Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
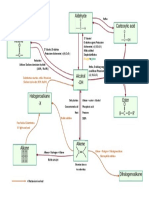
Reaction Summary: ALKENES: Reagent Conditions Products Observations Example/Diagram
Transféré par
Victoria Kairoo0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues1 pageThis document summarizes common reactions of alkenes. It lists various reagents and conditions used to react alkenes, such as bromine, hydrogen halides, acids, and bases. The main products formed from these reactions include vicinal dibromides, bromoalcohols, halogenoalkanes, vicinal diols, carbonyl compounds, alcohols, and alkanes. Observable color changes or temperature conditions are also noted.
Description originale:
reaction of alkenes summary sheet
organic chemistry cape
Titre original
Reactions of Alkenes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document summarizes common reactions of alkenes. It lists various reagents and conditions used to react alkenes, such as bromine, hydrogen halides, acids, and bases. The main products formed from these reactions include vicinal dibromides, bromoalcohols, halogenoalkanes, vicinal diols, carbonyl compounds, alcohols, and alkanes. Observable color changes or temperature conditions are also noted.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues1 pageReaction Summary: ALKENES: Reagent Conditions Products Observations Example/Diagram
Transféré par
Victoria KairooThis document summarizes common reactions of alkenes. It lists various reagents and conditions used to react alkenes, such as bromine, hydrogen halides, acids, and bases. The main products formed from these reactions include vicinal dibromides, bromoalcohols, halogenoalkanes, vicinal diols, carbonyl compounds, alcohols, and alkanes. Observable color changes or temperature conditions are also noted.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Reaction Summary: ALKENES
Reagent Conditions Products Observations Example/Diagram
Br(l) Room temperature Vicinal dibromide Bromine decolorized
No light
Br(aq) Room temperature Vicinal dibromide Bromine decolorized
NB: CAPE just uses the dibromide (minor product)
as the product. They disregard the Bromoalcohol (major
alcohol. product)
Hydrogen halide Room temperature Halogenoalkane
HX where X is F, Cl, Br, I Hydrogen halide either
dissolved in ethanoic
acid or gaseous HX
bubbled through alkene
H+(aq)/KMnO4(aq) Cold dilute Vicinal diol Purple colour of KMnO4(aq) decolorized
H+(aq)/KMnO4(aq)
H+(aq)/KMnO4(aq) Hot concentrated Mixture of compounds Purple colour of KMnO4(aq) decolorized
H+(aq)/KMnO4(aq) containing a carbonyl
group (C=O) (ketones,
carboxylic acids,
aldehydes which are
oxidized to acids)
Sometimes CO2 and
H2O formed as well
Hydration Acidic catalyst Alkyl hydrogensulfate
(concentrated H2SO4) which is then
hydrolyzed with H2O to
an alcohol and the
sulphuric acid is
regenerated
Hydrogenation Room temperature Corresponding alkane
(addition of hydrogen) (150oC) (unsaturated
High pressure compound)
Catalyst – nickel or
platinum
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions of Alkanes: Mechanism Reaction Reagent Condition Catalysts Product(s)Document9 pagesChemical Reactions of Alkanes: Mechanism Reaction Reagent Condition Catalysts Product(s)Sam LeePas encore d'évaluation
- ORGANIC REACTIONS GRADE 12 Summary 2018Document2 pagesORGANIC REACTIONS GRADE 12 Summary 2018Wanga MdallPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ReactionsDocument1 pageOrganic ReactionsFerro FlowPas encore d'évaluation
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 21: Organic SynthesisDocument4 pagesCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 21: Organic SynthesisahumanbeinginearthPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Reaction Reagents Conditions Organic Products Side ProductsDocument2 pagesTypes of Reaction Reagents Conditions Organic Products Side ProductsFakhar LateefPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions Unit 2 ChemDocument4 pagesReactions Unit 2 Chemsmithsashay74Pas encore d'évaluation
- ALDEHYDE AND KETONE REACTIONSDocument4 pagesALDEHYDE AND KETONE REACTIONSBILL RUSSO100% (4)
- Done By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocument10 pagesDone By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim Papersdiejunqs sPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalyst Note: (PT, Ni, PD)Document8 pagesCatalyst Note: (PT, Ni, PD)Justin Victor AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDocument41 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDEEBANPas encore d'évaluation
- 51 Reactions From PDFDocument5 pages51 Reactions From PDFAbhinandan Sinha33% (3)
- Organic-Chemistry (As Level)Document8 pagesOrganic-Chemistry (As Level)Pirate HunterPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ReactionsDocument1 pageOrganic ReactionsMasrulIsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Organic Chemistry Reactions - CopyDocument5 pagesImportant Organic Chemistry Reactions - CopyK VIKASPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 2 5 Revision Guides Organic SynthesisDocument5 pages6 2 5 Revision Guides Organic SynthesisAddan AddanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry Synthesis IedxcelDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Synthesis IedxcelAliya Rahman100% (2)
- Substitution Reaction, Reflux Potassium /sodium Hydroxide (Koh /naoh)Document1 pageSubstitution Reaction, Reflux Potassium /sodium Hydroxide (Koh /naoh)Abed AymanPas encore d'évaluation
- As Chemistry Organic MindmapDocument1 pageAs Chemistry Organic MindmapDương Thị Ngọc HiềnPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing Halogen DerivativesDocument49 pagesPreparing Halogen DerivativesRenish AryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Major organic reactions and their mechanismsDocument9 pagesMajor organic reactions and their mechanismsRajendra ThamerciPas encore d'évaluation
- Named Reaction Cheatsheet For Organic Chemistry by MeritnationDocument2 pagesNamed Reaction Cheatsheet For Organic Chemistry by Meritnationhanushvenkat6Pas encore d'évaluation
- CIE A Level Chemistry Organic Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesCIE A Level Chemistry Organic Synthesis Noteszarfan sabriPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.14 Revision Guide Organic Synthesis AqaDocument7 pages3.14 Revision Guide Organic Synthesis AqaRutba SafdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Flow Chart MrSyed PDF NewDocument1 pageOrganic Flow Chart MrSyed PDF Newmuhammadim2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Carbonyl Compounds: Carboxylic Acids & EsterDocument28 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Carboxylic Acids & Esterrustam effendyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Recap SheetsDocument4 pagesChem Recap Sheetsv57kk67tqpPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthetic Routes (A Level) - Reaction Pathways Aliphatic CompoundsDocument6 pagesSynthetic Routes (A Level) - Reaction Pathways Aliphatic CompoundsJunior GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Organic SynthesisDocument8 pages12 Organic SynthesisDanyal AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthetic Routes for Organic ReactionsDocument8 pagesSynthetic Routes for Organic ReactionsPedro Moreno de SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsMuredzwa MuzendaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbonyl Compounds A-Level NotesDocument4 pagesCarbonyl Compounds A-Level Notesbumblebee9323Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids: Start With: Use: Product: NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 20: Carboxylic Acids: Start With: Use: Product: NotesElizabeth Jean BaumeisterPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkenes P2Document28 pagesAlkenes P2Nazil HaziqPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Organic Chemistry Synthesis Iedxcel PDFDocument10 pages20 Organic Chemistry Synthesis Iedxcel PDFMohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- NEO NEET 12 P1 CHE E Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. S13 211Document432 pagesNEO NEET 12 P1 CHE E Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. S13 211surajkumarmeher314Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ncea L3 Organic Chemistry NotesDocument14 pagesNcea L3 Organic Chemistry NoteszepphiagonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Summar PDFDocument7 pagesOrganic Summar PDFjackeducator49Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-level Organic Synthesis NotesDocument8 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-level Organic Synthesis NotesCornflake 25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oxidation, Reduction, HydrolysisDocument19 pagesOxidation, Reduction, HydrolysisTEJA SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- COLOUR INTENSITY AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF GROUP 17 ELEMENTSDocument21 pagesCOLOUR INTENSITY AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF GROUP 17 ELEMENTSGracia Blessina FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Hadepe Aldehid Dan KetonDocument31 pagesHadepe Aldehid Dan KetonBagusSatriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions and Interconversions of Organic Functional GroupsDocument3 pagesReactions and Interconversions of Organic Functional Groupsmichelsonyip100% (1)
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument16 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsTr Mazhar PunjabiPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument5 pages4.1.2 Carbonyl CompoundsFin BrickmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Namedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Document11 pagesNamedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Vishant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- Reaction List v002Document5 pagesReaction List v002cecil3414Pas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main Hydrocarbons Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument20 pagesJEE Main Hydrocarbons Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadpurple youPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Reagent List & FunctionsDocument2 pagesOrganic Reagent List & FunctionsHishq Dhiman79% (29)
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument17 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsSohamPas encore d'évaluation
- Named ReactionsDocument5 pagesNamed ReactionsJoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkenes: 1. From Dehydration of AlcoholDocument14 pagesAlkenes: 1. From Dehydration of AlcoholPratik TimalsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrocarbons NotesDocument13 pagesHydrocarbons NotesShivansh Pundir100% (1)
- Alkyl HalidesDocument16 pagesAlkyl HalidesGmd MrloPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic SynthesisDocument1 pageOrganic Synthesiszozoxo0% (1)
- Reaksi EliminasiDocument23 pagesReaksi EliminasiAde FadilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Aldehydes & Ketones MKA SIRDocument51 pagesAldehydes & Ketones MKA SIRcrawlskullPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971D'EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyzing Strategies in a Teen Sexting ArticleDocument2 pagesAnalyzing Strategies in a Teen Sexting ArticleVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- 1: Language Vs A Language Characteristics of LanguageDocument6 pages1: Language Vs A Language Characteristics of LanguageVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Essay On Language Variation and Attitudes in PygmalionDocument1 pageCommunication Essay On Language Variation and Attitudes in PygmalionVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Essay For Passage TwoDocument2 pagesPractice Essay For Passage TwoVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Answer For Module 3Document2 pagesSample Answer For Module 3edlinrochford853368% (22)
- Module 2 Essay QuestionsDocument4 pagesModule 2 Essay QuestionsVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggestions For Module 2 Essay in Communication Studies For ScribdDocument5 pagesSuggestions For Module 2 Essay in Communication Studies For Scribdedlinrochford853392% (50)
- Bridge TemplateDocument2 pagesBridge TemplateVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of AlcoholsDocument2 pagesReactions of AlcoholsVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 9 - Power of LensDocument2 pagesLab 9 - Power of LensVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Sign LanguageDocument8 pagesSign LanguageVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of AlcoholsDocument2 pagesReactions of AlcoholsVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 9 - Power of LensDocument2 pagesLab 9 - Power of LensVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- RRRDocument4 pagesRRRVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Stream Epiphany You CowardDocument1 pageStream Epiphany You CowardVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining a Suitable Indicator for Weak Acid-Strong Base TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermining a Suitable Indicator for Weak Acid-Strong Base TitrationVictoria Kairoo0% (1)
- Stream Boy With Luvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVDocument1 pageStream Boy With Luvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper Six BooklistDocument1 pageUpper Six BooklistVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- WertyuiopDocument1 pageWertyuiopVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Marking Criteria For Cs IaDocument5 pagesMarking Criteria For Cs IaVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Studies Language Techniques NotesDocument5 pagesCommunication Studies Language Techniques NotesMillian Hector100% (2)
- Management and MoneyDocument1 pageManagement and MoneyVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper Six BooklistDocument1 pageUpper Six BooklistVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Sailent Characteristics of English CreoleDocument11 pagesSailent Characteristics of English CreoleVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining a Suitable Indicator for Weak Acid-Strong Base TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermining a Suitable Indicator for Weak Acid-Strong Base TitrationVictoria Kairoo0% (1)
- Upper Six BooklistDocument1 pageUpper Six BooklistVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- WertyuiopDocument1 pageWertyuiopVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Mother Nature's Role in Beach PollutionDocument1 pageMother Nature's Role in Beach PollutionVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- XFGHJKLDocument1 pageXFGHJKLVictoria KairooPas encore d'évaluation
- Streeter-Phelps equation for predicting dissolved oxygen levelsDocument7 pagesStreeter-Phelps equation for predicting dissolved oxygen levelsAditya SheoranPas encore d'évaluation
- David Yu Zhang - Dynamic DNA Strand Displacement CircuitsDocument290 pagesDavid Yu Zhang - Dynamic DNA Strand Displacement CircuitsCogsmsPas encore d'évaluation
- Notice IchloreDocument228 pagesNotice IchloreHervé MunozPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeDocument45 pagesInterpretation of Batch Reactor Data: Chapter ThreeAnnisa RizqiaPas encore d'évaluation
- WPS MCC 001 PDFDocument1 pageWPS MCC 001 PDFNuwan RanaweeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Straight Objective Type: Part-IDocument4 pagesStraight Objective Type: Part-Iaditya aryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation of Heat and Mass BalanceDocument18 pagesCalculation of Heat and Mass BalanceJitendra Bhatia100% (3)
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFDocument49 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFabhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDocument4 pages01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDaniel Angelo MiradorPas encore d'évaluation
- Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient and Pipe Length CalculationDocument2 pagesOverall Heat Transfer Coefficient and Pipe Length CalculationCaleb FalcoteloPas encore d'évaluation
- Morbido Af-99100 v12 Msds enDocument14 pagesMorbido Af-99100 v12 Msds enjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Terluran GP-22: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)Document3 pagesTerluran GP-22: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)Mahdi VolgarPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics of Methanol Production From Natural GasDocument56 pagesEconomics of Methanol Production From Natural Gaspabel lema0% (1)
- AkzoNobel - Colloidal Silica For Adhesives BrochureDocument6 pagesAkzoNobel - Colloidal Silica For Adhesives BrochureCarlos GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- The Solar Still: Duncan KunzDocument5 pagesThe Solar Still: Duncan KunzNicu VisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pamphlet 152 - Edition 4 - April 2018Document29 pagesPamphlet 152 - Edition 4 - April 2018acidoanimalPas encore d'évaluation
- CONSTRUCTION CHEMISTRY ROOF WATERPROOFINGDocument2 pagesCONSTRUCTION CHEMISTRY ROOF WATERPROOFINGAmar WadoodPas encore d'évaluation
- B42 - Midterm10w CH 15-16-17-1Document7 pagesB42 - Midterm10w CH 15-16-17-1Siao Ryan YangPas encore d'évaluation
- Tensile Testing Basics Tips TrendsDocument5 pagesTensile Testing Basics Tips TrendsJonathan Elias MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- HSC 2016 March ChemistryDocument3 pagesHSC 2016 March ChemistryRohit GherePas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Evaluation of Various Cosmetic and Dental ProductDocument42 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Various Cosmetic and Dental ProductMarcelo Partes de OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Models of Molecular Shapes LabDocument3 pagesModels of Molecular Shapes LabSam Bisaria Student - GreenHopeHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Failure Analysis: Lucjan Witek, Micha Ł Sikora, Feliks Stachowicz, Tomasz TrzepiecinskiDocument10 pagesEngineering Failure Analysis: Lucjan Witek, Micha Ł Sikora, Feliks Stachowicz, Tomasz TrzepiecinskisobhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2.P.2.3 Manufacturing Process Development (92 Págs) PDFDocument92 pages3.2.P.2.3 Manufacturing Process Development (92 Págs) PDFaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Structure, Properties and Behavior of MatterDocument49 pagesChapter 2 Structure, Properties and Behavior of Matteraxeman1nPas encore d'évaluation
- DicyanineDocument4 pagesDicyanineHennie Namløs ThornePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Biomass Power Plant EfficiencyDocument12 pagesBasic Biomass Power Plant EfficiencyPichai ChaibamrungPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen IcsDocument16 pagesHydrogen IcsVũ PhươngPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Heat Transfer Model Research For The Improve-Ment of Continuous Casting Slab TemperatureDocument6 pagesMathematical Heat Transfer Model Research For The Improve-Ment of Continuous Casting Slab TemperatureSanjeev SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- EVA Test PropeetiesDocument37 pagesEVA Test Propeetiessimon sembiringPas encore d'évaluation