Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
1279879
Transféré par
MuhammadCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1279879
Transféré par
MuhammadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
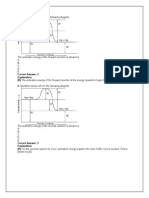
1.
The graph that best shows the relationship of gas volume to temperature, with pressure held constant
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
(A) The volume of a gas increases as temperature increases provided that pressure remains constant.
This is a direct proportion. Heating a balloon is a good example.
2.
The graph that best shows the relationship of gas volume to pressure, with temperature held constant
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) The volume of a gas decreases as the pressure is increased provided that the temperature is held
constant. This is shown by the inversely proportional curve in (C). Pressure increase on a closed cylinder
is a good example.
3.
The graph that best shows the relationship of the number of grams of a solid that are soluble in 100
grams of H2O at varying temperatures if the solubility begins at a small quantity and increases at a slow,
steady pace as the temperature is increased
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
(E) The graph shows that there is a starting quantity in solution, and a slight positive slope to the right
indicates a directly proportional change in the solubility as temperature rises.
4. The simplest unit of water that retains its properties
A. A molecule
B. A mixture of compounds
C. An isotope
D. An isomer
E. An acid salt
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
(A) This is the definition of any molecule.
5. A commercial cake mix
A. A molecule
B. A mixture of compounds
C. An isotope
D. An isomer
E. An acid salt
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
(B) A commercial cake mix is a mixture of ingredients.
6. An atom with the same number of protons as another atom of the same element but a different number
of neutrons
A. A molecule
B. A mixture of compounds
C. An isotope
D. An isomer
E. An acid salt
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) This is the definition of an isotope.
7. Classification of Ca(HCO3)2
A. A molecule
B. A mixture of compounds
C. An isotope
D. An isomer
E. An acid salt
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
(E) An acid salt contains one or more H atoms in the salt formula separating a positive ion and the
hydrogen-bearing negative ion. For example, Na2SO4 is a normal salt and NaHSO4 is an acid salt
because of the presence of H in the hydrogen sulfate ion. In Ca(HCO3)2, the same is true. This is
classified as an acid salt
8. The atomic number of an atom with an electron dot arrangement similar to
A. 1
B. 6
C. 9
D. 10
E. 14
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) An atom with atomic number 9 would have a 2,7 electron configuration, which matches the outer
energy level of iodine.
9. The number of atoms represented in the formula Na2CO3
A. 1
B. 6
C. 9
D. 10
E. 14
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
(B) There are 2 Na, 1 C, and 3 O, which add to 6 atoms.
10. The number that represents the most acid pH
A. 1
B. 6
C. 9
D. 10
E. 14
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
(A) pH from 0 to 6 is acid, 7 neutral, 8 to 14 basic. Most acid is 1.
11. Can be expressed in moles of solute per liter of solution
A. Density
B. Equilibrium constant
C. Molar mass
D. Freezing point
E. Morality
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
(E) Morality is defined as moles of solute/liter of solution.
12. Can be expressed in grams per liter of a gas
A. Density
B. Equilibrium constant
C. Molar mass
D. Freezing point
E. Morality
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
(A) Gas densities can be expressed in grams/liter.
13. Will NOT be affected by changes in temperature and pressure
A. Density
B. Equilibrium constant
C. Molar mass
D. Freezing point
E. Morality
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) Molar mass is not affected by pressure and temperature.
14. At STP, can be used to determine the molecular mass of a pure gas
A. Density
B. Equilibrium constant
C. Molar mass
D. Freezing point
E. Morality
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
(A) If the density of a gas is known, the mass of 1 L can be multiplied by 22.4 to find the molecular mass
because 1 mol occupies 22.4 L at STP.
15. Resists a rapid change of pH
A. Buffer
B. Indicator
C. Arrhenius acid
D. Arrhenius base
E. Neutral condition
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
(A) Buffers resist changes in pH.
16. Exhibits different colors in acidic and basic solutions
A. Buffer
B. Indicator
C. Arrhenius acid
D. Arrhenius base
E. Neutral condition
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
(B) Color change is the function of indicators.
17. At 25°C, the aqueous solution has a pH < 7.
A. Buffer
B. Indicator
C. Arrhenius acid
D. Arrhenius base
E. Neutral condition
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) On the pH scale, from 0 to 6 is acid and 7 is neutral.
18. At 25°C, the aqueous solution has a pH > 7.
A. Buffer
B. Indicator
C. Arrhenius acid
D. Arrhenius base
E. Neutral condition
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
(D) On the pH scale, from 8 to 14 is basic.
19. In the stratosphere, screens out a large fraction of the ultraviolet rays of the sun.
A. H2
B. SO2
C. CO
D. HCl
E. O3
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
(E) The ozone (O3) in the stratosphere absorbs ultraviolet rays from the sun.
20. Is a product of the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons.
A. H2
B. SO2
C. CO
D. HCl
E. O3
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) When hydrocarbons containing C and H do not have enough oxygen to combust with O 2(g)
completely, the product will be CO, carbon monoxide.
21. A gas produced by the heating of potassium chlorate
A. H2
B. SO2
C. CO
D. HCl
E. O3
Correct Answer: E
Explanation:
(E) 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2(g) is the reaction that occurs.
22. A gas that is slightly soluble in water and gives a weakly acid solution
A. H2
B. SO2
C. CO
D. HCl
E. O3
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
(C) CO2 is slightly soluble in water, forming carbonic acid, H2CO3, which is a weak acid.
23. Contributes to acid rain.
A. H2
B. SO2
C. CO
D. HCl
E. O3
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
(B) SO2 that is found in the upper atmosphere is dissolved in water molecules to form sulfurous acid that
is corrosive acid rain.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Do Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalDocument7 pagesDo Not Allow "Gravity". N MG: G GravitationalMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- P1 HomeworkDocument5 pagesP1 HomeworkMuhammad0% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument4 pagesAsexual Reproduction Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument5 pagesCells Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- ThermalDocument9 pagesThermalMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- 0972 w19 GT PDFDocument1 page0972 w19 GT PDFMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Grade 8Document1 pageWorksheet Grade 8MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerDocument11 pagesChemistry For The IB MYP 4&5: by Concept: Unit PlannerMuhammad80% (5)
- Quiz Grade 10 OctoberDocument2 pagesQuiz Grade 10 OctoberMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibrations and Waves: Additional Practice ADocument4 pagesVibrations and Waves: Additional Practice AMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- S 2 in One Orbital P 6 in Three Orbital D 10 in Five Orbital F 14 in Seven OrbitalDocument6 pagesS 2 in One Orbital P 6 in Three Orbital D 10 in Five Orbital F 14 in Seven OrbitalMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher Notes and Answers 11 Vibrations and WavesDocument3 pagesTeacher Notes and Answers 11 Vibrations and WavesMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Key: Holt PhysicsDocument8 pagesAnswer Key: Holt PhysicsMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Measures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitDocument1 pageMeasures of Simple Harmonic Motion: Term Example S UnitMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- The Activation Energy of The Forward Reaction Is Shown by A. B. C. D. EDocument7 pagesThe Activation Energy of The Forward Reaction Is Shown by A. B. C. D. EMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Of Water (HDocument7 pagesOf Water (HMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ag + C H ODocument9 pagesAg + C H OMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
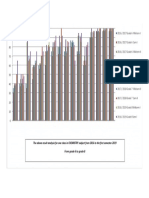
- The Above Result Analysis For One Class in CHEMISTRY Subject From 2016 To The First Semester 2019 From Grade 6 To Grade 8Document1 pageThe Above Result Analysis For One Class in CHEMISTRY Subject From 2016 To The First Semester 2019 From Grade 6 To Grade 8MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Timetable - Alton - London Timetable May 2019 PDFDocument35 pagesTimetable - Alton - London Timetable May 2019 PDFNicholas TuanPas encore d'évaluation
- HAYAT - CLINIC BrandbookDocument32 pagesHAYAT - CLINIC BrandbookBlankPointPas encore d'évaluation
- ThaneDocument2 pagesThaneAkansha KhaitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialog+ SW9xx - SM - Chapter 7 - 2-2013 - EN - Rinsing Bridge Version 5Document1 pageDialog+ SW9xx - SM - Chapter 7 - 2-2013 - EN - Rinsing Bridge Version 5Al ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Data Sheet TR24-3-T USDocument2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet TR24-3-T USDiogo CPas encore d'évaluation
- Zahid Imran CVDocument4 pagesZahid Imran CVDhia Hadj SassiPas encore d'évaluation
- Endometab Exam 2018Document8 pagesEndometab Exam 2018teabagmanPas encore d'évaluation
- The BetterPhoto Guide To Creative Digital Photography by Jim Miotke and Kerry Drager - ExcerptDocument19 pagesThe BetterPhoto Guide To Creative Digital Photography by Jim Miotke and Kerry Drager - ExcerptCrown Publishing GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- CDR Writing: Components of The CDRDocument5 pagesCDR Writing: Components of The CDRindikuma100% (3)
- Principles of Business Grade 10 June 2021 Time: 1 1/2 Hrs. Paper 2 Answer ONLY 1 Question in Section I. Section IDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Business Grade 10 June 2021 Time: 1 1/2 Hrs. Paper 2 Answer ONLY 1 Question in Section I. Section Iapi-556426590Pas encore d'évaluation
- ATADU2002 DatasheetDocument3 pagesATADU2002 DatasheethindPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Samsung Galaxy S Duos GT-S7562Document151 pagesManual Samsung Galaxy S Duos GT-S7562montesjjPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Final Quarter 1 Tos-Rbt-Sy-2022-2023 Tle-Cookery 10Document6 pagesRevised Final Quarter 1 Tos-Rbt-Sy-2022-2023 Tle-Cookery 10May Ann GuintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade9 January Periodical ExamsDocument3 pagesGrade9 January Periodical ExamsJose JeramiePas encore d'évaluation
- Onset Hobo Trade T Cdi 5200 5400 User ManualDocument3 pagesOnset Hobo Trade T Cdi 5200 5400 User Manualpaull20020% (1)
- TMPRO CASABE 1318 Ecopetrol Full ReportDocument55 pagesTMPRO CASABE 1318 Ecopetrol Full ReportDiego CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- SEC CS Spice Money LTDDocument2 pagesSEC CS Spice Money LTDJulian SofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Phrasal Verbs 1 ColumnDocument12 pagesList of Phrasal Verbs 1 ColumnmoiibdPas encore d'évaluation
- LM2TB8 2018 (Online)Document252 pagesLM2TB8 2018 (Online)SandhirPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Air QualityDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Air Qualityluwahudujos3100% (1)
- Daikin FUW Cabinet Fan Coil UnitDocument29 pagesDaikin FUW Cabinet Fan Coil UnitPaul Mendoza100% (1)
- Final Prmy Gr4 Math Ph1 HWSHDocument55 pagesFinal Prmy Gr4 Math Ph1 HWSHKarthik KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Mechanism Used in Laparoscopic Surgical InstrumentsDocument15 pagesA Review of Mechanism Used in Laparoscopic Surgical InstrumentswafasahilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pest of Field Crops and Management PracticalDocument44 pagesPest of Field Crops and Management PracticalNirmala RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- LRAD Datasheet 2000XDocument2 pagesLRAD Datasheet 2000XOkkar MaungPas encore d'évaluation
- Rockwell Collins RDRDocument24 pagesRockwell Collins RDRMatty Torchia100% (5)
- Pricing of A Revolutionary ProductDocument22 pagesPricing of A Revolutionary ProductiluvparixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh Assignment PDFDocument18 pagesContoh Assignment PDFSiti Fatimah A Salam67% (3)
- Monitor Stryker 26 PLGDocument28 pagesMonitor Stryker 26 PLGBrandon MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- F5 Chem Rusting ExperimentDocument9 pagesF5 Chem Rusting ExperimentPrashanthini JanardananPas encore d'évaluation