Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Amplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A Listener
Transféré par
Tatadarz Auxtero Lagria0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues2 pagesaptitude
Titre original
aptitude
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentaptitude
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues2 pagesAmplitude: Loudness Refers To How Loud or Soft A Sound Seems To A Listener
Transféré par
Tatadarz Auxtero Lagriaaptitude
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
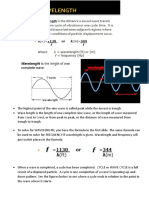
Amplitude
This in light refers to the amount of energy in an electromagnetic wave
and its meaning is the same here. Amplitude refers to the distance of the
maximum vertical displacement of the wave from its mean position.
Larger the amplitude, the higher the energy. In sound, amplitude refers to
the magnitude of compression and expansion experienced by the
medium the sound wave is traveling through. This amplitude is perceived
by our ears as loudness. High amplitude is equivalent to loud sounds.
Frequency/ Pitch of the Sound Waves
Frequency in a sound wave refers to the rate of the vibration of the sound
traveling through the air. This parameter decides whether a sound is
perceived as high pitched or low pitched. In sound, the frequency is also
known as Pitch. The frequency of the vibrating source of sound is
calculated in cycles per second.
The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature
and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency
and pressure in ordinary air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In
common everyday speech,speed of sound refers to
the speed of sound waves in air.
The basic properties of sound are: pitch, loudness and tone. Figure
10.2: Pitch and loudness of sound.Sound B has a lower pitch (lower
frequency) thanSound A and is softer (smaller amplitude)
than SoundC. The frequency of a sound wave is what your ear
understands as pitch.
Loudness refers to how loud or soft a sound seems to a listener.
The loudness of sound is determined, in turn, by the intensity, or
amount of energy, in soundwaves. The unit of intensity is the decibel
(dB). As decibel levels get higher, sound waves have greater intensity
and sounds are louder.
he most common approach to sound intensity measurement is to use
the decibel scale: Decibels measure the ratio of a given intensity I to
the threshold of hearing intensity, so that this threshold takes the value
0 decibels (0 dB).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- JBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementD'EverandJBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Acoustics Design 1Document57 pagesAcoustics Design 1Swathika KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Document97 pagesBuilding Services Iii - Sar 1302: Unit - 1Mahamud MusaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-I (INTRODUTION)Document30 pagesUnit-I (INTRODUTION)GokulPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 Arc 74 AcousticsDocument25 pages18 Arc 74 Acousticssuryaa ksPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017-09-17 Architecture Acoustics (F D Architect's Conflicted Copy)Document69 pages2017-09-17 Architecture Acoustics (F D Architect's Conflicted Copy)HARSHITA JAINPas encore d'évaluation
- Acoustics NotesDocument34 pagesAcoustics NotesAshutosh AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 (Basic Physics of Sound and The Decibe Scale)Document31 pagesLecture 2 (Basic Physics of Sound and The Decibe Scale)Geoffrey AlleynePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 2 PDFyashaswiniPas encore d'évaluation
- SoundDocument1 pageSoundShōyōHinataPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 SOUNDDocument18 pagesChapter 3 SOUNDGaliasis Akoualefo nkefackPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound Amplitude PitchDocument19 pagesSound Amplitude PitchVase VaseskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound WavesDocument5 pagesSound WavesSun Hee ParkPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of Auditory SystemDocument32 pagesPhysiology of Auditory SystemDr. T. Balasubramanian75% (4)
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronPas encore d'évaluation
- 04.3 UNIT - 4 Surface Mining Env - IDocument117 pages04.3 UNIT - 4 Surface Mining Env - Inumendrakumarpandey2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sound Is A Sensation of Acoustic Waves (Disturbance/pressure Fluctuations Setup in A Medium)Document31 pagesSound Is A Sensation of Acoustic Waves (Disturbance/pressure Fluctuations Setup in A Medium)Raja KeshavPas encore d'évaluation
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledErika ParambitaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 The Basics of SoundDocument2 pages01 The Basics of SoundFrançois HarewoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Hearing and BalanceDocument72 pagesHearing and BalanceMAMAN100% (1)
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Sound and Classification of SoundDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Sound and Classification of SoundBRIGHT CHIWEVUPas encore d'évaluation
- Acoustics Module 1Document33 pagesAcoustics Module 1mariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound & AudioDocument37 pagesSound & Audioapi-27285803Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7 Sound WavesDocument44 pagesLesson 7 Sound WaveskhiananoribsPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTES-Speed of Sound - F5Document2 pagesNOTES-Speed of Sound - F5Anonymous OZtBA0FzPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound 8Document10 pagesSound 8Shanto NiceschoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave 7Document2 pagesWave 7Ma. Bernadette EballePas encore d'évaluation
- Techniques de La Prise de Son Et Du Mixage I - Chapitre-1Document4 pagesTechniques de La Prise de Son Et Du Mixage I - Chapitre-1Samah KanaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vũ Trư NG GiangDocument4 pagesVũ Trư NG Gianghung6d5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Propagation of Sound PDFDocument16 pagesPropagation of Sound PDFHASAN SAIFPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics of Sound or Basic Theory of Sound: OctaveDocument8 pagesPhysics of Sound or Basic Theory of Sound: OctaveErika Parambita100% (1)
- Acoustics PDFDocument28 pagesAcoustics PDFCharles Harvey Cabrezos DaabayPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject:: Audio, Video & TV EngineeringDocument71 pagesSubject:: Audio, Video & TV EngineeringNilesh KalePas encore d'évaluation
- Section 1 PDFDocument2 pagesSection 1 PDFCallumPas encore d'évaluation
- Intensity and The Decibel ScaleDocument4 pagesIntensity and The Decibel ScaleantoniobhPas encore d'évaluation
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Arc 7.3 Mod 1-1Document9 pages15 Arc 7.3 Mod 1-1Prakruthi PrashanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Acoustic Fundamentals - A: Tn312 Broadcast Technology and AcousticsDocument5 pagesAcoustic Fundamentals - A: Tn312 Broadcast Technology and AcousticsloloyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2Document38 pagesUnit 2saahasitha 14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sound: Sound Is Produced When An Object Vibrates. The Vibrating Object Pushes TheDocument3 pagesSound: Sound Is Produced When An Object Vibrates. The Vibrating Object Pushes ThePablo Acierto Ragay Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction - AcousticDocument22 pagesIntroduction - Acousticpatel shivanginiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound and Its CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesSound and Its CharacteristicsGian Louise BarolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics CHPT 15Document42 pagesPhysics CHPT 15Sahil MistryPas encore d'évaluation
- BNCA Architectural AcousticsDocument35 pagesBNCA Architectural AcousticsSakshi DeshmukhPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2Document23 pagesUnit 2ASRPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Sound WavesDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Sound WavesDom Christian LastPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is SoundDocument22 pagesWhat Is SoundAbigail de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- DefinitionsDocument2 pagesDefinitionsdianaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nature and Perception of SoundDocument21 pagesThe Nature and Perception of Soundsheila louisePas encore d'évaluation
- 8 LsoundDocument2 pages8 LsoundTamara Martínez LiriaPas encore d'évaluation
- SOUNDDocument4 pagesSOUNDHitesh kalraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: Articulatory, Auditory and Acoustic Phonetics. PhonologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Articulatory, Auditory and Acoustic Phonetics. PhonologycalluraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter TwoDocument15 pagesChapter TwoMilat KifluPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound: A "Physical Phenomenon That Stimulates The Sense of Hearing."Document11 pagesSound: A "Physical Phenomenon That Stimulates The Sense of Hearing."shreeratan910100% (1)
- Is A Sound, Especially One That Is Loud or Unpleasant or That Causes DisturbanceDocument10 pagesIs A Sound, Especially One That Is Loud or Unpleasant or That Causes DisturbanceRajnish AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound Power and IntensityDocument8 pagesSound Power and Intensitymandeep singhPas encore d'évaluation
- IMMERSION PortfolioDocument49 pagesIMMERSION PortfolioTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Rules About SubjectDocument2 pages20 Rules About SubjectTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- In Human Development People SayDocument2 pagesIn Human Development People SayTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- David WestDocument1 pageDavid WestTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume TeacherDocument3 pagesResume TeacherTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Two BrothersDocument6 pagesThe Two BrothersTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- UntrueDocument6 pagesUntrueTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject DescriptionDocument1 pageSubject DescriptionTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Could Dog Poop Help Communities Meet Their Energy NeedsDocument2 pagesCould Dog Poop Help Communities Meet Their Energy NeedsTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cocacola Case StudyDocument4 pagesThe Cocacola Case StudyTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Rules About SubjectDocument2 pages20 Rules About SubjectTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nestle Controversial IssuesDocument2 pagesNestle Controversial IssuesTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Could Dog Poop Help Communities Meet Their Energy NeedsDocument2 pagesCould Dog Poop Help Communities Meet Their Energy NeedsTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis Physiological IndicatorsDocument8 pagesAnalysis Physiological IndicatorsTatadarz Auxtero Lagria100% (1)
- Journal of The Different SenateDocument2 pagesJournal of The Different SenateTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Licensing and FranchisingDocument5 pagesDifference Between Licensing and FranchisingTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum VitaeDocument1 pageCurriculum VitaeTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Economic Issues With SolutionDocument2 pagesPhilippine Economic Issues With SolutionTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nestle Controversial IssuesDocument2 pagesNestle Controversial IssuesTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Animals That Live'S in Water and LandDocument3 pagesAnimals That Live'S in Water and LandTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Avocado Graham FloatDocument2 pagesAvocado Graham FloatTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Economic Issues With SolutionDocument2 pagesPhilippine Economic Issues With SolutionTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ronald Son Gica FarmDocument1 pageRonald Son Gica FarmTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Happy 1st Monthsary BalDocument1 pageHappy 1st Monthsary BalTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- This Article Is About The Social ScienceDocument1 pageThis Article Is About The Social ScienceTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analysis: Global MarketingDocument3 pagesCase Analysis: Global MarketingTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Timeline Chart Journalist Code of Ethics Journalist Creed: Paquit Jenelyn PDocument2 pagesTimeline Chart Journalist Code of Ethics Journalist Creed: Paquit Jenelyn PTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE STUDY - DocxggggggggggggggggDocument3 pagesCASE STUDY - DocxggggggggggggggggTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Famous Mathematicians Everyone Should KnowDocument3 pages6 Famous Mathematicians Everyone Should KnowTata LagriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil ErosionDocument1 pageSoil ErosionTatadarz Auxtero LagriaPas encore d'évaluation