Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Criteria For Ethical Reasoning
Transféré par
Zara Imran0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
176 vues14 pagesThis document provides an outline for a course on ethical reasoning. It includes readings and discussion topics
Description originale:
ethical reasoning
Titre original
Decision Criteria for Ethical Reasoning
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document provides an outline for a course on ethical reasoning. It includes readings and discussion topics
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
176 vues14 pagesDecision Criteria For Ethical Reasoning
Transféré par
Zara ImranThis document provides an outline for a course on ethical reasoning. It includes readings and discussion topics
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 14
TOK Chs. 7-8, p.
237-257
Team 1: 237-241
Team 2: 242-246
Team 3: 246-251
Team 4: 251-257
Team 5: Case Study 1
Team 6: Case Study 2
Week 4: Ethical Reasoning
PP: Team 1-3: Mill
Team 4-6: Kant
AIO: Gene
Modification
Socratic Seminar
• SS: TYFA selected ch. 1-3, 14-16
Discussion:
– What did your section reveal
about the nature of persuasion?
– How might it interact with
specific concepts of TOK? Why
is persuasion a part of knowing
and arguing?
• AIO: Discrimination Discussion
– Discuss your problems of Knowledge
– Combine your problems into an
overarching question for futher research?
– How might the AIO topic be related to
the TYFA readings?
Where are we Going?
• Activity: Island
Rescue
– Definition of Ethics
through concept
clarification modeling
• Warrants (Toulmin)
– Presuppositions and
challenges
• 6 categories of
Ethical Knowing
• Blog: Ethical Agents
What is Ethics? Rescue Activity
• Situation, you are stranded on
Primavera Island in the “Ring of
Fire”
• Due to volcanic activity, there is a
record tsunami that will make
landfall in 10 minutes. Causalities
are expected to be absolute.
• Mr. Morris is the pilot of the only
F77 to successfully reach land in
time to make a rescue.
• Normally, the helicopter can
carry only six passengers, but it is
thought that it could be
overloaded to the maximum of
eight. (7 passengers plus the
pilot)
What is Ethics? Rescue Activity
• Consider the
people and make a
case for who should
be on the
helicopter.
• You must come to
agreement about 7
survivors.
What is Ethics? Rescue Activity
Breakdown
1. Whom did you select to survive?
2. What were your reasons for the
choices?
3. How much agreement and
disagreement did you find among
your choices?
4. What values do the choices
reflect?
5. How do you feel about yourselves
in relation to this exercise?
6. Did you use rationalizations to
avoid making the decisions in this
learning activity?
7. What working definition
can we make about Ethics from this
activity?
Why Ethical Reasoning?
1. Ethics makes clear to us why one
act is better than another
2. Ethics contributes an orderly social
life by providing humanity some
basis for agreement,
understanding some principles or
rules of procedure
3. Moral conduct and ethical
systems, both of the past and the
present, must be intelligently
appraised and criticized.
4. Ethics seeks to point out to men
the true values of life
Warrants Towards Ethical
Reasoning
• Two basic assumptions of Ethical Reasoning:
– Man is a rational being
– Man is free to make choices
• How might the goal and method of ethics change if one or
both of these presuppositions were shown to be false?
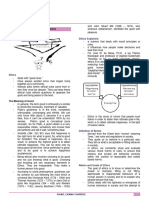
The Objects of Ethical Reasoning
• The doer of the action
(The subject)
• The action done
– Formal Object of Ethics is
the Action, not the
subject.
• How might the
emphasis on one
object or the other
effect ethical
reasoning? What is the
functional difference
between “morality”
and “ethics”?
The Spectrum of Ethical
Reasoning
• Consequentialist • Non-consequentialist
(Deontological) Ethics
(Teleological) Ethics
– Ethical Actions have moral,
– Ethical Actions have categorical imperatives
consequences – If everyone were to do this
– Do the consequences result action, would the resulting
in a positive outcome? world be rational? (queue
allegory)
– How many people benefit?
How many people are – Ethical Actions participate in
rational truths despite
hurt?
consequences.
– Are more benefiting than – Nay/Horray judgement on the
hurting? action itself
External v. Internal Ethical
Reasoning
• External: • Internal:
– Ethical actions are a result – Called “Virtue Ethics”.
of the cultural, societal, – Focusing on the Subject, not the
religious, and political action (i.e. “be an honest
person”)
evolution of group identity
– Philosophical roots in Socrates
– One does the “right” and Aristotle
action in order to belong.
– Do “right” actions because one
– What other reasons would must have “right” ethical
one do “right” in this character.
category? What other reasons would one
want to do “right” in this
category?
Practical v. Theoretical Ethics
• Practical Ethics Involves
the Application of
reasoning in a complex
society
– Often results in an
imperfect synthesis of
various theories
• Theoretical Ethics is
meant to practice
reasoning within general
frameworks.
• How might these two
categories be
associated with the
theories of truth?
Blog Activity: Other Categories?
• What might be some
other categories of
Ethical reasoning?
• Consider two ethical
characters
throughout history,
one that operates
under a category we
discussed, and one
that operates under
a category we have
not. Identify and
explain both.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lesson 2 EthicsDocument20 pagesLesson 2 Ethicselle lee100% (1)
- Ethics FinalDocument73 pagesEthics FinalPatel ChiragPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Mod 1 & 2Document43 pagesEthics Mod 1 & 2sakoPas encore d'évaluation
- BEG - IntroductionDocument25 pagesBEG - IntroductionManisha PaliwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring'24 Ethics Midterm NightDocument43 pagesSpring'24 Ethics Midterm Nightforgamesforgames7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cpelaws PrelimDocument38 pagesCpelaws PrelimNeru RoriPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Ethics and MoralityDocument39 pages1 Ethics and MoralitymamaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Ethics Session 3Document44 pagesBusiness Ethics Session 3jitender KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- PurposiveDocument89 pagesPurposiveVictoria DegorioPas encore d'évaluation
- ETHICS111Document36 pagesETHICS111Aime Mvuyekure100% (1)
- Chapter One: Understanding Civics and Ethics: A Seed Will Only Become A Flower If ItDocument113 pagesChapter One: Understanding Civics and Ethics: A Seed Will Only Become A Flower If ItAdane BekelePas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Lesson 1 Notes Fall2020Document5 pagesEthics Lesson 1 Notes Fall2020Janai DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 LessonDocument3 pagesWeek 1 LessonDhave Airen DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials On Research Publication and Ethics NBU 2020Document37 pagesMaterials On Research Publication and Ethics NBU 2020mirandasuryaprakash_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Ethical Theories and Promblem Solving TechniquesDocument84 pagesChapter 3 - Ethical Theories and Promblem Solving TechniqueszulhairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ged107 M1WK1Document12 pagesGed107 M1WK1Karylle AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- To EthicsDocument10 pagesTo EthicsEmmanuel AlcantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gist of Coceptual SessionsDocument26 pagesGist of Coceptual SessionsRahul RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics, Morality, Education Types of Ethical ReasoningDocument35 pagesEthics, Morality, Education Types of Ethical Reasoningshabbir531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I: Conceptual Considerations (Teacher'S Notes)Document7 pagesUnit I: Conceptual Considerations (Teacher'S Notes)Alyssa MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Ethics: GADTC: Ethics (Unit I)Document3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Ethics: GADTC: Ethics (Unit I)Prince Mark RodaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics ReviewerDocument2 pagesEthics ReviewerSICAT, Keeshan KeithPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics (Also Known As Moral Philosophy) Is A Branch Of: Philosophy Morality Good Bad Right Wrong Justice VirtueDocument10 pagesEthics (Also Known As Moral Philosophy) Is A Branch Of: Philosophy Morality Good Bad Right Wrong Justice VirtueKrunal MendparaPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 2 - Overview of EthicsDocument55 pagesSession 2 - Overview of EthicsSalna Susan AbrahamPas encore d'évaluation
- Besr3ch 090850Document17 pagesBesr3ch 090850Nursefa HussenPas encore d'évaluation
- Conceptual Framework For Ethical Decision Making in Business PDFDocument21 pagesConceptual Framework For Ethical Decision Making in Business PDFSouvik RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bsba 2-A Foundation of EthicsDocument4 pagesBsba 2-A Foundation of EthicsVanito SwabePas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophy and Ethics Moral DilemmasDocument3 pagesPhilosophy and Ethics Moral DilemmasErica VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module I - Philosophy and EthicsDocument19 pagesModule I - Philosophy and EthicsTinselpolecat 14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gec 8 EthicsDocument22 pagesGec 8 EthicsHANNAH FAYE VALDEZ100% (2)
- The Psychology Behind Ethics and IntegrityDocument44 pagesThe Psychology Behind Ethics and Integritysargism15Pas encore d'évaluation
- ETHICS - Week 1 PreliminariesDocument8 pagesETHICS - Week 1 PreliminariesMacky AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics 01 Reboot EnhancedDocument118 pagesEthics 01 Reboot EnhancedAljun EstipularPas encore d'évaluation
- General Review And,: Moral Reasoning and Ethical AnalysisDocument25 pagesGeneral Review And,: Moral Reasoning and Ethical AnalysisMonina JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON 1 ReadingDocument8 pagesLESSON 1 Readingcha rishPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Outcomes: Unit 1: What Is Ethics?Document17 pagesLearning Outcomes: Unit 1: What Is Ethics?Julius Amarille100% (1)
- Ethics Notes 1Document100 pagesEthics Notes 1Serge Guzman ImperioPas encore d'évaluation
- Office of The President Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationDocument33 pagesOffice of The President Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationCarolPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To General EthicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To General EthicsEvelyn LazaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical Theories 01Document86 pagesEthical Theories 01Kate ClomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Lesson 2 ValuationDocument36 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 2 ValuationKimberly Jane TogñoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is This Lesson About?: Lesson 1 Ethics: Fundamental Concepts and IssuesDocument15 pagesWhat Is This Lesson About?: Lesson 1 Ethics: Fundamental Concepts and IssuesDaniellPas encore d'évaluation
- Etic211 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEtic211 ReviewerdzdooPas encore d'évaluation
- Module For Prelim (Ethics)Document5 pagesModule For Prelim (Ethics)Aeila WpPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics and Rwandan CultureDocument87 pagesEthics and Rwandan CultureAnonymous oZtC0g63% (8)
- Ethical Issues in Health and Social Care Intro Session 1Document55 pagesEthical Issues in Health and Social Care Intro Session 1Anonymous cPDz1BINPPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical and Legal Issues in Nursing and HealthDocument33 pagesEthical and Legal Issues in Nursing and HealthSofonias Selamu100% (1)
- Bioethics: EthicsDocument40 pagesBioethics: EthicsPamela MorcillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gethics Midterm PDFDocument6 pagesGethics Midterm PDFMark HerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Virtue EthicsDocument21 pagesAn Introduction To Virtue Ethicsroselyn ayensaPas encore d'évaluation
- EthicsDocument7 pagesEthicsJenMarlon Corpuz AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Module 1Document34 pagesEthics Module 1carloibanez946Pas encore d'évaluation
- Business Ethics - Lec 2Document16 pagesBusiness Ethics - Lec 2mdyusufhushye12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of EthicsDocument23 pagesTheories of Ethicsnathalie dylanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Deparment of Electrical EngineeringDocument34 pagesMirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Deparment of Electrical Engineeringabout the pointPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 1ethicsDocument11 pagesUNIT 1ethicsangelfaithdelacruz50Pas encore d'évaluation
- Running Ethical Discussions 3Document8 pagesRunning Ethical Discussions 3martin pontPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical Decision Making in BusinessDocument19 pagesEthical Decision Making in Businessaditya0376Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics TransesDocument12 pagesEthics TransesCienna IganoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dewey and Schopenhauer Point of ViewsDocument6 pagesDewey and Schopenhauer Point of ViewsZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Principle of MKTDocument1 pagePrinciple of MKTZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher Name: Ms. Zara Imran: Check List For Course FileDocument1 pageTeacher Name: Ms. Zara Imran: Check List For Course FileZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Institutional Voids and OrganizationDocument22 pagesInstitutional Voids and OrganizationZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary-Stephen Ackroyd - Critical Realism, Organizational Theory, Methodology and The Emerging Science of ReconfigurationDocument5 pagesSummary-Stephen Ackroyd - Critical Realism, Organizational Theory, Methodology and The Emerging Science of ReconfigurationZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To BusinessDocument2 pagesIntroduction To BusinessZara Imran100% (1)
- Check List For Course File Teacher Name: Ms Zara ImranDocument2 pagesCheck List For Course File Teacher Name: Ms Zara ImranZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ten Basic Pricing StrategiesDocument21 pagesThe Ten Basic Pricing StrategiesZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Program: BS Accounting and Finance Subject: Marketing Presented To: Mam Zara Presented By: Firzok Ghauri, Roll No: LF-1092, Date: December 23, 2020Document26 pagesProgram: BS Accounting and Finance Subject: Marketing Presented To: Mam Zara Presented By: Firzok Ghauri, Roll No: LF-1092, Date: December 23, 2020Zara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Check List For Course File: Course Title: Consumer Behavior Bba Vii Shift: MorningDocument1 pageCheck List For Course File: Course Title: Consumer Behavior Bba Vii Shift: MorningZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Marketing: Submitt by Usama Yousaf (L21226) Submitted To Mam Zara Imran Class Mba 5Document28 pagesDigital Marketing: Submitt by Usama Yousaf (L21226) Submitted To Mam Zara Imran Class Mba 5Zara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Check List For Course File: Teacher Name: Ms Zara ImranDocument2 pagesCheck List For Course File: Teacher Name: Ms Zara ImranZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Plan Outline Context: Pakistan: 1. Executive Summary 2. Introduction-BrandDocument1 pageMarketing Plan Outline Context: Pakistan: 1. Executive Summary 2. Introduction-BrandZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Marks-Jeremiah Gill (L-1094) - Ibrahim Ejaz (L-1093)Document24 pages8 Marks-Jeremiah Gill (L-1094) - Ibrahim Ejaz (L-1093)Zara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Marks-Sania Nawaz (LF-1057) - Muhammad Mehran (LF-1102)Document23 pages9 Marks-Sania Nawaz (LF-1057) - Muhammad Mehran (LF-1102)Zara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Dell-Big Data-AnalysisDocument18 pagesDell-Big Data-AnalysisZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- National University of Modern Languages Lahore Campus: Assignment TitleDocument29 pagesNational University of Modern Languages Lahore Campus: Assignment TitleZara Imran100% (1)
- Pricing Stratigies: Preented To: Maam ZaraDocument31 pagesPricing Stratigies: Preented To: Maam ZaraZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Dell-Big Data-AnalysisDocument39 pagesDell-Big Data-AnalysisZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Selling - CH 7 - ProspectingDocument57 pagesPersonal Selling - CH 7 - ProspectingZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Forcasting Techniques in SMDocument43 pagesForcasting Techniques in SMZara Imran100% (1)
- Dell-Big Data-AnalysisDocument18 pagesDell-Big Data-AnalysisZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Nishat Textile - Strategic Management FrameworkDocument39 pagesNishat Textile - Strategic Management FrameworkZara Imran50% (2)
- Coca Cola - PresentationDocument13 pagesCoca Cola - PresentationZara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- ZARA BM New ..Document8 pagesZARA BM New ..Zara ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Corbin, Henry - 'Temple and Contemplation', PT (1) - 2Document81 pagesCorbin, Henry - 'Temple and Contemplation', PT (1) - 2datki90100% (1)
- Gustav Radbruch's Concept of LawDocument14 pagesGustav Radbruch's Concept of LawFiandy MauliansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gitaa SaaramDocument26 pagesGitaa SaaramRj YashPas encore d'évaluation
- Unchanging Values in A Changing WorldDocument2 pagesUnchanging Values in A Changing Worldkemerut100% (11)
- Knowing and The Known by Dewey & BentleyDocument115 pagesKnowing and The Known by Dewey & BentleyJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Kenneth HandsomeDocument25 pagesKenneth HandsomeTristane Eric SumandePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1RajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebeling, Gerhard. The Beginnings of Luther's Hermeneutics 1 PDFDocument31 pagesEbeling, Gerhard. The Beginnings of Luther's Hermeneutics 1 PDFsanchezmeladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case For A Creator - StrobelDocument5 pagesCase For A Creator - StrobelLight Learning Club100% (1)
- Pascale Gillot, Theory of Ideology & UnconsciousDocument18 pagesPascale Gillot, Theory of Ideology & UnconsciousEdward GreenePas encore d'évaluation
- Positive Aryan Kristian Philosophy Oregoncougs BlogDocument12 pagesPositive Aryan Kristian Philosophy Oregoncougs BlogErik De RidderPas encore d'évaluation
- Edward N. Lee, Plato On Negation and Not-Being in The SophistDocument39 pagesEdward N. Lee, Plato On Negation and Not-Being in The SophistOnCe NatividadPas encore d'évaluation
- Seership & Initiatory IlluminationDocument4 pagesSeership & Initiatory IlluminationAethyriusPas encore d'évaluation
- Exposition, Critique and New Directions For Pantayong PananawDocument22 pagesExposition, Critique and New Directions For Pantayong Pananawapi-26570979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2.the Human Person.a Pre Socratic ViewDocument7 pagesLesson 2.the Human Person.a Pre Socratic ViewDwyne MariquitPas encore d'évaluation
- Bok:978 1 137 40883 9Document273 pagesBok:978 1 137 40883 9fivalen1_443898619Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure of The Cognitive RevolutionDocument26 pagesThe Structure of The Cognitive Revolutiontomor2100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Lesson 2 Material Self: To Buy or Not To Buy?: Understanding The Self Miss KZ Ulboc Reference: Cierva, MCDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Lesson 2 Material Self: To Buy or Not To Buy?: Understanding The Self Miss KZ Ulboc Reference: Cierva, MCKimPas encore d'évaluation
- Ryle PleasureDocument31 pagesRyle PleasureCaglar KocPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuhn and Paradigm ShiftDocument17 pagesKuhn and Paradigm ShiftJK_Perry_8536100% (1)
- An Interview With Thomas Metzinger What Is The SelfDocument2 pagesAn Interview With Thomas Metzinger What Is The SelfIdelfonso Vidal100% (1)
- A Computational Model of Inferencing in Narrative: James Niehaus and R. Michael YoungDocument8 pagesA Computational Model of Inferencing in Narrative: James Niehaus and R. Michael Youngpandithapreethi12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of Nature: Western Perspectives: Dr. Keith Chan (2017)Document37 pagesConcept of Nature: Western Perspectives: Dr. Keith Chan (2017)ERICPas encore d'évaluation
- Hall L. Michael Achieving Peak Performance PDFDocument296 pagesHall L. Michael Achieving Peak Performance PDFEduardo Belmar100% (5)
- Madhyamaka and Yogacara-VajrayanadocxDocument7 pagesMadhyamaka and Yogacara-VajrayanadocxMilan ShakyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Person As An: Embodied SpiritDocument48 pagesHuman Person As An: Embodied SpiritJonas ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Myth and Reality - Mircea EliadeDocument217 pagesMyth and Reality - Mircea EliadeFreyja100% (5)
- PlatoDocument16 pagesPlatofordmay100% (1)
- Postmodern Nihilism Theory and LiteratureDocument336 pagesPostmodern Nihilism Theory and LiteratureCátia Tavares100% (3)