Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of Speech Table
Transféré par
Christopher John0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
83 vues1 pageParts of english
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentParts of english
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
83 vues1 pageParts of Speech Table
Transféré par
Christopher JohnParts of english
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
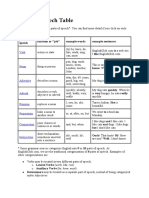
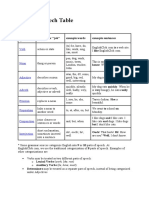
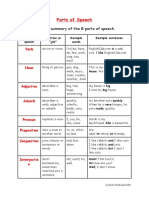
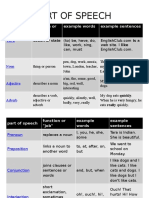
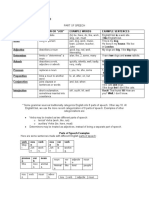
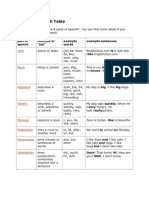
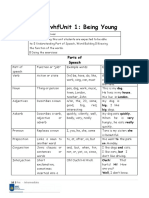
Parts of Speech Table
This is a summary of the 8 parts of speech.
Part of speech Function or “job” Example words Example sentences
Verb Action or state (to) be, have, do, like, Garfield is a cat.
work, sing, can, must I like Garfield.
Noun Thing or person pen, dog, work, music, This is my dog.
town, London, teacher, He lives in my house.
John We live in London.
Adjectives Describes a noun a/an, the, 23, some, good, My dog is big.
big, red, interesting I like big dogs.
Adverb Describes a verb, quickly, silently, well, My dog eats quickly.
adjective or adverb badly, very, really When he is very hungry,
he eats really quickly.
Pronoun Replaces a noun I, you, he, she, some Tara is my sister; she is
beautiful.
Preposition Links a noun to to, at, after, on, but We went to the park on
another word Monday.
Conjunction Joins clauses or and, but, when, for, nor, I like dogs and cats.
sentences or words or, yet, so, since, I like cars, but I don’t like
driving.
Interjection Short exclamation, Oh! Ouch! Hi! Well. Ouch! That hurts!
sometimes inserted Hi! How are you?
into a sentence Well, I don’t know.
Verbs may be treated as two different parts of speech:
Lexical Verbs (work, like, run)
o I like Vampire Diaries.
Auxiliary Verbs or Helping Verbs (be, have, must)
o I have watched it.
Auxiliary verbs are always followed by another verb. Some auxiliary verbs can
become lexical verbs if they are not used with other verbs, such as:
o I have seven pairs of shoes.
Determiners (a, the, every, this, that) modify and determine the kind of reference a noun
or noun group has.
They may be treated as a separate part of speech, instead of being categorized
under Adjectives.
o These apples are rotten.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Parts of Speech Table-WsheetDocument3 pagesParts of Speech Table-WsheetPriti DedhiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument3 pagesParts of Speech TableNurul Hildayanti ILyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Charl FranciscoDocument1 pageCharl FranciscoMaralyssa Dela Rosa BicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn the 8 Parts of Speech with Examples and DefinitionsDocument2 pagesLearn the 8 Parts of Speech with Examples and DefinitionsAinn DolhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Parts of Speech Table ExplainedDocument2 pages8 Parts of Speech Table ExplainedJovis ChiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument1 pageParts of Speech TableNur SolikhahPas encore d'évaluation
- The Parts of Speech: Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesDocument3 pagesThe Parts of Speech: Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesYaser8Pas encore d'évaluation
- GrammarDocument1 pageGrammarMaiElGebaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument1 pageParts of Speech TableSalwani Bt Mohd HaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech AssignmentDocument2 pagesParts of Speech Assignmentroyce542Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument4 pagesParts of Speech TableVisnudaran NaIRPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument1 pageParts of Speech Tableklares_0528Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument1 pageParts of SpeechJared DoylePas encore d'évaluation
- Part of Speech Functio Nor "Job" Exampl e Words Exampl e Senten CesDocument4 pagesPart of Speech Functio Nor "Job" Exampl e Words Exampl e Senten CesJabez KirubakaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of speech functions and examplesDocument1 pageParts of speech functions and examplesdayakalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of speech explained in 40 charactersDocument1 pageParts of speech explained in 40 charactersEder R. PlataPas encore d'évaluation
- Part of SpeechDocument8 pagesPart of SpeechNovita sariPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Parts of Speech ExplainedDocument2 pages9 Parts of Speech ExplainedM TPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechAmy ShahuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech Table: A/an, The SomeDocument3 pagesParts of Speech Table: A/an, The SomeMazlin MuratPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech, Phrase and ClauseDocument16 pagesParts of Speech, Phrase and ClauseImam Syafi'iPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechJani PatiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Parts of Speech TableDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Parts of Speech TableReden DumaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument4 pagesParts of Speech TableDahliya DwitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part of Speech Unit 1: Tim MKU Bahasa Inggris UnesaDocument16 pagesPart of Speech Unit 1: Tim MKU Bahasa Inggris UnesaDzaky PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Parts of SpeechDocument1 page01 Parts of SpeechLuisPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume Parts - of - Speech4Document13 pagesResume Parts - of - Speech4Mahesa Pama AdhiswaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure ModulDocument80 pagesStructure ModulHafsah NurFitriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech GuideDocument11 pagesParts of Speech GuideDaniela HolguinPas encore d'évaluation
- Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesDocument4 pagesPart of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesArif Tirtana Lie0% (1)
- Parts of Speech PDFDocument17 pagesParts of Speech PDFshubha chowdharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument4 pagesParts of Speech TableAnbuPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Parts of Speech TableDocument1 page8 Parts of Speech TableCarmen SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechNuhaPas encore d'évaluation
- S1.Parts of SpeechDocument5 pagesS1.Parts of SpeechIlias JanatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 Parts of Speech IntroDocument7 pages0 Parts of Speech IntroMSQ GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech: Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesDocument3 pagesParts of Speech: Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesMuhammad ShoaobPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Parts of SpeechChandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech Table EXERCISES tareaDocument5 pagesParts of Speech Table EXERCISES tareaMaria ValdiviezoPas encore d'évaluation
- This Is A Summary of The 9 Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesThis Is A Summary of The 9 Parts of SpeechPatsy Valderrama MoronesPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechKaung HeinPas encore d'évaluation
- GRAMMAR Fresh BeginningDocument33 pagesGRAMMAR Fresh BeginningRitesh PoojaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech Table: Examples More Than One Job QuizDocument5 pagesParts of Speech Table: Examples More Than One Job QuizlanrrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument1 pageParts of SpeechKayla SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechjaquelinePas encore d'évaluation
- Cours N°02 Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesCours N°02 Parts of SpeechHaroun SaīdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech - Grammar - EnglishClubDocument3 pagesParts of Speech - Grammar - EnglishClubLouvelia Jane BudiasPas encore d'évaluation
- GrammerDocument44 pagesGrammerancino_leoboy33% (3)
- Parts of Speech: Jenis Kata/kelas KataDocument6 pagesParts of Speech: Jenis Kata/kelas KataSri NurhidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument1 pageParts of Speech TableShahzad BhuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part of Speech UnitDocument7 pagesPart of Speech Unitrebeca23cardozoPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument3 pagesParts of Speech TableEka YulianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: English: Martes, 12 de Abril de 2016Document5 pagesSubject: English: Martes, 12 de Abril de 2016danilo villegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech Grammar EnglishClubDocument1 pageParts of Speech Grammar EnglishClubᎻPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument2 pagesParts of Speech TableErrmer XanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of speech overviewDocument5 pagesParts of speech overviewLienardPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech TableDocument2 pagesParts of Speech TablemarihutmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech: A Concise GuideDocument20 pagesParts of Speech: A Concise GuideMayla Lei PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Afcgcvvhfunit 1: Being Young: Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesAfcgcvvhfunit 1: Being Young: Parts of SpeechLusiyana AmandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Based Task For General Physics 02Document1 pagePerformance Based Task For General Physics 02Christopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity Conservation Plan AsmodDocument6 pagesElectricity Conservation Plan AsmodCarl Dhenzel ManibogPas encore d'évaluation
- TheoDocument8 pagesTheoChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 8 Empowered To Take Off FinalDocument13 pagesModule 8 Empowered To Take Off FinalRomeo Abrigo100% (1)
- Epa Water Treatment Manual Filtration 1Document80 pagesEpa Water Treatment Manual Filtration 1alkemeya100% (1)
- Mil Mil ProjDocument3 pagesMil Mil ProjChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Eapp SheetttttsDocument3 pagesEapp SheetttttsChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- In The FilmDocument1 pageIn The FilmChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Film Review: The Handmaid'S TaleDocument2 pagesFilm Review: The Handmaid'S TaleChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflect LangDocument1 pageReflect LangChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 21STDocument11 pagesAssignment 21STChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Solvation and Freezing Point Depression: Experiment 4Document10 pagesSolvation and Freezing Point Depression: Experiment 4Christopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 21STDocument11 pagesAssignment 21STChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- DepressedDocument5 pagesDepressedChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Eapp SheetttttsDocument3 pagesEapp SheetttttsChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Film Review: The Handmaid'S TaleDocument2 pagesFilm Review: The Handmaid'S TaleChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Steps To A Basic Essay PDFDocument2 pagesSteps To A Basic Essay PDFChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- The 'What' and 'Why' of Love'S Reasons: Michael SmithDocument17 pagesThe 'What' and 'Why' of Love'S Reasons: Michael SmithChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Person-Centredness:: Conceptual and Historical PerspectivesDocument13 pagesPerson-Centredness:: Conceptual and Historical PerspectivesChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- APJARBA 2015 1 002 Operational Performance of Purified Water Business in Batangas City Basis of An Enhanced Business Operation Initiatives PDFDocument9 pagesAPJARBA 2015 1 002 Operational Performance of Purified Water Business in Batangas City Basis of An Enhanced Business Operation Initiatives PDFChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Cover Letter AsmodDocument1 pageCover Letter AsmodChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- CommunicationDocument18 pagesCommunicationsandeep11661Pas encore d'évaluation
- Writing A Research PaperDocument14 pagesWriting A Research PaperSaeed Soroush MoghaddamPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Technical Papers PDFDocument32 pagesWriting Technical Papers PDFletter_ashish4444Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research Made Easy RevisedDocument60 pagesResearch Made Easy RevisedjovinerPas encore d'évaluation
- PageNumbering PDFDocument12 pagesPageNumbering PDFChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Essay Turabian Style PDFDocument10 pagesSample Essay Turabian Style PDFRenePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Background of Study: Solar Insolation and Electricity Demand For Cooling Versus TimeDocument48 pages1.1 Background of Study: Solar Insolation and Electricity Demand For Cooling Versus TimeChristopher JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of Speech Handout2 PDFDocument3 pagesParts of Speech Handout2 PDFArfiyah NoviyantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh Soal TOEFL Dan PembahasannyaDocument5 pagesContoh Soal TOEFL Dan Pembahasannyaiqbal mohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Possessive Adjectives Practice RecDocument2 pagesPossessive Adjectives Practice RecRENZO RODRIGO DE LA QUINTANA BEJARPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary - Grammar Basic Points Units 1-6Document33 pagesSummary - Grammar Basic Points Units 1-6alesales89Pas encore d'évaluation
- English Grammar For Tesl TeachersDocument2 pagesEnglish Grammar For Tesl TeachersNur AthirahPas encore d'évaluation
- If Clauses - Conditional Sentences - English GrammarDocument2 pagesIf Clauses - Conditional Sentences - English GrammarpercytinPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjective Clause WorksheetDocument3 pagesAdjective Clause WorksheetAbel MarcellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintaksa EJ 1Document2 pagesSintaksa EJ 1Branislava DilparićPas encore d'évaluation
- Phrase and clause structure explainedDocument15 pagesPhrase and clause structure explainedAnas AliPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Inggris Kel.1 (Skil 20 - 25)Document26 pagesB. Inggris Kel.1 (Skil 20 - 25)handaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cot 1 Kinds of AdjectivesDocument12 pagesCot 1 Kinds of AdjectivesKris Ann PasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clause and Types of SentencesDocument21 pagesClause and Types of SentencesHaunting XanePas encore d'évaluation
- New Pronouncing Di 01 Vel RichDocument714 pagesNew Pronouncing Di 01 Vel Richsingadishivu28Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Nature of Affixes and The Hierarchical Structure of The WordDocument14 pagesThe Nature of Affixes and The Hierarchical Structure of The WordShofia NafisahPas encore d'évaluation
- English Syntax Topics Word Order CategoriesDocument4 pagesEnglish Syntax Topics Word Order CategoriesRahmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Possessive Pronouns WorksheetDocument2 pagesBasic Possessive Pronouns Worksheetjorge bustamante83% (12)
- Sentence CompletionDocument7 pagesSentence Completionsiksac123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sentence StructureDocument155 pagesSentence Structureapi-3808291100% (4)
- Beginners Verb List (Reg-Irreg) PDFDocument4 pagesBeginners Verb List (Reg-Irreg) PDFAnonymous uFXGazIhv100% (1)
- An Adjective Modifies A Noun or A Pronoun by DescribingDocument3 pagesAn Adjective Modifies A Noun or A Pronoun by Describinglabastidalucy1394100% (1)
- XI SCIENCE - New Model Questions - by NEBDocument54 pagesXI SCIENCE - New Model Questions - by NEBThe Special ThingPas encore d'évaluation
- QSE B1-B2 Int WB p36 Unit15-1Document1 pageQSE B1-B2 Int WB p36 Unit15-1Mario ZaratePas encore d'évaluation
- Learn the differences between can, could and be able toDocument5 pagesLearn the differences between can, could and be able toMarcosTupiaAronesPas encore d'évaluation
- Duroos-Ul-Lughah Book 1 Lessons 1-7Document5 pagesDuroos-Ul-Lughah Book 1 Lessons 1-7Spy ninjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Au L 526385 Proper and Common Noun Sort Worksheet Ver 6Document4 pagesAu L 526385 Proper and Common Noun Sort Worksheet Ver 6Ania StartekPas encore d'évaluation
- Pronouns and AdjectivesDocument13 pagesPronouns and AdjectivesDayanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5007201132-Rizky Amalis Zhuraida-Sentence TypeDocument2 pages5007201132-Rizky Amalis Zhuraida-Sentence TypeMarseliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Memorize Irregular Verbs GroupsDocument2 pagesMemorize Irregular Verbs GroupsPaulieDomPas encore d'évaluation
- The Syntax of The Simple SentenceDocument58 pagesThe Syntax of The Simple SentenceAnca-Simina MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is VerbsDocument19 pagesWhat Is VerbsShahrouq Asmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation