Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Well Integrity PDF
Transféré par
Adolfo AnguloDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Well Integrity PDF
Transféré par
Adolfo AnguloDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
WIP
Knowledge – Basics 1
Well Integrity
Definitions
Michael Prohaska, July 2017 WIP Knowledge
Well integrity is defined by the common applied standards NORSK D-0101 as “application of
technical, operational and organizational solutions to reduce risk of uncontrolled release of
formation fluids throughout the life cycle of a well“. In general, well integrity engineers must
assure that a well has lowest possible down-times (and losses of production) due to well
integrity related work-over. During abandonment well integrity engineers also assure that
regulatory well flow restrictions are properly in place.
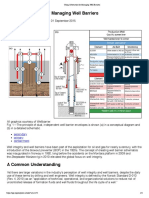
Well integrity is critical in all stages during the life of a well, from well construction,
completing, producing to finally abandoning of well installations (see Figure2). The terms
‘well barrier failure’ and ‘well integrity failure’ are differentiated3. ‘Well integrity failure’ by
definition is used for cases where all well barriers fail to establish leakages into the
surrounding environment (e.g. groundwater, soil, atmosphere). As wells have typically
several barriers, a well integrity failure is usually rare and redundant barriers are available to
take over leakage loads. ‘Well barrier failure’ is used to refer to the failure of individual or
multiple well barriers that has not resulted in a detectable leak into the surrounding
environment. However, the failure of one individual barrier is a ‘well integrity issue’ as it
weakens the whole installation and thus contributes to the ‘loss of well integrity’.
References
1. NORSOK D-010, Well integrity in drilling and well operations, Rev. 3, August 2004
2. Figure adopted from halliburtonblog.com
3. King, G. E and King, D. E: „Environmental Risk Arising From Well-Construction Failure,“ SPE 166142,
SPE Journal Paper - 2013
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 03 - WellSharp WC Methods and Subsea - Day 2 Pre - CourseDocument5 pages03 - WellSharp WC Methods and Subsea - Day 2 Pre - CourseAdolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chios Reiki Attunement ManualDocument12 pagesChios Reiki Attunement Manualkeithmac100% (1)
- Awodele - Observations On W.D. Gann, Vol. 1 PeriodicityDocument82 pagesAwodele - Observations On W.D. Gann, Vol. 1 Periodicityforex50087% (23)
- Planning in Oil and Gas FieldsDocument44 pagesPlanning in Oil and Gas FieldsRachan EngchanilPas encore d'évaluation
- SrgewDocument37 pagesSrgewHugo DuchovnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Minor II Mid Review - FinalDocument10 pagesMinor II Mid Review - FinalArsh Attri100% (1)
- Virginia Henderson TheoryDocument20 pagesVirginia Henderson Theoryezvip100% (2)
- CIMTDocument21 pagesCIMTankit0% (1)
- Advanced Water Injection for Low Permeability Reservoirs: Theory and PracticeD'EverandAdvanced Water Injection for Low Permeability Reservoirs: Theory and PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Integrated Sand Management For Effective Hydrocarbon Flow AssuranceD'EverandIntegrated Sand Management For Effective Hydrocarbon Flow AssurancePas encore d'évaluation
- WellMaster - 05 10 2011Document16 pagesWellMaster - 05 10 2011Zayed AlkatheeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Site SelectionDocument14 pagesSite SelectionmardiradPas encore d'évaluation
- Marathon Digital OilfieldDocument24 pagesMarathon Digital Oilfieldakashmehta10Pas encore d'évaluation
- About Shale Gas and Hydraulic Fracturing Dec 2013Document27 pagesAbout Shale Gas and Hydraulic Fracturing Dec 2013Richard ObinnaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE-185428-MS Optimizing Cost and Effectiveness of Well Interventions: An Holistic ApproachDocument17 pagesSPE-185428-MS Optimizing Cost and Effectiveness of Well Interventions: An Holistic ApproachQaiser HafeezPas encore d'évaluation
- Peak OilDocument55 pagesPeak OilMahant MotheyPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Wellwork ValueDocument7 pagesInjection Wellwork Valuedriller22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Well IntegrityDocument2 pagesWell IntegrityAnubhuti Purohit BhatnagarPas encore d'évaluation
- 75 AbDocument79 pages75 AbGeorgescuMihaelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Fracture Design Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs - A Case History PDFDocument14 pagesHydraulic Fracture Design Optimization in Unconventional Reservoirs - A Case History PDFblackoil1981Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asset Team PresentationDocument23 pagesAsset Team PresentationChigozie ObiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 IPTC Conference Preview FINALDocument72 pages2008 IPTC Conference Preview FINALHing Chai ShingPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Gas Production Engineering WebsiteDocument5 pagesOil Gas Production Engineering Websitelepro brunelPas encore d'évaluation
- Peterhead CCS Project: Doc Title: Abandonment Concept For Injection WellsDocument43 pagesPeterhead CCS Project: Doc Title: Abandonment Concept For Injection WellsSusin LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Oil Exploration in The WorldDocument229 pagesCrude Oil Exploration in The WorldReinaldo Alexandre Fonseca67% (3)
- The Value of 3d Seismic in TodayDocument13 pagesThe Value of 3d Seismic in TodayMikhail LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Jubilee Field Eia Chapter 4 Pt1Document42 pagesJubilee Field Eia Chapter 4 Pt1rinshonsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Subsea Well Response Project Newsletter #1Document3 pagesSubsea Well Response Project Newsletter #1Subsea Well Response ProjectPas encore d'évaluation
- Mega-Field Developments Require Special Tatics, Risk Management PDFDocument3 pagesMega-Field Developments Require Special Tatics, Risk Management PDFGILBERTO YOSHIDAPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow AssuranceDocument7 pagesFlow AssuranceMubarik AliPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE 40036 Economic Eval of Logs For ConformanceDocument11 pagesSPE 40036 Economic Eval of Logs For ConformanceLeo Rojas Dom100% (1)
- PetroSkills - Surface Production OperationsDocument2 pagesPetroSkills - Surface Production OperationsMausam GauravPas encore d'évaluation
- 9607 BRO 0008 03 Flexible Riser Brochure SCREENDocument4 pages9607 BRO 0008 03 Flexible Riser Brochure SCREENsiswoutPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study On The Effect of Production Segmentation CompletionDocument9 pagesA Case Study On The Effect of Production Segmentation CompletionSara Kamil Abd Al-RedahPas encore d'évaluation
- 1330 Case Study Shell UK Subsea Wellhead Recovery Campaign 2017Document24 pages1330 Case Study Shell UK Subsea Wellhead Recovery Campaign 2017Hafiz RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- An Approach To Reservoir Management PDFDocument7 pagesAn Approach To Reservoir Management PDFMiguel Angel100% (1)
- Off Shore Drilling NotesDocument15 pagesOff Shore Drilling NotesAamir LokhandwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Exploration ProspectsDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Exploration ProspectsJubilee316Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Increase Recovery of Hydrocarbons Utilizing Subsea Processing TechnologyDocument14 pagesHow To Increase Recovery of Hydrocarbons Utilizing Subsea Processing TechnologySara AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Otc 20113 MSDocument15 pagesOtc 20113 MSguerraromanPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Application of The Petroleum Resources Management SystemDocument30 pagesGuidelines For Application of The Petroleum Resources Management SystemRafael MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE 135669 Best Practices For Candidate Selection, Design and Evaluation of Hydraulic Fracture TreatmentsDocument13 pagesSPE 135669 Best Practices For Candidate Selection, Design and Evaluation of Hydraulic Fracture TreatmentsJuan SuePas encore d'évaluation
- Otc 10979 MS PDFDocument8 pagesOtc 10979 MS PDFChinmaya Ranjan JenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Reservoir Characterization Studies PDFDocument3 pagesIntegrated Reservoir Characterization Studies PDFMohamedSaidShahatPas encore d'évaluation
- Gordy Shan Ore orDocument25 pagesGordy Shan Ore orAndy ColePas encore d'évaluation
- Hebron Development Plan Hda Vol 2Document551 pagesHebron Development Plan Hda Vol 2doombuggyPas encore d'évaluation
- Engi 9625 Assignment 1Document6 pagesEngi 9625 Assignment 1nuvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Gas Your DoorDocument235 pagesOil Gas Your DoorLuis EspinozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Norway-Guidelines For Oil&Gas Field Development PlanDocument14 pagesNorway-Guidelines For Oil&Gas Field Development PlanJesus BetancourtPas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document1 page2luketsghghPas encore d'évaluation
- VICTORY VICTORY 1512032 Wells-Rosie Field 2638904 843650952Document22 pagesVICTORY VICTORY 1512032 Wells-Rosie Field 2638904 843650952Agube VictoryPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE 94377 Abandonment of Seabed Deposition of Drill Cuttings During Offshore DrillingDocument4 pagesSPE 94377 Abandonment of Seabed Deposition of Drill Cuttings During Offshore Drillingmsmsoft90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water FloodingDocument94 pagesWater FloodingOlusegun OyebanjiPas encore d'évaluation
- 20160126Document47 pages20160126SATRIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Aminu - M - 2018 Final PHD ThesisDocument227 pagesAminu - M - 2018 Final PHD ThesisshkhawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Engineer Development Manager in Houston Texas Resume R Yvonne ScherzDocument2 pagesReservoir Engineer Development Manager in Houston Texas Resume R Yvonne ScherzR Yvonne Scherz100% (1)
- Wettability Approach in Rock SystemDocument59 pagesWettability Approach in Rock SystemAchmad Rafiq Alfaruqi100% (2)
- DDocument15 pagesDJuan Lopez100% (2)
- Spe 39437 MSDocument14 pagesSpe 39437 MSAndrés Bojacá MatizPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Reserve EstimationDocument21 pagesGas Reserve EstimationAtif AbassPas encore d'évaluation
- Recommend Frequency of Well Integrity MonitoringDocument1 pageRecommend Frequency of Well Integrity MonitoringalizareiforoushPas encore d'évaluation
- Ekofisk FieldDocument6 pagesEkofisk FieldfalkhaldiPas encore d'évaluation
- Iadc/Spe Asia Pacific Drilling Technology ConferenceDocument28 pagesIadc/Spe Asia Pacific Drilling Technology ConferenceadrianbfilgueiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Offshore Gas Hydrates: Origins, Development, and ProductionD'EverandOffshore Gas Hydrates: Origins, Development, and ProductionPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploiting the Digital Oilfield: 15 Requirements for Business ValueD'EverandExploiting the Digital Oilfield: 15 Requirements for Business ValueÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- DIT Audit Report: - Business Information General Audit InformationDocument20 pagesDIT Audit Report: - Business Information General Audit InformationAdolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling IntroductoryDocument2 pagesDrilling IntroductoryAdolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Classroom Application Form v2.0Document7 pagesVirtual Classroom Application Form v2.0Adolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Integrity Analysis Applied To WorkoDocument8 pagesWell Integrity Analysis Applied To WorkoAdolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Rig Inspection OutlineDocument4 pagesRig Inspection OutlineAdolfo Angulo100% (1)
- Using Schematics For Managing Well BarriersDocument4 pagesUsing Schematics For Managing Well BarriersAdolfo Angulo100% (1)
- AC-0025 Practical Assessor and Instructor Additional Primary Centre Application FormDocument5 pagesAC-0025 Practical Assessor and Instructor Additional Primary Centre Application FormAdolfo Angulo100% (1)
- SCO-01E ELearnReq Rev0Document2 pagesSCO-01E ELearnReq Rev0Adolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Ghis Manual (New)Document18 pagesGhis Manual (New)rookie100% (1)
- Flame Resistant Conveyor Belts To EN 14973 and EN 12882Document6 pagesFlame Resistant Conveyor Belts To EN 14973 and EN 12882luis martinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of Communication in SocietyDocument16 pagesImportance of Communication in SocietyPh843 King's Kids StudentCenterPas encore d'évaluation
- MulticollinearityDocument25 pagesMulticollinearityDushyant MudgalPas encore d'évaluation
- SFIDocument64 pagesSFIashwin71184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elder Abuse: How The Moderns Mistreat Classical Realism: Analytical Essays: Evaluation, Synthesis, ReflectionsDocument21 pagesElder Abuse: How The Moderns Mistreat Classical Realism: Analytical Essays: Evaluation, Synthesis, ReflectionsElvira ToktasinovaPas encore d'évaluation
- SICK DT35 Setup InstructionsDocument6 pagesSICK DT35 Setup InstructionsTalicni TomPas encore d'évaluation
- TCR PDF Spring 2013 Vol 25 No 1Document224 pagesTCR PDF Spring 2013 Vol 25 No 1Teresinha Pereira100% (1)
- Resume of Tahmina Hossain BitheeDocument3 pagesResume of Tahmina Hossain BitheeJahid HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- EpdmDocument2 pagesEpdmhappale2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- MBDRDocument4 pagesMBDRenjoydasilencePas encore d'évaluation
- Sap WM Organization StructureDocument7 pagesSap WM Organization StructureNarendra KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of USCS and AASHTODocument2 pagesComparison of USCS and AASHTOkitefly100% (2)
- UK Environment Agency RM-QG6 - Calibrating Particulate-Monitoring Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMs), Especially For Low Concentrations of Particulate MatterDocument7 pagesUK Environment Agency RM-QG6 - Calibrating Particulate-Monitoring Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMs), Especially For Low Concentrations of Particulate MatterTomy SetiyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Template CVDocument2 pagesTemplate CVadera32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shopping Centres, 10?FIRE?ENGINEERING ?CASE? STUDIES? IN? FINLAND?Document52 pagesShopping Centres, 10?FIRE?ENGINEERING ?CASE? STUDIES? IN? FINLAND?Bambang Setyo UtomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Stereotypes in General-Advantages and Disadvantages: Being Typically EnglishDocument2 pagesStereotypes in General-Advantages and Disadvantages: Being Typically EnglishDiana IrimieaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7 Identifying and Analyzing ClaimsDocument11 pagesLesson 7 Identifying and Analyzing ClaimsConnieRoseRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Historian's Craft - Early Modern Europe, Darnton, Burke, Historical Anthropology and MentalitiesDocument6 pagesHistorian's Craft - Early Modern Europe, Darnton, Burke, Historical Anthropology and MentalitiesAbhinava GoswamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lessons Learned in Startup and Commissioning of Simple Cycle and Combined Cycle Combustion Turbine PlantsDocument114 pagesLessons Learned in Startup and Commissioning of Simple Cycle and Combined Cycle Combustion Turbine PlantsTerry A. Waldrop50% (4)
- Systems Design: C H A P T E RDocument39 pagesSystems Design: C H A P T E Reve2495Pas encore d'évaluation
- LittleProfessor ManualDocument48 pagesLittleProfessor ManualÜMineiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit Report Summary and ConclusionDocument13 pagesAudit Report Summary and ConclusionSunday OluwolePas encore d'évaluation
- CofisaDocument2 pagesCofisaTony Starks0% (1)
- Layout Strategies: © 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. 9 - 1Document17 pagesLayout Strategies: © 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. 9 - 1jeams vidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bihar SI Mains Syllabus-024b287317594Document3 pagesBihar SI Mains Syllabus-024b287317594Aryan KhanPas encore d'évaluation