Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sains Exam Paper Form2 2016
Transféré par
peisuanyapCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sains Exam Paper Form2 2016
Transféré par
peisuanyapDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Answer ALL questions:
1. Diagram 1 shows two systems of human body.
(a) In Diagram 1, name the system K and L using the following words. (2m)
Blood Circulatory System Respiratory system Digestive System
(b) State the functions of systems K and L. (2m)
(c) Give ONE example of organ that can be found in the system K and L. (2m)
2. (a) Microorganisms can be classified into unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms. Diagram
below shows a number of microorganisms. Tick (/) for the correct class of the microorganisms. (4m)
(b) Complete the meaning of unicellular organism and multicellular organism.
Unicellular organisms are organisms made up of ____________________ while multicellular
organisms are organisms made up of ____________________________. (2m)
3. (a) Table 1 shows five substances with different densities.
(i) Based on the table above, label the substances in Diagram 2 with correct letters. (2m)
(ii) The volume of substance D is 30cm3. What is the mass of substance D?
Mass
Density = (2m)
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
(b) Based on table 1, which substance is the least dense? Give you reason (2m)
4. (a) State the forms of energy represented by each of the following pictures. (4m)
(b) Tick (/) the correct statements and cross (X) the wrong statements. (2m)
(i) Both chicken rice and natural gas have the same form of energy.
(ii) A lighted bulb gives out light energy only.
5. Food Guide Pyramids are used to help people to plan a healthy diet. Diagram 3 shows a Food Guide
Pyramid.
(a) In Digram 3, label P and R using the words given in the box below. (2m)
Fats Carbohydrates Proteins
(b) Ali is a national body builder. He works hard to ensure that his body looks muscular that his
muscle can be clearly seen. Suggest ONE class of food that need to be taken by Ali and explain
about the function of that class of food. (2m)
(c) State the main function of class of food R in Diagram 3 to human body. (2m)
6. (a) Diagram 4 shows a disease causes by nutrient deficiency.
(i) Name the disease of the child as shown in Diagram 4. (2m)
(ii) Suggest a class of food that need to be taken by the child shown in Diagram 4 and give
ONE example of food in that class of food. (2m)
(iii) Explain how does the food suggested in 3(a)(ii) help to overcome this disease. (2m)
7. Diagram 5 shows pictures of living things in a paddy field.
Paddy Grasshopper Swallow
Frog Caterpillar Snake
(a) Based on Diagram 5,
(i) Construct a food web. (2m)
(ii) Predict what will happen if all frogs are captured. (1m)
(iii) Based on the constructed food web in 7(a)(i), construct a pyramid of numbers involving
any of the food chains. Then, draw an arrow to show how the energy flows in the
pyramid of numbers. (3m)
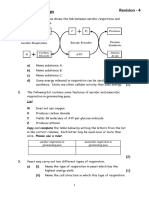
8. The following diagram shows parts of human digestive system.
(a) Arrange the letters in correct order to show the flow of food in the digestive system. (2m)
(b) Based on the above diagram, which part digests fats? (1m)
(c) Name the enzyme that helps the digestion of proteins in K. (1m)
(d) Your mom had running nose and lost her appetite. Your sister prepared porridge for your
mom because porridge is easier to be digested compares to rice. Explain why. (2m)
9. (a) Complete the table below to show the characteristics of different animals. Write your
answers in the spaces provided below.
Characteristics Mammals Amphibians Fish
Habitat Live on land (i) Live in water
Blood type Warm-blooded Cold-blooded (ii)
Reproduce by… (iii) Lay eggs Lay eggs
Body surface Covered by hair or fur (iv) Covered by slimy scales
(4m)
(b) Give an example of the following groups of animal:
(i) Mammals
(ii) Amphibians (2m)
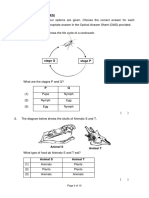
10. The following diagrams show two types of vision possessed by animal P and Q.
(a) Identify the types of vision of P and Q. (2m)
(b) State the advantage of vision: P, Q (2m)
(c) State the disadvantage of vision: P, Q (2m)
11. (a) Pollutants are being released into the air by various human activities. The diagram below
shows a phenomenon caused by air pollution.
(i) Based on the above diagram, name the phenomenon. (1m)
(ii) Explain on how this phenomenon happens. (2m)
(iii) State the effects towards sea level caused by this phenomenon. (1m)
(b) Pie chart below shows the sources of air pollutants of year 2014 in Malaysia.
(i) State the gases released by motor vehicles and explain about the dangerous effects. (4m)
(ii) Suggest TWO ways to overcome these problems. (2m)
12. All living things including human, need air, water, food and living space to live. There are
resources known as renewable resources, which can be replaced soon after being used.
However, there are other resources known as non-renewable resources that cannot be readily
replaced by natural means. To ensure the continuity of these resources, we must preserve and
reserve our natural resources.
(a) Give an example of:
(i) Renewable resources :
(ii) Non-renewable resources: (2m)
(b) Human activities can lead to damage of Earth’s resources. The diagram below shows an
human activity of deforestation.
How does this activity gives impact toward Earth’s resources? (2m)
(c) State what will happen to the quantity of oxygen in atmosphere if all green plants have been
destroyed. Explain. (2m)
(d) Suggest four ways to preserve and to reserve the natural resources on Earth to ensure its’
continuity. (4m)
13. (a) Diagram 6 shows juices of four different fruits are being dripped onto blue litmus paper
respectively. The colour changes of blue litmus paper was being observed.
TOMATO STAR FRUIT
BITTER GOURD LIME
(i) In Table 2, state the observation on the colour changes of the litmus paper.
Fruits Colour changes
Bitter Gourd Blue
Lime Blue
Table 2 (2m)
(ii) In Table 3, classify all fruits shown in Diagram 6 based on their properties.
Properties Fruits
Acidic
Alkaline
Table 3 (4m)
(b) Diagram 7 shows two full scoop of washing powder in two beakers, J and K. Water was added
into beaker K.
Observation was recorded as below.
J-No changes on red litmus paper
K- Red litmus paper changed to blue
Give one inference based on the observation in beaker J and beaker K. (1m)
(c) Diagram 8 shows a dry soap was tested with red litmus paper.
Predict the colour changes of the red litmus paper. (1m)
(d) Substance X, doesn’t change the colour of red litmus paper nor blue litmus paper.
(i) Predict the pH value of substance X. (1m)
(ii) Suggest a substance that could possibly be substance X. (1m)
14. (a) (i) State a force that is present in the above situation. (1m)
(ii) Based on Diagram 9, label the position of frictional force and pulling force that acted on the
object. (2m)
(b) Mr. Sufian tries to move a box from his office to the storeroom by pulling the box with a rope.
Tick (/) to choose for the easier method for Mr. Sufian to move the box. (1m)
(c) State two advantages of frictional force in our daily life. (2m)
(d) State two disadvantages of frictional force in our daily life. (2m)
(e) Diagram 11 shows the view from a steep cliff.
A climber with the weight of 600N has climbed the cliff. Calculate the work done by the climber
if he has climbed up to 50m. (2m)
You can use the formula shown: Work (Nm) = Force (N) x Distance (m)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Go Betweens For HitlerDocument402 pagesGo Betweens For HitlerSagyan Regmi Regmi100% (1)
- Success in BiologyDocument97 pagesSuccess in BiologyJoan Banda83% (24)
- Harrah's Entertainment Inc: Submitted To: Prof. Shubhamoy DeyDocument6 pagesHarrah's Entertainment Inc: Submitted To: Prof. Shubhamoy DeyAbhinav UtkarshPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs2-782021-Atika School-5172016 - Bioform4 Paper 1Document7 pagesCs2-782021-Atika School-5172016 - Bioform4 Paper 1bosirejanet526Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 2 QDocument13 pagesBiology Form 2 QEazi X AnzigarePas encore d'évaluation
- Home Test (Jan-21)Document10 pagesHome Test (Jan-21)Damon SalvatorePas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 2.2 EcosystemDocument7 pagesBio 2.2 EcosystemSuzuko YukinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 1half Term Assignment 2Document7 pagesForm 1half Term Assignment 2sylvesterokiringPas encore d'évaluation
- First Term Examination Year 9 Biology Revision Paper - January 2022Document9 pagesFirst Term Examination Year 9 Biology Revision Paper - January 2022Mohamed Elshadi Elshaikh Mohamed Ahmed YassinPas encore d'évaluation
- EvolutionDocument5 pagesEvolutiongospakopaPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 11 Mock ExamDocument7 pagesGRADE 11 Mock ExamRashawn WilkinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- F2 Chap 2 Subjective TestDocument2 pagesF2 Chap 2 Subjective TestSuriya GunalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 22072021 012 pp1Document13 pagesBio 22072021 012 pp1MARK SIMIYUPas encore d'évaluation
- s5 Welcome Test Third TermDocument9 pagess5 Welcome Test Third TermHakizimana GerardPas encore d'évaluation
- HKCEE - Biology - 1996 - Paper IDocument9 pagesHKCEE - Biology - 1996 - Paper ICharlie Ng1216Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Past Paper Questions PDocument155 pagesBiology Past Paper Questions Pblessed cccPas encore d'évaluation
- F3 Bio Et3 QNDocument11 pagesF3 Bio Et3 QNBenjamin mwanikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ut 1Document6 pagesUt 1SUHANEERIYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Agric Paper 2-1Document3 pagesAgric Paper 2-1chifambaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSLE Foundation ScienceDocument25 pagesPSLE Foundation ScienceNiladri ChatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Set2 Bio MidTerm 1 2021 Teacher - Co .Ke F2 ExamDocument5 pagesSet2 Bio MidTerm 1 2021 Teacher - Co .Ke F2 ExamDenisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology SPM 2004 Paper 2Document12 pagesBiology SPM 2004 Paper 2Sherlock Wesley ConanPas encore d'évaluation
- BOOKLET Science Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesBOOKLET Science Exam QuestionscheetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology - IIDocument8 pagesBiology - IImohamed rahilPas encore d'évaluation
- Int. Science 2008 P2Document16 pagesInt. Science 2008 P2Luke NancooPas encore d'évaluation
- Sri Kumaran Children's Academy: Periodic Test 1 (2019-20)Document3 pagesSri Kumaran Children's Academy: Periodic Test 1 (2019-20)Aries AAPas encore d'évaluation
- 4003 Biology Section Topic by TopicDocument27 pages4003 Biology Section Topic by TopicNoel MakambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stephjoy Boys High Shool: April Holiday Assignment Biology Term 1 2019Document6 pagesStephjoy Boys High Shool: April Holiday Assignment Biology Term 1 2019CarolPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsgurlavatarPas encore d'évaluation
- S5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEDocument16 pagesS5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEmunyanezaolivier422Pas encore d'évaluation
- F2 Bio Et3 QNDocument10 pagesF2 Bio Et3 QNOlando simidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 2.2Document7 pagesBio 2.2zwindows123456789Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology-Form-3-Term-1-Opener-2022-Qn 3Document10 pagesBiology-Form-3-Term-1-Opener-2022-Qn 3mayramramoPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM 4551 2005 Biology k2Document24 pagesSPM 4551 2005 Biology k2pss smk selandarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ucd 2020 Bio f5Document13 pagesUcd 2020 Bio f5NOOR HAFEZAH BT MOHD MOKHTIAR MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Questions From Our EnvironmentDocument3 pagesQuestions From Our Environmentnihar.sarkar1975Pas encore d'évaluation
- November Midterm 2021Document9 pagesNovember Midterm 2021PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- S3 Biology End of Term2 District Exam, 2023-2024Document4 pagesS3 Biology End of Term2 District Exam, 2023-2024NSABIMANA JANVIERPas encore d'évaluation
- CE BIO LQ Section 2.1 PDFDocument5 pagesCE BIO LQ Section 2.1 PDFKaito MagicPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper 1Document24 pagesBiology Paper 1Nyakweba DenisPas encore d'évaluation
- ReseachDocument4 pagesReseachitangishaka alphonse100% (1)
- Class 5 Sample Questions: International Olympiad of Science - iOS' 19Document2 pagesClass 5 Sample Questions: International Olympiad of Science - iOS' 19Kadambary JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecology - QuestionsDocument14 pagesEcology - QuestionsDerrick M100% (1)
- U1Test 1.2022Document4 pagesU1Test 1.2022Kelly SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology SPM 2004 Paper 2Document12 pagesBiology SPM 2004 Paper 2Sean100% (3)
- Form Ii Biology End Term of Term IiDocument7 pagesForm Ii Biology End Term of Term IioyooPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO-PP1-Teacher Co KeDocument7 pagesBIO-PP1-Teacher Co KelyshantahlynahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2024 Mock 5 Science 2Document3 pages2024 Mock 5 Science 2philomenaanderson3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 2023 Mocks BookletDocument167 pagesBiology 2023 Mocks BookletMasega Daniel ManaliPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 THDocument6 pages5 THArnav GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Class IX Science Sample Paper - 5 Time: 3 Hrs Total Marks: 80Document18 pagesCbse Class IX Science Sample Paper - 5 Time: 3 Hrs Total Marks: 80Vedang GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- EcosystemDocument7 pagesEcosystemgospakopaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Quizs FNLDocument92 pagesBiology Quizs FNLAbdul WasayPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio IgcseDocument33 pagesBio IgcseAxjxlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Email.: by Foozi SilagiDocument9 pagesEmail.: by Foozi SilagiHasifa KonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- S3 Biology Exercises Term3 2024Document6 pagesS3 Biology Exercises Term3 2024NSABIMANA JANVIERPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE AnswersDocument22 pages2020 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE AnswersAaron HeePas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 Biology 1998 Paper 1Document16 pagesPaper 1 Biology 1998 Paper 1api-3812894100% (1)
- S.3 Term 3 Biology Questions From All Topics of Third Term: (02marks)Document12 pagesS.3 Term 3 Biology Questions From All Topics of Third Term: (02marks)Anonymous R7NoMuy8Pas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Rca Dan Pdca (Intervensi) Bct1Document4 pagesRca Dan Pdca (Intervensi) Bct1peisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Curricular Elements Assessment HotsDocument20 pagesCross Curricular Elements Assessment HotspeisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Curricular Elements Assessment HotsDocument20 pagesCross Curricular Elements Assessment HotspeisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Energy Flow in EcosystemDocument1 page2.1 Energy Flow in EcosystempeisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- SC Midyr2010 FullDocument11 pagesSC Midyr2010 FullpeisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Lower6 Final Exam 09 (P2)Document8 pagesBio Lower6 Final Exam 09 (P2)peisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1peisuanyapPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Four-Scroll Chaotic System With A Self-Excited Attractor and Circuit ImplementationDocument5 pagesA New Four-Scroll Chaotic System With A Self-Excited Attractor and Circuit ImplementationMada Sanjaya WsPas encore d'évaluation
- Week1 - Introduction To Business Process ManagementDocument29 pagesWeek1 - Introduction To Business Process ManagementRamsky Baddongon PadigPas encore d'évaluation
- Polynomial Functions 1Document19 pagesPolynomial Functions 1Arafath Basheer100% (1)
- Nuclie PDFDocument34 pagesNuclie PDFlvnarsingaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wahs 1 PDFDocument12 pagesWahs 1 PDFKadek Deddy TaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges To FreedomDocument11 pagesChallenges To Freedomgerlie orquePas encore d'évaluation
- Gupta R. S., Principles of Structural Design Wood, Steel, and Concrete, 2nd Ed, 2014Document58 pagesGupta R. S., Principles of Structural Design Wood, Steel, and Concrete, 2nd Ed, 2014reyPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfred Nobel and The Nobel PrizesDocument17 pagesAlfred Nobel and The Nobel PrizesElizabethDarcyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gradasi Perilaku (Taksonomi) Pada Kur 2013Document17 pagesGradasi Perilaku (Taksonomi) Pada Kur 2013imamPas encore d'évaluation
- The Science of Bonding From First To Sixth GenerationDocument6 pagesThe Science of Bonding From First To Sixth GenerationRolzilah RohaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Sans Nom 2Document320 pagesSans Nom 2khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Google Calendar Integrator - v2.0Document21 pagesGoogle Calendar Integrator - v2.0Sumedh KakdePas encore d'évaluation
- Psy 1 Chap 3 Human DevelopmentDocument24 pagesPsy 1 Chap 3 Human Developmentjeanette8riosPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics Mid-Term Exam - February 2023Document18 pagesStatistics Mid-Term Exam - February 2023Delse PeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Exadata Technical Whitepaper 134575Document31 pagesExadata Technical Whitepaper 134575Jyothi JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Ellenberger - Psychiatry From Ancient To Modern TimesDocument76 pagesEllenberger - Psychiatry From Ancient To Modern TimesSiegfriedCristoforPas encore d'évaluation
- Doc 01 DE 20190115144751 PDFDocument20 pagesDoc 01 DE 20190115144751 PDFAdi MPas encore d'évaluation
- The Essential Guide To Developing A Social Recruiting StrategyDocument48 pagesThe Essential Guide To Developing A Social Recruiting Strategysubzzz222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Accessing I/O DevicesDocument33 pagesAccessing I/O DevicesKishore SKPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010-2011 CatalogDocument339 pages2010-2011 CatalogSimon TabPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MappingDocument26 pagesConcept Mappingdbryant0101100% (16)
- MGT602 Quiz 2 290411Document8 pagesMGT602 Quiz 2 290411sonutilkPas encore d'évaluation
- A High Voltage HalloweenDocument84 pagesA High Voltage HalloweenAntony BurgersPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On Hand Gesture RecognitionDocument5 pagesReview On Hand Gesture RecognitiondbpublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- The MES Performance Advantage Best of The Best Plants Use MESDocument20 pagesThe MES Performance Advantage Best of The Best Plants Use MESNiraj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- GE Power System and Corporate ExpressDocument8 pagesGE Power System and Corporate ExpressdolliePas encore d'évaluation
- Imp Ob QuestionsDocument2 pagesImp Ob QuestionsPrabhakar RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Qlikview 10 Accesspoint SSODocument21 pagesQlikview 10 Accesspoint SSOAlberto AlavezPas encore d'évaluation