Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Second Language Acquisition
Transféré par
Indah SafitriDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Summary of Second Language Acquisition
Transféré par
Indah SafitriDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1st Group SLA:
1. Rulia Iva Dhalina 0203517053
2. Adhe Risky Mayasari 0203518072
3. Diah Ayu Setianingrum 0203518073
Summary of Second Language Acquisition
Group 1.3 Introduction & Methode of Researching learning in the Second Language
Classroom
Introduction
There are three different perspectives among second language researcher in classroom
interaction research, the first perspective is that found in comparative method studies. A
second perspective involves going inside the ‘black box’ (learner mind) of the classroom it
self. A third perspective involves investigating the effect of the formal interaction.
First of all, this chapter will consider some of the principal resaecrh methods that have been
used to investigate the role of classroom interaction in language learning. Finally
consideration is given to the relationship between classroom interaction and L2 learning and
in particular, whether classroom environtment are capable of providing the kinds of
opportunities needed to develop full L2 competence.
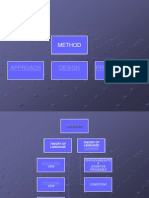
Methods of researching learning in the second language classroom:
Tradition Typical Issues Methods
Psychometric Language gain from different Experimental method- pre-
methods, materials, and post-tests with
treatments experimental and control
groups
Interaction Analysis Extent to which learner Coding classroom
behaviour is a function of interactions in terms of
teacher determined various observation systems
interaction and schedules
Discourse Analysis Analysis of classroom Study classroom transcripts
discourse in linguistics terms and assign utterances to pre
determined categories
Ethnographic Obtain insights into the Naturalistic ‘uncontrolled’
classroom as a cultural observation and description
system
A summary of Chaudron’s Four Research Traditions in L2 Classroom Research
(Taken from Nunan 1990 b: 23)
Psychometric and Interaction analysis traditions typically involve ‘quantitative’ and
‘explanatory’ research, while the discourse analysis and ethnographic traditions make use of
more ‘qualitative’ and ‘descriptive’ methods.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Dialogic Learning: Shifting Perspectives to Learning, Instruction, and TeachingD'EverandDialogic Learning: Shifting Perspectives to Learning, Instruction, and TeachingPas encore d'évaluation
- Classroom Interaction and Second Language AcquisitionDocument9 pagesClassroom Interaction and Second Language AcquisitionRaniena Chokyuhyun100% (1)
- Mental Processes in Teachers' Reflection Papers-1Document13 pagesMental Processes in Teachers' Reflection Papers-1Siti NuranisahPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nature of Approaches and Methods in LanguageDocument12 pagesThe Nature of Approaches and Methods in LanguageFedrata100% (1)
- Handout 3 Research in English Language Teaching (Research Method and Traditions)Document3 pagesHandout 3 Research in English Language Teaching (Research Method and Traditions)bambangPas encore d'évaluation
- Method of Teaching English As A ForeignDocument73 pagesMethod of Teaching English As A ForeignJester PagkaliwaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Teaching MethodologyDocument3 pagesSummary Teaching MethodologyRian Indra FadillahPas encore d'évaluation
- TEFL Assignment - 1Document2 pagesTEFL Assignment - 1Asfariz Naufal50% (2)
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4Phuong ChiPas encore d'évaluation
- Capaian Pembelajaran Matakuliah/Kompetensi: Rps Matakuliah Program Studi S1 Sastra InggrisDocument4 pagesCapaian Pembelajaran Matakuliah/Kompetensi: Rps Matakuliah Program Studi S1 Sastra InggrisLarasati WardaniPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG 467 - Course OutlineDocument7 pagesENG 467 - Course OutlineAbdullah Khalid Turki AlmutairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Thinking in The Moroccan Textbooks of English: Ticket To English As A Case StudyDocument1 pageCritical Thinking in The Moroccan Textbooks of English: Ticket To English As A Case StudyMartin HopePas encore d'évaluation
- Methodologies of Translation: V. Jai Vasumathi Valli RaniDocument4 pagesMethodologies of Translation: V. Jai Vasumathi Valli RaniHADJER DIBPas encore d'évaluation
- Discourse Analysis in The ESL ClassroomDocument18 pagesDiscourse Analysis in The ESL ClassroomAli Alfaridzi100% (2)
- Approach Method Technique in Language TeDocument75 pagesApproach Method Technique in Language TeConsulado100% (1)
- Natural CLT SaitoDocument8 pagesNatural CLT SaitoJúlia BánságiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter III FerdiDocument11 pagesChapter III FerdiferdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Approaches Methods Techniques: Farhana Ahasan Assistant Professor Department of EnglishDocument32 pagesApproaches Methods Techniques: Farhana Ahasan Assistant Professor Department of EnglishMd SarroarPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL - Week 3Document5 pagesDLL - Week 3Ralph Ryan TooPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigating Expertise in Materials EvaluationDocument7 pagesInvestigating Expertise in Materials EvaluationJames LomasPas encore d'évaluation
- GIG5211 Research Methods and Ethics and Scientific PublicationsDocument9 pagesGIG5211 Research Methods and Ethics and Scientific PublicationsAnisa Ayu LestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedagogy and Language Teaching 1Document5 pagesPedagogy and Language Teaching 1Danna GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop-Methodology Efl Research - 2Document8 pagesWorkshop-Methodology Efl Research - 2Katerine Katiusca Mejía CantilloPas encore d'évaluation
- M1 Guides-Area2Document12 pagesM1 Guides-Area2Apis meliferaPas encore d'évaluation
- Method: Approach Design ProcedureDocument16 pagesMethod: Approach Design ProcedurehorogoPas encore d'évaluation
- Part1-Chapter 2-RevisedDocument21 pagesPart1-Chapter 2-RevisedYohanes GirsangPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundations in EFL ResearchDocument9 pagesFoundations in EFL ResearchStephanie PinillaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Discourse AnalysisDocument2 pagesWhat Is Discourse Analysisfabriciogerig100% (2)
- Qualitative ResearchDocument7 pagesQualitative ResearchAngelo BarquillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching (2010) PDFDocument94 pagesApproaches and Methods in Language Teaching (2010) PDFabobodaPas encore d'évaluation
- 364 555 1 SMDocument18 pages364 555 1 SMAnton DorsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Strategies Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesReading Strategies Lesson Planapi-360199282100% (1)
- Jurnal Ilmiah Simantek ISSN: 2550-0414: Vol. 2, No. 1 Januari 2018Document7 pagesJurnal Ilmiah Simantek ISSN: 2550-0414: Vol. 2, No. 1 Januari 2018IlaavyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapa ConceptualDocument6 pagesMapa ConceptualMONIQUE ZAMOPas encore d'évaluation
- Uncommon Qualitative MethodsDocument8 pagesUncommon Qualitative MethodsAllen MarcPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach, Method and Technique?: IS Axiomatic UnquestionableDocument8 pagesApproach, Method and Technique?: IS Axiomatic Unquestionablecarolina reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Universitas Mulawarman Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Program Pascasarjana Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesUniversitas Mulawarman Fakultas Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan Program Pascasarjana Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisJohn RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Classroom InteractionDocument2 pagesClassroom InteractionMs. MeylinaPas encore d'évaluation
- RPS SociolinguisticsDocument7 pagesRPS SociolinguisticsREGINA CAHYANIPas encore d'évaluation
- Tefl Approach, Method and Technique Approach, Method and TechniqueDocument38 pagesTefl Approach, Method and Technique Approach, Method and TechniqueRiskaLestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Language Education ResearchDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Language Education ResearchJohn Michael ManjaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Week3 Celce MurciaDocument15 pagesWeek3 Celce MurciacuisineksmPas encore d'évaluation
- English: Stage 6Document15 pagesEnglish: Stage 6FlaaffyPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach, Method and Technique: Elih Sutisna Yanto-FKIP PBI Unsika West-Java IndonesiaDocument38 pagesApproach, Method and Technique: Elih Sutisna Yanto-FKIP PBI Unsika West-Java IndonesiaAxel ValkiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 PBDocument10 pages2 PBGlenn CuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Categories LT BakulDocument10 pagesCategories LT BakulPourya HellPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemberton 2018 MaterialsDocument49 pagesPemberton 2018 MaterialsEmad OmidpourPas encore d'évaluation
- Methodology Lecture Notes 1Document35 pagesMethodology Lecture Notes 1Chala KelbessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Grammar Autonomously Through MetacognitivDocument6 pagesLearning Grammar Autonomously Through MetacognitivJomar MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Presentation 2009Document23 pagesSeminar Presentation 2009Nur AliaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach, Method, TechniqueDocument4 pagesApproach, Method, TechniqueHendra RaharjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach, Method & TechniqueDocument52 pagesApproach, Method & TechniqueJONATHAN BORGESPas encore d'évaluation
- Ideational Meaning I N Students' Self-Introduction: What Are Realized? Candradewi Wahyu AnggraeniDocument16 pagesIdeational Meaning I N Students' Self-Introduction: What Are Realized? Candradewi Wahyu AnggraeniAris HidayatullohPas encore d'évaluation
- Dcorrea 0813@ Gmail - ComDocument8 pagesDcorrea 0813@ Gmail - ComStrahinja StepanovPas encore d'évaluation
- Discourse Analysis. InternationalDocument7 pagesDiscourse Analysis. InternationalAlireza KheirolahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Science and PhilosophyDocument3 pagesSocial Science and Philosophyjennyzelle caberte88% (16)
- Sample-Unit-Standard-Year-12-Common-Module-Past-The-Shallows 2Document13 pagesSample-Unit-Standard-Year-12-Common-Module-Past-The-Shallows 2mahla fzpoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Sempro - Rulyana ManurungDocument12 pagesSempro - Rulyana Manurungrulya manurungPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 Pedagogic 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1 Pedagogic 1Danna GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Katrin NooreensarticleDocument17 pagesKatrin NooreensarticleAnnisa NurinzaniPas encore d'évaluation
- INSET Narrative Report 2021 (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesINSET Narrative Report 2021 (AutoRecovered)Ana Alberte100% (1)
- 3rd Grade Math and ELA FocusDocument18 pages3rd Grade Math and ELA FocusLAUSDCCSSPas encore d'évaluation
- ELTCDocument10 pagesELTCAliza Alexander Selvaratnam SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Machinery Lubrication EbookDocument14 pagesMachinery Lubrication Ebookganeshji@vsnl.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Oak Hill SH PDFDocument29 pagesOak Hill SH PDFLanie MarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109Document2 pagesAnatomy of An FEI Lesson.1109arudenstinePas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of E-LearningDocument8 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of E-LearningSourabh Agarwal100% (1)
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Stat3332.001.11f Taught by Robert Serfling (Serfling)Document4 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Stat3332.001.11f Taught by Robert Serfling (Serfling)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Brand Awareness Is Related To The Strength of The Brand Node in Memory, As Reflected byDocument1 pageBrand Awareness Is Related To The Strength of The Brand Node in Memory, As Reflected byAashish GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- KM Exam NotesDocument3 pagesKM Exam NotesShreya GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renaissance Lesson Plan PDFDocument6 pagesRenaissance Lesson Plan PDFianpaolo100% (1)
- Reviewer For Principals With KeyDocument56 pagesReviewer For Principals With KeyGeosippi San Antonio Layman100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Types of SpeechesDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Types of Speechesjumari sapio75% (12)
- Sandwich IndiaDocument4 pagesSandwich Indiaarun7sharma78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ought To, Should, Must and Have ToDocument2 pagesOught To, Should, Must and Have Topinay athena100% (1)
- 201 SyllabusDocument2 pages201 Syllabuskevin jonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiplication Lesson Plan (Repeated AdditionDocument5 pagesMultiplication Lesson Plan (Repeated AdditionHamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument16 pagesBloom TaxonomySitiNorhafizahDollahPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Student-Teacher Relationships and Classroom Management Action Research 1Document15 pagesEffects of Student-Teacher Relationships and Classroom Management Action Research 1api-443176637Pas encore d'évaluation
- NAEP PowerPoint For Alabama SBOE June 13, 2019Document13 pagesNAEP PowerPoint For Alabama SBOE June 13, 2019Trisha Powell CrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Making Good DecisionsDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Making Good DecisionsErich2kPas encore d'évaluation
- Action Research DesignsDocument20 pagesAction Research DesignsElaine Chin100% (2)
- Fluid MechanicsDocument8 pagesFluid MechanicsVinicius Carvalho PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Intervention Plan For Teacher in Need of AssistanceDocument4 pagesIntervention Plan For Teacher in Need of Assistanceapi-302124409Pas encore d'évaluation
- Student l1 Annotated DiagramsDocument4 pagesStudent l1 Annotated Diagramsapi-207724778Pas encore d'évaluation
- UGC NET EducationDocument11 pagesUGC NET EducationSudipta BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hannah Richardson CV PDFDocument3 pagesHannah Richardson CV PDFapi-447492645Pas encore d'évaluation
- Speculating!: Things That Go Bump in The Night!Document2 pagesSpeculating!: Things That Go Bump in The Night!BixinisPas encore d'évaluation
- Morris 3880 SSII19 SyllabusDocument10 pagesMorris 3880 SSII19 SyllabusAbigailMorrisPas encore d'évaluation