Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Itest Intrebari Navigatie
Transféré par
Comanita Ion BogdanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Itest Intrebari Navigatie
Transféré par
Comanita Ion BogdanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
1. __________ is the angular distance between the prime meridian and the meridian of a point on the earth, measured eastward or westward from the
prime meridian through 180 degree.
a. Latitude
b. Longitude
c. Difference of Latitude
d. Difference of Longitude
2. The process where a navigator constantly evaluates the ship s position, anticipates dangerous situations well before they arise, and always keeps ahead
of the vessel.
a. Evaluation
b. Instruction
c. Navigation
d. Situation
3. __________ is the angular distance from the equator, measured northward or southward along a meridian from 0 degree at the equator to 90 degree at
the poles.
a. Latitude
b. Longitude
c. Difference of Latitude
d. Difference of Longitude
4. __________ is the direction in which a vessel is pointed, expressed as angular distance from 000 degree clockwise through 360 degree.
a. Bearing
b. Heading
c. Course
d. Track
5. __________ is the direction from the ship to another ship and/or one terrestrial point/object , expressed as angular distance from 000 degree (North)
clockwise through 360 degree.
a. Bearing
b. Heading
c. Course
d. Track
6. ____________ termed as latitude and longitude, can define any position on earth.
a. Coordinates
b. DLAT
c. Tide and Current
d. Altitude
7. The difference between the magnetic meridian and the geographical meridian.
a. Compass Bearing
b. Compass Error
c. Deviation
d. Variation
8. The_________ is a great circle midway between the poles.
a. Equator
b. Bearing
c. Meridian
d. Courses
9. The difference between the magnetic compass needle point and the magnetic meridian.
a. Compass Bearing
b. Compass Error
c. Deviation
d. Variation
10. _____________ is the rate of motion, or distance per unit of time
a. Speed
b. Course
c. Bearing
d. Time
11. It is a compass error caused by the magnetic properties of any metal in the immediate vicinity of the compass
iTEST for Dohle Page 1 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
a. Deviation
b. Variation
c. Compass Error
d. Magnetic Error
12. ____________ the unit of speed commonly used in navigation, is a rate of 1 nautical mile per hour.
a. Centimeter
b. Knots
c. Kilometer
d. Bearing
13. It is caused by the difference in position of the Geographic Poles and the Magnetic Poles.
a. Deviation
b. Variation
c. Compass Error
d. Magnetic Error
14. The algebraic sum of deviation and variation
a. Deviation
b. Variation
c. Compass Error
d. Magnetic Error
15. _____________ is the horizontal direction in which a vessel is steered or intended to be steered, expressed as angular distance from north clockwise
through 360.
a. Bearing
b. Course
c. Altitude
d. Distance
16. Tides are the periodic motion of the waters of the sea due to changes in the attractive force(s) of the _____.
a. Moon and Sun upon the rotating earth
b. Moon upon the rotating earth
c. Sun upon the rotating earth
d. Planets
17. A great circle through the geographical poles of the earth.
a. Equator
b. Longitude
c. Latitude
d. Meridian
18. The terrestrial great circle whose plane is perpendicular to the polar axis. It is midway between the poles.
a. Equator
b. Longitude
c. Latitude
d. Meridian
19. The meridian used as the origin for measurement of longitude.
a. Prime meridian
b. Latitude
c. Longitude
d. Meridian
20. A nautical mile is equal to _________meters
a. 1852 meters
b. 1600 meters
c. 6080 meters
d. 1500 meters
21. A circle on the surface of the earth, parallel to the plane of the equator. It connects all points of equal latitude.
a. Difference of Latitude
b. Departure
c. Parallel of latitude
d. Latitude
iTEST for Dohle Page 2 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
22. _____________ difference between the compass heading and the magnetic heading, due to ships construction and ship location.
a. Deviation
b. Application
c. Correction
d. Intention
23. What does RADAR mean?
a. Radio Detection And Ranging
b. Radio Distance Apparatus
c. Remote Detecting and Range
d. None of the above
24. The point on the celestial sphere vertically overhead of an observer _____.
a. Zenith
b. Nadir
c. North Pole
d. North Point
25. The point on the opposite side of the sphere vertically below the observer.
a. Zenith
b. Nadir
c. South Pole
d. South Point
26. Which is NOT a distress signal under the Rules?
a. International Code Signal "AA"
b. Orange-colored smoke
c. Red flares
d. The repeated raising and lowering of outstretched arms
27. A light signal of three flashes means _________.
a. "My engines are full speed astern"
b. "I am in doubt as to your actions"
c. "I am operating astern propulsion"
d. "I desire to overtake you"
28. A power driven vessel "not under command" at night shall show her sidelights when ______.
a. making no headway
b. not at anchor
c. making headway
d. moored to a buoy
29. A power-driven vessel underway in fog making NO way must sound what signal?
a. one long blast
b. one prolonged blast
c. one prolonged and two short blasts
d. two prolonged blasts
30. How long is the duration of a PROLONGED BLAST?
a. 4 to 6 seconds duration
b. 2 to 4 seconds duration
c. 6 to 8 seconds duration
d. 8 to 10 seconds duration
31. A self propelled dredger not engaged in dredging but proceeding to a dredging position shall exhibit __________.
a. not required to show any light but all round white light
b. lights of a dredger
c. an all-round white light
d. lights of a power driven vessel
32. A vessel 75 meters in length and restricted in her ability to maneuver is carrying out her work at anchor. What signal should be sounded in restricted
visibility?
a. 4 short blasts at intervals of not more than 2 minutes
b. 5 seconds ringing of a bell and 5 seconds sounding of a gong at intervals of not more than 1 minute
c. 1 prolonged blast followed by 2 short blasts at intervals of not more than 2 minutes
iTEST for Dohle Page 3 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
d. 5 seconds ringing of a bell at intervals of not more than 1 minute
33. A vessel aground must display by day __________ in a vertical line.
a. three black balls
b. two black balls
c. two black balls and a black diamond shape in between
d. two black diamond shapes and a black ball in between
34. A vessel aground must display by night __________ in a vertical line, in addition to the lights required for a vessel at anchor.
a. two white lights
b. three white lights
c. three red lights
d. two red lights
35. A vessel shall be deemed to be ____________ when coming up with another vessel from a direction more than 22.5 degrees abaft her beam and at
night she would be able to see only the stern light of that vessel but neither of her sidelights.
a. overtaking
b. crossing
c. passing
d. meeting
36. A vessel at anchor shall display ________ between sunrise and sunset on the forward part of the vessel where it can be best seen.
a. 1 black ball
b. 2 black balls
c. 1 red ball
d. 2 orange and white balls
37. A vessel is "in sight" of another vessel when ________.
a. she can be seen well enough to determine her heading
b. she can be observed visually or by radar
c. she can be observed visually from the other vessel
d. her fog signal can be heard
38. A vessel is being propelled both by sail and by engines. Under the Rules, the vessel is _______.
a. considered a power-driven vessel
b. considered a "special circumstance" vessel
c. could not cover under any category
d. considered as a sailing vessel
39. A vessel is considered "engaged in fishing" according to the Rules of the Road, when ________.
a. showing lights and shapes for a vessel restricted in her ability to maneuver
b. using trawling lines
c. when a vessel is power driven
d. using fishing apparatus that restricts her maneuverability
40. A vessel must proceed at a safe speed _______.
a. in restricted visibility
b. at all times
c. in congested waters
d. during darkness
41. A vessel showing the International Code Flag "A" is engaged in ________.
a. mine clearing operations
b. dredging
c. fishing
d. diving operations
42. A vessel which is "restricted in her ability to maneuver" is one which _______.
a. has lost steering and is unable to maneuver
b. through some exceptional circumstances is unable to maneuver as required by the rules
c. due to adverse weather conditions is unable to maneuver as required by the rules
d. from the nature of her work is unable to maneuver as required by the rules
43. A vessel which is unable to maneuver due to some exceptional circumstances, shall exhibit __________.
a. when making way at night, a masthead light, sidelights, and a sternlight
b. when making way at night, 2 all-round red lights, sidelights, and a sternlight
iTEST for Dohle Page 4 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
c. during the day, 3 balls in a vertical line
d. during the day, 3 shapes, the highest and lowest being balls and the middle being a diamond
44. If you are approaching a bend and a whistle signal of one prolonged blast from around the bend, you should answer with a signal of ________.
a. 1 short, 1 prolonged, and 1 short blast
b. one prolonged blast
c. a long blast
d. a short blast
45. If you are the stand-on vessel in a crossing situation, you may take action to avoid collision by your maneuver alone. When should this action be
taken?
a. at any time you feel it is appropriate
b. when it becomes apparent to you that the give-way vessel is not taking appropriate action
c. only when you have reached extremis
d. when you determine that your present course will cross ahead of the other vessel
46. The Regulations for Preventing Collision At Sea allows under Rule 2 __________.
a. crossing the bow of a stand on vessel
b. a vessel to sail without operational radar
c. a vessel to anchor in a roadstead during emergency
d. a departure from the rules to avoid immediate danger
47. The rules concerning lights shall be complied within all weathers from sunset to sunrise. The lights _______.
a. need not be displayed by unmanned vessels
b. need not be displayed when no other vessels are in the area
c. shall be set at low power when used during daylight hours
d. shall be displayed in restricted visibility during daylight hours
48. The word "vessel" in the Rules includes __________.
a. sailing ships
b. non-displacement craft
c. seaplanes
d. all of these
49. Two vessel meeting in a "head on" situation are directed by the Rules to ______.
a. alter course to port and pass starboard to starboard
b. alter course to starboard and pass port to port
c. decide on which side the passage will occur by matching whistle signals
d. slow to bare steerageway
50. What must a vessel display during the day if she is constrained by her draft?
a. a cylinder
b. a black cone, apex downward
c. a black cone, apex upward
d. two black balls in a vertical line
51. When shall the stand-on vessel change course and speed?
a. After the give-way vessel sounds 1 blast in a crossing situation
b. when two vessels become less than half a mile apart
c. The stand-on vessel may change course and speed at any time as it has the right-of-way
d. when the action of the give-way vessel alone cannot prevent collision
52. When two vessels are in an overtaking situation, which light does the overtaking vessel see?
a. stern light only
b. stern light and a sidelight
c. stern light and the after mast light
d. stern light, sidelight and the after mast light
53. ______________ is the state of the earths atmosphere with respect to temperature, humidity, precipitation, visibility,cloudiness, and other factors.
a. Weather
b. Sailing
c. Celestial
d. Azimuth
54. ______________ refers to the average long-term meteorological conditions of a place or region. All weather may be traced to the effect of the sun on
the earth.
iTEST for Dohle Page 5 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
a. Weather
b. Climate
c. Sea Condition
d. Tide and Current
55. The rotation of the earth exerts an apparent force which diverts the air from a direct path between high and low pressure areas.
a. Coriolis force
b. Celestial force
c. Wind force
d. Weather Change
56. It is relatively thin shell of air, water vapor, and suspended particulates surrounding the earth. Air is a mixture gases and, like any gas, is elastic and
highly compressible.
a. Weather
b. Climate
c. Atmosphere
d. Pressure
57. A standard sea level pressure is __________.
a. 1013.25 millibars of mercury
b. 1015.25 millibars of mercury
c. 1018.25 millibars of mercury
d. 1020.25 millibars of mercury
58. It is a visible aggregate of tiny water droplets and/or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere and can exist in a variety of shapes and sizes.
a. Cloud
b. Smoke
c. Rain
d. Fog
59. It consists of fine dust or salt particles in the air, too small to be individually apparent, but in sufficient number to reduce horizontal visibility and cast
a bluish or yellowish veil over the landscape, subduing its colors and making objects appear indistinct.
a. Advection fog
b. Radiation fog
c. Haze
d. Mist
60. It is synonymous with drizzle in the United States but is often considered as intermediate between haze and fog in its properties. If it is heavy, it can
reduce visibility to a mile or less.
a. Haze
b. Mist
c. Snow
d. rain
61. The compass deviation changes as the vessel changes.
a. geographical position
b. speed
c. heading
d. longitude
62. When reporting wind direction, you should give the direction in __________.
a. true degrees
b. magnetic compass degrees
c. relative degrees
d. isobaric degrees
63. The annual change in variation for an area can be found in __________.
a. the handbook for Magnetic Compass Adjustment, Pub 226
b. the center of the compass rose on a chart of the area
c. the compass deviation table
d. Variation does not change.
64. Inferior conjunction is possible for __________.
a. Mercury
b. Saturn
iTEST for Dohle Page 6 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Deck - F1 Navigation
Operational Level
c. Mars
d. Jupiter
65. The chart indicates the variation was 3Deg45MinW in 1988, and the annual change is decreasing 6Min. If you use the chart in 1991 how much
variation should you apply?
a. 03Deg 27MinW
b. 03Deg 27MinE
c. 04Deg 03MinW
d. 04Deg 03MinE
66. The angle measured from the observer's meridian, clockwise or counterclockwise up to 180Deg, to the vertical circle of the body is the __________.
a. local hour angle
b. azimuth angle
c. meridian angle
d. observer's longitude
67. Horizontal movement of water is called:
a. variation
b. deviation
c. current
d. leeway
68. To find a magnetic compass course from a true course you must apply __________.
a. deviation
b. variation
c. deviation and variation
d. compass error
69. A vessel heading SSE is on a course of __________.
a. 112.5Deg
b. 135.0Deg
c. 157.5Deg
d. 180.0Deg
iTEST for Dohle Page 7 of 7
02 Nov 2017 1903
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Maritime English, Pilot On The BridgeDocument5 pagesMaritime English, Pilot On The BridgeMariappan Na0% (1)
- Seagull - Products 16 59 14 115952Document11 pagesSeagull - Products 16 59 14 115952Vardias0% (1)
- NAVIGATIONDocument6 pagesNAVIGATIONKilo Marine100% (1)
- 3rd OfficerDocument42 pages3rd OfficerRost Hariton100% (4)
- Maintain Seaworthiness of The Ship9okeDocument2 pagesMaintain Seaworthiness of The Ship9okeDinda Oktaviana100% (1)
- Operate Life-Saving AppliancesDocument1 pageOperate Life-Saving AppliancesDinda OktavianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solas-Lsa RegsDocument21 pagesSolas-Lsa RegsJai Shankar JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Stabillity 1 2009Document6 pagesTest Stabillity 1 2009Yuriy Kakaranze0% (1)
- Bridge WatchesDocument7 pagesBridge WatchesNico Tanchuan100% (3)
- ECDISDocument27 pagesECDISnjirtak92100% (8)
- CES Test Deck Department Oil TankerDocument169 pagesCES Test Deck Department Oil TankerChantal Athena InocencePas encore d'évaluation
- B. Longitude: Deck - F1 NavigationDocument13 pagesB. Longitude: Deck - F1 NavigationBoboc Vlad0% (1)
- Chapter 7Document29 pagesChapter 7Vinay Mathad100% (1)
- 3.DETERMINE AND ALLOW FOR COMPASS ERROR (Ok)Document23 pages3.DETERMINE AND ALLOW FOR COMPASS ERROR (Ok)agum sulistyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Competence 1 DeckDocument9 pagesCompetence 1 DeckEric Luther Calunnag67% (6)
- GBLT Interview of 30Document6 pagesGBLT Interview of 30Christina PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Itest Dhoole 2Document12 pagesItest Dhoole 2Boboc VladPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 ColregDocument43 pages01 ColregSalam Alecu100% (1)
- GMDSSDocument4 pagesGMDSSMithun Gopinath100% (1)
- AB Question BookletDocument12 pagesAB Question BookletMonalisa ChatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Curs Actualizare Brevet Ofiter Punte Modulul 1Document27 pagesCurs Actualizare Brevet Ofiter Punte Modulul 1Alexandru Ioan RazvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Colregs Self Evaluation Instrument Part 1Document56 pagesColregs Self Evaluation Instrument Part 1Robert M. Maluya100% (3)
- 7 Pravila Za Izbjegavanje Sudara FormattedDocument13 pages7 Pravila Za Izbjegavanje Sudara Formattedfewewf100% (1)
- 3rd Officer 2013Document2 pages3rd Officer 2013api-242002578100% (1)
- Project D3 - Bridge Team, Navigation, Passage Planning, Brem PavloDocument19 pagesProject D3 - Bridge Team, Navigation, Passage Planning, Brem PavloПавел Брем100% (1)
- Kisi-Kisi Uas Sem 3 Nautika 2020Document21 pagesKisi-Kisi Uas Sem 3 Nautika 2020Dewa NataPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of ECDIS To Maintain The Safety of NavigationDocument6 pagesUse of ECDIS To Maintain The Safety of NavigationKevin Krisdianto100% (2)
- Use The IMO SMCPDocument5 pagesUse The IMO SMCPjhon100% (1)
- CLOP Explanation and MethodsDocument27 pagesCLOP Explanation and MethodsKarthick100% (1)
- MGN152Document2 pagesMGN152Polaris BridgemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Escape RouteDocument5 pagesEngine Escape RoutePranshu Singh Birthal100% (2)
- Third Officer Handover 12 July 2023Document10 pagesThird Officer Handover 12 July 2023Sahil Biswas100% (1)
- Lesson 3: Perform Manual Radar PlottingDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Perform Manual Radar PlottingDennis DoronilaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Respond To A Distress Signal at Sea.060717Document5 pages6 Respond To A Distress Signal at Sea.060717CINTIAPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.maintain and Safe Navigation PDFDocument12 pages10.maintain and Safe Navigation PDFAl Ikhwan100% (1)
- Navigation 224 DepartmentalsDocument7 pagesNavigation 224 DepartmentalsJohn Ronnel Bulawan100% (1)
- Student Guide For ECT PDFDocument18 pagesStudent Guide For ECT PDFЕвгений СеменовPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions Oral Brevet OowDocument51 pagesQuestions Oral Brevet OowvincnetPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Autopilot For Marine VesselsDocument6 pagesAdaptive Autopilot For Marine VesselsGAMMA FACULTYPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix B Master Pilot Exchange of Essential Information On Boarding Mar 2014 PDFDocument1 pageAppendix B Master Pilot Exchange of Essential Information On Boarding Mar 2014 PDFCapt. Sikandar MhaisalePas encore d'évaluation
- Wheel Over PointDocument5 pagesWheel Over PointKim HerbillaPas encore d'évaluation
- 0perational Use of Ecdis Question SetDocument17 pages0perational Use of Ecdis Question SetAbu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al Masum100% (2)
- Ecdis NotesDocument112 pagesEcdis Notesmhegden100% (2)
- Question & Answer For PSSR - 021739Document5 pagesQuestion & Answer For PSSR - 0217398173Shailesh YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Deck CadetDocument24 pagesDeck CadetAbhishekh100% (3)
- PDF Ces 41 and 5 Seagull Test DLDocument511 pagesPDF Ces 41 and 5 Seagull Test DLshubham purohitPas encore d'évaluation
- KKN - Blind PilotageDocument6 pagesKKN - Blind Pilotagetokbom67% (3)
- MARPOL Annex 1 (O) 1000-1020Document22 pagesMARPOL Annex 1 (O) 1000-1020rajeevkokane9211Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Communicative Features SMCPDocument8 pagesBasic Communicative Features SMCPSari NPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge of Blind Pilotage TechniquesDocument5 pagesKnowledge of Blind Pilotage TechniquesBerbaño, Jan Joshua100% (1)
- Test Item Bank Management - Ay - 1091-1091Document1 pageTest Item Bank Management - Ay - 1091-1091NoNo67% (3)
- OOW Post HND Information Pack 2013-2014Document10 pagesOOW Post HND Information Pack 2013-2014Tom Alex100% (2)
- How Do You Prevent Unauthorized Person From Coming On Board?Document4 pagesHow Do You Prevent Unauthorized Person From Coming On Board?Febri SusantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbal Questions AssessmentDocument7 pagesVerbal Questions AssessmentPaiusi Emanuel-geluPas encore d'évaluation
- Cargo Handling ConversationDocument7 pagesCargo Handling ConversationSari NPas encore d'évaluation
- ROR (Questions and Answers - 2Document19 pagesROR (Questions and Answers - 2Ankit Vyas100% (1)
- Wallem Interview Questions For Deck CadetsDocument3 pagesWallem Interview Questions For Deck CadetsNavaneeth K P BalakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- CE TestDocument8 pagesCE TestBrooke ClinePas encore d'évaluation
- 2MFG - MMD Ques Set Till July 2018 PDFDocument327 pages2MFG - MMD Ques Set Till July 2018 PDFindumarnicaraguaPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Standing Order GuidelinesDocument11 pagesMaster Standing Order GuidelinesImroz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- DW 1 Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesDW 1 Midterm Reviewerfreescribd021100% (1)
- Coal Sampling and Analysis Standards - ccc235 PDFDocument123 pagesCoal Sampling and Analysis Standards - ccc235 PDFAparkenthonPas encore d'évaluation
- MA Thesis Belanina FINAL Report On IndonesiaDocument113 pagesMA Thesis Belanina FINAL Report On IndonesiaAsebaho BadrPas encore d'évaluation
- Carriage of Solid Bulk Cargoes PDFDocument34 pagesCarriage of Solid Bulk Cargoes PDFComanita Ion BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
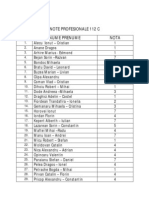
- Note Prof 113C AGTSDocument3 pagesNote Prof 113C AGTSComanita Ion BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Prof 112C AGTSDocument2 pagesNote Prof 112C AGTSComanita Ion BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
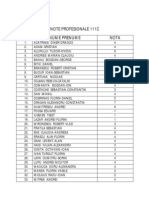
- Note Prof 111C AGTSDocument2 pagesNote Prof 111C AGTSComanita Ion BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Monitoring Water Quality Using Satellite Image ProcessingDocument49 pagesMonitoring Water Quality Using Satellite Image ProcessingτPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach For Poly-Trauma PatientDocument63 pagesApproach For Poly-Trauma PatientvadimmadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Derate Takeoff by CFMDocument17 pagesDerate Takeoff by CFMJeffrey Ford100% (1)
- Climate AnalysisDocument23 pagesClimate AnalysisDIVYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Preparedness For Severe WeatherDocument2 pagesEmergency Preparedness For Severe WeatherRandy PedrozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capiz 2nd June 16, 2017-May-5Document36 pagesCapiz 2nd June 16, 2017-May-5ilvin jr palermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Steps To Determine Wind Loads On MWFRS Rooftop Equipment and Other Structures (Solid Freestanding)Document8 pagesSteps To Determine Wind Loads On MWFRS Rooftop Equipment and Other Structures (Solid Freestanding)Jephte Soriba DequiniaPas encore d'évaluation
- STS Notes On Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesSTS Notes On Climate Changetabeb chanPas encore d'évaluation
- Schedule of Column Column No C1 C4 C5 C2 C3 C6 C7: Typical Column Footing (Sec.X:X)Document1 pageSchedule of Column Column No C1 C4 C5 C2 C3 C6 C7: Typical Column Footing (Sec.X:X)Dhairya ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Hurricane-2006 12 46-53Document8 pagesHurricane-2006 12 46-53Ton PhichitPas encore d'évaluation
- Geochronology of Turkana Depression N-Kenya & S-Ethiopia Brown & McDougallDocument11 pagesGeochronology of Turkana Depression N-Kenya & S-Ethiopia Brown & McDougallShirley CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- IDCJAC0009 023002 1800 NoteDocument3 pagesIDCJAC0009 023002 1800 NoteCraig SchillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4: Prepared By: Faculty, College of EducationDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4: Prepared By: Faculty, College of EducationChristy YpulongPas encore d'évaluation
- Focus3 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit5 GroupADocument1 pageFocus3 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit5 GroupARoma MykhalchukPas encore d'évaluation
- NextGen WeatherDocument2 pagesNextGen WeatherAli AlshaqahPas encore d'évaluation
- Whaether DataDocument2 pagesWhaether DataSaji NilanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 VolcanoesDocument19 pagesChapter 9 VolcanoesaaahhhPas encore d'évaluation
- VKM Lecture-Smog Part ADocument23 pagesVKM Lecture-Smog Part AvinodkumarmishraPas encore d'évaluation
- MOCH - ADITYA SAPUTRA - Sipil21Document8 pagesMOCH - ADITYA SAPUTRA - Sipil21Try KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatics 2Document25 pagesElectrostatics 2Kyra BudhuPas encore d'évaluation
- What Causes Convection Currents?Document2 pagesWhat Causes Convection Currents?Mary Rose DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Value Stream Map PDFDocument1 pageValue Stream Map PDFXavi JuradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot Weather ConcretingDocument3 pagesHot Weather ConcretingOzanYükselPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Load Reaction Force Due To Wind Action From Stack Acting On The Fan DeckDocument3 pagesWind Load Reaction Force Due To Wind Action From Stack Acting On The Fan Deckikanyu79Pas encore d'évaluation
- 50 Questions About The AtmosphereDocument9 pages50 Questions About The AtmosphereHilma KhoirunnissaPas encore d'évaluation
- G12 Makabansa (Stem) 2 Semester Q2: Written and Performance ActivityDocument13 pagesG12 Makabansa (Stem) 2 Semester Q2: Written and Performance ActivityFritzie Corpuz0% (1)
- Diagnostic 7th SCIENCEDocument6 pagesDiagnostic 7th SCIENCEKarla MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe610sa ReemplazoDocument8 pagesPe610sa ReemplazoDavid Enrique Rivero CahuichPas encore d'évaluation
- TTDB 609015d172717d172719der 656533FT2Document1 pageTTDB 609015d172717d172719der 656533FT2Anonymous OM5uU6Pas encore d'évaluation