Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled 2
Transféré par
Rowena CanerCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Untitled 2
Transféré par
Rowena CanerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ONCOLOGY NURSING
JOANNE MARIE S. GARCIA, RN, MAN
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 1 of 176
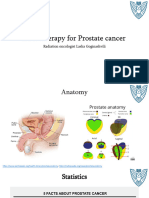
Oncology defined
• Branch of medicine that deals
with the study, detection,
treatment and management of
cancer and neoplasia
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 2 of 176
Cancer
• A disease resulting from the
uncontrolled growth of cells,
which causes malignant cellular
tumors.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 3 of 176
STATISTICAL BACKGROUND ON
MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY RATES
• In the Philippines, cancer ranks third
in leading causes of morbidity and
mortality after communicable
diseases and cardiovascular diseases
• In the Philippines, 75% of all
cancers occur after age 50 years,
and only about 3% occur at age 14
years and below
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 4 of 176
•If the current low cancer
prevention consciousness persists,
it is estimated that for every 1800
Filipinos, one will develop cancer
annually
•most Filipino cancer patients seek
medical advice only when
symptomatic or at advanced stages:
for every two new cancer cases
diagnosed annually, one will die
within the year
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 5 of 176
• The top cancer sites in the Philippines
include those cancers whose major causes
are known (where action can therefore be
taken for primary prevention), such as
cancers of the lung/larynx (anti-smoking
campaign), liver (vaccination against
hepatitis B virus), cervix (safe sex) and
colon/rectum/stomach (healthy diet).
Except for the liver, the top Philippine
cancer sites are also the top cancers
worldwide
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 6 of 176
Cancer Yearly Morbidity & Mortality by
Sex & Site
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 7 of 176
What Is a Tumor?
• A tumor is an abnormal lump or
growth of cells. When the cells in
the tumor are normal, it is
benign.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 8 of 176
Definition of Benign Tumors:
• Noncancerous. If the cells are
not cancerous, the tumor is
benign. It won't invade nearby
tissues or spread to other areasof the
body (metastasize)Benign
tumors usually don't recur once
removed, but if they do
it is usuallyin the same place.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 9 of 176
Definition of Malignant Tumors:
Cancerous
• A malignant tumor (cancerous
tumor) is one that is invasive and
can spread to other parts of the
body.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 10 of 176
Comparison of Benign & Malignant Tumors
Characteristic Benign malignant
Cell characteristic Well differentiated Undifferentiated little
Resemble normal cells resemblance on normal
cells
Local Invasion Grows by expansion Grows at the periphery,
Not infiltrate the infiltrate and destroys
surrounding tissue the surrounding tissue
Rate of growth Slow, may come to a Erratic & may be slow to
standstill or regress rapid, fast
Metastasis absent Access to blood,
lymphatics and other
areas
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 11 of 176
Benign Malignant
General localized Anemia, weakness, weight loss
effects
Tissue No tissue damage Extensive tissue damage
destructio
n
Ability to Does not usually cause Usually causes death
cause death
death
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 12 of 176
well-differentiated
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 13 of 176
poorly-differentiated
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 14 of 176
Proliferative Growth Patterns
• Cell proliferation
• is the process by which cells divide &
reproduce . In normal tissue, cell
proliferation is regulated so that the
number of cells actively dividing is
equal to the number of cells dying or
being shed. Abnormal cell
differentiation & growth results in an
abnormal mass of tissue, called
NEOPLASM
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 15 of 176
• NEOPLASIA means “new growth” &
refers to an abnormal mass of tissue
characterized by autonomous , excessive
& uncoordinated growth.
• Although they are not synonymous, the
terms neoplasm & tumor are often used
interchangeably . Neoplasms are
classified as BENIGN OR
MALIGNANT.
• Cancer is the common term for all
malignant tumors
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 16 of 176
Benign Growth Patterns
1. Hypertrophy
2. Hyperplasia
3. Metaplasia
• Ex. Metaplasia
• substitution of columnar epithelial cells of the
respiratory tract by squamous epithelial cells in
response to inhaled irritants such as cigarette
smoke. The process is reversible if the stimulus is
removed or metaplasia may prgress to dysplasia
if the stimulus persists.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 17 of 176
4. Dysplasia
• reversible if stimulus is removed.
• Dysplasia often precedes a tissue’s
becoming cancerous, & some forms
of dysplasia are as pre-cancerous
lesions”
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 18 of 176
COMMON TERMINOLOGIES
1. Oncogene – cancer genes that alter
normal genes
2. Proto-oncogenes – a normal gene
w/c when altered by mutation ,
becomes an oncogene. It regulates
programmed cell death (
apoptosis)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 19 of 176
3. Anaplasia – no resemblance to
tissues of origin
4. Mutation – occurs when a DNA gene
is damaged or changed as to alter the
genetic message carried by that gene.
5. Mutagen – is an agent of substance
that can bring about a permanent
alteration to the physical composition
of a DNA gene such that the genetic
message is changes
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 20 of 176
“Root words”
•Neo- new
•Plasia- growth
•Plasm- substance
•Trophy- size
•+Oma- tumor
•Statis- location
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 21 of 176
“Root words”
• A- none
• Ana- lack
• Hyper- excessive
• Meta- change
• Dys- bad, deranged
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 22 of 176
TUMOR GROWTH
• The rate of tissue growth in normal &
cancerous tissue depends on three
factors:
1. The duration of the cell cycle
2. The number of cells that are actively
dividing
3. Cell loss
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 23 of 176
Pathophysiology
• Cancer characterized by
neoplasms, abnormal growth of
new tissue.
• Neoplasms can be benign (not
progressive, and thus, favorable
for recovery) or malignant
(becoming progressively worse
and often resulting in death).
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 24 of 176
Neoplasia
Uncontrolled growth of Abnormal
cells
• 1. Benign
• 2. Malignant
• 3. Borderline
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 25 of 176
Characteristics of Neoplasia
• BENIGN
• Well-differentiated
• Slow growth
• Encapsulated
• Non-invasive
• Does NOT metastasize
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 26 of 176
Characteristics of Neoplasia
• MALIGNANT
• Undifferentiated
• Erratic and Uncontrolled Growth
• Expansive and Invasive
• Secretes abnormal proteins
• METASTASIZES
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 27 of 176
Nomenclature of Neoplasia
Tumor is named according to:
1. Parenchyma, Organ or Cell
• Hepatoma- liver
• Osteoma- bone
• Myoma- muscle
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 28 of 176
• Carcinoma – originates in the epithileal
tissue ex. Skin & lining of body tissue
(squamous cell Ca – surface epithelium)
• Adenocarcinoma – originates in
glandular tissue like in the breast &
prostate gland
• Sarcoma – originates in connective &
supportive tissue like in the bone &
nerves..
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 29 of 176
• Embryonal – originates in
embryonic tissue
• Lymphomas – originates n the
lymphatic system
• Leukemia – originates in the blood
forming organs ( RBC< WBC, bone
marrow) ( more on WBC)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 30 of 176
Nomenclature of Neoplasia
Tumor is named according to:
2. Pattern and Structure, either
GROSS or MICROSCOPIC
• Fluid-filled CYST
• Glandular ADENO
• Finger-like PAPILLO
• Stalk POLYP
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 31 of 176
NOMENCLATURE BENIGN TUMORS
• Suffix- “OMA” is used
• Adipose tissue- LipOMA
• Bone- osteOMA
• Muscle- myOMA
• Blood vessels- angiOMA
• Fibrous tissue- fibrOMA
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 32 of 176
MALIGNANT TUMOR
NOMENCLATURE
1. Glandular, Epithelial
• Use the suffix- “CARCINOMA”
• Pancreatic AdenoCarcinoma
• Squamos cell Carcinoma
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 33 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 34 of 176
MALIGNANT TUMOR
2. connective tissue origin
• Use the suffix “SARCOMA
• FibroSarcoma
• Myosarcoma
• AngioSarcoma
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 35 of 176
“PASAWAY”
1. “OMA” but Malignant
– HepatOMA, lymphOMA, gliOMA,
melanOMA
2. THREE germ layers
– “TERATOMA”
3. Non-neoplastic but “OMA”
– Choristoma
– Hematoma
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 36 of 176
REVIEW OF NORMAL CELL CYCLE
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 37 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 38 of 176
3 types of cells
1. PERMANENT cells- out of the cell cycle
• Neurons, cardiac muscle cell
2. STABLE cells- Dormant/Resting (G0)
• Liver, kidney
3. LABILE cells- continuously dividing
• GIT cells, Skin, endometrium , Blood
cells
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 39 of 176
Cell Cycle
- Is the coordinated sequence of events
resulting in duplication of the DNA &
division into 2 daughter cells. The 4
Phases of the cell cycle are:
1. G1 or Gap1– lasts from hours to days
or longer, RNA and protein synthesis
occurs in preparation for DNA
replication.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 40 of 176
2. S or Synthesis – lasts approximately 10 to 20
hours, DNA synthesis occurs in preparation for
division.
3. G2 or Gap2 – lasts 2 to 10 hours;DNA replication
ceases while RNA replication continues;
Premitotic phase
4. M or Mitosis –30 to 60 mins; cell division occurs;
G0 – resting phase, the cells perform all functions
other than those related to proliferation
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 41 of 176
• M Phase is further subdivided into 5 stages:
• Prophase
• Prometaphase
• Metaphase
• Anaphase
• Telophase
• = after mitosis, the daughter cells enter the
G1 phase & begin the cell reproductive
cycle again or redirect themselves into a
resting phase G0
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 42 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 43 of 176
CELL CYCLE VIDEO –
AMOEBA SISTERS
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 44 of 176
Cell cycle time
= is the time required for one tissue cell to
divide and reproduce two identical
daughter cells
• Doubling time
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 45 of 176
• It may take 10 years for a tumor to reach 1 cm in size.
In only another year , that same tumor may grow to 8
cm.Factors that affect doubling time are cell cycle time,
growth fraction, & cell loss by either cell death ,
differentiation or metastasis.
• A tumor is usually clinically undetectable until it has
doubled 30 times & contain more tham 1 billion cells.
At this point, it is approximately 1 cm in size & equals 1
gm in weight. With only 10 more doublings , the tumor
contains more than 1 trillion cells or weighs 1 kg which
is enough to cause DEATH.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 46 of 176
SUMMING IT ALL UP BY PROF DAVE
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 47 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 48 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
1. PHYSICAL AGENTS
• Radiation
• Exposure to irritants
• Exposure to sunlight
• Altitude, humidity
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 49 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
2. CHEMICAL AGENTS
• Smoking
• Dietary ingredients
• Drugs
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 50 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
3. Genetics and Family History
• Colon Cancer
• Premenopausal breast cancer
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 51 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
4. Dietary Habits
● Low-Fiber
● High-fat
● Processed foods
● Alcohol
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 52 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
5. Viruses and Bacteria
• DNA viruses- Hep, Herpes, EBV,
CMV, Papilloma Virus
• RNA Viruses- HIV, HTLCV
• Bacterium- H. pylori
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 53 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
6. Hormonal agents
• OCP especially estrogen
• DES
• HRT
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 54 of 176
ETIOLOGY OF CANCER
7. Immune Disease
• AIDS
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 55 of 176
CARCINOGENESIS
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 56 of 176
Carcinogenic Factors
• 1. Heredity
• 2. Hormonal Factors
• 3. Environmental Agents
– = Urban vs. Rural
– = Geographic Distribution
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 57 of 176
• 4. Radiation
• 5. Oncogenic Virus
• 6. Bacteria & Parasites
• 7. Immune System Deficiencies
• 8. Age – older individuals are prone to cancer
• 9. Occupation
• 10. Stress
11. Precancerous lesions
- Pigmented moles, burn scars, benign polyps, adenoma,
fibrocystic disease of the breast
12. Obesity
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 58 of 176
1. Heredity
Oncogenes ( hidden/repressed genetic code
for Ca that exist in all individuals
2. Hormones
Oral contraception or HRT, Inc. incidence of
hepatocellular, endometrial and breast Ca
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 59 of 176
3. Environmental Factors
A. Viral carcinogens
• Oncogenic viruses
• Epstein Bar virus, burkitt’s lymphoma,
nasopharyngeal Ca, non-Hodgkin and hodgkin’s
lymphoma; Hepa B v.
• Herpes simplex Type II, cytomegalovirus and HPV
type 16,18,31,33, = Cervix Ca
• HIV = kaposi sarcoma
• H. pylori = gastric Ca
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 60 of 176
B. Physical carcinogen
- Ultraviolent radiation, especially in fair
skinned blue or green eyed people, ( causes
skin Ca)
- Ex. Sun, tanning beds,germicidal lights
- Radiation from x-ray or nuclear machines (
dx & therapeutic x-rays)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 61 of 176
C. Chemical Agents
- 75% related to environment
- Tobacco smoking, single most lethal
carcinogen, 30% of Ca deaths, lung, head
and neck esophagus, bladder pancreas,
cervix ca
- chewing tobacco, ca of the oral cavity in
men younger than 40 years old
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 62 of 176
4. Industrial compounds
- Vinyl chloride (plastics, asbestos)
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (burning,
auto and truck emission)
- Fertilizers and weed killers
- Dyes, (analine dyes, hair dyes)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 63 of 176
4. Dietary Factors
- Carcinogenic
high fat low fiber diet,high animal fat intake,
alcohol, salt cured or smoked meats, high
caloric content, processed foods; preservatives,
contaminants, additives & nitrates
- Proactive
high fiber, Cruciferous vegetables ( cabbage,
broccoli, cauliflower, brussels, sprouts)
Carotenoids (carrots, tomatoes, spinach,
apricots, peaches, dark green and yellow
vegetables), vit E, C, zinc and selenium
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 64 of 176
5. Genetics
6. Age: Advancing age is a significant risk
factor
7. Immune Function:
a. Immunosuppressed individuals more
susceptible to cancer ( ex. Organ transplant
recipients taking immunosuppressive
medication; AIDS)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 65 of 176
Carcinogenesis
• 1. Initiation
- first step, chemicals, physical factors
and biologic agents, escape the
normal enzymatic mechanisms and
alter the genetic structure of the
cellular DNA
- normally these alterations are
reversed by DNA repair mechanism
or programmed cellular suicide
(apoptosis)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 66 of 176
• 2. Promotion
- Repeated exposure
- Causes expression of abnormal or mutant
genetic information
- Proto-oncogenes, “on switch”
- Ca suppressor genes, “turn off”
- P53 gene, a tumor suppressor gene
regulates whether cells repair or die after
DNA is damaged
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 67 of 176
CARCINOGEN
INITIATION
DNA repair
Bind to DNA
Normal Cell
Permanent DNA damage Cell Death
Cell Proliferation
PROMOTION
NEOPLASTIC CELLS
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 68 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 69 of 176
• 3. Progression
- Third step of cellular carcinogenesis
- The cellular changes formed during
initiation and promotion now exhibit
increased malignant behavior
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 70 of 176
What Do These Factors Have In
Common?
Fragments
Direct Damage & Deletions
To DNA
(e.g., CANCER
radiation)
Chemical Base Mutations
Mutagens & Substitutions
(e.g.,
pollutants, Membrane damage
additives,drugs causing internal mutagens
and hormones) Miscellaneous to form
Mutagens (dietary
fat and free radicals)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 71 of 176
Immune response
• T lymphocytes = recognize tumor associated
antigens, possesses cytotoxic abilities
• Lymphokines= capable of killing and damaging
Ca cells
• Macrophages = disrupt Ca cells
• B lymphocytes antibodies = defends the body
against malignant cells
• Natural killer cells = directly destroy Ca
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 72 of 176
ROUTES OF TUMOR SPREAD
Tumor spread throughout the body can occur
by direct extension or local invasion of
adjacent organs, metastases by
implantation or serosal seeding, &
metastases to distant organs by the lymph
or circulatory system.
Factors affecting tumor spread:
1. rate of cell growth
2. degree of differentiation
3. location
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 73 of 176
Metastatic Process
1. Local invasion – is the first step in metastatic process &
may occur as a function of direct tumor extension.
Mechanism important in local invasion includes:
A. Tumor growth
B. Mechanical pressure
C. Tumor-secreted enzymes
D. Decreased cellular adhesion
E. Increased motility
** Serosal seeding occurs when tumors, which have
invaded a body cavity from surrounding tissue, attach
to the surface of an organ within the cavity. (most often
the peritoneal cavity)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 74 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 75 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 76 of 176
Metastasis
• - is the spread of cancer cells from a primary tumor to
organs & distant sites in the body
• 1. Lymphatics
= the most common route
Ex. breast tumors, axillary, clavicular, and thoracic LN
Metastatic Cascade:
• Growth & progression of the primary tumor
- rapid growth of the primary tumor. Most tumors must reach 1
billion cells or 1 cm in size before metastasis is possible
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 77 of 176
• 2. Angiogenesis at the primary site – extensive vascularization is
necessary for the tumor to exceed 1 mm in diameter. The release of
angiogenic factors by tumor cells is necessary to stimulate new
capillary formation. The growth of the tumor & the rate of spread
are correlated with tumor vascularity.
• 3. Local Invasion – to reach blood vessels or lymphatics, tumor cells
must break down the tissue stroma & the basment membrane
• 4. Detachment & Embolization – millions of cells are shed into the
circulation daily from locally invasive cancer, but fewer than 0.01%
successfully survive to grow into a metastatic lesion. Once into the
circulation, tumor cells are vulnerable to destruction by the host
immune cells.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 78 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 79 of 176
• 5. Arrest in distant organ capillary beds –
• 6. Extravasation –
• 7. Proliferation -
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 80 of 176
PREVENTION, SCREENING &
DETECTION
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 81 of 176
Cancer Diagnosis & Staging
• Diagnosis:
1. Tumor Markers –
a. Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) can be found in prostate cancer
b. S-100 – can be found in melanoma cells
c. Thyroglobulin – protein made by the thyroid gland
d. Estrogen & Progesterone Receptors – elevated in breast CA
e. CA 15-3 & CA 27-29 – specific test for breast Ca
f. Carcinoembryonic Antigen ( CEA) & CA 19-9 – elevated in colorectal
cancer , condidered “golden standard” tumor marker for colorectal
Ca
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 82 of 176
• G. CA-125 -elevated in women with epithelial ovarian
cancer ( most common ovarian cancer )
• H. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin ( HCG) & Alpha-
Fetoprotein (AFP) – ovarian & testicular cancer
• I. Beta-2-Microglobulin (B2M) – elevated in persons with
multiple myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) &
some lymphomas as well as some types of kidney disease
• J. HER-2/neu - elevated in breast cancer. Used to predict
response to therapy
• K. CHROMOGRANIN A (CgA) – produced by
neuroendocrine tumors including carcinoid, neuroblastoma
& small cell lung cancers. It is the most sensitive tumor
markar for carcinoid tumors.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 83 of 176
Cancers in which markers
Tumor Markers maybe found
• 1. Carcinoembryonic Antigen • 1. Colon – rectal; breast; lungs
• CEA)
• 2. Alfa-feto protein ( AFP) • 2. Testicular; liver; lungs,
gastric; pancreatic; colon
• 3. Prostatic Acid Phosphatse
• 3. Metastatic prostate
• (PAP)
• 4. primary & metastatic prostate
• 4. Prostate – specific Antigen
• (PSA)
• 5. Ovarian cancer
• 5. Cancer Antigen 125 ( CA)
• 6. Pancreatic
• 6. Pancreatic Oncofetal
• 7. Medullary cancer of the
Antigen
thyroid
• 7. Calcitonin
• 8. throphoblastic tumor, germ
• 8. HCG cell; overy
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 84 of 176
• BRCa1- large gene located on chromosome 17 . BRCA1
may be responsible for as much as 90% of hereditary
breast & ovarian cancer. Persons carrying a BRCA1
mutation have up to 85% lifetime risk of developing breast
cancer, compared to a 12% risk in the general population ,
& a 40% lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer
compared to 2% risk in the general population.
• BRCA2 – is a tumor suppressor gene & is inherited in an
autosomal dominated fashion
• BRCA2 mutations are responsible for about 35% of all
inherited breast cancers . The lifetime risk of developing
breast cancer in a woman with a BRCA2 mutation is 50%
to 85%. However, the lifetime risk of developing ovarian
cnacer is 10% to 20% (lower than BRCA1)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 85 of 176
American Ca Society recommendation
Site Gender Age Evaluation Frequency
Breast Female >/-20 y/o Clinical Q 3 yrs
BE, Q month
BSE
>40 CBE Q year
BSE Q month
Mammog Q year
ram
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 86 of 176
Colon/rectum M/F >/- 50y/o Fecal occult Q year
blood starting at age
50
and Flexible Q 5 years
sigmoidoscop
y
or Colonoscopy Q 10 years
or Double Q 5 years
contrast
barium
enema
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 87 of 176
Prostate M >50 or < 50 if PSA and DRE Q year
high risk
Cervix F >18 or Pap smear Q year
younger if Pelvic exam
sexually
Endometr Women at active
menopause Report
ial menopaus
unexpected
e bleeding or
spotting
Cancer M/F >20-39 Other Ca Q 3 years
related check >40 types Q year
up
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 88 of 176
• B. Staging – determines
the size of the tumor
and the existence of
metastasis
• TNM Classification:
T – tumor size
N – degree of involvement
of lymph nodes
M – absence or presence of
distance metastasis
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 89 of 176
• Primary Tumor (T)
TX – primary tumor cannot be assessed
TO – no evidence of primary tumor
Tis – carcinoma in situ
T1,2,3,4 –ascending degrees of increasing size or
local extent of primary tumor
• Regional lymph nodes (N)
NX – regional LN cannot be evaluated
NO – no clinical evidence of regional LN
involvement
N1,2,3,4 – increasing involvement of LN
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 90 of 176
• Distant Metastasis (M)
MX – Distance metastasis cannot be assessed
MO – No evidence of distant metastasis
M1,2,3,4 –ascending degrees of distant
metastasis, including lymph nodes
• Grading
- Classification of tumor cells
- Grade I – IV, define the type of tissue which
the tumor originated
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 91 of 176
2. Histologic
a. Grade 1 - well differentiated
b. Grade 2 - Moderately
differentiated more abnormal
c. Grade 3 - Poorly
differentiated, Very abnormal
d. Grade 4 - Very immature
cells, undifferentiated ;
anaplastic hard to even
determine the tissue of origin
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 92 of 176
Staging:
• Normal T0, N0, M0
• Stage I T1, N0, M0
• Stage II T2, N1, M0
• Stage III T3, N2, M0
• Stage IV with metastasis
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 93 of 176
• Staging:
• Stage 0 : Carcinoma in
situ
• Stage I : tumor limited to
the tissue of origin;
localized tumor growth
• Stage II: limited local
spread
• Stage III: Extensive local
& regional spread
• Stage IV with
metastasis
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 94 of 176
Screening
a. Early detection and treatment are the
cornerstones of cancer survival
b. Educating the public about a healthy
lifestyle and early detection
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 95 of 176
Warning signs of Ca in Adults:
• C – change in bowel or bladder habits
• A – any sore that does not heal
• U – unusual bleeding or discharge
• U – unexplained sudden weight loss
• U – unexplained anemia
• T – thickening or lump
• I – indigestion or difficulty in swallowing
• O – obvious change in wart or mole
• N – nagging cough or hoarseness of voice
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 96 of 176
Cancer warning Signs in
Children:
• 1. Weight loss ( unexplained)
• 2. Anemia ( sudden )
• 3. Weakness
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 97 of 176
• 1.Marked change in bowel & bladder ; nausea &
vomiting for no apparent cause.
• 2. Generally run down condition and increased
susceptibility to infection
• 3. Spontaneous bleeding episodes like epistaxis ( failure
to stop bleeding in a normal time period)
• 4. Swelling or lump or masses anywhere in the child’s
body
• 5. Persistent crying or pain when there’s no apparent
cause
• 6. Any change in the size of a mole or birthmark
• 7. Unexpected stumbling or lack of coordination in the
child
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 98 of 176
Early Detection:
• Mammography
• Papanicolaou ‘s ( “Pap”) test
• Stools for occult blood
• Sigmoisdoscopy, Colonoscopy
• Breast self – examination
• Testicular self – examination
• Skin inspection
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 99 of 176
Health education
1. Reduce and avoid exposure to
known carcinogens
2. Eat a balanced diet of
vegetables, fruits and whole
grains, reducing fat and red
smoked and cured meat.
3. Limit alcohol beverages
4. Exercise regularly
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 100 of 176
5. Reduce stress and encourage adequate rest
and relaxation
6. Follow screening recommendations
7. Know the warning signs
8. Seek medical attention
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 101 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect Cancer:
A. Common Dx Cancer studies:
TUMOR MARKERS
➢ Breast
➢ Colon
➢ Lung
➢ Ovarian
➢ Testicular
➢ Prostate cancer
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 102 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
➢ Neurologic
➢ Pelvic
➢ Abdominal
➢ Thoracic cancers
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 103 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
➢ Neurologic
➢ Pelvic
➢ Abdominal
➢ Skeletal
➢ Thoracic cancers
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 104 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
FLOUROSCOPY
➢ Skeletal
➢ Lung
➢ GI
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 105 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
ULTRASONOGRAPHY
➢ Pelvic
➢ Abdominal
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 106 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
ENDOSCOPY
➢ Bronchial
➢ GI
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 107 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
NUCLEAR MEDICINE IMAGING
➢ Bone
➢ Liver
➢ Kidney
➢ Spleen
➢ Brain
➢ Thyroid
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 108 of 176
Diagnostic Aids used to detect
Cancer:
POSITRON EMISSION
TOMOGRAPHY
➢ Lung
➢ Colon
➢ Liver
➢ Pancreatic
➢ Head and Neck cancers
➢ Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin
Lymphoma and Melanoma
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 109 of 176
Diagnostic Surgery:
B. Biopsy – is the definitive means of diagnosing
cancer & provides histological proof of malignancy
- only true diagnosis of cancer
- it involves the surgical incision of a small piece of
tissue for microscopic examination
1. Excisional biopsy
- is the complete removal of the entire tumor
- provides the pathologist the cells and the entire tissue
- decreases the chance of seeding the tumor
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 110 of 176
2. Incisional Biopsy
- used if the tumor mass is too large to be
removed
- a wedge of tissue from the tumor is taken from
a larger mass
- This may be done for staging the disease level
3. Needle Biopsy
- Aspiration of cells
- done on suspicious masses that are easily
accessible
- fast, inexpensive and easily performed
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 111 of 176
4. Endoscopic biopsy – direct
biopsy through an endoscopy
of the area ( GIT, GUT,
respiratory ( bronchoscopy)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 112 of 176
Pre-procedure:
a. Depends on the location and type of
biopsy
b. May need to be on NPO if sedation or
contrast is used
c. Inform the client about the procedure
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 113 of 176
Post-procedure
a. Control bleeding
b. Monitor for infection
c. Manage pain
d. Inform the client how to
obtain the results
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 114 of 176
Client Reaction during Diagnoses
• Client will use coping strategies to his anxiety
level such as:
• Denial-
• Rational inquiry-seek more information
• Affect Reversal-make light of the situation
(laughing etc.)
• Mutuality-share concerns and talk with other
persons
• Suppression-conscious forgetting
• Displacement or redirection-do other things
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 115 of 176
Points to Remember
• Most clients fear of death upon
confirmation of Cancer
• Clients usually ignored cardinal signs of
Cancer
• Most often cancer is detected during
routine exam
• Questions that need to be answered:
Example (Is the disease curable or not?)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 116 of 176
Nursing Diagnosis
• Ineffective coping
• Anticipatory grieving
• Disturbed body image
• Fatigue
• Impaired elimination
• Hopelessness
• Impaired oral mucous membrane
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 117 of 176
• Nausea
• Impaired nutrition less than body
requirements
• acute pain
• Impaired skin integrity
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 118 of 176
Signs and symptoms of malignant neoplasia:
• Proliferation of Ca cells
➢ Pressure
➢ Obstruction
➢ Pain ( late sign of Ca )
- Pressure on nerve endings
- Distention of organs/vessels
- Lack of O2 to tissue and organ
- Release of pain mediators
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 119 of 176
➢ Pleural effusion and ascites
➢ Ulceration and necrosis
- As tumor erodes BV and pressure on tissue
causes ischemia, tissue damage, bleeding
and infection
➢ Vascular thrombosis, Embolus,
Thrombophlebitis
➢ Tumors tends to produce abnormal
coagulation factors
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 120 of 176
• Paraneoplastic Syndrome:
1. Anemia
- Ca cells produces chemicals that interfere
with rbc production
- Iron uptake is greater in the tumor than that
deposited in the liver
- Blood loss from bleeding
2. Hypercalcemia
- Increases and accelerates bone breakdown
and release of Calcium
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 121 of 176
3. Anorexia –
-Final outcome of unrestrained Ca growth
-Ca deprive normal cells of nutrition
-Protein depletion, serum albumin decreases
-Tumors take up Na
-Act in the satiety center causing anorexia
-Taste sensation diminishes
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 122 of 176
• Take pain seriously, recognizing that only the
person in pain knows how it feels.
• Provide information and resources for pain
control.
• Communicate with genuineness, accurate empathy,
and nonpossessive warmth.
• Encourage sufferers to share their feelings and
network with other survivors.
• Respect culture norms and wishes of sufferers,
maximizing their control
• Encourage release of energy through joy-
producing activities.
• Monitor pain medications, effectiveness, and
adverse effects
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 123 of 176
NURSING INTERVENTION:
• Take pain seriously, recognizing that only the person in pain
knows how it feels.
• Provide information and resources for pain control.
• Communicate with genuineness, accurate empathy, and
nonpossessive warmth.
• Encourage sufferers to share their feelings and network with
other survivors.
• Respect culture norms and wishes of sufferers, maximizing
their control
• Encourage release of energy through joy-producing activities.
• Monitor pain medications, effectiveness, and adverse effects
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 124 of 176
MANAGEMENT OF CANCER
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 125 of 176
Goals of Therapy:
1. Curative :
- Patients will be disease free & live a normal life
expectancy
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 126 of 176
2. Control surgery
• Is a “ debulking procedure” that
consists of removing part of the
tumor.
• Surgery decreases the number of
cancer cells & increases the chance
that other therapies will be successful
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 127 of 176
3. Palliative Surgery
- when cure is not possible, the goal of
treatment is to make the patient as
comfortable as possible and to promote a
satisfying and productive life for as long as
possible
- Performed to improve quality of life during
the survival time
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 128 of 176
4. Prophylactic Surgery
- performed in clients with an existing
premalignant condition or a known family
history that strongly predisposes the person to
the development of cancer
- Removal of non-vital structures that are likely
to develop Ca
- An attempt is made to remove the tissue organ
at risk & thus prevent the development of Ca
-
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 129 of 176
Therapeutic Modalities for Cancer
• 1. Surgery
• 2. Radiation Therapy
• 3. Chemotherapy
• 4. Immunotherapy
• 5. Bone Marrow Transplantation
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 130 of 176
1. Surgery
= The ideal and most frequently used
= most successful single therapy if cancer has not yet spread
= very often performed on an OPD or short stay basis
a.Diagnostic = primarily for the purpose of obtaining tissue
sample for diagnostic purposes & to determine methods of
treatment
b.Staging = performed to determine the extent of cancer
presence & location of metastatic lesions.
c.Curative =removal of cancer that are blocalized to the area
of origin; extent of ressection is determined by the type of
tumor
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 131 of 176
•D. Reconstructive = restoration of the
patient’s form, function & appearance of
the radical surgery for cancer
•E. Preventive =n for patient’s that are in
a high risk category, certain surgical
procedures that may prevent further
development of cancer
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 132 of 176
Tissue Examination:
• Following excision , a frozen section or a permanent paraffin section is
prepared to examine the specimen
• The advantage of the frozen section is the speed with which the section can
be prepared & the dx made because only minutes are required for this test
• Permanent paraffin section takes about 24 hours however, it provides
clearer details than does the frozen section
• INTERVENTION: 1. The procedure is usually done in an out patient
surgical setting
• Obtain an informed consent
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 133 of 176
CAUSES OF PAIN IN CANCER:
•1. Bone destruction
•2. Obstruction of an organ
•3. Compression of peripheral nerves
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 134 of 176
2. Radiation Therapy
• Used to control malignant disease when a
tumor cannot be removed surgically
• Destroys the cell’s ability to reproduce by
damaging the cellular DNA
• A radiosensitive tumor is one that can be
destroyed by a dose of radiation that still
allows for cell regeneration in the normal
tissue
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 135 of 176
• Uses ionizing radiation to kill or limit
the growth of cancer cells. May be
internal or external
• Effect cannot be limited to cancer cells
only
• Cells that are rapidly reproducing are
vulnerable to the effects of radiation
• Normal healthy cells recover more
effectively from the damage caused by
radiation
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 136 of 176
• is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of
radiation to kill cancer cells and stop them
from spreading. At low doses, radiation is
used as an x-ray to see inside your body
and take pictures, such as x-rays of your
teeth or broken bones.
• Radiation use in cancer treatment works in
much the same way, except that it is given
at higher doses.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 137 of 176
Radiation therapy is used to:
•Treat cancer. Radiation can be used to cure, stop,
or slow the growth of cancer.
•Reduce symptoms. When a cure is not possible,
radiation may be used to shrink cancer tumors in
order to reduce pressure. Radiation therapy used in
this way can treat problems such as pain, or it can
prevent problems such as blindness or loss of bowel
and bladder control.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 138 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 139 of 176
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 140 of 176
• Cells are most vulnerable to radiation during
DNA synthesis and mitosis
• Most sensitive are those body tissue that
undergo frequent cell division. (BM,
Lymphatic, GIT, gonads)
• Tumors that are well oxygenated are more
sensitive to radiation
• Cells most sensitive during M and G2 phase
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 141 of 176
Radiosensitivity
• Highly sensitive
- ovaries, testes, bone marrow,
blood, intestines
• Low sensitivity
- muscle, brain, spinal cord
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 142 of 176
Types:
A. Teletherapy (External Beam radiation)
- x-rays are used to destroy cancerous cells at the
skin surface or deeper
- radiation source is outside the body ( Cobalt)
- radiation source is directed toward the area
- Client is not radioactive during treatment
- Simulation – X-ray or Ct planning session to
identify the field which delivers maximum
radiation to the tumor and minimal to normal
tissue. Involves skin markings
- Administered in fractions of the full dose, 5 days a
week for 4-6 weeks
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 143 of 176
Client Education: Teletheraphy
* Wash area with water or mild soap & water using the hand
rather than a washcloth; rinse the soap thoroughly, & pat
dry with a soft towel or cloth
*Do NOT remove the radiation markings from the skin
* Use no powders, ointments, lotions or creams on the area
unless prescribed
* Wear soft clothing over the area, avoiding belts, buckles,
straps or any clothing that binds or rubs the skin
* Avoid sun & heat exposure
* Monitor for moist desquamation (weeping of the skin). If
moist desquamation occurs, cleanse the area with warm
water & pat dry, apply antibiotic ointment or steroid
cream as prescribed & expose the site to air
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 144 of 176
B. Brachytherapy ( Implant Therapy) (Internal)
( closed therapy) Sealed source Therapy)
1.The radiation source comes into direct,
continuous contact with tumor tissues for a
specific time.
2. The radiation source is within the client; for a
period of time, the client emits radiation & can
pose a hazard
3. Brachytherapy includes an unsealed source or a
sealed source of radiation
- Client is radioactive only when implant is in place
- plan cares efficiently to minimize nurses, exposure
to implant, use shielding, wear a film badge and
maintain safe distance.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 145 of 176
3. Unsealed radiation source ( Isotope or
radiopharmaceutical )
A. Administration is via the oral or IV route or by
instillation into body cavities
B. The source is not confined completely to one
bodily area, & it enters body fluids & eventually is
eliminated via various excreta, which are radioactive
& harmful to others; most of the source is
eliminated from the body within 48 hours, then
neither the client nor the excreta are radioactive or
harmful.
C. has a very short half life & because it is not
sealed, the body fluids become contaminated
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 146 of 176
Sealed radiation source
A. A sealed, temporary or permanent radiation
source (solid implant ) is implanted within the
tumor target tissues or into a body cavity
B. The client emits radiation while the implant is
in place, but the excreta are not radioactive.
C. this delivers a large amount of radiation to a
small area of the body
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 147 of 176
Removal of sealed radiation sources:
A. The client is no longer radioactive
B. Inform the client that sexual partners cannot “catch”
cancer
C. Inform the female client that she may resume sexual
intercourse after 7 to 10 days , if the implant was cervical or
vaginal
D. Provide a povidone –iodine douche if prescribed, if the
implant was placed in the cervix
E. Administer a Fleet enema if prescribed
F. Advise the client who had a cervical or vaginal implant to
notify the physician if nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, frequent
urination , vaginal or rectal bleeding, hematuria, foul-
smelling vaginal discharge, abdominal pain or distention, or
a fever occurs.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 148 of 176
Care of the Client with a Sealed Radiation
Source ( Internal Radiation )
* Place the client in a private room with a private bath
* Place a caution sign on the client’s door
A lead container & tongs should be present in the client’s
room
* Organize nursing tasks to minimize exposure to the
radiation source
* Nursing assignments to a client with a radiation
implant should be rotated
* Limit time to 30 minutes per care provider per shift
* Wear a dosimeter film badge to measure radiation
exposure
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 149 of 176
*Inform all people coming in contact with the
patient the specific precautions necessary.
Wear a lead shield to reduce the transmission of
radiation
* A nurse should never care for more than one
client with a radiation implant at one time
* Do not allow a pregnant nurse to care for the
client
* Do not allow children under the age of 16 or a
pregnant woman to visit the client
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 150 of 176
* Limit visitors to 30 minutes per day;
visitors should be at least 6 feet from the
source
* Save bed linens & dressings until the
source is removed, then dispose of in the
usual manner
* Other equipment can be removed from the
room at any time
*Examples of the type of radiation therapy
include uterine implant, testicular
implant; implant used in head & neck
tumor.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 151 of 176
* Utilize badges or radiation monitors for caregivers having
direct contact with the patient.
* List on the chart:
1. Type of radiation
2. Time inserted & where
3. Anticipated removal time
4. Specific precaution for the type of radiation
– Private room & bath
– Plan care so that minimal time is spent in the room
– When prolonged care is required, wear a lead shield or
apron
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 152 of 176
• Wear a monitoring device to measure
exposure
• Mark on the room & in the kardex that
pregnant women, infants & young
children should not come in contact
with the patient during treatment
• Check all linens & materials removed
from the bed for the presence of
foreign bodies that could be a source of
radioactivity
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 153 of 176
• Keep long handled forcep & lead
container in the room of a patient
with an implant in place
• Do not wash off marks placed on
patient’s body for the purpose of
identifying area for external
radiation
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 154 of 176
A Dislodged Radiation Source
*Do not touch a dislodged radiation source with
bare hands
* If the radiation source dislodges, use long
handled forceps to place the source in the lead
container kept in the client’s room, & call the
radiation therapist & the physician
* If unable to locate the radiation source, bar
visitors & notify the radiation therapist .
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 155 of 176
-Body fluids of clients treated with systemic
radioactive iodine are radioactive
-( flush toilet 3x)
- fluids of client with implants are not
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 156 of 176
4. Systemic Radiation Therapy
= radiation source is absorbed
into the circulation & travels
throughout the body
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 157 of 176
Care of patients receiving Systemic
Radiation Therapy
* Systematically administered radionuclitides (
radioisotope) may cause radioactive body secretions.
> wear gloves when handling patient’s body
secretions
> It may be necessary to have the linens & trash
cgecked for radioactivity prior to removing them
from the room
> keep linens & trash in room until they have been
checked for radioactivity by radiation therapy
deparment
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 158 of 176
Radiation Safety
Distance - the greater the distance the lesser
the exposure ( 6 feet)
Time - the less time spent close to radiation the
less exposure (max of 30 min per shift)
Shielding - use lead aprons and gloves
Standards - kept as low as reasonably
achievable
Monitoring device - film badge (measure the
whole exposure of the nurse)
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 159 of 176
Adverse Effects of Radiation Therapy
A. Skin: Itching, redness, burning, sloughing
1.Keep skin free of foreign substance
2.Avoid use of medicated solutions
3.Avoid pressure, trauma, infection
4.Avoid exposure to heat, cold or sunlight
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 160 of 176
B. GI Disturbances
A. Anorexia, Nausea & Vomiting
1.Provide small, attractive feedings
2.Avoid extremes of temperatures
3.Administer antiemetics before meals
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 161 of 176
c. Diarrhea
• Encourage low residue, bland,
high protein foods
• Provide good perineal hygine
• Monitor electrolytes, Na,K,Cl
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 162 of 176
d. Anemia. Leukopenia,
thrombocytopenia
• Isolate patient
• provide frequent rest period
• Encourage high protein diet
• Assess for bleeding
• Monitor lab results CBC, WBC,
Plt
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 163 of 176
Effects of Radiation Therapy in
Pediatrics:
Long Term of treatment in a child:
1. Impaired growth & development especially from
radiation to growth center of bone during early
childhood & adolesce3nce.
2. Damage to CNS in terms of psychological,
neurologic & intellectual activity.
3. Gonadal aberration including reproductive ,
hormonal , genetic & teratogenic effects.
Decrease fertility in adolescents.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 164 of 176
4. Disturbances to other organs including
pneumonitis, pericarditis, pleurisy,
hypothyroididm, (cretinism or dwarfism)
cystitis
5. Development of a secondary malignancy
especially after a successful treatment of
acute lymphocytic leukemia ( ALL – most
common type of cancer among children) ;
lymphomas, Wilm’s tumor , nephroblastoma,
retinoblastoma..
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 165 of 176
CHEMOTHERAPY
• Kills or inhibits the reproduction of neoplastic cells & also
attacks & kill normal cells
• The effects are systemic: chemotherapy affects healthy
cells & cancerous cells
• Normal cells most profoundly affected include those of the
skin, hair & lining of the GI tract, spermatocytes, &
hematopoietic cells
• Cell cycle phase –specific medications affect cells only
during a certain phase of the reproductive cycle, and cell
cycle phase non- specific medications affect cells in any
phase of the reproductive cycle
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 166 of 176
• Usually several medications are used in
combination ( combination therapy) to
increase the therapeutic response.
• Combination chemotherapy is planned to
avoid prescribing medications during the
time in which bone marrow activity &
WBC counts are at their lowest or near
the same time to minimize
immunosuppression.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 167 of 176
• Antineoplastic therapy maybe combined with
other treatments, such as surgery and radiation.
• The preferred route of administration is
intravenously
• Side effects include alopecia, N & V, mucositis,
skin changes, immunosuppression, anemia &
thrombocytopenia.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 168 of 176
Goal:
• Destroy all malignant cells
without excessive destruction of
normal cell
• Control growth of tumor when
cure is not possible
• Note: all rapid dividing cells
(GI mucosa, hair follicles and
bone marrow) are susceptible
to the action of chemo and
radiation therapy
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 169 of 176
Reasons for combining Drugs:
• Synergy-two or more agents works
together to enhance the effect of one
another
• Adjuvant-an additional treatment
• ’s malignant cell destructions, ’s
the SE
• Principle of MDT may be instituted
to avoid and prevent the SE
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 170 of 176
Chemotherapy may be given in many
ways:
1. INJECTION = the chemotherapy is
given by a shot in a muscle in your
arm, thigh, or hip or right under
the skin in the fatty part of your
arm, leg or belly
2. Intra-arterial ( IA) = the
chemotherapy goes directly into the
artery that is feeding the cancer
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 171 of 176
3. Intraperitoneal (IP ) The chemotherapy goes directly
into the peritoneal cavity the area that contains organs
such as your intestines, stomach, liver, and ovaries).
4. Intravenous (IV) = . The chemotherapy goes directly
into a vein.
5. Topically. The chemotherapy comes in a cream that you
rub onto your skin.
6. Orally. The chemotherapy comes in pills, capsules, or
liquids that you swallow.
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 172 of 176
Contraindication
• Infection
• Recent surgery
• Impaired renal or hepatic
function
• Recent radiation therapy
• Pregnancy
• Bone marrow depression
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 173 of 176
• Extravasation –
cause tissue necrosis
and damage to
tendons, nerves and
blood vessels
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 174 of 176
• TOXICITY – nauseas and
vomiting usually last about 1
week
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 175 of 176
ANTI NEOPLASTIC
https://cdn.fbsbx.com/v/t59.2708-21/46820680_209603409951644_77041558183665…_nc_ht=cdn.fbsbx.com&oh=6a23971fd7e7d1667dd968a2b0f2016e&oe=5C01E758&dl=1 29/11/2018, 8G00 PM
Page 176 of 176
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GlioblastomaDocument10 pagesGlioblastomaapi-451330223Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics of Karyotyping - Nandini IB BiologyDocument2 pagesEthics of Karyotyping - Nandini IB BiologySummayya Kanwal AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphoema v17Document78 pagesLymphoema v17CherryPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast Cancer July18ECDocument88 pagesBreast Cancer July18ECCherryPas encore d'évaluation
- Penile CancerDocument18 pagesPenile CancerSmiley QueenPas encore d'évaluation
- Report Adil'12Document6 pagesReport Adil'12adilhusain1710465482Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell Cycle and Cancer 2011Document28 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Cancer 2011Rajesh BalakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Technology For Cancer TreatmentDocument3 pagesNuclear Technology For Cancer TreatmentWaqas AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Acrr 2018Document28 pagesAcrr 2018Aliyan ZafarPas encore d'évaluation
- HPIM 20 OncologyDocument244 pagesHPIM 20 OncologyapeachPas encore d'évaluation
- CeleBritys4africA Ebook Final VersionDocument16 pagesCeleBritys4africA Ebook Final VersionceleBritys4africAPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL 1301 Discussion Assignment Unit 4 16Document2 pagesBIOL 1301 Discussion Assignment Unit 4 16Jobayer BsmrmuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer in Africa: Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention Strategies - Too Little, Too LateD'EverandCancer in Africa: Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention Strategies - Too Little, Too LatePas encore d'évaluation
- Decoding Cancer - Lesson 1 - Interactive Lesson - July - 2018Document46 pagesDecoding Cancer - Lesson 1 - Interactive Lesson - July - 2018NisrinPas encore d'évaluation
- The Surgical Oncology Review: For the Absite and BoardsD'EverandThe Surgical Oncology Review: For the Absite and BoardsPas encore d'évaluation
- A Foe With Many FacesDocument2 pagesA Foe With Many FacesJuan TamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer Detection by Machine LearningDocument7 pagesCancer Detection by Machine Learningsiddub1721Pas encore d'évaluation
- Detection of VEGF 2 Gene Polymorphism in Renal Cell CancerDocument22 pagesDetection of VEGF 2 Gene Polymorphism in Renal Cell CancerDebabrata SamantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sourav Bio3Document7 pagesSourav Bio3manojoram709Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prostate Cancer Treatment in India Detailed InformationDocument3 pagesProstate Cancer Treatment in India Detailed InformationinadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer Surge Effective Solutions For RemissionDocument25 pagesCancer Surge Effective Solutions For RemissionTina Kroger100% (1)
- SSC SkinDocument16 pagesSSC SkinNandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Code: Cbp102: Epidemiology of Breast Cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)Document17 pagesCourse Code: Cbp102: Epidemiology of Breast Cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)Laban MurgorPas encore d'évaluation
- Prostate CancerDocument30 pagesProstate CancerMetal GearPas encore d'évaluation
- THC Cures CancerDocument3 pagesTHC Cures CancerAlexander ValsamisPas encore d'évaluation
- Phyllodes Tumours:: Borderline Malignant and MalignantDocument7 pagesPhyllodes Tumours:: Borderline Malignant and Malignantreeves_coolPas encore d'évaluation
- Wise 2018Document1 pageWise 2018investigadora1Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCR 2017 MoH Final Report Nov 2018 10.12.2018Document33 pagesNCR 2017 MoH Final Report Nov 2018 10.12.2018Veden SoobenPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Cancer Center in KMUHDocument36 pagesIntroduction of Cancer Center in KMUHSantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Cancer Center in KMUHDocument36 pagesIntroduction of Cancer Center in KMUHSantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ihc ColecchiaDocument32 pagesIhc ColecchiaDima PathPas encore d'évaluation
- The Global Cancer Burden 2018: Key findings and implications for cancer prevention and controlDocument70 pagesThe Global Cancer Burden 2018: Key findings and implications for cancer prevention and controlalam25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer: An Overview: Academic Journal of Cancer Research January 2015Document10 pagesCancer: An Overview: Academic Journal of Cancer Research January 2015Thesis Writing Services and Research InstitutePas encore d'évaluation
- Skin CancerDocument9 pagesSkin Cancerapi-550307464Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Articulo de MedicinaDocument10 pages1 Articulo de MedicinaLucía LlanquileoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cáncer:overviewDocument10 pagesCáncer:overviewkashirokoshiroPas encore d'évaluation
- CA A Cancer J Clinicians - 2018 - Bray - Global Cancer Statistics 2018 GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and MortalityDocument31 pagesCA A Cancer J Clinicians - 2018 - Bray - Global Cancer Statistics 2018 GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and MortalityAngelia Adinda AnggonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone - Cancer - First Report-Abstrat & IntroductionDocument3 pagesBone - Cancer - First Report-Abstrat & Introductionharish gowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- BREAST CANCER PREDICTION MODELDocument3 pagesBREAST CANCER PREDICTION MODELShreya PandurangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternative Cancer Treatment: Sergey Kalitenko MD Workshop Series - For More Go ToDocument33 pagesAlternative Cancer Treatment: Sergey Kalitenko MD Workshop Series - For More Go ToSergey kalitenko100% (1)
- Bollinger Sneaky Cancer SymptomsDocument19 pagesBollinger Sneaky Cancer SymptomsDumitru Tocan100% (1)
- Prostate Cancer in TripuraDocument13 pagesProstate Cancer in TripuraSnehendu BhowmikPas encore d'évaluation
- © 2010 Mcgraw-Hill Companies. All Rights ReservedDocument36 pages© 2010 Mcgraw-Hill Companies. All Rights ReservedThalia SandersPas encore d'évaluation
- understanding-prostate-cancer-booklet-informationDocument76 pagesunderstanding-prostate-cancer-booklet-informationrexmarteston01Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To CancerDocument42 pagesAn Introduction To CancerAmjadRashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Jia W H - Trends in IncidenceDocument8 pagesJia W H - Trends in IncidencemecyalvindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automated Leukemia Detection by Using Contour Signature MethodDocument8 pagesAutomated Leukemia Detection by Using Contour Signature MethodIJAFRCPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical and Breast Cancer ScreeningDocument12 pagesCervical and Breast Cancer ScreeningIndonesian Journal of CancerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung Cancer Pathology and DiagnosisDocument28 pagesLung Cancer Pathology and DiagnosismadvincyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.6 Cyclins and CancerDocument30 pages1.6 Cyclins and Canceralina bluePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerDocument24 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerAthiya Zainab100% (1)
- Male Genital Mutilation Fact SheetDocument2 pagesMale Genital Mutilation Fact SheetMatthew Hess100% (1)
- Cancer Research AssignmentDocument5 pagesCancer Research Assignmentapi-212901753Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neoplasia - Pathology SattarDocument3 pagesNeoplasia - Pathology SattarGursimranKaurSehgalPas encore d'évaluation
- UrooncologyDocument49 pagesUrooncologyanwar jabariPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Simple Steps To Prevent Cancer NewsmaxDocument9 pages7 Simple Steps To Prevent Cancer Newsmaxfabrignani@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Male Breast Cancer Research PaperDocument5 pagesMale Breast Cancer Research Paperj0b0lovegim3100% (1)
- Cancer CareDocument84 pagesCancer Careakoeljames8543Pas encore d'évaluation
- KLYuChI 2 Kurs-Arakin PDFDocument159 pagesKLYuChI 2 Kurs-Arakin PDFSayfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Interim Public Health Operational Guidelines For Amoebiasis: (Entamoeba Histolytica)Document34 pagesInterim Public Health Operational Guidelines For Amoebiasis: (Entamoeba Histolytica)QworldPas encore d'évaluation
- Catheterization ChecklistDocument3 pagesCatheterization ChecklistAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Fibre Cement Slates Fixing GuideDocument26 pagesFibre Cement Slates Fixing GuideMuhammad HafizuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Colegiul National SF - Sava Catedra de Limba Engleza Prof. Speteanu Alexandra GabrielaDocument3 pagesColegiul National SF - Sava Catedra de Limba Engleza Prof. Speteanu Alexandra Gabrielaannem29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Two Chinese Food Therapies To Prevent UTIDocument2 pagesTwo Chinese Food Therapies To Prevent UTIvivianPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Employee Attitudes and Well-BeingDocument2 pagesManaging Employee Attitudes and Well-BeingJayChristian QuimsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Session Evaluation Form InstructionsDocument8 pagesTraining Session Evaluation Form Instructionsaaronjules100% (1)
- ORA.007 Pharmaceutical Microbiology ManualDocument92 pagesORA.007 Pharmaceutical Microbiology ManualNindyPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Mental Health and Stress Online CourseDocument2 pagesManaging Mental Health and Stress Online CourseDakota624Pas encore d'évaluation
- Umesh Pharma 1507821908 - 365Document22 pagesUmesh Pharma 1507821908 - 365Training and PlacementPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholera FinalDocument57 pagesCholera FinalBinayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paragraph TypesDocument4 pagesParagraph TypesZayb EhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- APSACS Summer Holiday Homework Guide Warm Region 2023 24 Dated 02 June 2023 - CompressedDocument17 pagesAPSACS Summer Holiday Homework Guide Warm Region 2023 24 Dated 02 June 2023 - CompressedGaming 7HawkPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Abbreviations, Acronyms and Symbols QuizDocument3 pagesNursing Abbreviations, Acronyms and Symbols QuizAjeng Citra S SeptiyantriPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-1-2021 Response To LandlordDocument2 pages2-1-2021 Response To LandlordJessica SwarnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition of Sexual Abuse of ChildrenDocument2 pagesDefinition of Sexual Abuse of ChildrenRadhika RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- Mary Law PEO Model PDFDocument15 pagesMary Law PEO Model PDFalepati29Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Star News November 20, 2014Document37 pagesThe Star News November 20, 2014The Star NewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Water QualityDocument41 pagesWater QualityPaschal MazikuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of EU Regulatory Affairs, Fifth Edition Comparative MatrixDocument42 pagesFundamentals of EU Regulatory Affairs, Fifth Edition Comparative Matrixasifmdzakaria57% (7)
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- People Pleasing Patterns Are Learned When Needs Are Not Met PDFDocument10 pagesPeople Pleasing Patterns Are Learned When Needs Are Not Met PDFPamela RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sma - Ma Bahasa Inggris Ipa - Ips - Bahasa SecuredDocument39 pagesSma - Ma Bahasa Inggris Ipa - Ips - Bahasa SecuredJohnson LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Profile of Hoarseness of Voice: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional StudyDocument5 pagesClinical Profile of Hoarseness of Voice: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Studynurul atika havizPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast Feeding Final ProposalDocument16 pagesBreast Feeding Final ProposalDeborah BoahemaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manuale Advantage 350Document50 pagesManuale Advantage 350PaulmankePas encore d'évaluation
- TB Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesTB Teaching PlanTrisha Fae Loyola Balagot100% (1)
- Admin of Meds Prof GuidanceDocument8 pagesAdmin of Meds Prof GuidanceStacyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 18Document36 pagesChapter 18hussein harbPas encore d'évaluation