Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Design Terms
Transféré par
Niyitegeka SimonCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Design Terms
Transféré par
Niyitegeka SimonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
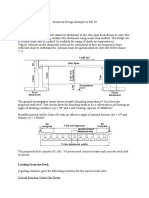
INTRODUCTIVE DEFINITIONS
1. Structure: a structure is a body, composed of several structural elements so assembled that it can set
up resistance against deformation caused by the applied external forces. The various structural
elements that may be present in a structure are: tension members, compression members, flexural
members, and foundation elements.
2. Structural Engineering: it is that branch of Civil Engineering that deals with both the Structural
Analysis as well as Structural Design.
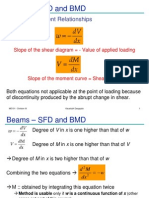
3. Structural analysis: this branch deals with the determination of internal stresses in these members as
well as the determination of reaction components, when the structure is subjected to external forces.
4. Structural design: this part deals with the selection of proper material, proper sizes, proportion and
shape of each member and its connecting details. The selection is such that it is economical and safe. It
satisfies all the stress requirements imposed by the most severe combination of loads to which the
structure is required to transmit or resist including its self-weight.
5. The design of a structure has two aspects: functional aspect and strength aspect. In the first aspect,
called functional design, a structure a structure is so proportioned and constructed that it serves the
needs efficiently for which it is constructed. In the second aspect, called structural design, the structure
should be strong enough to resist external forces to which it is subjected during its entire period of
service. The structural design in a limited sense also deals with the design of various parts or members
of a structure. The structural design is governed with the standard specifications. The hand-books are
used as working tools in the structural design.
6. Design of Steel Structures: it is a structural design, when the structural steel is used as a material for
the structure.
7. Design of Timber Structures: it is a structural design, when the timber is used as a material for the
structure.
Requirements governing any structural design: these are conditions that must satisfy any designed
structure. The structure must:
Have adequate strength
Have adequate stability and rigidity
Be durable
Fit the functional requirements
Etc.
The aim of the structural designer is to produce a safe and economical structure to meet certain
functional and esthetic requirements. The general design procedure consists of the following steps:
Selection of type of structure,
Layout of the structure,
Determination of forces on the structure in elements (or components) of the structure and,
Checking the performance of the structure under service condition
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Technical Manual Tractors 6820, 6920 and 6920S RepairDocument21 pagesTechnical Manual Tractors 6820, 6920 and 6920S RepairQuer Quer0% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Instruction Manual CMO 24-26-28/TCMO 28 MK 2: Reciprocating CompressorDocument185 pagesInstruction Manual CMO 24-26-28/TCMO 28 MK 2: Reciprocating CompressorGiovanni Colonna67% (3)
- Push Valve ExperienceDocument13 pagesPush Valve ExperienceIan Mann100% (1)
- Why Two Factors 1.5 in ConcreteDocument1 pageWhy Two Factors 1.5 in ConcreteNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Merits of Structural SteelDocument2 pagesMerits of Structural SteelNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Abutment Design Example To BD 30Document32 pagesAbutment Design Example To BD 30Elton MaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Merits of Structural SteelDocument2 pagesMerits of Structural SteelNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Merits of Structural SteelDocument2 pagesMerits of Structural SteelNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Ii: Strain Energy Strain EnergyDocument7 pagesUnit Ii: Strain Energy Strain EnergyNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- StairsDocument21 pagesStairstomnubiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Strain EnergyDocument10 pages2 Strain EnergyNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Archicad90 Mario BottaDocument44 pagesArchicad90 Mario BottajoesrbPas encore d'évaluation
- DimensionDocument1 pageDimensionNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit V: Columns and StrutsDocument15 pagesUnit V: Columns and StrutsNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Work No 1 PDFDocument1 pageWork No 1 PDFNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit V: Columns and StrutsDocument15 pagesUnit V: Columns and StrutsNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Steel Fibers and GFRP Sheet On PDFDocument8 pagesEffect of Steel Fibers and GFRP Sheet On PDFNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Sachpazis - Pad Footing Example PDFDocument8 pagesSachpazis - Pad Footing Example PDFMohan ManickamPas encore d'évaluation
- Design-Build-Maintain Approach - Feeder Road PDFDocument1 pageDesign-Build-Maintain Approach - Feeder Road PDFNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual)Document72 pagesCE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual)Niyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- ME101 Lecture11 KDDocument21 pagesME101 Lecture11 KDmoondonoo7Pas encore d'évaluation
- CEE 3100 Method of Joints: ProblemDocument2 pagesCEE 3100 Method of Joints: ProblemNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Drawing PDFDocument21 pagesGuide To Drawing PDFAmigo IncomodoPas encore d'évaluation
- BeamDesign PDFDocument52 pagesBeamDesign PDFPcEngPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical ExamplesDocument23 pagesNumerical ExamplesBharat BhushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Strip Method For Thin Cylindrical ShellsDocument118 pagesAnalytical Strip Method For Thin Cylindrical ShellsNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Beam Design To Bs8110Document3 pagesBeam Design To Bs8110Niyitegeka Simon100% (1)
- Schedule of The Training For CST: Day 1 Duration Key Points ResponsibleDocument2 pagesSchedule of The Training For CST: Day 1 Duration Key Points ResponsibleNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Eurocode 8 Paragraphs For Direct Use in DesignDocument1 pageOverview of Eurocode 8 Paragraphs For Direct Use in DesignNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Analysis and Design of Steel Roof Trusses To Eurocode 3 PDFDocument15 pagesPractical Analysis and Design of Steel Roof Trusses To Eurocode 3 PDFNiyitegeka Simon89% (9)
- CEE 3100 Method of Joints: ProblemDocument2 pagesCEE 3100 Method of Joints: ProblemNiyitegeka SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- HD Manual - COP For Structure Use of Concrete 2004 Rev - 2.3Document346 pagesHD Manual - COP For Structure Use of Concrete 2004 Rev - 2.3yin169Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rolling Element Bearing Failure AnalysisDocument4 pagesRolling Element Bearing Failure AnalysisYanuar KrisnahadiPas encore d'évaluation
- VegetaterDocument5 pagesVegetaterLogeshMechPas encore d'évaluation
- Avtp 03 180Document8 pagesAvtp 03 180lupuPas encore d'évaluation
- CRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part27Document4 pagesCRSI Manual To Design RC Diaphragms - Part27Adam Michael GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document18 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Ramiro Pedro Tarazona Hinostroza100% (1)
- Columns - Homework Solutions 2 PDFDocument6 pagesColumns - Homework Solutions 2 PDFChristopher GeerePas encore d'évaluation
- Part.a.classification of Heat ExchangersDocument11 pagesPart.a.classification of Heat ExchangersAhmed GadPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 - Papanikolaou E. - Markatos N. - Int J Hydrogen EnergyDocument9 pages2011 - Papanikolaou E. - Markatos N. - Int J Hydrogen EnergyNMarkatosPas encore d'évaluation
- VPS 504Document12 pagesVPS 504José Ginés Abellan GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Underground Construction TechnologyDocument74 pagesUnderground Construction TechnologyChin Thau WuiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 Annexure-1 Calibration CylinderDocument2 pages2023 Annexure-1 Calibration CylinderShiv Shankar YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Obd VNL VolvoDocument23 pagesObd VNL Volvosalvatore702100% (2)
- Waukesha Gas EngineDocument2 pagesWaukesha Gas Enginepolaris44Pas encore d'évaluation
- P & ID Review Check List: Chemical Engineering SiteDocument7 pagesP & ID Review Check List: Chemical Engineering SiteMayur ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) : (Applicable Code/Standard: ISO 15614-2 Edition 2005)Document2 pagesWelding Procedure Specification (WPS) : (Applicable Code/Standard: ISO 15614-2 Edition 2005)saioman100% (7)
- Practice - Mechanical Waves BasicsDocument6 pagesPractice - Mechanical Waves Basicsfrancis solivenPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor 3612Document238 pagesMotor 3612royert80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uses and Applications of Cast Aluminium AlloysDocument6 pagesUses and Applications of Cast Aluminium AlloysrahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Development of Pneumatic Cotton Picker: Durgesh Gupta, Jayesh Teli, Paras Badhe, Suraj BanhattiDocument3 pagesDesign and Development of Pneumatic Cotton Picker: Durgesh Gupta, Jayesh Teli, Paras Badhe, Suraj Banhattidurgesh3guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Packing ListDocument28 pagesPacking ListsryPas encore d'évaluation
- Lifting LugDocument39 pagesLifting LugSasikumar JothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Selecting Centrifugal Pumps Data KSB 28Document1 pageSelecting Centrifugal Pumps Data KSB 28avinashuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Main EnginesDocument79 pagesMain EnginesRajesh Kumar100% (1)
- Collet ChuckDocument4 pagesCollet ChuckMoco DocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipes b16.25 PDFDocument11 pagesPipes b16.25 PDFAsep DarojatPas encore d'évaluation
- Owner ManualDocument21 pagesOwner ManualMárcio TakitaPas encore d'évaluation