Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
All About HIV (TX & OIs) - Sheet1
Transféré par
Anisha Gill0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
29 vues3 pagesHiv
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentHiv
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
29 vues3 pagesAll About HIV (TX & OIs) - Sheet1
Transféré par
Anisha GillHiv
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
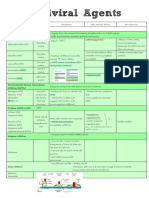
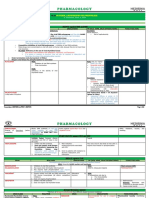
GROUP OF ANTI-VIRAL MOA DRUGS COMMENTS PHARMACOKINETICS A/E
NRTIs -prodrugs: phosphorylation by intracellular kinases-->active triphosphate
Abacavir
forms (ABC) -add w 3TC -good oral bioavailibility -hypersensitivity rx
-compete for HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) -slowly develop resistance -renal elimonation
-avoid use w d4T: overlapping mitochondrial toxicities-->
-inhibit its DNA polymerisation Didanosine (ddl) peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis & hyperlactatemia -mitochondrial toxicity & myopathy
-chain terminator in growing viral DNA Emtricitabine (FTC) -activity vs HBV -C/I in children & pregnant, renal/hepatic dysfx pt
Lamivudine (3TC) -exacerbation of HBV -mild A/E: gut disturbances, headache, fatigue
-avoid use w FTC
-synergistic effect w ZDV&d4T
-avoid use w ZDF: d/t they antagonize each other effect
Stavudine (d4T) on HIV-1 -mitochondrial toxicity & myopathy
-fat atrophy (lipoatrophy)
Tenofavir (TDF) -add w FTC -nephrotoxicity
-reduce renal elimination of acyclovir & ganciclovir -decrease bone marrow density
Zidovudine (AZT,ZDF) -add w 3TC and ddl -mitochondrial toxicity & myopathy
-prevent vertical transmission HIV-1 -bone marrow suppression
-azole antifungals & PIs increases plasma level
-rifampicin increases the clearance
NNRTIs -not a prodrug Nevirapine (NVP) -single dose: a)during onset of labor -good oral bioavailability -fatal hepatotoxicity
-bind directly to hydrophobic near catalytic site on HIV-1 RT-->
*not effective vs HIV-2 blockade of RNA & DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity b)to newborn after delivery -good penetration
-CYP 3A4 inducer -hepatic metabolism by CYP34A
*2-NNRTIs combo (NOT recommended): high incidence of A/E -increase by enzyme inhibitors (macrolide&cimetidine)
-reduce by enzyme inducers (rifampim)
Efavirenz (EFV) -mixed inducers/inhibitors of CYP3A4 -fatty food enhances oral bioavailibility -CNS effect (dizziness, headache, nightmare,
-reduce PIs, simvastatin, methadone -penetrates CNS delusion, euphoria, insomnia, amnesia)
-teratogenicity (avoid in 1st trimester)
-avoid use w PI, saquinavir
Delavirdine (DLV) -CYP 3A4 inhibitor -antacids reduces oral bioavailability *Generally: 1)GI tolerance
-enzyme inhibitors reduced it -less penetration to CNS 2)Skin rashes-->C/I in pt w hx of severe rash
-azole, antifungals & macrolides increase it -hepatic metabolism by CYP3A & CYP 2D6 3)Teratogenicity
-benzodiazepines, PIs increase it
-HIV-1 protease cleaves precusor polyprotein to form proteins of
PIs mature virions Atazanavir (ATV) -potent inhibitor of CYP 3A4 & CYP 2C9 *Generally: 1)exacerbate emergence of resistant HIV strain -no lipodystrophy
-hyperbilirubinemia w overt jaundice: inhibit hepatic
-avoid use w IDV: d/t it will exacerbate A/E 2)varying bioavailability UGT1A1 glucuronidation enzyme
-PIs inhibit protease active site-->immature, non-infectious viral particles
Darunavir (DRV,TMC114)
-resistance is common Fosamprenavir (FPV)
-always combined! Indinavir (IDV) -inhibitor of CYP 3A4 -kidney stones & renal failure (d/t x soluble in urine)
Lopinavir (LPV) -inhibitor of CYP 3A4
Nelfinavir (NFV)
Ritonavir (RTV) -add with other PIs & act as PI booster -higher oral bioavailability (by fatty meal&increase gastric pH) *Generally: 1)Hyperglycaemia - insulin resistance
-inhibitor of CYP 3A4 2)High cholesterol & TG levels
-inhibit metabolism of drugs (erythromycin, ketoconazole,
prednisolone, rifampin & squamavir) 3)GI side effect - bloating, nausea, diarrhoea
Saquinavir (SQV) -inhibitor of CYP 3A4 -oral bioavailability (by fatty meal&increase gastric pH)
Tipranavir (TPV)
Booster -inhibit P 450 isozymes, act as booster for HIV-1 PIs Cobicistat -inhibit CYP 3A4,CYP 2D6 & transporter(p-glycoprotein) -metabolized by CYP 3A4 & CYP 2D
-increase systemic exposure of ATV/DRV
-binds integrase--> interferes w integration of RT HIV DNA into the
IIs chromosome of host cell Raltegravir (RAL) -for resistant strains tx -metabolized by glucuronidation Diarrhoea, nausea, dizziness, headache
-caution use w antacids: Ca, Mg, Fe bind to IIs & interfere
w absorption -not interact w P450
-rifampin reduce it level
Entry Inhibitors (EIs) -binds to gp41 subunit of viral envelope glycoprotein Enfurvirtide (ENF,T-20) -combine w other anti-HIV in pt w persistent HIV-1 replication -metabolized by protein hydrolysis -local injection site rx
-prevents confirmational changes necessary for viral fusion -S/C injection -hypersensitivity & eosinophilia
-cough, URTI, muscle pain, diarrhoea, increased hepatic
-binds selectively to CCR5 coreceptor Maraviroc (MVC) -tx of tx-expereinced adult pt infected w CCR5-tropic HIV-1 transaminase activity
-CYP 3A4 substrate -MI & infarction
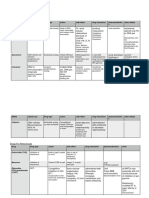
GROUP OF ANTI-FUNGAL MOA DRUGS COMMENTS/CLINICAL USES PHARMACOKINETICS A/E
-bind w sterols in fungal cell membrane (ergosterol) --> -infusion-related: 1)fever, chills, muscle spasm,
Polyenes leak out of cell's contents & the cell dies Amphotericin B -tx for systemic fungal disease -poorly absorbed orally shake & bake syndrome
-also bind to humam membrane sterols --> prominent toxicity -broad antifungal -synergistic effect w flucytosine -given by IV/intrathecal 2)hypotension w hypokalemia
-vs molds & yeast -systemic candidiasis -liposomal formulation: for intolerant pt 3)local thrombophlebitis
-cumulative toxicity: 1)renal toxicity --> acidosis & severe K
-initial induction for immunosuppressed pt w: -penetrates poorly into CNS & Mg wasting
1)severe fungal pneumonia, severe cryptococcal meningitis/
disseminated histoplasmosis & coccidioidomycosis -excreted in urine 2)neurotoxicity--> seizure, paresthesia
2)continue w maintenance therapy w azole 3)reduce erythropoietin
-mycotic corneal ulcers & keratitis
-aminoglycosides,vancomycin,furosemide reduce renal fx
-corticosteroids, skeletal muscle relaxants, thiazole
cause hypokalemia
-hypokalemia & digoxin will increase risk of digoxin toxicity
-bind w sterols in fungal cell membrane (ergosterol) -->
leak out of cell's contents & the cell dies Nyastin -candidal infection of vagina, skin & mouth -used topically
-mycostatin -oralpharyngeal trush, vaginal candidiasis -little toxicity
-nilstat
-nystex
-inhibit CYP450 14alpha-demethylase(convert lanosterol-->ergosterol)
Imidazole required in fungal cell membrane synthesis Miconazole -local fungal infection: vaginal & vulvar candidiasis
-topical fungal infection: chronic candidiasisof skin &
mucous membranes -used topically
-orally given for GIT infection
Ketoconazole -not use for systemic infection -used topically -hepatic toxicity & antiandrogenic, anaphylaxis
-tx for dermatophytosis & candidiasis -astemizole w ketoconazole is C/I --> cause long QT
-tx of seborrheic dermatitis, pityriasis versicolor (shampoo)
-inhibit liver enzyme
Clotrimazole -tx for oral trush (clotrimazole troche)
-inhibit CYP450 14alpha-demethylase(convert lanosterol-->ergosterol)
Triazoles required in fungal cell membrane synthesis Fluconazole -2ndary prophylaxis of cryptococal meningitis -given orally / IV -well tolerated
-greater specificity for fungal P450 -mouth, throat, oesophageal candidiasis -good oral bioavailability -minor GI upset
-serious systemic candidal infection -good CNS penetration -abnormalities in liver enzyme
-fewer hepatic enzyme interaction compared to ketoconazole -hepatic metabolism -clinical hepatitis
-inhibitors of CYP 3A4 & CYP 2C9 -renal elimantion
-increase saquinavir, tipranavir, nevirapine & etravirine
Itraconazole -blastomycosis -given orally / IV -minor GI upset
-histoplasmosis -absorption increased by food & low gastric pH -quinidine coadministration --> QT prolongation
-aspergillosis: for pt intolerent to amphotericin B -absorption reduced by ranitidine / antacid tx
-onychomycosis d/t dermatophytes -poor CSF penetration
-rifampin, NNRTIs reduce it bioavailability -hepatic metabolism
-PIs increase its level -biliary excretion
-increase itraconazole, PIs & statins level
Echinocandins *Generally: fungal cell wall distruption Caspofungin -tx of invasive Aspergillus in pt who can't tolerate amphotericin B -given IV *Generally: 1)lesser than amphotericin B & triazoles
-non-competitive inhibition of B-(1,3)-D-glucansynthase -tx of oral candidiasis refractory to azoles & amphotericin B -increase protein bound 2)infusion-related A/E
-blockade of this enzyme complex Micafungin -tx of invasive candida infection in bone marrow transplant pt -excreted via gut & kidneys 3)increase in hepatic enzyme
-inability of the fungal cell to synthesise B-(1,3)-D-glucan Anidulafungin *Generally: 1)fungicidal activity vs candida sp 4)pregnancy (category C)
-osmotic instability & cell death 2)fungistatic activity vs aspergillus sp
3)vs molds, given w ampB / broad spectrum triazole
Flucytosine *Generally: inhibit DNA synthesis -tx of serious candida and/or cryptococcus infection -given orally -close monitoring of hematologic, renal & hepatic status
-anti-metabolite -excreted via kidneys (extreme ⚠ in impaired renal fx) -reversible bone marrow toxicity
-narrower spectrum than ampB -hepatotoxicity
Griseofulvin -inhibit mitosis -tx vs dermatophyte (ring worm)
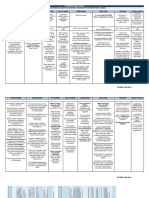
TYPE OF FUNGAL TYPE OF INFECTION/THERAPY TYPE OF DRUGS
Candidiasis Oral candidiasis -topical tx: 1)clotrimazole troches
-nyastin suspension (nyastin swish & swallow)
Oropharyngeal candidiasis -systemic anti-fungal drug: 1)fluconazole
2)itraconazole
Candida esophagitis -oral/IV fluconazole
-oral itraconazole
-amphotericin B (in severe/azole resistant)
Genitourinary tract candidiasis -topical antifungal
-single dose of oral fluconazole
Disseminated candidiasis w end organ infection -fluconazole
-echinocandins
Crytococcosis Initial therapy -amphotericin B (2 weeks)
-w/ or w/out flucytosine (2 weeks)
-followed by fluconazole (8-10 weeks)
Alternative initial therapy -lipid formulation of amphotericin B (3 weeks)
-fluconazole/flucytosine (amphotericin B intolerance pt)
Maintenance therapy -fluconazole for life
Fungal Severe histoplasmosis -itraconazole
Chronic histoplasmosis -itraconazole
Disseminated histoplasmosis -itraconazole
Coccidioidomycosis -fluconazole
-itraconazole
-amphotericin B
Coccidioidal meningitis -fluconazole
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Antiretrovirals: MOA/ Metabolism Patient Considerations SE ResistanceDocument3 pagesAntiretrovirals: MOA/ Metabolism Patient Considerations SE ResistanceshinbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Chart 3Document2 pagesPharmacology Chart 3Omar ClorPas encore d'évaluation
- Nrtis: (Nucleoside/ Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase) : "Eatz LSD"Document3 pagesNrtis: (Nucleoside/ Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase) : "Eatz LSD"Mohammad KatatoPas encore d'évaluation
- V Antiviral Agent (Preclinic)Document2 pagesV Antiviral Agent (Preclinic)KHETSOPHON POOCHIPAKORNPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm Chemo Drugs SauldDocument6 pagesPharm Chemo Drugs Sauldneal100% (1)
- Anti ViralsDocument4 pagesAnti ViralsJas GandingcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Antiviral DrugsDocument2 pagesSummary of Antiviral DrugsKate Sarah GabasaPas encore d'évaluation
- ART Guide HA 11.2021Document3 pagesART Guide HA 11.2021jqmrtc8cfgPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV Drugs Class and DDIDocument5 pagesHIV Drugs Class and DDIkaylakmills_101358680% (1)
- Antivirals: Drug Clinical Use Drug Type Action Side Effect Drug Interaction Pharmacokinetic S Other DetailsDocument10 pagesAntivirals: Drug Clinical Use Drug Type Action Side Effect Drug Interaction Pharmacokinetic S Other DetailshectorPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiretroviral DrugsDocument4 pagesAntiretroviral DrugsPrince Kevin AdinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analgesia For InternsDocument4 pagesAnalgesia For InternsjsdlzjPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Sheet 2Document88 pagesDrug Sheet 2Umbe ChinakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugstudy Ferrous SulfateDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Ferrous SulfateRJ JOHNPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti ViralsDocument14 pagesAnti ViralsparinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDocument6 pagesNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Respiratory MedicationDocument4 pagesRespiratory MedicationShang MacarayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Viral TableDocument8 pagesAnti Viral TablekvmPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BDocument30 pagesDrug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BCess Lagera Ybanez0% (1)
- EtravirineDocument3 pagesEtravirineRosher Deliman JanoyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Board II Review PDFDocument131 pagesBoard II Review PDFJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Board II Review PDFDocument131 pagesBoard II Review PDFJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Chart Antibiotics IDocument1 pageChart Antibiotics IRedPas encore d'évaluation
- TB DRUGS 2023-2024 SummaryDocument4 pagesTB DRUGS 2023-2024 SummaryMark Lorenz NaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Usage - HTMLDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Usage - HTMLChristine Joy MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- ActivationDocument1 pageActivationEkoy TheRealPas encore d'évaluation
- Table: Aed Summary: Older AedsDocument3 pagesTable: Aed Summary: Older AedsAmit PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Dooley PDFDocument18 pagesDooley PDFMualliful UmmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudybalingbinglorieannePas encore d'évaluation
- Antiviral Chemotherapy and Prophylaxis: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and FamciclovirDocument8 pagesAntiviral Chemotherapy and Prophylaxis: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and FamciclovirDasha VeePas encore d'évaluation
- RUG Tudy: Medicatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerati ONDocument4 pagesRUG Tudy: Medicatio N Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerati ONGiselle EstoquiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotic Moa Mor Indication Formulation/ Dose Typical Sensitivities Adverse Effects Interactions Other InfoDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Moa Mor Indication Formulation/ Dose Typical Sensitivities Adverse Effects Interactions Other Infokalli987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study. GeamhDocument5 pagesDrug Study. GeamhMacky RobentaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hiv Current Trend in The Use of HaartDocument19 pagesHiv Current Trend in The Use of Haartapi-3705046Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - DopamineDocument1 page1 - DopaminedianneangelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook Mosbys 2017 Nursing Drug Reference PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Mosbys 2017 Nursing Drug Reference PDF Full Chapter PDFgeorge.messano625100% (26)
- Drug Study For HepatitisDocument4 pagesDrug Study For Hepatitisunyokies100% (1)
- BangkasDocument5 pagesBangkasJulianne BangkasPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionShara Lailanie A. AzisPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 - Tetracyclines and Other AntimicrobialsDocument6 pages06 - Tetracyclines and Other Antimicrobialsjulinka beyla yansonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLouisse Angeli AbucejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mosbys 2017 Nursing Drug Reference 30Th Edition Edition Skidmore Roth Full ChapterDocument67 pagesMosbys 2017 Nursing Drug Reference 30Th Edition Edition Skidmore Roth Full Chapterdawn.drewry941100% (17)
- Brand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX ReviewDocument72 pagesBrand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX Reviewbapimirab654Pas encore d'évaluation
- VaccinesDocument2 pagesVaccinesZaid uaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antifungal Agents: EchinocandinsDocument2 pagesAntifungal Agents: EchinocandinsCourtney TownsendPas encore d'évaluation
- NON Malig HaemDocument49 pagesNON Malig HaemNisini ImanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyTanya Victoria Lean ClaudioPas encore d'évaluation
- Rifaximin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesRifaximin Drug StudySTORAGE FILEPas encore d'évaluation
- Pen G Drug StudyDocument1 pagePen G Drug Studyjean therese100% (1)
- Daniel - Assignment On AntibioticsDocument6 pagesDaniel - Assignment On AntibioticsArun Roa DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Concise Notes NEET-PGDocument30 pagesPharmacology Concise Notes NEET-PGMohamed TayyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Name and Classification of DrugDocument3 pagesName and Classification of DrugAnicas, Ralph Joshua V.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Drug Interactions Associated With Antiretroviral DrugsDocument136 pagesPharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Drug Interactions Associated With Antiretroviral DrugsNenad PanzalovićPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Drug Study - MethylergonovineDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - MethylergonovineJustin Ancog0% (1)
- STUDYDocument2 pagesSTUDYMarie Ashley CasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- AbxDocument9 pagesAbxAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 1 SummaryDocument10 pagesYear 1 SummaryAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Terms Yeast Mold Dimorphic Fungi Colony: 1. Candida AlbicansDocument6 pagesTerms Yeast Mold Dimorphic Fungi Colony: 1. Candida AlbicansAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- All Diuretics - Sheet1Document1 pageAll Diuretics - Sheet1Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia 3Document1 pageNokia 3Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- PBL Group 1Document29 pagesPBL Group 1Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia 3Document1 pageNokia 3Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- GINA Pocket 2015Document32 pagesGINA Pocket 2015Ramzi AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Day 2016Document1 pageInstallation Day 2016Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Jadual Waktu Akademik PST Modul 2Document46 pagesJadual Waktu Akademik PST Modul 2Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Suicide RatesDocument3 pagesSuicide RatesAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- PT3 2016 BK5 KHB KT PDFDocument15 pagesPT3 2016 BK5 KHB KT PDFAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- The Main Structural Difference Between Starch Glycogen Cellulose Comes FromDocument1 pageThe Main Structural Difference Between Starch Glycogen Cellulose Comes FromMelissa Ann VannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jadual Waktu Akademik PST Modul 1Document70 pagesJadual Waktu Akademik PST Modul 1Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Riding Cap Drama Script - OdtDocument8 pagesRed Riding Cap Drama Script - OdtAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Gridlock 2Document3 pagesGridlock 2Anisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Law NewDocument6 pagesLinear Law NewAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal KhasDocument1 pageJurnal KhasAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Afternoon To The Honorable JudgesDocument3 pagesGood Afternoon To The Honorable JudgesAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Riding Cap Drama Script - OdtDocument8 pagesRed Riding Cap Drama Script - OdtAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Nelson MandelaDocument1 pageNelson MandelaAnisha GillPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Kesesuaian Penggunaan Antiinfeksi Pada Infeksi Oportunistik Pasien Hiv/Aids Rawat Inap Di Rsup Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaDocument7 pagesAnalisis Kesesuaian Penggunaan Antiinfeksi Pada Infeksi Oportunistik Pasien Hiv/Aids Rawat Inap Di Rsup Dr. Sardjito YogyakartaindahPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of InterventionsDocument7 pagesSummary of InterventionsShawna RoddPas encore d'évaluation
- Candida Infection, Integrated Science, 4.3Document13 pagesCandida Infection, Integrated Science, 4.3Anesia Andrews100% (1)
- Woman With DysuriaDocument26 pagesWoman With DysuriaAlFi KamaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- CANDIDIASISDocument20 pagesCANDIDIASISKylie GolindangPas encore d'évaluation
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleapi-3797941100% (1)
- PRESENTATION ON STI'sDocument52 pagesPRESENTATION ON STI'sEBENEZER OPPONGPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Side Effects of Inhaled Glucocorticoids - UpToDateDocument37 pagesMajor Side Effects of Inhaled Glucocorticoids - UpToDateAmr MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology and Etiology of Denture Stomatitis: KeywordsDocument10 pagesEpidemiology and Etiology of Denture Stomatitis: Keywordsluthfia choirunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Viruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi: Module Two: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue Level Paper OneDocument52 pagesViruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi: Module Two: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue Level Paper Oneapi-279296553Pas encore d'évaluation
- Candida Nad PsychDocument6 pagesCandida Nad PsychJelica ŠutovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Nasonex PpiDocument6 pagesNasonex PpiStefan BezoPas encore d'évaluation
- Beximko Annual Report 2013Document97 pagesBeximko Annual Report 2013বিধান রয়Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kodamaea Ohmeri InfectionDocument8 pagesKodamaea Ohmeri InfectionMufti DindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal InfectionDocument19 pagesNeonatal InfectionLekshmi ManuPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Candidiasis: An Overview: Arun Singh, Renuka Verma, Aditi Murari, Ashutosh AgrawalDocument5 pagesOral Candidiasis: An Overview: Arun Singh, Renuka Verma, Aditi Murari, Ashutosh AgrawalazyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis, 2017Document2 pagesVulvovaginal Candidiasis, 2017Rhobbigfirly UnggulPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyDocument7 pagesEnt Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyAileen EmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Olive Leaf ExtractDocument29 pagesOlive Leaf Extractallmag100% (6)
- Imci Repaired NotesDocument136 pagesImci Repaired NotesGladys WarighePas encore d'évaluation
- Current Treatment of Oral Candidiasis: A Literature ReviewDocument12 pagesCurrent Treatment of Oral Candidiasis: A Literature ReviewgilangPas encore d'évaluation
- KetoconazoleDocument9 pagesKetoconazolePradeep BhimaneniPas encore d'évaluation
- Yeast Free Anti Candida FoodDocument18 pagesYeast Free Anti Candida FoodJorgeAlcarazPas encore d'évaluation
- Lingua - Anatomi Dan Kelainan LidahDocument51 pagesLingua - Anatomi Dan Kelainan LidahKemalLuthfanHindamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Candida AlbicansDocument14 pagesCandida AlbicansDhynda ARwolge CixicheuyyPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership & Management - Prioritization: Pressure. This Increased NorepinephrineDocument46 pagesLeadership & Management - Prioritization: Pressure. This Increased NorepinephrineregisterednursePas encore d'évaluation
- CandidiasisDocument11 pagesCandidiasisShakti RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficacy of Nystatin For The Treatment of OralDocument11 pagesEfficacy of Nystatin For The Treatment of OralRegita AyuPas encore d'évaluation
- MycologyDocument17 pagesMycologyRachana PurohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Egyptian: Denture Biofilm and Dentureassociated Stomatitis, A Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesEgyptian: Denture Biofilm and Dentureassociated Stomatitis, A Literature ReviewShankar arumugamPas encore d'évaluation