Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Dengue
Transféré par
Jonavia Jumaylab MahumasDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Dengue
Transféré par
Jonavia Jumaylab MahumasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral disease that has rapidly spread in all regions of WHO in recent
years. Dengue virus is transmitted by female mosquitoes mainly of the species Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser
extent, Ae. albopictus. This mosquito also transmits chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika infection.
The human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes HIV infection and over time acquired
immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS is a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system
allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive.
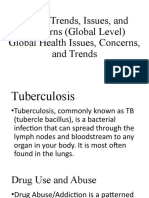
Transcript of Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Global Level)Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, commonly known as TB (tubercle bacillus), is a bacterial infection that can spread through the lymph
nodes and bloodstream to any organ in your body. It is most often found in the lungs.
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) HIV is transmitted
primarily via unprotected sexual intercourse (including anal and oral sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic
needles, and from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding.
Drug Use and Abuse
Drug Abuse/Addiction is a patterned use of a drug in which the user consumes the drug substance in amounts or with
methods which are harmful to themselves or others.
Global Health Issues, Concerns, and Trends
Non-communicable disease
A non-communicable disease, or NCD, is a medical condition or disease that can be defined as non-infectious and non-
transmissible among people. NCDs can refer to chronic diseases (heart diseases, stroke, cancers, asthma, diabetes,
kidney diseases, osteoporosis, others) which last for long periods of time and progress slowly.
UNIT 3: Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Global Level)
Malaria and other vector-borne
Malaria (mosquito-borne infectious disease) causes symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue, vomiting and
headaches. In severe cases it can cause yellow skin, seizures, coma or death.
Communicable diseases
Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases or transmissible diseases, are illnesses that result from the
infection, presence and growth of pathogenic (capable of causing disease) biologic agents in an individual human or
other animal host. Examples are: Ebola virus disease; flu, measles; tuberculosis; sexually transmitted diseases (STDs);
HIV/AIDS; among others.
Climate Change
Mental Health and Mental Disorder
Mental health is a level of psychological well-being and the absence of a mental disorder (autism, alcohol dependence,
extreme anxiety, phobias, bipolar disorder, caffeine dependence, dyslexia, depression, kleptomania, obsessive-
compulsive disorder, among others).
Immunization and Vaccines
Immunization, or vaccination is the safe and effective use of a small amount of a weakened or killed virus or bacteria or
bits of lab-made protein that imitate the virus in order to prevent infection by that same virus or bacteria. When you get
an immunization, you're injected with a weakened form of (or a fragment of) a disease. This triggers your body's
immune response, causing it to either produce antibodies to that particular ailment or induce other processes that
enhance immunity.
Prevention is better than cure.
Alcohol and Tobacco Abuse/Addiction
The excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco
Causes non-communicable and communicable diseases
ACTIVITY 17: INFOTOGRAPHY GROUP 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Document12 pagesHealth Trends, Issues, and Concerns (Trisha PaclebPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeDocument28 pagesAcquired Immunodeficiency SyndromeM Rocky PramanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapeh 9 DTDocument3 pagesMapeh 9 DTSantos JewelPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused by InfectionDocument15 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) Is A Disease of The Human Immune System Caused by InfectionMuhàmmàdIsmàilBàhtiarPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) : Classification and External ResourcesDocument33 pagesAcquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) : Classification and External Resourcesanand011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Lujain Alkhazrajy: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Document11 pagesDr. Lujain Alkhazrajy: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Saman SarKoPas encore d'évaluation
- Viral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensD'EverandViral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensPas encore d'évaluation
- بحث عن مرض الأيدز باللغة الانجليزيةDocument5 pagesبحث عن مرض الأيدز باللغة الانجليزيةdrkamal2Pas encore d'évaluation
- AIDSDocument4 pagesAIDSAna-maria DumitrascuPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) Is A Disease of TheDocument6 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV/AIDS) Is A Disease of TheDhea Fajeria FitriPas encore d'évaluation
- TP 1Document8 pagesTP 1nitesh tirkeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Immune DeficiencyDocument225 pagesAcquired Immune DeficiencybharatPas encore d'évaluation
- Aids ProjectDocument7 pagesAids Projectapi-270625016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do We Fall Ill 2Document3 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill 2Shreyashkar JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioterrorism Agents/Diseases: Student Name: Ayesha AndleebDocument15 pagesBioterrorism Agents/Diseases: Student Name: Ayesha AndleebAisha rana100% (1)
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument20 pagesBacterial InfectionsFahad RasheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicable DiseasesDocument3 pagesCommunicable DiseasesJea OrlinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2Document53 pagesLecture 2Amar Wadood KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NSC 322 LectureDocument52 pagesCOMMUNITY HEALTH NSC 322 LectureChinenye LovethPas encore d'évaluation
- AidsDocument46 pagesAidsPrakash Giri100% (2)
- Hivebolatuberculiosis DiabetesDocument18 pagesHivebolatuberculiosis DiabetesImDaniella DelBirutPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 014Document4 pagesChapter 014Princess AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical HealthDocument4 pagesPhysical HealthatzinucoPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicable Diseases: Upgrade To Access Full EssayDocument2 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Upgrade To Access Full EssayBrendan B. MastayPas encore d'évaluation
- Hiv and AidsDocument5 pagesHiv and AidsMhie RecioPas encore d'évaluation
- Health and DiseaseDocument3 pagesHealth and DiseaseMehbub LaskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Infectious Diseases: Bioed OnlineDocument14 pagesInfectious Diseases: Bioed OnlineMohamed Saidu MansarayPas encore d'évaluation
- By: Axel Jusuf (1461050177)Document9 pagesBy: Axel Jusuf (1461050177)AxelJusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Symptoms: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsDocument7 pagesSymptoms: Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsAdalbert Carl CabritoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases Caused by PathogensDocument2 pagesDiseases Caused by PathogensbrajanosmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is HIV.Document2 pagesWhat Is HIV.Chiranth ChandPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Why Do We Fall IllDocument43 pagesGrade 9 Why Do We Fall IllMehala Sri AurobindoPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Hiv and AidsDocument27 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Hiv and AidsMajkel Benche CustodioPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 38: Human Diseases Caused by VirusesDocument13 pagesChapter 38: Human Diseases Caused by Virusesharold_gravity9885Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is HivDocument3 pagesWhat Is HivFly YtPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus) : Kelompok: 1.desy Puspitasari 2.indah Sari 3.reni Hayati A. 4.roro Asih SDocument15 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus) : Kelompok: 1.desy Puspitasari 2.indah Sari 3.reni Hayati A. 4.roro Asih SRoro AshPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Health ExplainationDocument2 pagesGlobal Health ExplainationBlessy BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Common DiseasesDocument11 pagesHuman Common Diseasessadia khan SultaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah HIV Bahasa IngDocument10 pagesMakalah HIV Bahasa IngNovi FitriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio InvestigatoryDocument15 pagesBio InvestigatoryShrilata EruguralaPas encore d'évaluation
- A. PandemicsDocument21 pagesA. Pandemicsakarshverma01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Virus Host Interaction PDFDocument25 pagesVirus Host Interaction PDFVEENA DEVIPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument4 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesTamilore WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- EpidemiologyDocument4 pagesEpidemiologyObiora Ekene HilaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Chiv Cintroduction Ctypes Ctransmission CtreatmentDocument14 pagesChiv Cintroduction Ctypes Ctransmission Ctreatmentkaranarjun91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Who Influenza 21082009Document2 pagesWho Influenza 21082009SikainfluenssaPas encore d'évaluation
- Many People Aff 9Document10 pagesMany People Aff 9Joshua QuezanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do We Fall Ill - Part IiDocument12 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill - Part IiChhaya GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Infectious DiseaseDocument62 pagesInfectious DiseaseGauri GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology ResearchDocument8 pagesBiology ResearchMayi PennylPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Document7 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill Class 9Madhav Lohchab100% (1)
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired ImmunodeficiencyDocument8 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Infection / Acquired ImmunodeficiencyAurelia Cristina DumitruPas encore d'évaluation
- HealthDocument10 pagesHealthAthul ShajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 - Disease ConceptDocument56 pagesLesson 2 - Disease Conceptpc.bhcPas encore d'évaluation
- IM. ID Topic 5. Chibueze AfugbuomDocument3 pagesIM. ID Topic 5. Chibueze AfugbuomChibueze AfugbuomPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeDocument19 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeBahaa ShaabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsDocument22 pagesAcquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) IsKhilvesh AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesD'EverandThe Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteria (Unit I)Document22 pagesBacteria (Unit I)Muhammad KaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- 9700 s15 Ms 23 PDFDocument7 pages9700 s15 Ms 23 PDFRuthPas encore d'évaluation
- Sas 9-14Document8 pagesSas 9-14Bráian Tzéims άλμπαPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument2 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsWallen LagradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Transfer Teniques in PlantDocument21 pagesGene Transfer Teniques in PlantRakesh GedalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Policies Differential Counting and Morphology Lab 5074Document14 pagesLab Policies Differential Counting and Morphology Lab 5074Egil SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Cell DivisionDocument96 pagesComplete Cell DivisionAbegail Reyes100% (1)
- M6a Rna MethylationDocument14 pagesM6a Rna Methylation畏Pas encore d'évaluation
- Proteomics by SWATH MSDocument23 pagesProteomics by SWATH MSRenu GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch11 Lecture PPT ADocument50 pagesCh11 Lecture PPT ACamille Lopez50% (2)
- Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplant: Zeina Al-Mansour, MDDocument22 pagesHaploidentical Stem Cell Transplant: Zeina Al-Mansour, MDAymen OmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspergillus Fumegatus 46645Document2 pagesAspergillus Fumegatus 46645Olga BurduniucPas encore d'évaluation
- Esophages and Stomach ...........Document65 pagesEsophages and Stomach ...........Gebrie DinkayehuPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibody StructureDocument9 pagesAntibody StructureNikhil BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacte ReviewerDocument124 pagesBacte ReviewerMarie LlanesPas encore d'évaluation
- European S3-Guidelines On The Systemic Treatment of PsoriasisDocument208 pagesEuropean S3-Guidelines On The Systemic Treatment of Psoriasisghitza80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eng Brochure Comvat Duo3Document8 pagesEng Brochure Comvat Duo3Daniel Fialho FerreiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Albumin Solution, HumanDocument3 pagesAlbumin Solution, HumanMulayam Singh Yadav67% (3)
- Successful Treatment of Multiple Common Warts With Intralesional OzoneDocument6 pagesSuccessful Treatment of Multiple Common Warts With Intralesional OzoneRubensPas encore d'évaluation
- Scdal 1Document23 pagesScdal 1Cwali MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Luc Montagnier Pasteur Institute Paris France Cancer AIDS and Neurodegenerative DiseasesDocument13 pagesLuc Montagnier Pasteur Institute Paris France Cancer AIDS and Neurodegenerative DiseasesEnrico Perez BressanPas encore d'évaluation
- No.22 Ogbeukwu Road Ndoni Rivers StateDocument26 pagesNo.22 Ogbeukwu Road Ndoni Rivers StateGift NkwochaPas encore d'évaluation
- B.SC Biotech Syllabus-1Document41 pagesB.SC Biotech Syllabus-1Dr. Maruti K. R SDM Degree College UjirePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts of EpigeneticsDocument10 pagesBasic Concepts of EpigeneticsRaju MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plasma ProteinDocument102 pagesPlasma ProteinazeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatitis B VaccineDocument4 pagesHepatitis B VaccineShantal AbelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Module 3rd Year MBBSDocument8 pagesMid Module 3rd Year MBBSShahzaib Ullah ChatthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network and Machine Learning Approaches To Dengue Omics DataDocument183 pagesNetwork and Machine Learning Approaches To Dengue Omics Datamaxence tricaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch05 Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDocument95 pagesCh05 Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingbearrePas encore d'évaluation
- Aiims BiochemDocument39 pagesAiims Biochemshalialoo22Pas encore d'évaluation