Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
PLC and Scada Abstract PDF
Transféré par
Tushar Kant100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
513 vues6 pagesThis document discusses programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and their use in industrial automation and control systems. It provides a brief history of PLCs, describing how they were invented in response to industry needs as replacements for hard-wired relay systems. It also outlines some key features of PLCs, including their ability to interface with sensors and actuators through extensive input/output arrangements and their use of programming to control industrial processes. The document concludes with descriptions of SCADA systems and human-machine interfaces used to monitor and operate automation systems.
Description originale:
Titre original
plc and scada abstract.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document discusses programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and their use in industrial automation and control systems. It provides a brief history of PLCs, describing how they were invented in response to industry needs as replacements for hard-wired relay systems. It also outlines some key features of PLCs, including their ability to interface with sensors and actuators through extensive input/output arrangements and their use of programming to control industrial processes. The document concludes with descriptions of SCADA systems and human-machine interfaces used to monitor and operate automation systems.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
513 vues6 pagesPLC and Scada Abstract PDF
Transféré par
Tushar KantThis document discusses programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and their use in industrial automation and control systems. It provides a brief history of PLCs, describing how they were invented in response to industry needs as replacements for hard-wired relay systems. It also outlines some key features of PLCs, including their ability to interface with sensors and actuators through extensive input/output arrangements and their use of programming to control industrial processes. The document concludes with descriptions of SCADA systems and human-machine interfaces used to monitor and operate automation systems.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 6
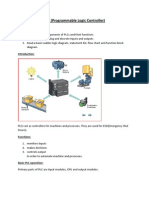
“INDUSTRIAL DRIVES & AUTOMATION USING PLC”
Bhagyashree Nagarkar
th
EX-5 sem, All Saints’ College of Technology,Bhopal
e-mail:- bhagyashreenagarkar@rocketmail.com
Abstract Introduction
Automation devices such as controllers Automation is the use of control systems
and data systems and/or services. (such as numerical control,
Systems and methods are provided that programmable logic control, and other
receive statements or other unit of data industrial control systems), in concert
interaction from an automation device, with other applications of information
provide the statements to an appropriate technology (such as computer-aided
system or service for processing, and technologies [CAD, CAM, CAx]), to
optionally return a response such as a control industrial machinery and
result set. Furthermore, in accordance processes, reducing the need for human
with an aspect of the invention native intervention. In the scope of
controller code, variables, or tags can be industrialization, automation is a step
mapped to stored data, procedures or beyond mechanization. Whereas
combinations of data and/or procedures mechanization provided human
and updated automatically or semi- operators with machinery to assist them
automatically. A programmable logic with the muscular requirements of work,
controller (PLC) or programmable automation greatly reduces the need for
controller is a digital computer used for human sensory and mental requirements
automation of electromechanical as well. Processes and systems can also
processes, such as control of machinery be automated.Automation plays an
on factory assembly lines, amusement increasingly important role in the global
rides, or lighting fixtures. PLCs are used economy and in daily experience.
in many industries and machines. Unlike Engineers strive to combine automated
general-purpose The subject invention devices with mathematical and
pertains to facilitating communication organizational tools to create complex
between industrial computers, the PLC is systems for a rapidly expanding range of
designed for multiple inputs and output applications and human activities. Many
arrangements, extended temperature roles for humans in industrial processes
ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and presently lie beyond the scope of
resistance to vibration and impact. automation. Human-level pattern
Programs to control machine operation recognition, language recognition, and
are typically stored in battery-backed or language production ability are well
non-volatile memory. A PLC is an beyond the capabilities of modern
example of a real time system since mechanical and computer systems.
output results must be produced in Tasks requiring subjective assessment or
response to input conditions within a synthesis of complex sensory data, such
bounded time, otherwise unintended as scents and sounds, as well as high-
operation will result. level tasks such as strategic planning,
currently require human expertise. In cylinders, magnetic relays, solenoids, or
many cases, the use of humans is more analog outputs. The input/output
cost-effective than mechanical arrangements may be built into a simple
approaches even where automation of PLC, or the PLC may have external I/O
industrial tasks is possible.Specialised modules attached to a computer network
hardened computers, referred to as that plugs into the PLC
programmable logic controllers (PLCs),
are frequently used to synchronize the Architecture of PLCs
flow of inputs from (physical) sensors
and events with the flow of outputs to
actuators and events. This leads to
precisely controlled actions that permit a
tight control of almost any industrial
process.
History
The PLC was invented in response to the
needs of the American automotive
manufacturing industry. In 1968 GM
Hydramatic (the automatic transmission
division of General Motors) issued a
request for proposal for an electronic Developments in PLC
replacement for hard-wired relay
systems. The first PLC, designated the Early PLCs were designed to replace
084 because it was Bedford Associates' relay logic systems. These PLCs were
eighty-fourth project, was the result. programmed in "ladder logic", which
Dick Morley, who is considered to be strongly resembles a schematic diagram
the "father" of the PLC. of relay logic. This program notation
was chosen to reduce training demands
Features of PLC for the existing technicians. Other early
PLCs used a form of instruction list
The main difference from other programming, based on a stack-based
computers is that PLCs are armored for logic solver.
severe conditions (such as dust,
moisture, heat, cold) and have the Modern PLCs can be programmed in a
facility for extensive input/output (I/O) variety of ways, from ladder logic to
arrangements. These connect the PLC to more traditional programming languages
sensors and actuators. PLCs read limit such as BASIC and C. Another method
switches, analog process variables (such is State Logic, a very high-level
as temperature and pressure), and the programming language designed to
positions of complex positioning program PLCs based on state transition
systems. Some use machine vision. On diagrams.
the actuator side, PLCs operate electric
motors, pneumatic or hydraulic Programming in PLC
Early PLCs, up to the mid-1980s, were
programmed using proprietary
programming panels or special-purpose
programming terminals, which often had
dedicated function keys representing the
various logical elements of PLC
programs. Programs were stored on
cassette tape cartridges. Facilities for
printing and documentation were very
minimal due to lack of memory capacity.
The very oldest PLCs used non-volatile
magnetic core memory.
SCADA
The term SCADA usually refers to
centralized systems which monitor and
control entire sites, or complexes of
systems spread out over large areas
(anything between an industrial plant
and a country). Most control actions are
performed automatically by Remote
Terminal Units ("RTUs") or by
Programmable Logic Controllers Data acquisition begins at the RTU or
("PLCs"). Host control functions are PLC level and includes meter readings
usually restricted to basic overriding or and equipment status reports that are
supervisory level intervention. For communicated to SCADA as required.
example, a PLC may control the flow of Data is then compiled and formatted in
cooling water through part of an such a way that a control room operator
industrial process, but the SCADA using the HMI can make supervisory
system may allow operators to change decisions to adjust or override normal
the set points for the flow, and enable RTU (PLC) controls. Data may also be
alarm conditions, such as loss of flow fed to a Historian, often built on a
and high temperature, to be displayed commodity Database Management
and recorded. The feedback control loop System, to allow trending and other
passes through the RTU or PLC, while analytical auditing.SCADA systems
the SCADA system monitors the overall typically implement a distributed
performance of the loop. database, commonly referred to as a tag
database, which contains data elements
called tags or points. A point represents
a single input or output value monitored
or controlled by the system. Points can
be either "hard" or "soft". A hard point
represents an actual input or output
within the system, while a soft point
results from logic and math operations
applied to other points. (Most
implementations conceptually remove of a pump connected to a pipe can show
the distinction by making every property the operator that the pump is running
a "soft" point expression, which may, in and how much fluid it is pumping
the simplest case, equal a single hard through the pipe at the moment. The
point.) Points are normally stored as operator can then switch the pump off.
value-timestamp pairs: a value, and the The HMI software will show the flow
timestamp when it was recorded or rate of the fluid in the pipe decrease in
calculated. A series of value-timestamp real time. Mimic diagrams may consist
pairs gives the history of that point. It's of line graphics and schematic symbols
also common to store additional to represent process elements, or may
metadata with tags, such as the path to a consist of digital photographs of the
field device or PLC register, design time process equipment overlain with
comments, and alarm information. animated symbols.
Human Machine Interface The HMI package for the SCADA
system typically includes a drawing
A Human-Machine Interface or HMI is program that the operators or system
the apparatus which presents process maintenance personnel use to change the
data to a human operator, and through way these points are represented in the
which the human operator controls the interface. These representations can be
process. as simple as an on-screen traffic light,
which represents the state of an actual
traffic light in the field, or as complex as
An HMI is usually linked to the SCADA
system's databases and software a multi-projector display representing
programs, to provide trending, the position of all of the elevators in a
diagnostic data, and management skyscraper or all of the trains on a
information such as scheduled railway.
maintenance procedures, logistic
information, detailed schematics for a An important part of most SCADA
particular sensor or machine, and expert- implementations are alarms. An alarm is
system troubleshooting guides. This a digital status point that has either the
means that the operator can see a value NORMAL or ALARM. Alarms
schematic representation of the plant can be created in such a way that when
being controlled. For example, a picture
their requirements are met, they are The main disadvantages of automation
activated. An example of an alarm is the are:
"fuel tank empty" light in a car. The
SCADA operator's attention is drawn to Technology limits. Current
the part of the system requiring attention technology is unable to automate
by the alarm. Emails and text messages all the desired tasks.
are often sent along with an alarm Unpredictable development
activation alerting managers along with costs. The research and
the SCADA operator. development cost of automating
a process is difficult to predict
Advantages accurately beforehand. Since this
cost can have a large impact on
The main advantage of automation are: profitability, it's possible to finish
automating a process only to
Replacing human operators in discover that there's no economic
tedious tasks. advantage in doing so.
Replacing humans in tasks that Initial costs are relatively high.
should be done in dangerous The automation of a new product
environments (i.e. fire, space, required a huge initial investment
volcanoes, nuclear facilities, in comparison with the unit cost
under the water, etc) of the product, although the cost
Making tasks that are beyond the of automation is spread in many
human capabilities such as product batches. The automation
handling too heavy loads, too of a plant required a great initial
large objects, too hot or too cold investment too, although this cost
substances or the requirement to is spread in the products to be
make things too fast or too slow. produced.
Economy improvement.
Sometimes and some kinds of Applications
automation implies improves in
economy of enterprises, society 1. PLCs may need to interact with
or most of humankind. For people for the purpose of configuration,
example, when an enterprise that alarm reporting or everyday control.
has invested in automation
technology recovers its 2. Most modern PLCs can communicate
investment; when a state or over a network to some other system,
country increases its income due such as a computer running a SCADA
to automation like Germany or (Supervisory Control And Data
Japan in the 20th Century or Acquisition) system or web browser.
when the humankind can use the
internet which in turn use 3.Use of PLC in storing water-
satellites and other automated
engines. a facility needs to store water in a tank.
The water is drawn from the tank by
Disadvantages another system, as needed, and our
example system must manage the water activity. A technician adjusts this
level in the tank. deadband so the valve moves only for a
significant change in rate. This will in
Using only digital signals, the PLC has turn minimize the motion of the valve,
two digital inputs from float switches and reduce its wear.A real system might
(Low Level and High Level). When the combine both approaches, using float
water level is above the switch it closes a switches and simple valves to prevent
contact and passes a signal to an input. spills, and a rate sensor and rate valve to
The PLC uses a digital output to open optimize refill rates and prevent water
and close the inlet valve into the tank. hammer. Backup and maintenance
methods can make a real system very
When the water level drops enough so complicated .
that the Low Level float switch is off
(down), the PLC will open the valve to Conclusions
let more water in. Once the water level
rises enough so that the High Level A PAC provides in a single compact
switch is on (up), the PLC will shut the controller the advanced control features,
inlet to stop the water from overflowing. network connectivity, device
This rung is an example of seal in logic. interoperability, and enterprise data
The output is sealed in until some integration capabilities found in PLC- or
condition breaks the circuit. PC-based automation controllers. With
these features, the PAC has become an
| integral part ofmeeting the new and
|
| Low Level High Level diverse requirements demanded in a
Fill Valve | modern industrial application.
|------[/]------|------[/]-------
---------------(OUT)---------|
| |
Reference
|
| | http://www.plcs.net/chapters/hist
| ory2.htm
| | http://www.koldwater.com/down
|
| Fill Valve | loadform.htm
| http://www.htservices.com/Tutor
|------[ ]------| ials/plctutorial1.htm
| http://www.sea.siemens.com/step
|
|
/templates/lesson.mason?plcs:1:1
| :1
An analog system might use a water http://www.thelearningpit.com/ps
pressure sensor or a load cell, and an im/psim.html
adjustable (throttling) dripping out of the
tank, the valve adjusts to slowly drip
water back into the tank.In this system,
to avoid 'flutter' adjustments that can
wear out the valve, many PLCs
incorporate "hysteresis" which
essentially creates a "deadband" of
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NGPCL Users Guide v25Document42 pagesNGPCL Users Guide v25Sandu RaduPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Control Unit DCS PDFDocument44 pagesLocal Control Unit DCS PDFSaravanakumar KPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Meters CatalogueDocument40 pagesSecure Meters CatalogueHarman Preet100% (1)
- PLC ScanDocument8 pagesPLC Scanmoney_kandan2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- IT Support: QualificationsDocument3 pagesIT Support: QualificationsqwqwqwqPas encore d'évaluation
- Imcs Cbn-030 Hmi Scada Cimplicity FundamentalsDocument2 pagesImcs Cbn-030 Hmi Scada Cimplicity Fundamentalskhanghanh2017 aPas encore d'évaluation
- Agni PPT Presentation On PLCDocument19 pagesAgni PPT Presentation On PLCAgni BhattacharjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Bhel - CNC MachinesDocument60 pagesBhel - CNC MachinesAggyapal Singh JimmyPas encore d'évaluation
- BMS - SCADA ComparisonDocument14 pagesBMS - SCADA Comparisonbad manPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC FatekDocument36 pagesPLC FatekM7mud M7mdPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Noteshero_spaceboy3600Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On PLCDocument27 pagesPresentation On PLCTyrone Michaels100% (1)
- Presentation of Industrial Training ON: Industrial Automation PLC & ScadaDocument20 pagesPresentation of Industrial Training ON: Industrial Automation PLC & ScadaManika SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Interview Questions: 1. What Is The RS LINX Software Used For?Document5 pagesPLC Interview Questions: 1. What Is The RS LINX Software Used For?Pradip ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Report1 PLCDocument90 pagesComplete Report1 PLCRao Arslan Rajput100% (3)
- Programmable Logic Controller PLCDocument53 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller PLCokk chuPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between PLC and DCSDocument2 pagesDifference Between PLC and DCSatul96_aph100% (1)
- A Presentation On Scada System: (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)Document19 pagesA Presentation On Scada System: (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)Anis MaqboolPas encore d'évaluation
- Process - Control SimulatorDocument7 pagesProcess - Control SimulatorSakshi RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Course On Embedded SystemsDocument75 pagesOnline Course On Embedded SystemspandiPas encore d'évaluation
- WinRunner For BeginnersDocument62 pagesWinRunner For BeginnersMadhan RajPas encore d'évaluation
- MotionControlTerminologyPrimerv2 PDFDocument2 pagesMotionControlTerminologyPrimerv2 PDFFouad ElhajjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1: PLC Hardware FamiliarizationDocument5 pagesLab 1: PLC Hardware FamiliarizationTee CubePas encore d'évaluation
- PLC and Scada: Text BooksDocument5 pagesPLC and Scada: Text Booksshriram jadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Company Profile RDEPL Updated 1-08-15 AutomotiveDocument68 pagesCompany Profile RDEPL Updated 1-08-15 AutomotiveSubodh KothariPas encore d'évaluation
- Position Control of DC Motor Using Genetic Algorithm Based PID ControllerDocument35 pagesPosition Control of DC Motor Using Genetic Algorithm Based PID ControllerSarat Chandra100% (1)
- PLC and SCADA - Lecture 1Document34 pagesPLC and SCADA - Lecture 1Rajeevan ArunPas encore d'évaluation
- Taufik Tutorial PDFDocument97 pagesTaufik Tutorial PDFAdolfo Valdez Bahena100% (1)
- Difference Between PAC Hardware and PLC, DCSDocument2 pagesDifference Between PAC Hardware and PLC, DCSsuudonPas encore d'évaluation
- Control of Boiler Operation Using PLC - SCADADocument9 pagesControl of Boiler Operation Using PLC - SCADARoshan RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart Factory For Future Industry DevelopmentDocument5 pagesSmart Factory For Future Industry DevelopmentIAES International Journal of Robotics and AutomationPas encore d'évaluation
- Privacy Vs Security: The Byod Dilemma: Group 6Document10 pagesPrivacy Vs Security: The Byod Dilemma: Group 6ManishaPas encore d'évaluation
- SCADA - Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionDocument23 pagesSCADA - Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionSushant KambojPas encore d'évaluation
- 8-6 Data Transfer and ManipulationDocument16 pages8-6 Data Transfer and ManipulationSadaf RasheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Automation 1Document41 pagesIndustrial Automation 1Chandan Chandan100% (2)
- Assignment 3 FinalDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 FinalRizwan Aslam ButtPas encore d'évaluation
- ER-6000 English Operation Manual v20191005Document167 pagesER-6000 English Operation Manual v20191005seba deiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Controls Engineer InterviewDocument3 pagesControls Engineer Interviewrhoney0120% (1)
- Factoryio Parts EssentialsDocument82 pagesFactoryio Parts EssentialsAlexander Diaz AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 04 - Methods & RecursionDocument7 pagesLab 04 - Methods & RecursionSajid Ali0% (1)
- DCSDocument16 pagesDCSAnonymous AEYlyuzPas encore d'évaluation
- PLCDocument14 pagesPLCPrateek S VirdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th RTS SLTN SakDocument9 pages4th RTS SLTN SaknitishbhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Based Inspection, Packaging and Storing of MaterialsDocument5 pagesPLC Based Inspection, Packaging and Storing of MaterialsAlauddin khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Luanshya Technical and Business College Management Board Diploma in Electrical Engineering Electrical Instrumentation (Dee 231)Document5 pagesLuanshya Technical and Business College Management Board Diploma in Electrical Engineering Electrical Instrumentation (Dee 231)Alfred K ChilufyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Setting Up Electronically Controlled Complex SystemsDocument61 pagesSetting Up Electronically Controlled Complex Systemsfrezer mesfin100% (1)
- Sofcon Training AttachmentDocument3 pagesSofcon Training Attachmentjogeorge85Pas encore d'évaluation
- 01 - Background To SCADADocument44 pages01 - Background To SCADADwindawan Holandrio100% (1)
- Software Installation and HMI ConfigurationDocument11 pagesSoftware Installation and HMI ConfigurationKiên NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- FactoryTalk View SE v5 0 (CPR9) Distributed System Design Considerations 2007 12Document41 pagesFactoryTalk View SE v5 0 (CPR9) Distributed System Design Considerations 2007 12Jhon Ríos100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Software Engineering and Process ModelsDocument53 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Software Engineering and Process ModelsAshmeet AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Program To Perform Capping of Beverage Bottles - SanfoundryDocument6 pagesPLC Program To Perform Capping of Beverage Bottles - SanfoundryAhmad Hamouda100% (1)
- GxDTxp9VQN Q08afVQDfJw Activity Template Gantt ChartDocument5 pagesGxDTxp9VQN Q08afVQDfJw Activity Template Gantt ChartSoufiane EL BAROUDIPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 - DC Motor Control Using PLCDocument49 pages05 - DC Motor Control Using PLCKoppoju PadmaPas encore d'évaluation
- In The Name of Allah The Most Benificet and The Most MercifulDocument24 pagesIn The Name of Allah The Most Benificet and The Most MercifulAsad RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Btech/Mtech: Project List of PLC/SCADA AutomationDocument2 pagesBtech/Mtech: Project List of PLC/SCADA AutomationAmit SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Polution Control - Project (Rockwell)Document16 pagesAir Polution Control - Project (Rockwell)Chandan MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- RS 232 Instrument & Interfaces and ProtocolsDocument24 pagesRS 232 Instrument & Interfaces and ProtocolsJeyakumar VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Vendor Sample ProjectsDocument5 pagesVendor Sample ProjectsCassio Rafael R RPas encore d'évaluation
- PID For Dummies: SearchDocument13 pagesPID For Dummies: SearchChinmoy DasPas encore d'évaluation
- ScadaDocument34 pagesScadashikhafatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Time Operating System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionD'EverandReal Time Operating System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Supervisory control and data acquisition Third EditionD'EverandSupervisory control and data acquisition Third EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar 312: Variable Speed Drives For Asynchronous Motors PROFIBUS DP Communication ManualDocument37 pagesAltivar 312: Variable Speed Drives For Asynchronous Motors PROFIBUS DP Communication ManualMarcos AldrovandiPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Scada TrainingDocument51 pagesPLC Scada TrainingPriya HadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi Servo SystemDocument56 pagesMitsubishi Servo SystemGanesh100% (1)
- Introduction To PLC Programmable Logic Controller: Presented byDocument16 pagesIntroduction To PLC Programmable Logic Controller: Presented byFahad ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Takebishi DeviceXPlorer OPC Server BrochureDocument20 pagesTakebishi DeviceXPlorer OPC Server BrochureRazvan FilipPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction Manual: Microprocessor-Based Reference Adjuster RA-70Document55 pagesInstruction Manual: Microprocessor-Based Reference Adjuster RA-70luisPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Preventive MaintenanceDocument3 pagesElectrical Preventive MaintenanceZunnur ZamzamPas encore d'évaluation
- 3BSE040587-601 - en Compact HMI 6.0.1 Getting StartedDocument246 pages3BSE040587-601 - en Compact HMI 6.0.1 Getting StartedFabian Guzman100% (1)
- Power Amplifier With Profibus Eng 503366Document39 pagesPower Amplifier With Profibus Eng 503366Adelino UacatePas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Information Prosonic M FMU40, FMU41, FMU42, FMU43, FMU44Document56 pagesTechnical Information Prosonic M FMU40, FMU41, FMU42, FMU43, FMU44johnf2328Pas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Program Manual: GSK983M (T) CNC SystemDocument76 pagesPLC Program Manual: GSK983M (T) CNC SystemLeonardusPas encore d'évaluation
- ISE 511L Syllabus11 - 8 - 11Document4 pagesISE 511L Syllabus11 - 8 - 11Sajal JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview: Manuflo Equipment For Water in Batch Plants: Flow Measurement ProductsDocument24 pagesOverview: Manuflo Equipment For Water in Batch Plants: Flow Measurement ProductsDavid SarccoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi Melsec FX1S Harware ManualDocument84 pagesMitsubishi Melsec FX1S Harware ManualThành nguyễn ĐứcPas encore d'évaluation
- Propoint Plus 4-Stage Engineer Manual Issue 1Document57 pagesPropoint Plus 4-Stage Engineer Manual Issue 1Aldo CapristanoPas encore d'évaluation
- SoftSpeed UMDocument94 pagesSoftSpeed UMIon100% (1)
- Developers GuideDocument100 pagesDevelopers GuideRobson SpricigoPas encore d'évaluation
- MN05003001Z enDocument156 pagesMN05003001Z enLeo VesquePas encore d'évaluation
- Allen-Bradley SLC 500 DF1 Serial Driver Guide - AB - SLC5 - SerialDocument19 pagesAllen-Bradley SLC 500 DF1 Serial Driver Guide - AB - SLC5 - SerialMilko ColovicPas encore d'évaluation
- DP ManualDocument16 pagesDP Manualnguyễn hữu trườngPas encore d'évaluation
- H011809DA AdvantageOneOffshoreCementingSystemDocument3 pagesH011809DA AdvantageOneOffshoreCementingSystemAnonymous uKoNmLxk100% (1)
- Datasheet 593330 (98-6090) en 120V 60HzDocument98 pagesDatasheet 593330 (98-6090) en 120V 60Hzleonardo morenoPas encore d'évaluation
- VT3 UM GB WW 0116-1rDocument30 pagesVT3 UM GB WW 0116-1rgiapy0000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring Allen Bradley RSLinx and RSLogix For Use With The PLC TrainerDocument7 pagesConfiguring Allen Bradley RSLinx and RSLogix For Use With The PLC Trainertt_aljobory3911Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Automatic Inspection System Based On PLC and Machine VisionDocument5 pagesDesign of Automatic Inspection System Based On PLC and Machine VisionDaniel SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Factorytalk Linx Getting Results GuideDocument91 pagesFactorytalk Linx Getting Results GuideIngeniero aicPas encore d'évaluation