Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Equations On Graph
Transféré par
Thushanan Ananthalingam0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
43 vues1 pageThis document discusses representing the solution of simultaneous equations graphically. The point where the lines, curves, or equations intersect satisfies the equations and is the solution. Using the discriminant, you can determine if there are two solutions, one solution, or zero solutions by looking at whether the lines/curves intersect. For linear and quadratic equations, setting their y-values equal and solving for x allows you to determine the number of solutions based on whether the discriminant is greater than, equal to, or less than zero.
Description originale:
Maths: Equations on graph
Titre original
Equations on graph
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document discusses representing the solution of simultaneous equations graphically. The point where the lines, curves, or equations intersect satisfies the equations and is the solution. Using the discriminant, you can determine if there are two solutions, one solution, or zero solutions by looking at whether the lines/curves intersect. For linear and quadratic equations, setting their y-values equal and solving for x allows you to determine the number of solutions based on whether the discriminant is greater than, equal to, or less than zero.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
43 vues1 pageEquations On Graph
Transféré par
Thushanan AnanthalingamThis document discusses representing the solution of simultaneous equations graphically. The point where the lines, curves, or equations intersect satisfies the equations and is the solution. Using the discriminant, you can determine if there are two solutions, one solution, or zero solutions by looking at whether the lines/curves intersect. For linear and quadratic equations, setting their y-values equal and solving for x allows you to determine the number of solutions based on whether the discriminant is greater than, equal to, or less than zero.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
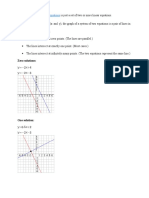
Simultaneous equations on graphs
Simultaneous equations on graphs
You can represent the solution of simultaneous equations graphically:
The point of intersection of the lines/curves/equations - satisfies it and is thus a solution
Using the discriminant - to find the number of solutions
A line or a quadratic could have:
- Two solutions
- One solution
- Zero solutions
Using the discriminant - you can determine the number of points of intersection
Linear: y = mx + c
Quadratic: y = ax + bx + c
Where they could potentially intersect - they would have the same y values where:
y=y
mx + c = ax + bx + c
0 = ax + (b − m)x + (c − c )
Now, you have an equation in the format: a + bx + c = 0
ax + (b − m)x + (c − c ) = 0
When b − 4ac > 0:
− There is two possible values of x
− Showing that there is two intersections/real soltuion
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Scrum: The Art of Doing Twice The Work in Half The TimeDocument3 pagesScrum: The Art of Doing Twice The Work in Half The TimeSyarifudin Zuhri100% (3)
- Introduction To Data Mining - Rev PDFDocument1 pageIntroduction To Data Mining - Rev PDFlhy20283Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 - Discriminants and RootsDocument21 pagesTopic 1 - Discriminants and RootsFrancis Ho HoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.4 Solving Quadratic InequalitiesDocument7 pages3.4 Solving Quadratic InequalitiesVon A. DamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic EquationDocument2 pagesQuadratic EquationDexanne BulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equations and FunctionsFons Roxas-ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Solving Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pagesChapter 6 - Solving Quadratic EquationsashPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 10 - Straight LinesDocument3 pagesUnit 10 - Straight LinesRaffaella LaxaldePas encore d'évaluation
- Matematik Noter: Linear EquationsDocument3 pagesMatematik Noter: Linear EquationsJolene RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- MathematicsDocument7 pagesMathematicsJay LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic FunctionDocument25 pagesQuadratic FunctionCherry Grace Sagde EuldanPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equations in Two Variables, Explain The Geometry of Lines or TheDocument10 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables, Explain The Geometry of Lines or Thejasmin jeharaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-Linear Programming (Theory)Document7 pages02-Linear Programming (Theory)THE MULTIVERSEPas encore d'évaluation
- Add Math Chapter 3Document4 pagesAdd Math Chapter 3SmarttuitionPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2. An Overview of Key IdeasDocument5 pages1.2. An Overview of Key IdeasTung TienPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Math OverviewDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Math OverviewmicjenPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Programming (Theory & Exercise) Module-6-BDocument10 pagesLinear Programming (Theory & Exercise) Module-6-BRaju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Neq1Document6 pagesSolving Neq1SAYID MABRUR RABBANI AL BABPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mathematical Problem of ParallelDocument3 pagesThe Mathematical Problem of ParallelIdeiasElevadas fatosPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratics Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesQuadratics Lecture NotesKaness Mathz100% (1)
- The Slope and Tangent LineDocument6 pagesThe Slope and Tangent LineDanniel EsteraPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix: Useful Mathematical Techniques: A.1 Solving TrianglesDocument23 pagesAppendix: Useful Mathematical Techniques: A.1 Solving Trianglessaleemnasir2k7154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations 4: Polynomial EquationDocument16 pagesQuadratic Equations 4: Polynomial EquationRithin NagarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic EquationDocument5 pagesQuadratic EquationteachersarasPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Reviewer 9Document8 pagesMath Reviewer 9Kurt Dela PenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic and Other Special Functions 1Document7 pagesQuadratic and Other Special Functions 1StoryKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 1A Quiz 4 Solution: February 29th, 2008 Name SIDDocument1 pageMath 1A Quiz 4 Solution: February 29th, 2008 Name SIDxradhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations: Solving The Quadratic Equation 1. Graphical MethodDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equations: Solving The Quadratic Equation 1. Graphical MethodManju SreePas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Calculus PrimerDocument17 pagesPre Calculus PrimeracsimsPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Calculus: H X F H X F X FDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Calculus: H X F H X F X FJonathan NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Class 9 Notes For Linear Equations in Two Variables PDFDocument3 pagesMaths Class 9 Notes For Linear Equations in Two Variables PDFLatoyaWatkinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecuaciones de 2do GradoDocument17 pagesEcuaciones de 2do GradoCARLOS LEONEL BARRERA GAMBOAPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW PW Live Chapter Polynomial 10Document7 pagesWWW PW Live Chapter Polynomial 10Shubham SutharPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 9 Lesson NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 9 Lesson Notesapi-291793268Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic !!!Document11 pagesQuadratic !!!Sridhar PantPas encore d'évaluation
- Catatan Bab 2Document2 pagesCatatan Bab 2no name namePas encore d'évaluation
- Previouspapers Intermediate 2021 Ib - 1Document3 pagesPreviouspapers Intermediate 2021 Ib - 1yachemanenisPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equations: Zero SolutionsDocument3 pagesLinear Equations: Zero SolutionsGul ZareenPas encore d'évaluation
- Linearequationsintwovariables 160208143945Document40 pagesLinearequationsintwovariables 160208143945Muhhamed NuuraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebraiic Expressions, Equations and Quadratic EquationsDocument37 pagesAlgebraiic Expressions, Equations and Quadratic EquationsNaomi NyambasoPas encore d'évaluation
- M1W5 Problem Solving Tips PDFDocument5 pagesM1W5 Problem Solving Tips PDFGirindhra A NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Book - 1 - Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument10 pagesBook - 1 - Co-Ordinate GeometrySusmita Mukherjee100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Straight Lines Exercise 10.3Document18 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Straight Lines Exercise 10.3ajithmanarcadu2024Pas encore d'évaluation
- STEP Support Programme Assignment 21 Warm-UpDocument4 pagesSTEP Support Programme Assignment 21 Warm-UpMike16KPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equation 1Document2 pagesLinear Equation 1Devansh DhiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 2 - Derivatives Solutions September 28, 2009Document4 pagesWorksheet 2 - Derivatives Solutions September 28, 2009Majd Abu KhalafPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 02 - Quadratic Equations - Study ModuleDocument27 pagesChapter 02 - Quadratic Equations - Study Modulevwxyzxyz729Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calc II ReviewDocument7 pagesCalc II ReviewPablo KhilopPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeDocument5 pagesUnit 18 - Curved Graphs - DerivativeRaffaella LaxaldePas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic EquationDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationHaimen BuisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesQuadratic EquationsLeo Jade AbiertasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pair of Linear Equation in Two VariablesDocument10 pagesPair of Linear Equation in Two VariablesAnonymous AKLRK6KNiRPas encore d'évaluation
- PolynomialsDocument42 pagesPolynomialsapi-296824694Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3Document3 pagesLecture 3Hari KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.0 Review FunctionsDocument12 pages3.0 Review Functionsummu***Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 24Document5 pagesLecture 24Syeda Farkhanda Batool NaqviPas encore d'évaluation
- Describing A Plane in 3-D Space - Graphical - Cramer's Rule (2-D and 3-D)Document29 pagesDescribing A Plane in 3-D Space - Graphical - Cramer's Rule (2-D and 3-D)MukkannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic EquationsDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationsRenDenverL.DequiñaIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equation-X CheatsheetDocument5 pagesLinear Equation-X CheatsheetJd AnimationPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics I Chapter 1: One-Variable Functions. ContinuityDocument64 pagesMathematics I Chapter 1: One-Variable Functions. ContinuityErnestPas encore d'évaluation
- P1T1 QuadraticsDocument36 pagesP1T1 QuadraticsAdeyemi SamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (8)
- Ecss Q ST 30 11c Rev1 (4october2011) PDFDocument71 pagesEcss Q ST 30 11c Rev1 (4october2011) PDFjsadachiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Chapter 1Document24 pages2 Chapter 1陳信宏Pas encore d'évaluation
- Setup Prometheus Monitoring On KubernetesDocument6 pagesSetup Prometheus Monitoring On KubernetesAymenPas encore d'évaluation
- Laptop Fault BookDocument38 pagesLaptop Fault Bookredsky991100% (1)
- Remote Procedure CallDocument6 pagesRemote Procedure CallJoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Career Planning Resources - 2021-22Document1 pageCareer Planning Resources - 2021-22Jessica NulphPas encore d'évaluation
- MP6000 PC v00Document262 pagesMP6000 PC v00Marcio York Cardoso100% (1)
- Basic Python NotesDocument8 pagesBasic Python NotesSreenivasulu reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Install and Configure Oracle Golden GateDocument12 pagesHow To Install and Configure Oracle Golden GatesadineniPas encore d'évaluation
- Allegro PCB Editor User Guide: Preparing Manufacturing Data: Product Version 16.0 June 2007Document132 pagesAllegro PCB Editor User Guide: Preparing Manufacturing Data: Product Version 16.0 June 2007a_damrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Ism FDocument128 pagesIsm FAmit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- SLR140 - ArDocument51 pagesSLR140 - ArDeepak Ojha100% (1)
- Accu-Chek Active User Manual PDFDocument70 pagesAccu-Chek Active User Manual PDFjoseluisblanco69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Harbinger VARI 4000 Series Owner ManualDocument20 pagesHarbinger VARI 4000 Series Owner ManualAbel AmadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Ds Futro x923Document6 pagesDs Futro x923conmar5mPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Programming Simple Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesLinear Programming Simple Word ProblemsWendy Millheiser Menard0% (1)
- Oopc++ Assignment G.Vaishnavi Btech Cse (2 Sem) ENR. NO:-A80105219022 Section:ADocument8 pagesOopc++ Assignment G.Vaishnavi Btech Cse (2 Sem) ENR. NO:-A80105219022 Section:ASanjana PulapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gernsback's Educational Library 60 Rapid TV RepairDocument228 pagesGernsback's Educational Library 60 Rapid TV RepairWillian LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- OmniOutliner 4 For Mac User ManualDocument124 pagesOmniOutliner 4 For Mac User Manualagostino_cirilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Gemini MIX2GO Quick Start GuideDocument2 pagesGemini MIX2GO Quick Start GuideAngel ObandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bumble BizzDocument38 pagesBumble BizzAxel RomanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy: by DR - LiewDocument41 pagesVisual Basic 2019 Made Easy: by DR - LiewAnup AravindakshanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4 GHZ Band Scanner With NRF24L01Document28 pages2.4 GHZ Band Scanner With NRF24L01Rafael LucasionistPas encore d'évaluation
- TMA4215 Report (10056,10047,10023)Document5 pagesTMA4215 Report (10056,10047,10023)EvacuolPas encore d'évaluation
- G. Gevorgyan, M.markosyan+ C++Document229 pagesG. Gevorgyan, M.markosyan+ C++HaykPas encore d'évaluation
- VTAM 4R2 Early User ExperiencesDocument248 pagesVTAM 4R2 Early User Experiencesgborja8881331Pas encore d'évaluation
- K Nearest Neighbor (KNN)Document9 pagesK Nearest Neighbor (KNN)simransolanki003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Judith Ainslie Jackson: Professional Experience Lice Ladies of AtlantaDocument4 pagesJudith Ainslie Jackson: Professional Experience Lice Ladies of AtlantaJudi JacksonPas encore d'évaluation