Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Otorhino Dr. R. Regalado
Transféré par
Doctor Castle0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues4 pagesThe document appears to be a test for the subject of otorhinolaryngology (ENT) containing 50 multiple choice questions testing knowledge about various ENT topics including the anatomy and physiology of the ear, common ear diseases and their treatments, audiology, and balance/vestibular system functions. Some sample questions cover the functions of cerumen, causes of otitis externa, management of otitis media, pathogens that cause fungal infections of the ear, and complications that can arise from ear infections.
Description originale:
Otorhino lec
Titre original
Otorhino Dr. r. Regalado
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe document appears to be a test for the subject of otorhinolaryngology (ENT) containing 50 multiple choice questions testing knowledge about various ENT topics including the anatomy and physiology of the ear, common ear diseases and their treatments, audiology, and balance/vestibular system functions. Some sample questions cover the functions of cerumen, causes of otitis externa, management of otitis media, pathogens that cause fungal infections of the ear, and complications that can arise from ear infections.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues4 pagesOtorhino Dr. R. Regalado
Transféré par
Doctor CastleThe document appears to be a test for the subject of otorhinolaryngology (ENT) containing 50 multiple choice questions testing knowledge about various ENT topics including the anatomy and physiology of the ear, common ear diseases and their treatments, audiology, and balance/vestibular system functions. Some sample questions cover the functions of cerumen, causes of otitis externa, management of otitis media, pathogens that cause fungal infections of the ear, and complications that can arise from ear infections.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Silliman University Medical School
Dumaguete City
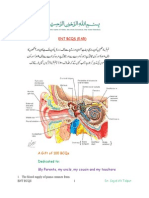
OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY
Dr. R. Regalado
Name: ____________________________________ Date: _______ Score: _______
1. Not a function of cerumen
a) Lubrication
b) Bactericidal
c) Carcinogenic
d) Facilitate removal of epithelial debris
2. Not an infection inflammation of the outer ear
a) Dermatoses
b) Viral
c) Pseudomonas
d) Aspergillus
3. Not a predisposing factor to occurrence of Otitis externa
a) Change in pH
b) Oral antibiotic intake
c) Temperature and humidity changes
d) Swimming
4. All are part of management of Otitis externa except
a) Suctioning of debris
b) Use of wick to apply medication
c) Use of topical drops
d) Oral steroids
5. “Pointing” is a common occurrence
a) Furuncolosis
b) Diffuse Otitis externa
c) Otomycosis
d) Perichondritis
6. Tragal tenderness is a diagnostic feature
a) Furuncolosis
b) Diffuse Otitis externa
c) Otomycosis
d) Perichondritis
7. “Boxer’s ear”
a) Furuncolosis
b) Diffuse Otitis externa
c) Otomycosis
d) Perichondritis
8. “Floppy ear”
a) Perichondritis
b) Relapsing polychondritis
c) Necrotizing external otitis
d) Eczematous dermatitis
9. Most common auricular deformity
a) Boxer’s ear
b) Floppy ear
c) Cauliflower ear
d) Lop-ear
10. Topical drugs for treatment of fungal organism except
a) Nystatin
b) Clotrimazole
c) Miconazole
d) Colistin
11. Most prevalent cause of hearing loss in school-age children
a) Serous Otitis media
b) Acute purulent Otitis media
c) Acute mastoiditis
d) Chronic mastoiditis
12. Most common site of barotrauma
a) Nasal passages
b) Sinuses
c) Middle ear
d) Inner ear
13. All these can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction except
a) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
b) Hypertrophied tonsils
c) Enlarged adenoids
d) All are correct
14. Tympanic membrane perforation can result from
a) Barotrauma
b) Blast injuries
c) Foreign bodies in the ear
d) All are correct
15. Basic causative factor in Acute Otitis media
a) Tympanic membrane perforation
b) Eustachian tube dysfunction
c) Infections in the outer ear
d) Non-judicious use of antibiotics
16. Most common organism in Acute Otitis media in children
a) H. influenzae
b) Strep. pneumoniae
c) B-hemolytic strep
d) Staph. aureus
17. Facial nerve paralysis is a ________ complication of Otitis media and mastoiditis
a) Middle ear
b) Inner ear
c) Extradural
d) CNS
18. Labyrinthitis is a ________ complication of Otitis media and mastoiditis
a) Middle ear
b) Inner ear
c) Extradural
d) CNS
19. Most common intracranial complication from suppurative Otitis media
a) Brain abscess
b) Otitic hydrocephalus
c) Meningitis
d) Labyrinthitis
20. Most common primary tumor of the middle ear
a) Rhabdomyoscrocoma
b) Adenocarcinoma
c) Glomus jugulare
d) Adenoid cystic carcinoma
21. Presence of this on X-ray is a primary indication for mastoidectomy
a) Cholesteatoma
b) Fluid in the middle ear
c) Granulation tissue
d) None of the above is correct
22. Type of hearing loss that can result from Chronic Otitis media
a) Conductive
b) Sensorineural
c) Both a & b are correct
d) Both a & b are incorrect
23. Primary purpose of surgery in middle ear infection
a) Eradicate infected tissue
b) Preservation of hearing
c) Both are correct
d) None of the above is correct
24. Presence of this indicates an impending serious complication
a) Vertigo
b) Hearing loss
c) Tympanic membrane perforation
d) Fluid in the middle ear
25. Multiple perforations in the ear drum suggest the possibility of
a) Cholesteatoma
b) Bacterial origin
c) Viral origin
d) Tuberculosis
26. Reason why external auditory canal infections are so painful
a) Absence of nerve endings
b) Absence of collateral blood supply
c) No subcutaneous tissue
d) All are correct
27. Primary agent in Ramsay Hunt disease
a) Herpes simplex
b) Pseudomonas
c) Herpes Zoster
d) Staphylococcus
28. All are causative factors in serous otitis media except
a) Allergy
b) Barotrauma
c) Upper respiratory tract infection
d) All of the above are correct
29. Central perforations of the tympanic membrane usually are caused by
a) Tuberculosis
b) Viruses
c) Bacteria
d. Fungus
30. Central nervous system complications of otitis media and mastoiditis except
a) Subdural abscess
b) Meningitis
c) Brain abscess
d) Otitic hydrocephalus
31. The most important sound pattern for human hearing
a. music
b. noise
c. speech
d. all of the above
32. All these borders are enclosed by the middle ear except
a. facial nerve
b. internal carotid artery
c. inner ear
d. all are correct
33. Main function of the middle ear
a. impedance matching
b. maintenance of equilibrium
34. Usual avenue of sound transmission
a. bone conduction
b. air conduction
c. both A and B
d. neither A or B
35. Not a goal of audiologic evaluation
a. detect hearing disorder
b. classify hearing disorder
c. quantify hearing disorder
d. treat hearing disorders
36. Balance depends upon these separate and independent systems except:
a. Gustatory System
b. Visual System
c. Central Nervous System
d. Vestibular System
37. Not a function of the Vestibular System
a. Spatial Orientation
b. Maintenance of posture
c. Maintenance of equilibrium
d. Sound transmission
38. Not a Standard Vestibular Test
a. Caloric Testing
b. Rombergs Test
c. Unterberger Stepping Test
d. Finger to Nose Test
39. Not a peripheral vestibular disease
a. Labyrinthitis
b. Meningitis
c. Meniere’s
d. Positional Vertigo
40. Not included in the classic clinical triad of Meniere’s Disease
a. Nystegmus c. Tinnitus
b. Hearing loss d. Vertigo
41. Sensory organ of hearing
a. basilar membrane
b. tectorial membrane
c. organ of corti
d. inner hair cells
42. A loss of 41-60 decibels is considered
a. mild hearing loss
b. moderate
c. severe
d. profound
43. When there is middle ear and cochlear problems producing a hearing loss, the hearing loss is
called:
a. conductive
b. sensorineural
c. mixed
d. central hearing impairment
44. This is usually used to test the hearing of 3-6 years of age children
a. play audiometry
b. behavioral observation audiometry
c. auditory brainstem response
d. visual reinforcement observation audiometry
45. A hearing screening tool appropriate from birth to childhood
a. otoacoustic emission test
b. play audiometry
c. auditory brainstem response
d. behavioral observation audiometry
46. Most cosmetically appealing type of hearing aid
a. behind the ear
b. in the ear
c. in the canal
d. completely in the canal
47. The external auditory meatus is about
a. 2.5 cm long
b. 3.5 cm long
c. 4.5 cm long
d. 5.5 cm long
48. This is not part of the membranous labyrinth
a. Eustachian tube
b. Vestibular organs
c. semicircular canals
d. cochleer ducts
49. About how much of our hair cells are lost by age 65?
a. 20% b. 30% c. 40% d. 50%
50. This is usually caused by pseudomonas and generally found in the elderly diabetics living in
warm climate
a. necrotizing external otitis
b. perichondritis
c. eczematous dermatitis
d. herpes zoster oticus
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ent Mcqcfor Ug CH-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesEnt Mcqcfor Ug CH-WPS OfficeJayahar AlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent MCQ 22-23 For StudentsDocument46 pagesEnt MCQ 22-23 For StudentsBharathi Sneha PeriasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- JSS Academy of Higher Education & Research, Mysuru: QP Code: 21016Document4 pagesJSS Academy of Higher Education & Research, Mysuru: QP Code: 21016Ramiz IsrafPas encore d'évaluation
- ORL(耳鼻咽喉科学)题, 班级:16秋网络班 学号:916905048 姓名:DIAN SRI WAHYUNI江迪燕Document10 pagesORL(耳鼻咽喉科学)题, 班级:16秋网络班 学号:916905048 姓名:DIAN SRI WAHYUNI江迪燕Hadhya MoppyPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Unas UGMDocument8 pagesSoal Unas UGMMonik AlamandaPas encore d'évaluation
- HAAD MCQ On ENTDocument21 pagesHAAD MCQ On ENTAsif Newaz100% (1)
- A. It Consists of Squamous EpitheliumDocument7 pagesA. It Consists of Squamous EpitheliumUzair KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Board Revision2014 2Document8 pagesBoard Revision2014 2Adham Sharaf AldeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Facial Vein: Superior Hiatus SemilunarisDocument5 pagesCommon Facial Vein: Superior Hiatus SemilunarissuntiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5) EntDocument16 pages5) EntZH. omg sarPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ in Orl CourseDocument46 pagesMCQ in Orl CoursesulnaikPas encore d'évaluation
- ENT BCQsDocument19 pagesENT BCQsSajid AliPas encore d'évaluation
- ENT exam ناقصDocument16 pagesENT exam ناقصmadara ëPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ S For StudentsDocument58 pagesMCQ S For StudentsJohn M. Hemsworth100% (2)
- امتحان ENT دفعة ٣١Document14 pagesامتحان ENT دفعة ٣١محمد عبد القاهر السروريPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ KhaldounDocument9 pagesMCQ Khaldounadham bani younesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent 25 ExamDocument8 pagesEnt 25 ExamAbd AlsalihiPas encore d'évaluation
- ENT Paper Mcqs (1) - 2Document9 pagesENT Paper Mcqs (1) - 2Muhammad Sheraz75% (4)
- McqssDocument6 pagesMcqssfatimaawan8989Pas encore d'évaluation
- OtorhinolaryngologyDocument10 pagesOtorhinolaryngologyRayyanPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Ent 2023-24-1Document37 pagesMCQ Ent 2023-24-1Mani MozhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymph Notes E.N.T MQsDocument65 pagesLymph Notes E.N.T MQsAli QuwarahPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQsin ENTwith Explanations Module 2 OtologyDocument7 pagesMCQsin ENTwith Explanations Module 2 OtologyFatina AryanPas encore d'évaluation
- ENTDocument2 pagesENTNikita Nanwani0% (1)
- 1-The Eustachian Tube Is Opened by Contraction ofDocument10 pages1-The Eustachian Tube Is Opened by Contraction ofNofouz MaswadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument24 pagesEar, Nose and ThroatcollinsmagPas encore d'évaluation
- Vea Endo PerioDocument20 pagesVea Endo PerioClaire CabigaoPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ NMCDocument17 pagesMCQ NMCBinek NeupanePas encore d'évaluation
- Questions ENT 2021Document28 pagesQuestions ENT 2021Ranjan Prasad100% (1)
- 1 - MOH Exam PaperDocument8 pages1 - MOH Exam PaperMohammed Jabr100% (4)
- MOH Exam PaperDocument8 pagesMOH Exam PaperSubhajit SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Endodontics and Periodontics PDFDocument16 pagesEndodontics and Periodontics PDFBoode Mo100% (1)
- ENT MCQs (Girls 1428-29)Document7 pagesENT MCQs (Girls 1428-29)Sheikha100% (9)
- Dr. Shazzly - 2015 PDFDocument8 pagesDr. Shazzly - 2015 PDFMohsen Saeed OzaibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Alternatives Are Given For Each Question. You Are Required To Fill The Most Appropriate Numbered Circle Completely in Section "A" of The Given OMR. Return This Question Paper Along With OMRDocument6 pagesFour Alternatives Are Given For Each Question. You Are Required To Fill The Most Appropriate Numbered Circle Completely in Section "A" of The Given OMR. Return This Question Paper Along With OMRMahesh ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dia - RayDocument16 pagesDia - Raymohamed awaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent MCQ'S 2Document37 pagesEnt MCQ'S 2Adham YounesPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0000Document16 pagesWa0000hassan qureshi100% (1)
- Gpat Opat Omae Microbio COMPILATIONDocument136 pagesGpat Opat Omae Microbio COMPILATIONDENTAL REVIEWER ONLYPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent Prelims Ears PDFDocument3 pagesEnt Prelims Ears PDFKenneth MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- C) Slow + Fast ComponentsDocument7 pagesC) Slow + Fast ComponentsUzair KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Test - 8 Retension, Dystopia, PericoronitisDocument5 pagesTest - 8 Retension, Dystopia, PericoronitisIsak ShatikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent MCQDocument6 pagesEnt MCQapi-26186766100% (8)
- General Pathology Oralpathology Microbiology Revalida 12Document38 pagesGeneral Pathology Oralpathology Microbiology Revalida 12KENT DANIEL SEGUBIENSEPas encore d'évaluation
- SAmple Questions of EndodonticsDocument19 pagesSAmple Questions of EndodonticsKhadija Kazoor100% (3)
- Ent ExaminationDocument9 pagesEnt ExaminationSheikha100% (2)
- Second and Third Year Ent McqsDocument6 pagesSecond and Third Year Ent Mcqsadham bani younesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent ExamDocument9 pagesEnt ExamChekole AdanePas encore d'évaluation
- I Am Sharing '100-mcq-complete-ENT' With YouDocument31 pagesI Am Sharing '100-mcq-complete-ENT' With Youhassan qureshi100% (1)
- MCQ On Periapical LesionsDocument3 pagesMCQ On Periapical LesionsSally MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ziauddin University College of Medical Technology Bs Batch Ii Sem Iii Periodontology MockDocument10 pagesZiauddin University College of Medical Technology Bs Batch Ii Sem Iii Periodontology MockHiba ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- SURGERY MockDocument15 pagesSURGERY MockFan Eli100% (1)
- Aiims 4 QuesDocument6 pagesAiims 4 QuesAyyagari Kameswar Rao50% (2)
- Multiple Choice Questions in Clinical Radiology: For Medical Practitioners and Medical StudentsD'EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Clinical Radiology: For Medical Practitioners and Medical StudentsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A Handbook on Biotelemetry and Radio Tracking: Proceedings of an International Conference on Telemetry and Radio Tracking in Biology and Medicine, Oxford, 20-22 March 1979D'EverandA Handbook on Biotelemetry and Radio Tracking: Proceedings of an International Conference on Telemetry and Radio Tracking in Biology and Medicine, Oxford, 20-22 March 1979Charles J. AmlanerPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitic Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidia, Pneumocystis, And MicrosporidiaD'EverandParasitic Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidia, Pneumocystis, And MicrosporidiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Genetic Communicative DisordersD'EverandHandbook of Genetic Communicative DisordersSanford E. GerberPas encore d'évaluation
- Effectiveness of MakahiyaDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of MakahiyaFrancis Errol EndozoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is DracunculiasisDocument1 pageWhat Is DracunculiasisSiti SyahirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Singapore and PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSingapore and Philippinessimon pragachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept PaperDocument12 pagesConcept Paperjlventigan100% (1)
- FFP and Cryoprecipitate FinalDocument6 pagesFFP and Cryoprecipitate FinalganotPas encore d'évaluation
- Criteria For The Ideal Treatment Option For Failed Tics Surgical or NonsurgicalDocument8 pagesCriteria For The Ideal Treatment Option For Failed Tics Surgical or NonsurgicalPaRpArOsSaPas encore d'évaluation
- Negative Entities: Entities, A Taboo TopicDocument15 pagesNegative Entities: Entities, A Taboo TopicZeljko Lav Pispek100% (5)
- VirologyDocument200 pagesVirologyVishal Singh GaharwarPas encore d'évaluation
- BiostatisticsDocument147 pagesBiostatisticskartik paulPas encore d'évaluation
- Staphylococcus EpidermidisDocument12 pagesStaphylococcus EpidermidisSim M ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Brain Function (Neurological) 3Document12 pagesDisorders of Brain Function (Neurological) 3Cres Padua QuinzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Malawi Public Health ActDocument63 pagesMalawi Public Health ActKondwani AndreahPas encore d'évaluation
- BBC - Future - Anthropology - The Sad Truth About Uncontacted Tribes PDFDocument10 pagesBBC - Future - Anthropology - The Sad Truth About Uncontacted Tribes PDFLevindo PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- AIIMS Question PaperDocument6 pagesAIIMS Question Papersharu4291100% (1)
- The Black DeathDocument3 pagesThe Black DeathErginDeğerPas encore d'évaluation
- Musana 2020 Come and See ApplicationDocument8 pagesMusana 2020 Come and See ApplicationCasey PaynePas encore d'évaluation
- DR Paul Harijanto - WS MALARIA-PIN PAPDI-19 PDFDocument33 pagesDR Paul Harijanto - WS MALARIA-PIN PAPDI-19 PDFMukhammadBurhanuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes On Public HealthDocument342 pagesLecture Notes On Public Healthredroseeeeee67% (3)
- Herpes Opportunity Disclosure Handout 2Document1 pageHerpes Opportunity Disclosure Handout 2Thong Huynh100% (1)
- Project On MalnutritionDocument14 pagesProject On MalnutritionVijay M100% (2)
- English Quarter 1 Week 1Document11 pagesEnglish Quarter 1 Week 1Meylene Balverde Ibarra100% (1)
- Why Isn't Kaieteur News Printing Rebuttals To Stella Ramsaroop Regarding Her Support For Gay Militancy in GuyanaDocument4 pagesWhy Isn't Kaieteur News Printing Rebuttals To Stella Ramsaroop Regarding Her Support For Gay Militancy in GuyanaRogerWilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Upcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 4 - Reading Comprehension v.5.26.2014Document16 pagesUpcat 2014 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 4 - Reading Comprehension v.5.26.2014Ivan PalenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia: Tuberculosis and Pneumonia in HIV-infected Children: An OverviewDocument10 pagesPneumonia: Tuberculosis and Pneumonia in HIV-infected Children: An OverviewIma SoniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Herbs-Gopi RadhaDocument4 pagesSkin Herbs-Gopi Radhagajendra_kPas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchopneumonia in ChildrenDocument3 pagesBronchopneumonia in ChildrenputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Document2 pagesHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Foot InfectionDocument40 pagesDiabetic Foot InfectionSuchie ILyasPas encore d'évaluation
- 0811 Hand Disinfectant and COVID-19Document54 pages0811 Hand Disinfectant and COVID-19Henrico ImpolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct Fecal Smear 3Document16 pagesDirect Fecal Smear 3Kenesa100% (2)