slide 28:
List the events involved in the creation of an unconformity.
a)_______________________________________________
b)_______________________________________________
c)_______________________________________________
d)_______________________________________________
Slide 31:
Define and draw and nonconformity
Name a place where you could see a nonconformity.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 8
Slides 35 – 46:
Reconstruct the geologic history of the area represented in the diagram.
a) ______________________________________________
b) ______________________________________________
c) ______________________________________________
d) ______________________________________________
e) ______________________________________________
f) ______________________________________________
g) ______________________________________________
h) ______________________________________________
i) ______________________________________________
j) ______________________________________________
Label the following block diagrams in order of geologic events: (1 is the
oldest)
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 9
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 10
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 11
Do diagram F as homework.
Slide 53:
The geologic time scale was established initially as a
____________________ scale using sedimentary rocks and
_______________________. Absolute ages were determined later
with ___________________________ dating
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 12
Slide 55:
Radiometric or absolute dating is done using ____________________
isotopes. _________________________ isotopes have
________________________ that spontaneously decay and in the
process emit or capture __________________________ particles and
energy. _______________________ is the original radioisotope that
is decaying and _________________________ is the product of the
decay. The loss or gain of a _________________________ converts
the parent to a daughter product of the same element. The loss or gain
of a proton changes the parent into an entirely new
________________.
Slide 56:
There are three primary ways radioactive decay occurs:
a) ___________________________________
b) ___________________________________
c) ___________________________________
Name, describe, and give an example of each of the different types of
radioactive decay.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 13
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 14
Slide 57:
____________________________dating used continuous decay to
measure the time since the rock formed. It has only been possible since
the late ____________________. Atoms of radioactive isotopes are
trapped in the ________________________ of minerals as they
crystallize from a magma. Radioisotopes
__________________immediately and continuously at a constant rate.
The rock contains less _____________________ and more
_________________________ as time passes.
Slide 58:
The amount of time it takes for half the atoms of the parent isotope to
decay is called ________________________ Different radioactive
isotopes have different and distinct ___________________________
If a rock has 12 parents and 12 daughters--ratio of 1:1, then …original
rock had ________________ parents and one half-life has elapsed.
After another half life, the rock will have ______________ parents and
18 daughters, a ratio of ___________________ The total number (24)
remains the same regardless of the isotope. The ratio of parent to
daughter atoms is ___________________________ at each half-life.
Slide 59:
If there is 12.5 % of the original radioisotope left in a rock, how many
half-lives has the rock gone through? _____________________
Slide 60:
Radioactive deacay is not a ________________________ relationship,
but is rather a ______________________ relationship.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 15
Slide 61:
What is the final product of the decay of U-
238?_______________________. How many steps are taken to get
to this product? _________________________
Slide 62:
Give the half-lives of the following isotope decay patterns.
Radioisotope/stable Half-life
daugh ter
U-238 to Pb-206
U-235 to Pb-207
U-232 to Pb 208
K-40 to Ar-40
Rb-87 to Sr-87
Slide 63: Be able to give the geologic time scale: eons, eras, periods,
epochs. Give the absolute date for the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic
boundaries.
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 16
Phys Geol Chapter 8 Page 17
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Blu Ray Disc and Copper Wires As Solar PanelDocument37 pagesBlu Ray Disc and Copper Wires As Solar PanelDavid Marc Josef Victorio67% (6)
- 2.6.3 Practice - Quadratic Functions (Practice)Document10 pages2.6.3 Practice - Quadratic Functions (Practice)HyounJoun KangPas encore d'évaluation
- C03-001-Structural Steel CalculationsDocument166 pagesC03-001-Structural Steel CalculationsNguyễnBìnhPhươngPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Source InverterDocument16 pagesCurrent Source Inverterjp-sharma100% (1)
- Rexroth 4we10 Data Sheet PDFDocument10 pagesRexroth 4we10 Data Sheet PDFSIVARAMANJAGANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- 62-00 ICAO+doc+9137 Airport+Services+Manual Part+9+-+Airport+Maintenance+Practices FR 110228 GanDocument56 pages62-00 ICAO+doc+9137 Airport+Services+Manual Part+9+-+Airport+Maintenance+Practices FR 110228 GanAnibal Jacek Quirós P.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 12135 2002 FR en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 12135 2002 FR en PDFPaquita Londdon100% (2)
- 3olve: 'RaphDocument4 pages3olve: 'Raphanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5SE AND:, Esson #OpyrightDocument5 pages5SE AND:, Esson #Opyrightanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assistive Technology Assessment Plan (ATAP) : DemographicsDocument5 pagesAssistive Technology Assessment Plan (ATAP) : Demographicsanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- 'Raph: 'Oal Standard 6/#!"5,!29 0arent 9ourDocument4 pages'Raph: 'Oal Standard 6/#!"5,!29 0arent 9ouranon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5SE 3trategies: %xampleDocument3 pages5SE 3trategies: %xampleanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Civil WarDocument2 pagesThe Civil Waranon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- 'Raph 4WO: #HeckingDocument3 pages'Raph 4WO: #Heckinganon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
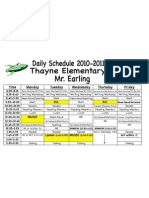
- Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: P.E. P.EDocument1 pageTime Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: P.E. P.Eanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Worksheet Section 1 & 2 Section 1Document2 pagesChapter 6 Worksheet Section 1 & 2 Section 1anon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- 'Oal 6/#!"5,!29 3lope 9our: %xampleDocument3 pages'Oal 6/#!"5,!29 3lope 9our: %xampleanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- $raw "Est: %stimateDocument3 pages$raw "Est: %stimateanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Questions?: Graduated Driver LicensingDocument2 pagesQuestions?: Graduated Driver Licensinganon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Weight Training Final ProjectDocument1 pageWeight Training Final Projectanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Driving Log: Drivers Education Practice ChecklistDocument1 pageDriving Log: Drivers Education Practice Checklistanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum For Aerobics Units To Be CoveredDocument1 pageCurriculum For Aerobics Units To Be Coveredanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Soccer Rules - IntroductionDocument6 pagesSoccer Rules - Introductionanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14-20 Year Old DriversDocument11 pages14-20 Year Old Driversanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lacrosse Study Guide: About The GameDocument2 pagesLacrosse Study Guide: About The Gameanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Beginning Keyboarding Numbers LessonDocument1 pageBeginning Keyboarding Numbers Lessonanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Education /aerobicsDocument1 pagePhysical Education /aerobicsanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wyoming Motorcycle Laws RoadDocument2 pagesWyoming Motorcycle Laws Roadanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rubric For Sport Skills: PointsDocument1 pageRubric For Sport Skills: Pointsanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Supply List: 1 Box of 8 Regular Crayons (Red, Yellow, Blue, Green, Purple, Orange, Black, and Brown)Document1 pageSupply List: 1 Box of 8 Regular Crayons (Red, Yellow, Blue, Green, Purple, Orange, Black, and Brown)anon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Team Frisbee Games: UltimateDocument3 pagesTeam Frisbee Games: Ultimateanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Use Is Required For PracticeDocument2 pagesInternet Use Is Required For Practiceanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Informal GeometryDocument3 pagesInformal Geometryanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svhs Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesSvhs Course Syllabusanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Usage Is RequiredDocument3 pagesInternet Usage Is Requiredanon-579447Pas encore d'évaluation
- BBP E Chapter 06Document8 pagesBBP E Chapter 06Danny CheongPas encore d'évaluation
- HS 420Document1 pageHS 420sayed abotalibPas encore d'évaluation
- TDS Total Dacnis-Se-46 1KV 202008 enDocument1 pageTDS Total Dacnis-Se-46 1KV 202008 enHendra KosasihPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Behavior of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite Reinforcement With Graphene Nano FillersDocument11 pagesMechanical Behavior of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite Reinforcement With Graphene Nano FillersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Review 2 ElectricalWiringDocument11 pagesReview 2 ElectricalWiringPriyaranjan DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaskets: Standard Definitions of Terms Relating ToDocument2 pagesGaskets: Standard Definitions of Terms Relating ToAhmad Zubair RasulyPas encore d'évaluation
- Compression Test For MetalsDocument11 pagesCompression Test For MetalsmohamedyahaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Specification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, High-Strength, Quenched and TemperedDocument4 pagesSpecification For Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, High-Strength, Quenched and TemperededwinbadajosPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Regulation of Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pagesVoltage Regulation of Single Phase TransformerMuhammad Ali HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind LoadDocument34 pagesWind LoadArah Louise ApostolPas encore d'évaluation
- Find The Six Circular Functions of The Below. 1. 8Document4 pagesFind The Six Circular Functions of The Below. 1. 8Sir LogPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Table Research PaperDocument8 pagesPeriodic Table Research Paperafnhlmluuaaymj100% (1)
- Me 630: Advanced Heat Transfer CH 3. Multidimensional Conduction Assoc. Prof. Dr. Barbaros ÇetinDocument34 pagesMe 630: Advanced Heat Transfer CH 3. Multidimensional Conduction Assoc. Prof. Dr. Barbaros ÇetinAaaerePas encore d'évaluation
- Subject Matter Budget (Chemistry)Document3 pagesSubject Matter Budget (Chemistry)Jennibeth TapangPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Engineering PaperDocument27 pagesCarbon Engineering PaperAdam KulikowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Guide Newton S Thanksgiving Tablecloth TrickDocument1 pageExperiment Guide Newton S Thanksgiving Tablecloth Trickapi-504410689Pas encore d'évaluation
- SVP2020 01 214 00199 PDFDocument7 pagesSVP2020 01 214 00199 PDFVikash KotteeswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Christian ControversiesDocument192 pagesChristian ControversiesAransh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis and Characterization of Superconductor Composite Bi SR Ca Cu O /la SR MnoDocument54 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Superconductor Composite Bi SR Ca Cu O /la SR MnoNacho Delgado FerreiroPas encore d'évaluation
- MELC 1bDocument31 pagesMELC 1bNorlie LamisPas encore d'évaluation
- Moores Law ForeverDocument3 pagesMoores Law ForeverCésar UribePas encore d'évaluation
- Mapua University: Experiment No. 4BDocument9 pagesMapua University: Experiment No. 4BGeojanni PangibitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex Product Overview Control Device System 8040 en GB RstahlDocument9 pagesEx Product Overview Control Device System 8040 en GB RstahlAriana GrandePas encore d'évaluation