Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DFVBDFGHDFG
Transféré par
JohnKierCorbitaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DFVBDFGHDFG
Transféré par
JohnKierCorbitaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
UCSP TEST POINTERS
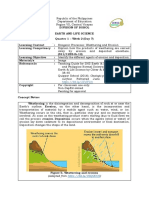
Evolution – is a natural process of biological changes occurring in a population across successive generations.
Species – is a group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding.
Homo Habilis – Species with a brain of a brocas area which is associated which speech in modern humans and was the first to make stone tools.
- Also knows as the “Handy Man“
Homo Rudolfensis – Species characterized by a longer face , larger molar and premolar teeth, and having a larger braincase.
- Lived about 1.9 to 1.8 million years ago.
Homo Erectus-The species name means “Upright Man” with body proportions similar to that of modern humans.
- They were the first hunters with improvised tools such as axes and knives, and were the first to produce fire.
Homo Heidelbergenesis- Species with large brow ridge and short wide bodies that lived about 700,000 to 200,000 years ago in Europe and Africa.
- They were the first of early human species to live in colder climates, first to hunt large animals on routine basis using spears, and first to
construct human shelters.
Homo Floresiensis- Species nicknamed “Hobbit” due to their small stature with a height of more or less 3 feet and lived 95,000 to 17,000 years ago in the island
of Flores, Indonesia along with other dwarfed animal species.
Homo Sapiens- The species means “Wise Man” that appeared from 200,000 years ago.
- The present human race belongs to this species.
Homo Sapiens Neanderthalensis- Subspecies with short yet stocky in body build adapted to winter climates especially in icy cold places in Europe and Asia.
- The first to practice burial of their dead, hunting and gathering food, and sewing clothes from animal skin using bone needles.
Homo Sapiens Sapiens- Subspecies knowns as Cro-Magnon characterized to be anatomically modern humans and lived in the last Ice Age of Europe from 40,000
to 10,000 years ago.
- They were the first to produce art in cave paintings and crafting decorated tools and accessories.
Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age)- Traditionally coincided with the first evidence of tool construction and use by Homosome 2.5 million years ago.
- Use of simple pebble tools, learned to live in caves, discovered the use of fire.
- Developed small sculptures and monumental painting, incised designs, and reliefs on the walls of caves. Food collecting cultures
Neolithic Age (New Stone Age)- Occurred sometime about 10,000 BCE. Stone tools were shaped by polishing or grinding. Settlement in permanent villages.
Dependence on domesticated plants or animals.
- Appearance of such crafts as pottery and weaving. Food producing cultures.
UCSP TEST POINTERS
Evolution – is a natural process of biological changes occurring in a population across successive generations.
Species – is a group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding.
Homo Habilis – Species with a brain of a brocas area which is associated which speech in modern humans and was the first to make stone tools.
- Also knows as the “Handy Man“
Homo Rudolfensis – Species characterized by a longer face , larger molar and premolar teeth, and having a larger braincase.
- Lived about 1.9 to 1.8 million years ago.
Homo Erectus-The species name means “Upright Man” with body proportions similar to that of modern humans.
- They were the first hunters with improvised tools such as axes and knives, and were the first to produce fire.
Homo Heidelbergenesis- Species with large brow ridge and short wide bodies that lived about 700,000 to 200,000 years ago in Europe and Africa.
- They were the first of early human species to live in colder climates, first to hunt large animals on routine basis using spears, and first to
construct human shelters.
Homo Floresiensis- Species nicknamed “Hobbit” due to their small stature with a height of more or less 3 feet and lived 95,000 to 17,000 years ago in the island
of Flores, Indonesia along with other dwarfed animal species.
Homo Sapiens- The species means “Wise Man” that appeared from 200,000 years ago.
- The present human race belongs to this species.
Homo Sapiens Neanderthalensis- Subspecies with short yet stocky in body build adapted to winter climates especially in icy cold places in Europe and Asia.
- The first to practice burial of their dead, hunting and gathering food, and sewing clothes from animal skin using bone needles.
Homo Sapiens Sapiens- Subspecies knowns as Cro-Magnon characterized to be anatomically modern humans and lived in the last Ice Age of Europe from 40,000
to 10,000 years ago.
- They were the first to produce art in cave paintings and crafting decorated tools and accessories.
Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age)- Traditionally coincided with the first evidence of tool construction and use by Homosome 2.5 million years ago.
- Use of simple pebble tools, learned to live in caves, discovered the use of fire.
- Developed small sculptures and monumental painting, incised designs, and reliefs on the walls of caves. Food collecting cultures
Neolithic Age (New Stone Age)- Occurred sometime about 10,000 BCE. Stone tools were shaped by polishing or grinding. Settlement in permanent villages.
Dependence on domesticated plants or animals.
- Appearance of such crafts as pottery and weaving. Food producing cultures.
Socialization – is a continuing process whereby an individual acquires a personal identity and learns the norms, values, behavior, and social skills appropriate to
his or her social position.
Social Status – refers to the position of an individual occupies in society and implies an array of rights and duties.
Conformity – behavior that is the same as the behavior of most other people in a society. Trying to “Fit-In”.
Deviance – different from what is considered to be normal or morally correct. A contrast to Conformity.
Society – is a social system that is composed of people assigned to perform a definite task and function in a social system called social institution.
Social Control – refers to the efforts of a group or society to regulate the behavior of its members in conformity with established norms.
Human Rights – are natural rights of all human beings whatever their nationality, religion, ethnicity, sex, language, and color.
Natural Rights – these rights are inherent to man and given to him by GOD as a human being.
Constitutional Rights – These are the rights guaranteed under the fundamental charter of the country.
Statutory Rights – These are rights provided by the lawmaking body of a country or by law.
Civil Rights – These are rights specified under the Bill of Rights
Economic Rights – These are rights to property, whether personal, real, or intellectual.
Political Rights – There are rights an individual enjoys as consequence of being a member of a body politic.
Group – is constituted by two or more persons who interact together and are together physically.
CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN SOCIETY
1. It is a social system.
2. A society is relatively large.
3. A society recruits most of its members from within.
4. A society sustains itself across generations.
5. A society member’s share a culture.
6. A society occupies a territory.
TYPES OF SOCIETIES
1. Hunting and Food Gathering Societies
2. Horticultural Societies
3. Pastoral Societies
4. Agricultural Societies
5. Industrial Societies
6. Post-Industrial Societies
2 TYPEFS OF FARMING
1. ubsistence Farming
2. Surplus Farming
Agents of Socialization
1. Family
2. School
3. Church
4. Peer Group
5. Work Place
6. Mass Media
Different Types of Conformity
1. Compliance
2. Internalization
3. Identification
4. Ingratiational
Functions of Deviance
1. Deviance serves as an outlet for diverse forms of expressions.
2. Deviance serves to define the limits of acceptable behavior.
3. Deviance may also promote in-group solidarity
4. Deviance can serve as a barometer of social strain.
Sociological Theories of Deviance
1. Functionalist Theory
2. Strain Theory
3. Control Theory
Social Control of Deviance
Three Requirements of a Group
1. There must two or more people.
2. There must be interaction.
3. The members of the group must be together physically
Socialization – is a continuing process whereby an individual acquires a personal identity and learns the norms, values, behavior, and social skills appropriate to
his or her social position.
Social Status – refers to the position of an individual occupies in society and implies an array of rights and duties.
Conformity – behavior that is the same as the behavior of most other people in a society. Trying to “Fit-In”.
Deviance – different from what is considered to be normal or morally correct. A contrast to Conformity.
Society – is a social system that is composed of people assigned to perform a definite task and function in a social system called social institution.
Social Control – refers to the efforts of a group or society to regulate the behavior of its members in conformity with established norms.
Human Rights – are natural rights of all human beings whatever their nationality, religion, ethnicity, sex, language, and color.
Natural Rights – these rights are inherent to man and given to him by GOD as a human being.
Constitutional Rights – These are the rights guaranteed under the fundamental charter of the country.
Statutory Rights – These are rights provided by the lawmaking body of a country or by law.
Civil Rights – These are rights specified under the Bill of Rights
Economic Rights – These are rights to property, whether personal, real, or intellectual.
Political Rigths – Therse are rights an individual enjoys as consequence of being a member of a body politic.
Group – is constituted by two or more persons who interact together and are together physically.
CHARACTERISTICS OF HUMAN SOCIETY
1. It is a social system.
2. A society is relatively large.
3. A society recruits most of its members from within.
4. A society sustains itself across generations.
5. A society member’s share a culture.
6. A society occupies a territory.
TYPES OF SOCIETIES
1. Hunting and Food Gathering Societies
2. Horticultural Societies
3. Pastoral Societies
4. Agricultural Societies
5. Industrial Societies
6. Post-Industrial Societies
2 TYPEFS OF FARMING
1. ubsistence Farming
2. Surplus Farming
Agents of Socialization
1. Family
2. School
3. Church
4. Peer Group
5. Work Place
6. Mass Media
Different Types of Conformity
1. Compliance
2. Internalization
3. Identification
4. Ingratiational
Functions of Deviance
1. Deviance serves as an outlet for diverse forms of expressions.
2. Deviance serves to define the limits of acceptable behavior.
3. Deviance may also promote in-group solidarity
4. Deviance can serve as a barometer of social strain.
Sociological Theories of Deviance
1. Functionalist Theory
2. Strain Theory
3. Control Theory
Social Control of Deviance
Three Requirements of a Group
1. There must two or more people.
2. There must be interaction.
3. The members of the group must be together physically.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- TOS Earth and Life 1Document18 pagesTOS Earth and Life 1JohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Empowerment Technologies 12: Internet As Credible Source of Information Background Information For LearnersDocument4 pagesEmpowerment Technologies 12: Internet As Credible Source of Information Background Information For LearnersJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 of Empowerment TechnologiesDocument4 pagesWeek 1 of Empowerment TechnologiesJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emtech Q2 Week 1Document5 pagesEmtech Q2 Week 1JohnKierCorbita0% (1)
- Empowerment Technologies 12: Productivity Tools-Mail Merge Background Information For LearnersDocument8 pagesEmpowerment Technologies 12: Productivity Tools-Mail Merge Background Information For LearnersJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cot Rating Sheet Cot Rating RemarksDocument1 pageCot Rating Sheet Cot Rating RemarksJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Avengers LicnseDocument1 pageAvengers LicnseJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oratorical PieceDocument1 pageOratorical PieceMary Fabillar93% (30)
- ContinuationDocument2 pagesContinuationJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- ContinuationDocument2 pagesContinuationJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) Grades 7-10 PDFDocument20 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) Grades 7-10 PDFRegiel Tolentino0% (1)
- DFVBDFGHDFGDocument5 pagesDFVBDFGHDFGJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- ApikiDocument1 pageApikiJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Transferable Non-Transferable Non-Transferable: Roque B. Abalo Judelito R. Arribado Cherry B. TorremochaDocument6 pagesNon-Transferable Non-Transferable Non-Transferable: Roque B. Abalo Judelito R. Arribado Cherry B. TorremochaJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st QuizDocument1 page1st QuizJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8-3 List of Students With IdDocument1 page8-3 List of Students With IdJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- ICT TroubleshootDocument1 pageICT TroubleshootJohnKierCorbitaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Conformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3Document53 pagesConformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3Dr-Dinesh Kumar100% (1)
- Sci NB Mod 2 LSN 3Document4 pagesSci NB Mod 2 LSN 3Ramses octavio Rodriguez ocanasPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument61 pagesCase StudyA GPas encore d'évaluation
- Basses: Pricelist March 2019Document3 pagesBasses: Pricelist March 2019zhaihaijunPas encore d'évaluation
- FAJASDocument891 pagesFAJASCecilia GilPas encore d'évaluation
- PTP S3Document8 pagesPTP S3Yongyin SHENGPas encore d'évaluation
- 9701 w09 QP 21Document12 pages9701 w09 QP 21Hubbak KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three: 1 - The Coarse Grain SoilsDocument21 pagesChapter Three: 1 - The Coarse Grain SoilsSalih MohayaddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Faults in MalaysiaDocument52 pagesActive Faults in MalaysiaHazim HaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fret Position Calculator - StewmacDocument1 pageFret Position Calculator - StewmacJuan Pablo Sepulveda SierraPas encore d'évaluation
- Do Roman Catholics KnOw About The Great Pyramids of China?Document11 pagesDo Roman Catholics KnOw About The Great Pyramids of China?.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Latihan To: Nilai: 7.4 Benar: 37 Salah: 13Document17 pagesLatihan To: Nilai: 7.4 Benar: 37 Salah: 13glensPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Processing Lines For Extruded Pet FoodDocument13 pagesComplete Processing Lines For Extruded Pet FoodденисPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor CAT C13 AcertDocument3 pagesMotor CAT C13 AcertJosé Gonzalez100% (4)
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument9 pagesVentricular Septal DefectpepotchPas encore d'évaluation
- THE WEATHER LISTENING - Stalin GuañunaDocument1 pageTHE WEATHER LISTENING - Stalin GuañunaSTALIN JESUS GUA�UNA CHICAIZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhagwati School Strap Report AnalysisDocument60 pagesBhagwati School Strap Report AnalysisReverse Minded100% (1)
- RUKUS April 2011Document40 pagesRUKUS April 2011RUKUS Magazine100% (2)
- Tabel Gsi, RMR, RmiDocument4 pagesTabel Gsi, RMR, RmiPup BooPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Cruise ControlDocument5 pagesAdaptive Cruise ControlIJIRSTPas encore d'évaluation
- E-OLSS: Electronic ControlDocument12 pagesE-OLSS: Electronic ControlSamidiPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerKristine SantominPas encore d'évaluation
- Milviz F-15e Poh V 2Document499 pagesMilviz F-15e Poh V 2Jose Ramon Martinez GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sw34 Religion, Secularism and The Environment by NasrDocument19 pagesSw34 Religion, Secularism and The Environment by Nasrbawah61455Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reactive Dyes For Digital Textile Printing InksDocument4 pagesReactive Dyes For Digital Textile Printing InksDHRUVPas encore d'évaluation
- Poems Prescribed For 2012-2014 English B CSEC ExamsDocument24 pagesPoems Prescribed For 2012-2014 English B CSEC ExamsJorge Martinez Sr.100% (2)
- IPC's 2 Edition of Guidance Manual For Herbs and Herbal Products Monographs ReleasedDocument1 pageIPC's 2 Edition of Guidance Manual For Herbs and Herbal Products Monographs ReleasedRakshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 - Maths - MatricesDocument87 pagesClass 12 - Maths - MatricesAishwarya MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp6.Single Phase Bridge Inverter Using PWMDocument6 pagesExp6.Single Phase Bridge Inverter Using PWMAbdullah MohammedPas encore d'évaluation