Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lechithin Ratio
Transféré par
Drbee100 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues1 pageDipalmityl lecithin (DPL) acts as a surfactant in lung alveoli and is secreted by Type-II pneumocytes. DPL lowers the surface tension of the air-alveolar interface and prevents alveolar collapse during expiration. Without DPL, premature infants can develop respiratory distress syndrome due to collapsed alveoli. The lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio (L/S ratio) in amniotic fluid is used to evaluate fetal lung maturity - a ratio above 5 indicates mature lungs while a ratio below 1 suggests a risk of respiratory distress. Estimating lecithin phosphorus levels is also clinically useful, with 0.100 mg/
Description originale:
Titre original
Lechithin ratio.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDipalmityl lecithin (DPL) acts as a surfactant in lung alveoli and is secreted by Type-II pneumocytes. DPL lowers the surface tension of the air-alveolar interface and prevents alveolar collapse during expiration. Without DPL, premature infants can develop respiratory distress syndrome due to collapsed alveoli. The lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio (L/S ratio) in amniotic fluid is used to evaluate fetal lung maturity - a ratio above 5 indicates mature lungs while a ratio below 1 suggests a risk of respiratory distress. Estimating lecithin phosphorus levels is also clinically useful, with 0.100 mg/
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues1 pageLechithin Ratio
Transféré par
Drbee10Dipalmityl lecithin (DPL) acts as a surfactant in lung alveoli and is secreted by Type-II pneumocytes. DPL lowers the surface tension of the air-alveolar interface and prevents alveolar collapse during expiration. Without DPL, premature infants can develop respiratory distress syndrome due to collapsed alveoli. The lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio (L/S ratio) in amniotic fluid is used to evaluate fetal lung maturity - a ratio above 5 indicates mature lungs while a ratio below 1 suggests a risk of respiratory distress. Estimating lecithin phosphorus levels is also clinically useful, with 0.100 mg/
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
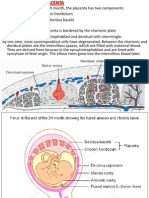
(a) Dipalmityl lecithin (DPL): DPL acts as a surfactant and lowers the
surface tension in lung alveoli. The lung alveoli contains 2 types of
cells.
• Type-I: These are thin cells which line the much of alveolar surface,
and
• Type-II: These are granular pneumocytes, round cells and contain
lamellar inclusions. These inclusions contain surfactant, DPL,
which is secreted from these cells by exocytosis.Surface activity
is that phenomenon whereby the surface tension of the air-
alveolar lining interface is lowered with expiration due to
presence of DPL. In absence of normal surface activity, if DPL is
absent, the alveolar radius becomes smaller with expirations, the
wall tension rises and the alveoli collapse. Absence of DPL, in
premature foetus, produces collapse of lung alveoli, which
produce respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline-membrane
disease). (b) Lecithin-Sphingomyelin Ratio (L/S ratio): L/S ratio in
Amniotic fluid has been used for the evaluation of fetal lung
maturity. Prior to 34 weeks gestation, the amniotic fluid lecithin
and sphingomyelin concentrations are approximately equal. After
this time, there is a marked increase in lecithin and L/S ratio
increases to greater than 5 at term.
• A L/S ratio of > 2 or > 5 indicate adequate foetal lung maturity
and suggests that respiratory distress after delivery is not
likely to develop.
• Delivery of a premature low weight fetus, with L/S ratio
approximately 1 or <1, indicate that the infant will probably
develop respiratory distress or hyaline membrane disease.
(c) Estimation of lecithin: Estimation of lecithin phosphorus
in amniotic fluid has been considered to be clinically more
useful. A lecithin phosphorus value of 0.100 mg/100 dl
indicates adequate foetal lung maturity.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1 Respiratory DiseasesDocument22 pages1 Respiratory Diseasesalielabadi10Pas encore d'évaluation
- RDS Ppts 2021Document37 pagesRDS Ppts 2021Mohammad NajjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Lung MaturityDocument10 pagesFetal Lung MaturityAtika SugiartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Fluid: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesAmniotic Fluid: Learning ObjectivesWho KnowsPas encore d'évaluation
- Resiratory Disorders in The NewbornDocument36 pagesResiratory Disorders in The NewbornRaquel CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatrics Exposition.: Pulmonary Respiratory Pathology in Preterm Infants (Under 37 Weeks of Gestation)Document2 pagesPediatrics Exposition.: Pulmonary Respiratory Pathology in Preterm Infants (Under 37 Weeks of Gestation)David Rodríguez GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- TTN AafpDocument9 pagesTTN Aafpsiti nur rachmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 Clearance of Fluid From LungsDocument7 pages2006 Clearance of Fluid From LungsyaritzaalviarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome Ped 401 MLDocument23 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome Ped 401 MLWongani ZuluPas encore d'évaluation
- From The Journal of The American Academy of PediatricsDocument10 pagesFrom The Journal of The American Academy of PediatricsMichi MichPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument10 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeKomang Rendy KrisnadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Fetal Lung MaturityDocument16 pagesAssessment of Fetal Lung MaturitybenPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument9 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeIrawati Eka PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Cyanosis in A NeonateDocument12 pagesApproach To Cyanosis in A NeonateXerxyllXyreaneLinaoPas encore d'évaluation
- ExamView - Chapter - 01Document2 pagesExamView - Chapter - 01Devin MckayPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Fetal Lung MaturityDocument2 pagesAssessment of Fetal Lung MaturitybebekbebekPas encore d'évaluation
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)Document6 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)suzela widya sariPas encore d'évaluation
- ExamView - Chapter - 0124Document2 pagesExamView - Chapter - 0124Devin MckayPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniocentesis Fetal Lung PDFDocument4 pagesAmniocentesis Fetal Lung PDFDevi Eliani ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Respiratory Distress Syndrome in The NewbornDocument3 pages4 Respiratory Distress Syndrome in The NewbornChristine Danica BiteraPas encore d'évaluation
- 3RD Lec Pulmonary Surfactant and RDSDocument40 pages3RD Lec Pulmonary Surfactant and RDSIbrahim MigdadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal CyanosisDocument13 pagesNeonatal CyanosisNadine BacalangcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient Tachypnea of The Newborn: Pediatrics in Review December 2008Document10 pagesTransient Tachypnea of The Newborn: Pediatrics in Review December 2008Haneen Dabbas2019Pas encore d'évaluation
- CASE 1: Manipac Yao: Cmmatias (Cmed 2022)Document3 pagesCASE 1: Manipac Yao: Cmmatias (Cmed 2022)Charm MatiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniocentrices (From The Greek Amnion For "Sac" and KenteDocument5 pagesAmniocentrices (From The Greek Amnion For "Sac" and KenteJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Enf Membrana HialinaDocument13 pagesEnf Membrana HialinaAlejandra MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Fluid AubfDocument5 pagesAmniotic Fluid AubfVicky ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Idiopathic Respiratory Disease SyndromeDocument30 pagesIdiopathic Respiratory Disease SyndromeAllan-VonPas encore d'évaluation
- RESPIRATORY DIS-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesRESPIRATORY DIS-WPS OfficeGiselle EstoquiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Distress Syndrome in The NewbornDocument7 pagesPathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Distress Syndrome in The NewbornSiti Novita KumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids - Strasinger, Susan King, Di Lorenzo, Marjorie Schaub (1) .pdf-258-268Document11 pagesUrinalysis and Body Fluids - Strasinger, Susan King, Di Lorenzo, Marjorie Schaub (1) .pdf-258-268Remark AmbananPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Fluid: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesAmniotic Fluid: Learning ObjectivesJym TampusPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Physiology of Newborn ResuscitationDocument8 pagesApplied Physiology of Newborn Resuscitationmichael andres bedoya vergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome: NewbornDocument17 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome: NewbornLoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument30 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeDennis MiritiPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Neonatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition Brian K Walsh DownloadDocument3 pagesTest Bank For Neonatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition Brian K Walsh DownloadLowell Garcia100% (28)
- Illness in The NewbornDocument34 pagesIllness in The NewbornVivian Jean TapayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aiims - Pediatrics Q&ADocument207 pagesAiims - Pediatrics Q&AqqypprcyxyPas encore d'évaluation
- Eni Rahmawati, S.Kep., NS., M.KepDocument46 pagesEni Rahmawati, S.Kep., NS., M.KepLisa Qoriana RohmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument18 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeMaricel DefiestaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCN Final Topic 2Document17 pagesMCN Final Topic 2Salea Fleur TaverronPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolytes ManagmentDocument13 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ManagmentSunardiasih100% (1)
- Amniotic FluidDocument33 pagesAmniotic FluidElsa Aprillia SujadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Fluid Lec.18Document32 pagesAmniotic Fluid Lec.18jayPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Update: Ricardo J Rodriguez MDDocument9 pagesManagement of Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Update: Ricardo J Rodriguez MDIndah Afriani NasutionPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface TensionDocument13 pagesSurface Tensionezeudunicholas16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Focus: Gestational AgeDocument82 pagesFocus: Gestational AgeVincent Jofette AventunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prematures With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Do Not Have Increased The Chance of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Requiring Indomethacin Therapy ThereafterDocument58 pagesPrematures With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Do Not Have Increased The Chance of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Requiring Indomethacin Therapy ThereafterAndy SungPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease, Most Often Occurs In: Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument6 pagesDisease, Most Often Occurs In: Respiratory Distress Syndromejoyrena ochondraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyaline Membrane DiseaseDocument31 pagesHyaline Membrane DiseaseWeng RamojalPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Lung DevelopmentDocument36 pages12 Lung Developmentf3er3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Support in ChildDocument8 pagesRespiratory Support in ChildHưng TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument25 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeVaishnaviPas encore d'évaluation
- 11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidDocument35 pages11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- Research DCCDocument19 pagesResearch DCCMuhammad ElshamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Critical Care Case StudiesDocument13 pagesPediatric Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Critical Care Case StudiesSyarifa ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Fluid As A Vital Sign For Fetal Wellbeing: ReviewDocument9 pagesAmniotic Fluid As A Vital Sign For Fetal Wellbeing: ReviewMeska AmeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- 834 Case REport An8oldmonthgirlDocument10 pages834 Case REport An8oldmonthgirlAnsar BashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Myeloperoxidase and Protein Oxidation in The Airways of Young Children With Cystic FibrosisDocument7 pagesMyeloperoxidase and Protein Oxidation in The Airways of Young Children With Cystic FibrosisMichael StudiofourteenohninePas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Ophthalmology for Primary CareD'EverandPediatric Ophthalmology for Primary CareÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Cardiovascular Heart MurmurDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Heart MurmurDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Surgery RemediationDocument14 pagesSurgery RemediationDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Baroreceptors & Chemoreceptors: ReceptorsDocument4 pagesBaroreceptors & Chemoreceptors: ReceptorsDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2021: All The New Changes. BiochemistryDocument4 pagesFA 2021: All The New Changes. BiochemistryDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heart BlocksDocument9 pagesHeart BlocksDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2022 (Original PDFDocument849 pagesFA 2022 (Original PDFDrbee10100% (12)
- UW Allergy + Immuno - Educational Objectives PDFDocument25 pagesUW Allergy + Immuno - Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDocument15 pagesFA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDocument15 pagesFA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2020 - Cardio EmbryoDocument7 pagesFA 2020 - Cardio EmbryoDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2020 - Cardio AnatomyDocument2 pagesFA 2020 - Cardio AnatomyDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Epi Cheatsheet PDFDocument4 pagesEpi Cheatsheet PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDocument15 pagesFA 2020 - Cardio Sterling Curve PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- UW (Step 1) Renal - Educational Objectives PDFDocument50 pagesUW (Step 1) Renal - Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renal 1 MTC PDFDocument31 pagesRenal 1 MTC PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- UW (Step 1) Neurology - Educational ObjectivesDocument86 pagesUW (Step 1) Neurology - Educational ObjectivesDrbee100% (1)
- UW (Step 1) GIT - Educational Objectives PDFDocument69 pagesUW (Step 1) GIT - Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap+14+CVSin+pathologyFall11 1Document19 pagesChap+14+CVSin+pathologyFall11 1Drbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap+13+CoordinatedCVSFall11 1Document10 pagesChap+13+CoordinatedCVSFall11 1Drbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap+12+CO, VRegul+Fall11 1Document17 pagesChap+12+CO, VRegul+Fall11 1Drbee100% (1)
- Renal 2 MTC PDFDocument55 pagesRenal 2 MTC PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renal 3 MTCDocument19 pagesRenal 3 MTCDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Epidemiology Biostats PDFDocument1 pageUSMLE Epidemiology Biostats PDFlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- UW Infectious Diseases + Microbiology Educational Objectives PDFDocument75 pagesUW Infectious Diseases + Microbiology Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Control of Blood Flow: After Reading This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDocument12 pagesControl of Blood Flow: After Reading This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- FirstAid 2017 PDFDocument412 pagesFirstAid 2017 PDFDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam Key (BB 451/551) : Section I: (40 Points Total) The Statements in This Section Can BeDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Key (BB 451/551) : Section I: (40 Points Total) The Statements in This Section Can BeDrbee10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Step 1 Micro ChartsDocument38 pagesStep 1 Micro ChartsRitika AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Step 1 Uworld PDFDocument25 pagesStep 1 Uworld PDFRegents Park Business Center100% (1)
- GTP GDP: UDP-galactose UDP-glucose ATPDocument2 pagesGTP GDP: UDP-galactose UDP-glucose ATPTyler KingPas encore d'évaluation