Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Capacitors Are Energy Storage Devices Which Have The Ability To Store An
Transféré par
Neha GoyalTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Capacitors Are Energy Storage Devices Which Have The Ability To Store An
Transféré par
Neha GoyalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Capacitors are energy storage devices which have the ability to store an
electrical charge across its plates. Thus capacitors store energy as a result of
their ability to store charge and an ideal capacitor would not loose its stored
energy.
The simplest construction of a capacitor is by using two parallel conducting
metal plates separated through a distance by an insulating material, called a
the dielectric as summarised below.
A capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by a dielectric.
The dielectric can be made of many insulating materials such as air, glass,
paper, plastic etc.
A capacitor is capable of storing electrical charge and energy.
The higher the value of capacitance, the more charge the capacitor can
store.
The larger the area of the plates or the smaller their separation the more
charge the capacitor can store.
A capacitor is said to be “Fully Charged” when the voltage across its plates
equals the supply voltage.
The symbol for electrical charge is Q and its unit is the Coulomb.
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized. They have a +ve and a -ve terminal.
Capacitance is measured in Farads, which is a very large unit so micro-
Farad ( μF ), nano-Farad ( nF ) and pico-Farad ( pF ) are generally used.
Capacitors that are daisy chained together in a line are said to be
connected in Series.
Capacitors that have both of their respective terminals connected to each
terminal of another capacitor are said to be connected in Parallel.
Parallel connected capacitors have a common supply voltage across them.
Series connected capacitors have a common current flowing through them.
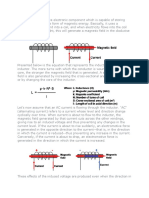
Capacitive reactance, XC is the opposition to current flow in AC circuits.
In AC capacitive circuits the voltage “lags” the current by 90o.
The basic construction and symbol for a parallel plate capacitor is given as:
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Grey Minimalist Business Project PresentationDocument19 pagesGrey Minimalist Business Project PresentationBeaver OrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Capacitors, Capacitance and ChargeDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors, Capacitance and ChargeZeeshan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- English Task Article About Capacitor: College Teacher: Nur Rosita, S.PD, M.ADocument5 pagesEnglish Task Article About Capacitor: College Teacher: Nur Rosita, S.PD, M.ABima MayesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro to Capacitors: Store Charge & VoltageDocument28 pagesIntro to Capacitors: Store Charge & Voltagestephen otienoPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Construction and Factors Affecting CapacitanceDocument4 pagesCapacitor Construction and Factors Affecting CapacitanceMinorPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitance: The Components of A CapacitorDocument7 pagesCapacitance: The Components of A CapacitorNaveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsBlueprint MihPas encore d'évaluation
- L5 Electricity and MagnetismDocument37 pagesL5 Electricity and Magnetismbussanmugwati2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsVenkatesh VenkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors and Its ApplicationsDocument3 pagesCapacitors and Its ApplicationsadeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument27 pagesChapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. Boylestadakankshag_13Pas encore d'évaluation
- BasementDocument19 pagesBasementProxima YusPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor and Paralell CapacitorDocument2 pagesCapacitor and Paralell CapacitorFatima KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors and Their CircuitsDocument19 pagesCapacitors and Their CircuitsPrince JairoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bản Tiếng Anh: I-Capacitor's Concept, structures and symbolsDocument3 pagesBản Tiếng Anh: I-Capacitor's Concept, structures and symbolslinh nguyễn thuỳPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesCapacitor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPRincess ScarLetPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting CapacitanceDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting CapacitanceKrati PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Document37 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Noli LlaneraPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorDocument1 pageCapacitordwarika2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors: BY: Janaki G. Nair Abhishek GautamDocument14 pagesCapacitors: BY: Janaki G. Nair Abhishek GautamAbhishek GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor BasicsDocument11 pagesCapacitor BasicsTuppada VeereshPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorsDocument17 pagesCapacitorsWani SageerPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSICS Project 30Document30 pagesPHYSICS Project 30SAHILPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is CapacitanceDocument2 pagesWhat Is CapacitanceSakinah KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorDocument1 pageCapacitorVadim GoykhmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors: Available Online atDocument21 pagesCapacitors: Available Online atOwen LuzPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorsDocument3 pagesCapacitorsAteek PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorsDocument86 pagesCapacitorsarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Capacitors: What They Are and How They WorkDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Capacitors: What They Are and How They WorkDilip KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Capacitors: ResistorDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: ResistorsxpPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor Basics: What They Are and How They WorkDocument2 pagesCapacitor Basics: What They Are and How They WorkSanjivee SachinPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy ProjDocument19 pagesPhy Projselavathy1937Pas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors: Widely Used in Many LanguagesDocument1 pageCapacitors: Widely Used in Many LanguagesmihikaPas encore d'évaluation
- What is a CapacitorDocument21 pagesWhat is a CapacitorZinedane PantonPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - CapacitorsDocument5 pages10 - Capacitorschie CPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Capacitors: What They Are and How They WorkDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Capacitors: What They Are and How They WorkJohn Renzo Vibar ToribioPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors Capacitance: Electrical CircuitsDocument4 pagesCapacitors Capacitance: Electrical CircuitsVivek PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- ENERGY STORAGE TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT: Capacitor Types and ApplicationsDocument35 pagesENERGY STORAGE TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT: Capacitor Types and ApplicationsN.K. ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitance and DielectricDocument3 pagesCapacitance and DielectricKazuki KazehayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capac ItDocument15 pagesCapac Iteta83275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorDocument3 pagesPassive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorRenielDelaCruzPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorDocument61 pagesCapacitorAngel Nuñez100% (1)
- Capacitor and CapacitanceDocument48 pagesCapacitor and CapacitanceDave Serapion50% (2)
- A CapacitorDocument1 pageA Capacitorrbharti59Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9FundamentalsofCapacitorsDocument25 pagesChapter 9FundamentalsofCapacitorsLyssa ChoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors P.naren KarthyDocument17 pagesCapacitors P.naren KarthyAnitha PragasamPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorDocument98 pagesCapacitorklprasdPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorDocument17 pagesCapacitorDivyapratap Singh ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- College Physics 2: Capacitors, Electric Storage, and DielectricDocument24 pagesCollege Physics 2: Capacitors, Electric Storage, and DielectricJohn Christopher SibalPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th WeekDocument7 pages4th WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitance and Its ApplicationDocument31 pagesCapacitance and Its ApplicationSuardi F. Seiei0% (1)
- CapasitorDocument21 pagesCapasitorayu widiana putriPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Class: Roll No: Subject: Topic:: Katrodiya Omee Jigneshkumar 12-B 17 Physics CapacitanceDocument42 pagesName: Class: Roll No: Subject: Topic:: Katrodiya Omee Jigneshkumar 12-B 17 Physics CapacitanceOmee KatrodiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitance: Figure 8-177Document8 pagesCapacitance: Figure 8-177Sandeep Guha NiyogiPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPACITORSDocument12 pagesCAPACITORSAnitha PragasamPas encore d'évaluation
- CapacitorDocument21 pagesCapacitorhetmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitor: Jump ToDocument22 pagesCapacitor: Jump ToRakesh GroverPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateDocument6 pagesTLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateNoli LlaneraPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Symbols: PassiveDocument4 pagesCircuit Symbols: PassiveAhmed RamziPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument31 pagesSyllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringdhruvaaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument31 pagesSyllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringdhruvaaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Resistor Basics Guide - All About Resistors in 38 CharactersDocument27 pagesResistor Basics Guide - All About Resistors in 38 CharactersNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Compact Broadband Circular Microstrip Feed Slot Antenna With Asymmetric Bevel On Ground Plane For Wimax and Wlan ApplicationsDocument7 pagesCompact Broadband Circular Microstrip Feed Slot Antenna With Asymmetric Bevel On Ground Plane For Wimax and Wlan ApplicationsNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument31 pagesSyllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringdhruvaaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress in Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 16, 13-23, 2010Document11 pagesProgress in Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 16, 13-23, 2010Neha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- An InductorDocument6 pagesAn InductorNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument31 pagesSyllabus of Undergraduate Degree Course: Electronics & Communication EngineeringdhruvaaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compact Broadband Circular Microstrip Feed Slot Antenna With Asymmetric Bevel On Ground Plane For Wimax and Wlan ApplicationsDocument7 pagesCompact Broadband Circular Microstrip Feed Slot Antenna With Asymmetric Bevel On Ground Plane For Wimax and Wlan ApplicationsNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 10050402Document15 pages12 10050402Neha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- ETF ListDocument1 pageETF ListNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- ETF ListDocument1 pageETF ListNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Futures MKTDocument2 pagesFutures MKTapi-3857574Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of Ceos and Punch LinesDocument10 pagesList of Ceos and Punch Linesvasi ahmad ansari57% (7)
- Low Profile Inverted-F-L Antenna For 5.5 GHZ WiMAX ApplicationsDocument5 pagesLow Profile Inverted-F-L Antenna For 5.5 GHZ WiMAX ApplicationsIDESPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Distribution PDFDocument11 pagesCurrent Distribution PDFNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Patch AntennaDocument9 pagesPatch AntennaNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Profile Inverted-F-L Antenna For 5.5 GHZ WiMAX ApplicationsDocument5 pagesLow Profile Inverted-F-L Antenna For 5.5 GHZ WiMAX ApplicationsIDESPas encore d'évaluation
- Patch AntennaDocument9 pagesPatch AntennaNeha GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Antenna Radiation Patterns: Laboratory ManualDocument44 pagesMeasurement of Antenna Radiation Patterns: Laboratory ManualMoBilbeisiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.-SEMIKRON DataSheet RT380MDocument2 pages1.-SEMIKRON DataSheet RT380MvaleriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Universal Modules TXM1.8X PDFDocument10 pagesSuper Universal Modules TXM1.8X PDFharishupretiPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual para Caminadora Landice (L-60 & L8622 SERIES Diagnostic)Document67 pagesManual para Caminadora Landice (L-60 & L8622 SERIES Diagnostic)José Carlos AscencioPas encore d'évaluation
- Troubleshoot no video or sound issuesDocument2 pagesTroubleshoot no video or sound issuesbur3bistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scada DocDocument6 pagesScada DocjupudiguptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lah 50-pDocument3 pagesLah 50-pHudson CostaPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT and MosfetDocument10 pagesBJT and MosfetankitabcPas encore d'évaluation
- Diode Wave Shaping Circuits: Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 / E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocument16 pagesDiode Wave Shaping Circuits: Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 / E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜPas encore d'évaluation
- AD5620 AnalogDevicesDocument28 pagesAD5620 AnalogDevicesPablo AllosiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scooba Drydock: Charging and Drying StandDocument8 pagesScooba Drydock: Charging and Drying Standir3678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Charging System Troubleshooting (1406) : Instrucción EspecialDocument16 pagesCharging System Troubleshooting (1406) : Instrucción EspecialMiguel GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- MicroEel Solid Analog Seismic StreamerDocument2 pagesMicroEel Solid Analog Seismic StreamerAntoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Power ProtectionDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Power Protectiontiegsti gebrehiwotPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Sheets 6.2.4 Terminate/Connect Electrical Wiring/ Electronic Circuits Follow Correct Sequence of OperationDocument5 pagesInformation Sheets 6.2.4 Terminate/Connect Electrical Wiring/ Electronic Circuits Follow Correct Sequence of Operationapi-196541959Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diagrama Makita HP1640Document2 pagesDiagrama Makita HP1640Julio Daniel MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 KV 250 A 3150 Din 42530 67 3370221Document2 pages1 KV 250 A 3150 Din 42530 67 3370221Yigit SarıkayaPas encore d'évaluation
- TDA7262Document9 pagesTDA7262Nelson PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Analisa Pekerjaan: 1 CA1 Unit 1Document730 pagesDaftar Analisa Pekerjaan: 1 CA1 Unit 1Implon CvvPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Theorems: S o U R Ce: Circuit Analysis: Theory and Practice Delmar Cengage LearningDocument19 pagesNetwork Theorems: S o U R Ce: Circuit Analysis: Theory and Practice Delmar Cengage LearningReselyn PalabinoPas encore d'évaluation
- #3 MV1000 Micro Technology Presentation - Sept 2018 VSADocument46 pages#3 MV1000 Micro Technology Presentation - Sept 2018 VSAadolfoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1s9aglen 20-9-16 Agl50-Ev enDocument64 pages1s9aglen 20-9-16 Agl50-Ev enMohd Abu AjajPas encore d'évaluation
- Radio Data Reference Book Jessop 1967Document148 pagesRadio Data Reference Book Jessop 1967Cubelinho ResuaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1SDA100467R1 xt5s 630 Ekip Dip Ls I in 630 4p F FDocument4 pages1SDA100467R1 xt5s 630 Ekip Dip Ls I in 630 4p F Fccssaa123Pas encore d'évaluation
- FSFR-XS Series - : Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™) For Half-Bridge Resonant ConvertersDocument14 pagesFSFR-XS Series - : Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™) For Half-Bridge Resonant ConvertersJean CianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vivo Area C April 2023 Price List and TecPro BundlesDocument10 pagesVivo Area C April 2023 Price List and TecPro Bundleslusiana hakim uciPas encore d'évaluation
- TD1 (Digital Electronic)Document11 pagesTD1 (Digital Electronic)KEO PHEAKDEYPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Report: Experiment NoDocument7 pagesLab - Report: Experiment NoRedwan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial Discharge in Gas Insulated Substations GIS Effects Mitigation AnalysisDocument6 pagesPartial Discharge in Gas Insulated Substations GIS Effects Mitigation AnalysisIndah PermataPas encore d'évaluation
- LG Indoor PCB Power SupplyDocument1 pageLG Indoor PCB Power SupplyP.Rajan GuruPas encore d'évaluation
- DB Range Catg - 2016 - v11 PDFDocument24 pagesDB Range Catg - 2016 - v11 PDFchaitanyaomronPas encore d'évaluation