Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Statistic Indeterminate Structures
Transféré par
m zulTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Statistic Indeterminate Structures
Transféré par
m zulDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
STATICALLY INDETERMINATE STRUCTURES
Solution. The give truss is statically indeterminate to the second degree. Note that it has on
extra diagonal in the upper panel and either one extra diagonal or one extra reaction component
in the lower panel.
In the solution belo, the basic determinate structure ia obtained by cutting the diagonals BC
and DC and replacing them by paire of forces 𝑥𝑎− 𝑥𝑎 and 𝑥5− 𝑥1 , whice act on the basic truss in
addition to the apphed loading (Fig. 106)
The conditions for consistent deformation are
x𝑎𝐿𝑎
∆𝛼 - 𝑥𝑎 𝛿𝑎𝑎 – 𝑥𝑏 𝛿𝑎𝑏 = AaE
x𝑏𝐿𝑏
∆𝑏 − 𝑥𝑎 𝛿𝑏𝑎 - 𝑥𝑏 𝛿𝑏 = A𝑏E
Where 𝑥𝑎 and 𝑥𝑏 = tensile stresses in the redundant diagonals
𝛿𝑝𝑏 = relative movement in the 𝒫 direction due to a pair of
Unit loads acting in the 𝔮 direction
By the unit-load method, the following are computed (unit Is the deflection in
Feet if E is considered to be 1 kip/in.²) :
∆𝛼 = 18. 38 units together
∆𝑏 = 41.86 units apart
𝛿𝑎𝑎 = 8.128 units together
𝛿𝑎𝑏 = 𝛿𝑏𝑎 = 0.540 unit together
𝛿𝑏𝑏 =7.588 units together
Substituting the values of ∆and 𝛿 found above into the equations of
Consistent deformation,
x𝑎(10)
(- 18.38 ) – 𝑥𝑎 (8.128) – 𝑥𝑏 (0.540) = (2)(1)
x𝑏(10)
(+41.86) – 𝑥𝑎 (0.540) – 𝑥𝑏 (7.588) = (2)(1)
Solving
𝑥𝑎 = stress in diagonal BC= -1.54 kips or 1.54 kipscompression
𝑥𝑏 = stress in diagonal DC = + 3.39 kips or 3.39 kips tension
The answer diagram is shown in Fig 107𝛼.
A check on the consistency of the geometry of deformation can be performed by cutting
the diagonals. AD and CF of the truss shown in fig. 107𝛼 and showing that the relative
movement along AD and CF are aqual to the changes in the lengths of diagonals AD and C.
From Fig 107 it is seen that the relative movement of 32.68 unitts together between joints A and
D is consistent with the total shortening
STATICALLY INDETERMINATE STRUCTURES
Solution. It has been computed in example 45 that, of the simple truss supported at 𝐿0
and 𝐿6 only,
1. A downward load of 1 kip at 𝐿2 causes
a Downword deflection of 4.4531 X 10−3 in. at 𝐿2
b Downword deflectionof 2.3844 X 10−2 in. at 𝐿6
2. A downward load of 1 kip at 𝐿𝐵 causes
a Downword deflection of 2,3844 X 10−3 in. at 𝐿2
b Downword deflection of 4.4531 X 10−2 in. at 𝐿6
In the present problem, let the unknown reactions be 𝑉2 kips down ward at 𝐿2 and 𝑉6 kips
downward at 𝐿6+ From the conditions of geometry if follows that
(4.4531 X 10−3 )( 𝑉2 ) + (2.3844 + 10−3 )( 𝑉6) = + 0.500
(2.3844 + 10−3 )( 𝑉2 ) + (4.4531 X 10−3 )( 𝑉6 )= 0
Solving,
𝑉2 = + 157.41 kips or 𝑉2= 157.41 kips downward
𝑉𝑐 = - 84.28 kips or 𝑉𝑐 = 84.28 kips upward
By statics
𝑉0 = 96.99 kips upward
𝑉8 = 23.86 kips downward
The stresses im all members corresponding to the four reactions as shown in Fig. 112b
can then be computed.
EXERCISE
1
𝜖5. Determine all reactions induced to act on the truss owing to a vertical settlement of 2
in. at the second support.
𝑈1 𝑈2 𝑈31 𝑈4 𝑈5 𝑈16
𝑉2 𝑉4
Area of all horizontal members = 6 sq. in
Area of all diagonal members = 4 sq. in
E = 30.000 k⁄in².
Exercise 65
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanical Vibration - MSD - Part 2Document9 pagesMechanical Vibration - MSD - Part 2Mohammad Saad SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- API 650 Design TanksDocument34 pagesAPI 650 Design TanksSyedZainAli100% (13)
- Equivalent Frame Method SampleDocument25 pagesEquivalent Frame Method SampleReiBañezPas encore d'évaluation
- Inverse KinematicsDocument5 pagesInverse KinematicsAmjad aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lug Analysis - MechaniCalcDocument21 pagesLug Analysis - MechaniCalcArunkumar RackanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Motion of Fluid Particles and StreamsDocument39 pagesChapter 4 - Motion of Fluid Particles and StreamsJabez RichardsPas encore d'évaluation
- T494Document28 pagesT494FERNANDO VALERA RUIZPas encore d'évaluation
- Refractories For Cement IndustryDocument246 pagesRefractories For Cement IndustryDang Do Minh100% (3)
- Nipping of Reformer PigtailsDocument12 pagesNipping of Reformer PigtailsVinh Do Thanh50% (2)
- Chapter 2 Analysis of Statically Determinate Structure (Part 1)Document38 pagesChapter 2 Analysis of Statically Determinate Structure (Part 1)Aubrey Anne Ilagan100% (1)
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsD'EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- TIL1292 Generator Rotor Dovetail CrackingDocument25 pagesTIL1292 Generator Rotor Dovetail CrackingzomglolzscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper. Design of Hydrogen Storage Tanks Fabricated From Composite MaterialsDocument7 pagesPaper. Design of Hydrogen Storage Tanks Fabricated From Composite MaterialsJosePPMolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basis of Design Principles For Timber StructuresDocument12 pagesBasis of Design Principles For Timber Structuresaturer_8346282320% (1)
- Lecture 03 PDFDocument20 pagesLecture 03 PDFعبدالقدوس التكباليPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Mekban HaekalDocument7 pagesTugas Mekban HaekalHaekal EmilchuzaemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Modeling of Mechanicalsystem (Spring, Mass, Damper)Document12 pagesMathematical Modeling of Mechanicalsystem (Spring, Mass, Damper)yasinPas encore d'évaluation
- SECOND TERM SS 3 FURTHER MATHS Ua5jsjDocument13 pagesSECOND TERM SS 3 FURTHER MATHS Ua5jsjdestiny michaelPas encore d'évaluation
- CE4 Module 2Document12 pagesCE4 Module 2bacalczynahmaePas encore d'évaluation
- Emg 2303 - 2Document15 pagesEmg 2303 - 2steve ogagaPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main 2023 Phy 25 Jan Shift 2 QPDocument9 pagesJEE Main 2023 Phy 25 Jan Shift 2 QPholkjhguPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas 5 Muhammad Jovan Ramadhan 02311740000117Document6 pagesTugas 5 Muhammad Jovan Ramadhan 02311740000117Jovan RamadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Work and Potential Energy: Quiz SM107Document15 pagesVirtual Work and Potential Energy: Quiz SM107Sumit RijalPas encore d'évaluation
- Practise Problems Set03Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set03rohit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 07 System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument32 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 07 System of Particles and Rotational MotionNilanjan BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main 2023 25th Jan Shift 2 QPDocument26 pagesJEE Main 2023 25th Jan Shift 2 QPPiyush BhatnagarPas encore d'évaluation
- AIIMSDocument72 pagesAIIMSMahesh Babu100% (1)
- END-SEM - July-Nov 2020 (30th Dec) AM5390: Advanced Solid Mechanics Total: (3x10) Marks, Time: 2 HoursDocument2 pagesEND-SEM - July-Nov 2020 (30th Dec) AM5390: Advanced Solid Mechanics Total: (3x10) Marks, Time: 2 HourssssPas encore d'évaluation
- Ioqjs (Part 1) 2021 SolutionDocument13 pagesIoqjs (Part 1) 2021 SolutionAnindita GhoshSatpathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Quiz Solution PDFDocument4 pagesModule 1 Quiz Solution PDFBanana QPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 14Document34 pagesLecture 14yakwetuPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Aerospace 2011 SolutionDocument33 pagesGate Aerospace 2011 SolutionJackobPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main 29th Jan Shift 2Document26 pagesJEE Main 29th Jan Shift 2trbhkhgcPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Annotated Notes - Variational Principles - Wed Sept 22, 2021Document8 pages3 - Annotated Notes - Variational Principles - Wed Sept 22, 2021Luay AlmniniPas encore d'évaluation
- PoW Endsem AnswerDocument11 pagesPoW Endsem Answerkumkariit9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 21Document12 pagesLecture 21I190845 Samana NayyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout - Equation Sheet and Review For First MidtermDocument8 pagesHandout - Equation Sheet and Review For First MidtermRahul CRPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF 7 Mechanics of DBDocument11 pagesPDF 7 Mechanics of DBRizette Palogan100% (1)
- JEE Main 2023 30th Jan Shift 2 QPDocument26 pagesJEE Main 2023 30th Jan Shift 2 QPShravani BaraskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 FinalDocument9 pagesChapter 4 FinalMuntazir MehdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Kinematics Solved Problems 2Document26 pagesFluid Kinematics Solved Problems 2Josiah AdesolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Stress Tut 1Document2 pagesAnalysis of Stress Tut 1Rahul PatraPas encore d'évaluation
- SummaryDocument32 pagesSummaryirem çelikPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 Beams Built in BeamsDocument9 pages3.1 Beams Built in BeamsDaniel MukuhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Mechanics-Statics III PDFDocument24 pagesApplied Mechanics-Statics III PDFTasha APas encore d'évaluation
- ME223-Lecture 29 Torsion Stress FunctionDocument14 pagesME223-Lecture 29 Torsion Stress FunctionArushiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 72Document62 pagesChapter 72Mario EscalonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Analysis On Aircraft Components: FuselageDocument7 pagesStress Analysis On Aircraft Components: FuselageBerns DulamPas encore d'évaluation
- AENG260 - Problem Set 3, Chapter 7Document4 pagesAENG260 - Problem Set 3, Chapter 7John Paulo PeridoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec#9, Deflection of Beam-Determinate BeamDocument30 pagesLec#9, Deflection of Beam-Determinate Beamchristianborlaza23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2D Cartesian ElasticityDocument13 pages2D Cartesian ElasticityMartin KoraPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 - Forces and EquilibriumDocument53 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Forces and EquilibriumLin YanPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGI9901/ME8506 Fluid Dynamics, Winter 2022 Assignment#3: Due: Wednesday, March 2, 2022, 11:00 PMDocument2 pagesENGI9901/ME8506 Fluid Dynamics, Winter 2022 Assignment#3: Due: Wednesday, March 2, 2022, 11:00 PMCodey Carter PikePas encore d'évaluation
- m4l29 Lesson 29 The Direct Stiffness Method: Beams (Continued)Document16 pagesm4l29 Lesson 29 The Direct Stiffness Method: Beams (Continued)Vitor Vale100% (1)
- Venturi Meter Report FinalDocument11 pagesVenturi Meter Report FinalSahibul IkhwanPas encore d'évaluation
- St-PhyChem-Chapter 19C-2020Document16 pagesSt-PhyChem-Chapter 19C-2020솜니아 (솜니아)Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 6 Work and Kinetik EnergyDocument28 pagesCHAPTER 6 Work and Kinetik Energyملهم العبدالسلامةPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Ii: Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures LECTURE 4 Part 1: Analysis of Statically Determinate BeamsDocument10 pagesChapter Ii: Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures LECTURE 4 Part 1: Analysis of Statically Determinate BeamsAnthony LoñezPas encore d'évaluation
- MAK523 Final 2017baharDocument2 pagesMAK523 Final 2017baharHilalAldemirPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main 2023 31st Jan Shift 1 QPDocument30 pagesJEE Main 2023 31st Jan Shift 1 QPhemantPas encore d'évaluation
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Prof. Suvranu deDocument40 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Prof. Suvranu devenky364Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8Document20 pagesLecture 8yakwetuPas encore d'évaluation
- CH6 PDFDocument34 pagesCH6 PDFteknikpembakaran2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem DescriptionDocument5 pagesProblem DescriptionAngel Lisette LaoPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4Document22 pagesCH 4Ala HijaziPas encore d'évaluation
- ProblemSet3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesProblemSet3 SolutionsnormanPas encore d'évaluation
- $RVLROJZDocument7 pages$RVLROJZhusseinmarwan589Pas encore d'évaluation
- Siap Pencairan Tamsil SMP Silakan Di Cek LagiDocument6 pagesSiap Pencairan Tamsil SMP Silakan Di Cek Lagim zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic Indeterminate StructuresDocument3 pagesStatistic Indeterminate Structuresm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- TP Guru Siap SKDocument2 pagesTP Guru Siap SKm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic Indeterminate StructuresDocument3 pagesStatistic Indeterminate Structuresm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Village Head Jaya Coral Prioritize Village Owned Enterprises (Bumdes) Capital For Agricultural and Duck AND RABBIT CultivationDocument1 pageVillage Head Jaya Coral Prioritize Village Owned Enterprises (Bumdes) Capital For Agricultural and Duck AND RABBIT Cultivationm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Salinan Terjemahan KEPALDocument1 pageSalinan Terjemahan KEPALm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic Indeterminate StructuresDocument3 pagesStatistic Indeterminate Structuresm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic Indeterminate StructuresDocument3 pagesStatistic Indeterminate Structuresm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistic Indeterminate StructuresDocument3 pagesStatistic Indeterminate Structuresm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological SciencesDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciencesm zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Siap Pencairan Tamsil SMP Silakan Di Cek LagiDocument6 pagesSiap Pencairan Tamsil SMP Silakan Di Cek Lagim zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of Shredder Machine For e - WaDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Shredder Machine For e - WaM A JomahPas encore d'évaluation
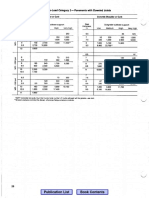
- Book Contents Publication List: Table 13s. Allowable ADTT, Axle-Load Category 3-Pavementa With Doweled JointsDocument9 pagesBook Contents Publication List: Table 13s. Allowable ADTT, Axle-Load Category 3-Pavementa With Doweled JointsSayuti YusofPas encore d'évaluation
- MD1 Quiz E02Document15 pagesMD1 Quiz E02tap isko006Pas encore d'évaluation
- W1 B Plane - Strain - TransformationDocument29 pagesW1 B Plane - Strain - TransformationSafwan RawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment2 Solution CIVE207 W24Document11 pagesAssignment2 Solution CIVE207 W24tasnim.tanvir99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prying ForceDocument133 pagesPrying Forcetigersronnie100% (1)
- Instructor: Lichuan Gui: Measurements in Fluid MechanicsDocument19 pagesInstructor: Lichuan Gui: Measurements in Fluid Mechanicshmxa91Pas encore d'évaluation
- BS-1377 P (ART8 (R) SOIL Soil Shear TestDocument32 pagesBS-1377 P (ART8 (R) SOIL Soil Shear TestAshraf TomizehPas encore d'évaluation
- Shervin Maleki - Deck Modeling For Seismic Analysis of Skewed Slab-Girder BridgesDocument12 pagesShervin Maleki - Deck Modeling For Seismic Analysis of Skewed Slab-Girder BridgesSaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr211402 Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesRr211402 Mechanics of SolidsSrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- The Distribution of Load and Stress in The Threads of Fasteners - A ReviewDocument20 pagesThe Distribution of Load and Stress in The Threads of Fasteners - A ReviewFernando FuentesPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering - MITDocument72 pagesDepartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering - MITPatrick DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Dashti - Out Plane Response - 2Document33 pagesDashti - Out Plane Response - 2Melo PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensors: The Micro-Pillar Shear-Stress Sensor MPS For Turbulent FlowDocument30 pagesSensors: The Micro-Pillar Shear-Stress Sensor MPS For Turbulent FlowJulio Herrera VenegasPas encore d'évaluation
- POS CAL 26PF No20 ST1 BCF Typ C200x80 R1 2018 07 06Document16 pagesPOS CAL 26PF No20 ST1 BCF Typ C200x80 R1 2018 07 06Nguyễn Duy QuangPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 2-2 - Axial LoadDocument4 pagesENGG 410 Problem Set 2-2 - Axial LoadJoana Rosette TordecillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shafts Subjected To LoadDocument27 pagesShafts Subjected To LoadMaria MeharPas encore d'évaluation
- LS-DYNA Manual Vol2Document18 pagesLS-DYNA Manual Vol2Mahmud Sharif SazidyPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 6 Weld JointDocument29 pagesCH 6 Weld JointIhsan Naufal RidhwanPas encore d'évaluation
- NPTEL - Mechanical Engineering - Strength of MaterialsDocument5 pagesNPTEL - Mechanical Engineering - Strength of MaterialsMir Mustafa AliPas encore d'évaluation