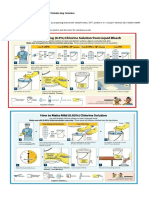
Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Wiring and Safety
Transféré par
Charo Nudo Pongasi0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
40 vues25 pagespdf science 8
Titre original
Electrical Wiring and Safety Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentpdf science 8
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
40 vues25 pagesElectrical Wiring and Safety
Transféré par
Charo Nudo Pongasipdf science 8
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 25
Electrical Wiring and Safety
1 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
2 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Electrical safety
3 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Why is electricity dangerous?
Warning signs are used to alert
people to the presence of high
voltage electricity.
When a current passes through
living material, it causes an
electric shock.
This interferes with nerve signals
from the brain to the body, and
can cause a heart attack, muscle
spasms and breathing difficulties.
Other dangers include overheated and faulty appliances,
which may lead to electrical fires.
4 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Using electricity safely
Although electricity can be very dangerous, it is also
incredibly useful and is essential for modern life.
What precautions can be taken to make electricity safer?
Do not overload sockets.
Wire plugs correctly.
Never mix water and electricity.
Regularly check cables for
breaks and loose wires.
Never stick anything other than a plug in a socket.
Use earth wires, fuses and circuit breakers to
prevent accidents in the event that a fault develops.
5 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
6 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Inside a cable
An electrical cable usually contains three wires.
These wires are made of copper because
it is a good conductor of electricity.
Each wire is made of thin strands of
copper to keep the cable flexible.
Each wire is encased in plastic to stop
the wires from touching and causing a
short circuit. Plastic is used as it is a
good insulator, as well as being tough
and flexible. The whole cable is
encased in another layer of plastic.
Two of the wires form the electrical circuit,
while the third wire is a safety feature.
7 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
What does each wire do?
Each of the wires in a cable performs a specific function.
The neutral wire completes the
circuit. It is kept at a zero voltage
by the electricity company.
The live wire carries
the high voltage.
The earth wire is a safety wire that is needed to earth
appliances with a metal case. This makes it safer to
touch the appliance if it develops a fault.
8 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Which wire is which?
9 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Inside a plug
The three pins in an electrical plug are connected to the
three wires inside a cable.
live
earth terminal
terminal
fuse
neutral
terminal
cable
grip
cable Could you wire a plug?
10 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Wiring a plug
11 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Materials inside a plug
12 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
What’s wrong?
13 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
14 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
What is a fuse?
A fuse is a safety device
containing a thin wire that
melts if the current
is too high, breaking the
circuit and protecting the fuse
cable from overheating
and catching fire.
Fuses act as an early warning
system, preventing appliances from
being damaged by surges in electricity
and warning owners of faults.
All UK plugs are fitted with fuses. Fuses are available in a
range of amperes to suit different current values.
15 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Investigating fuses
16 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Earthing
Earthing is a process used to increase the safety of
electrical appliances and prevent electric shocks.
An earth wire is essential for any
appliance with a metal case.
Without an earth wire, electricity
could begin to flow through the
metal casing if a fault developed.
The earth wire provides an
alternative path for the current.
If the live wire becomes loose and touches the metal
case, the very large current flows through the earth
wire and blows the fuse in the plug, breaking the circuit.
17 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
How on earth…?
18 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Circuit breakers
All homes have fuse boxes. These are safety
devices between the sockets in the home
and the mains supply from the street.
Newer fuse boxes contain
Residual Current Circuit
Breakers (RCCBs), which detect
a difference in current between
the live and neutral wires.
They use an electromagnet to
break the circuit if the current
difference becomes too large.
RCCBs detect current surges much quicker than a fuse.
19 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Fuse or circuit breaker?
20 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Double insulated
Another way of improving the
safety of electrical appliances is to
make them double-insulated.
Double-insulated
appliances have plastic
cases, without any wires
connected to the case.
The case cannot become
live, because plastic does
not conduct electricity.
In the UK, double-insulated
appliances are marked with
a symbol of two squares.
21 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Double insulated or not?
22 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
23 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Glossary
24 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Multiple-choice quiz
25 of 25 © Boardworks Ltd 2011
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Decay and RecyclingDocument46 pagesDecay and Recyclinganon_744165750Pas encore d'évaluation
- DLP For Cot-3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesDLP For Cot-3rd QuarterCharo Nudo Pongasi67% (3)
- Cell Theory Timeline ActivityDocument4 pagesCell Theory Timeline ActivityJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletPas encore d'évaluation
- KS4 Energy - Energy Transfers-2Document33 pagesKS4 Energy - Energy Transfers-2dipalidhuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Making Polymers v2.0Document43 pagesMaking Polymers v2.0Ricki HanPas encore d'évaluation
- Smackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Document23 pagesSmackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Aref DahabrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Turning EffectsDocument4 pagesTurning EffectsHenricus Galvin NaftaliPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 of 41 © Boardworks LTD 2008Document41 pages1 of 41 © Boardworks LTD 2008Hanifa Uly AmrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Feeding Relationships: 1 of 38 © Boardworks LTD 2008Document124 pagesFeeding Relationships: 1 of 38 © Boardworks LTD 2008jspfoiguw89Pas encore d'évaluation
- DynamicsDocument28 pagesDynamicsChaisePas encore d'évaluation
- Year 10 Physics LDRs and Thermistors PDF v2Document12 pagesYear 10 Physics LDRs and Thermistors PDF v2sweet.miyuxPas encore d'évaluation
- Nerves and ReflexesDocument14 pagesNerves and ReflexesjtPas encore d'évaluation
- Are Very Large Molecules Made When Hundreds of Join Together To Form Long ChainsDocument23 pagesAre Very Large Molecules Made When Hundreds of Join Together To Form Long ChainsAlaa Al HamedPas encore d'évaluation
- KS4 Transition MetalsDocument16 pagesKS4 Transition MetalsIsabel Iglesias QuintanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eukaryotic CellsDocument10 pagesEukaryotic CellsMaane BrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- MaterialsDocument34 pagesMaterialsdiane hoylesPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Redox ChemistryDocument30 pagesApplication of Redox ChemistryMurugan.Subramani100% (1)
- Equilibrium BWDocument54 pagesEquilibrium BWMichael EllisPas encore d'évaluation
- PressureDocument10 pagesPressureEvina Nelly Natalia SihitePas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases and Immunity: Defence Against MicrobesDocument55 pagesDiseases and Immunity: Defence Against MicrobesIvan Prasetya100% (1)
- 9 Wave Properties v2 0Document28 pages9 Wave Properties v2 0salmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Internet: Hardware and NetworksDocument21 pagesThe Internet: Hardware and Networksprincesstraill100% (1)
- Electricity Y7Document29 pagesElectricity Y7Susan ChongPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Exchange Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic ScreeningDocument49 pagesGas Exchange Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic Screeningmlk100% (1)
- Fotovoltaic ImprovementsDocument5 pagesFotovoltaic Improvements3dfelixPas encore d'évaluation
- Leaf and MineralsDocument16 pagesLeaf and MineralsfarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials Part 2 - PressureDocument26 pagesMaterials Part 2 - Pressurepeter liPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetics 1Document35 pagesKinetics 1Alex BoumanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 CollisionsDocument42 pages5 CollisionsClaudia PinnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics Part 1 - Enthalpy ChangesDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Part 1 - Enthalpy ChangesYacinePas encore d'évaluation
- Shock Protection in The ORDocument31 pagesShock Protection in The ORbeaz101Pas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Active TransportDocument10 pagesGCSE Active TransportNoel Johansen-BergPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical ChemistryDocument30 pagesAnalytical ChemistrySakib AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lenses 1Document13 pagesLenses 1Yuni MuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- KS4 InheritanceDocument36 pagesKS4 InheritancemoatazPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1-Introduction To Redox Reactions: Redox Chemistry and ElectrochemistryDocument100 pagesLesson 1-Introduction To Redox Reactions: Redox Chemistry and ElectrochemistryZheng JoeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive SystemDocument56 pagesDigestive SystemNimas PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Covalent StructuresDocument11 pagesCovalent StructuresjtPas encore d'évaluation
- AstrophysicsDocument39 pagesAstrophysicsKev Watts100% (1)
- Electrical Signals v2.0Document42 pagesElectrical Signals v2.0jt100% (1)
- Organic-Synthesis & ChiralityDocument34 pagesOrganic-Synthesis & ChiralityAlaa Al HamedPas encore d'évaluation
- The Atomic ModelDocument22 pagesThe Atomic ModelIntan CahyaningrumPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectricityDocument32 pagesElectricityShalini KulshresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 SL (WOW)Document40 pagesChapter 6 SL (WOW)muhammad ehsanullah sharifiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolysis: 1 of 6 © Boardworks LTD 2014Document6 pagesElectrolysis: 1 of 6 © Boardworks LTD 2014Angela GarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell MembranesDocument34 pagesCell MembranesayfilonPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification - 2015Document22 pagesClassification - 2015randyhmthsPas encore d'évaluation
- Coastal ProcessesDocument15 pagesCoastal Processesapi-258813608Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Solar Tracker-2Document17 pagesAutomatic Solar Tracker-2ShahnawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Physics: ObjectiveDocument60 pagesGrade 9 Physics: ObjectiveAngel Alexandra SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- 8A Food and DigestionDocument28 pages8A Food and DigestionAlicia HaughtonPas encore d'évaluation
- Boardworks GCSE Additional Science: Physics Energy and MovementDocument30 pagesBoardworks GCSE Additional Science: Physics Energy and MovementJayPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Training Awareness PPT-2020Document45 pagesElectrical Training Awareness PPT-2020Ishmael TettehPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics Part 4 - EntropyDocument26 pagesThermodynamics Part 4 - EntropyOrangesPlzPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicine and The Industrial RevolutionDocument52 pagesMedicine and The Industrial RevolutionHenriPas encore d'évaluation
- Finishing ProcessesDocument16 pagesFinishing ProcessesAjay P AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Trends in Period 3Document34 pagesTrends in Period 3Fildzah AdanyPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Indian & Iec Codes For Hazardous AreaDocument4 pagesList of Indian & Iec Codes For Hazardous AreaShirishPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Electrical Safety v1 - 0Document34 pages9 Electrical Safety v1 - 0Cinara RahimovaPas encore d'évaluation
- NEW 4.2 Electronics (S) %Document49 pagesNEW 4.2 Electronics (S) %Anisha BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8Document5 pagesElectrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8John Mark PrestozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity in The HomeDocument10 pagesElectricity in The HomeHomok NokiPas encore d'évaluation
- Discovery of Cell and Development of Cell Theory WorksheetDocument1 pageDiscovery of Cell and Development of Cell Theory WorksheetCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Space QUIZZESDocument8 pagesEarth and Space QUIZZESCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Home Made COVID 19 SolutionDocument1 pageHome Made COVID 19 SolutionCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Discovery of Cell and Development of Cell Theory WorksheetDocument1 pageDiscovery of Cell and Development of Cell Theory WorksheetCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 8 MatterDocument13 pagesGRADE 8 MatterCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Earth and Space 2Nd Quarter: San Roque National High SchoolDocument4 pages8 Earth and Space 2Nd Quarter: San Roque National High SchoolCharo Nudo Pongasi100% (1)
- Performance Task 4th QuarterDocument4 pagesPerformance Task 4th QuarterCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP For Cot-3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesDLP For Cot-3rd QuarterCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Earth and Space 2Nd Quarter: San Roque National High SchoolDocument4 pages8 Earth and Space 2Nd Quarter: San Roque National High SchoolCharo Nudo Pongasi100% (1)
- COMETS, METEORS and ASTEROIDSDocument3 pagesCOMETS, METEORS and ASTEROIDSCharo Nudo Pongasi100% (1)
- 8 Earth and Space 2Nd Quarter: San Roque National High SchoolDocument4 pages8 Earth and Space 2Nd Quarter: San Roque National High SchoolCharo Nudo Pongasi100% (1)
- Module 4: Difference Between Plants and Animals Cell: Lesson 3: Cell Technologies in The Field of MedicineDocument26 pagesModule 4: Difference Between Plants and Animals Cell: Lesson 3: Cell Technologies in The Field of MedicineCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 1 - Faults and EarthquakesDocument10 pagesActivity 1 - Faults and EarthquakesCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 and 2 ActivitiesDocument2 pagesModule 1 and 2 ActivitiesCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- HLP Grade 7 Week 1 QUARTER 2Document5 pagesHLP Grade 7 Week 1 QUARTER 2Charo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Tool No. 1Document3 pagesAssessment Tool No. 1Charo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 and 2 ActivitiesDocument2 pagesModule 1 and 2 ActivitiesCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Home-Made Covid-19 Solution Preparing Antiseptic, Cleaning, and Disinfecting SolutionDocument1 pageHome-Made Covid-19 Solution Preparing Antiseptic, Cleaning, and Disinfecting SolutionCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- HLP Grade 7 Week 1 QUARTER 2Document5 pagesHLP Grade 7 Week 1 QUARTER 2Charo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- HLP Science 7 Week 4 Quarter 2-Module 4 - MRN PONGASIDocument4 pagesHLP Science 7 Week 4 Quarter 2-Module 4 - MRN PONGASICharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheet Grade 7 ScienceDocument6 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Grade 7 ScienceCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Task 4th QuarterDocument4 pagesPerformance Task 4th QuarterCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Look at The Picture On The Side.: Think-Pair-ShareDocument26 pagesLook at The Picture On The Side.: Think-Pair-ShareCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4: Difference Between Plants and Animals Cell: Lesson 3: Cell Technologies in The Field of MedicineDocument26 pagesModule 4: Difference Between Plants and Animals Cell: Lesson 3: Cell Technologies in The Field of MedicineCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Waves Radiating Out After A Rupture/slip BDocument1 pageA. Waves Radiating Out After A Rupture/slip BCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Grade 8 Development of The Periodic Table, Reactivity Series and TrendsDocument31 pagesLesson Grade 8 Development of The Periodic Table, Reactivity Series and TrendsCharo Nudo PongasiPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL On Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesDLL On Laws of MotionCharo Nudo Pongasi100% (4)
- Bright Ideas 2 Unit 1 Test-Fusionado-Páginas-1-33Document33 pagesBright Ideas 2 Unit 1 Test-Fusionado-Páginas-1-33Eleonora Graziano100% (1)
- Pengaruh Volume Pemberian Air Terhadap Pertumbuhan Bibit Kelapa Sawit Di Pembibitan UtamaDocument11 pagesPengaruh Volume Pemberian Air Terhadap Pertumbuhan Bibit Kelapa Sawit Di Pembibitan UtamaTahum MatfuahPas encore d'évaluation
- School of Chemical Engineering - 20Document372 pagesSchool of Chemical Engineering - 20biroutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Zbus and Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument20 pagesZbus and Symmetrical Fault Analysishj203800Pas encore d'évaluation
- Systems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesDocument34 pagesSystems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesFatima KausarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia 6131 NFCDocument5 pagesNokia 6131 NFCvetvetPas encore d'évaluation
- Hearst Tower - New York City: Frank J. Dimauro Envs 662-660 Richard W. Berman Project: BuildingsDocument6 pagesHearst Tower - New York City: Frank J. Dimauro Envs 662-660 Richard W. Berman Project: BuildingsMohamed FawzyPas encore d'évaluation
- International Standard Paper SizesDocument34 pagesInternational Standard Paper SizesAman KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ficha Tecnica p501Document4 pagesFicha Tecnica p501LizbethPas encore d'évaluation
- Morning Star Cafe Menu Revised 08-14-2019 On Line Menu 1Document2 pagesMorning Star Cafe Menu Revised 08-14-2019 On Line Menu 1api-471935951Pas encore d'évaluation
- Commissioning Valve Product BrochureDocument14 pagesCommissioning Valve Product BrochureblindjaxxPas encore d'évaluation
- 4864.21 - Optics System 2Document39 pages4864.21 - Optics System 2Edgar Jose Aponte MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- .Cancer DiseaseDocument10 pages.Cancer DiseasejanakrajchauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Penerapan Metode Sonikasi Terhadap Adsorpsi FeIIIDocument6 pagesPenerapan Metode Sonikasi Terhadap Adsorpsi FeIIIappsPas encore d'évaluation
- BJT Common Emitter Characteristics: Experiment 6Document5 pagesBJT Common Emitter Characteristics: Experiment 6beesahPas encore d'évaluation
- القطع بالبلازماDocument27 pagesالقطع بالبلازماsamehPas encore d'évaluation
- Subcontracting Process in Production - SAP BlogsDocument12 pagesSubcontracting Process in Production - SAP Blogsprasanna0788Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mixing L 6-7Document60 pagesMixing L 6-7hyde2520015754Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tadabbur I Qur'ānDocument43 pagesTadabbur I Qur'ānamjad_emailPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: Higher Tier Paper 1HDocument28 pagesBiology: Higher Tier Paper 1HkaruneshnPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Sentences Is The Opposite ofDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Sentences Is The Opposite ofSpsc AspirantsPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech Brief 3: Digitally Control Phase Shift: Application Note 559Document6 pagesTech Brief 3: Digitally Control Phase Shift: Application Note 559Sreerag Kunnathu SugathanPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Document19 pagesSTPM Mathematics T Past Year Question P1 P2 P3Sou Voyage0% (3)
- 5980 10143 1 SM PDFDocument11 pages5980 10143 1 SM PDFfaustinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cast Your HoroscopeDocument27 pagesCast Your HoroscopeSunil ShastriPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Document28 pagesRebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Manuel Velasco100% (1)
- Pediatric Airway ManagementDocument2 pagesPediatric Airway ManagementSilvy AmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- S.No. Components Makes: 1 Grab Cranes - Gantry TypeDocument4 pagesS.No. Components Makes: 1 Grab Cranes - Gantry TypeHarish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Poem Summary - Keeping QuietDocument3 pagesPoem Summary - Keeping QuietVignesh Mohan100% (2)
- Laura Gentile Letter On Hampden County CourthouseDocument6 pagesLaura Gentile Letter On Hampden County CourthouseMassLivePas encore d'évaluation