Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rules of Thumb Geotech Monitoring
Transféré par
Madan Kumar AnnamCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rules of Thumb Geotech Monitoring
Transféré par
Madan Kumar AnnamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
C O L U M N
Rules of Keivan Rafie
Thumb Keivan is lead tunnel designer for Stantec,
and a columnist for Tunnels & Tunnelling
Interview with Shahram Siavash, business development WHAT ARE THE MOST IMPORTANT
PARAMETERS TO MONITOR?
manager, geotechnical engineering Soil and groundwater pressure at the
G
tunnel face during EPBM tunnelling,
eotechnical monitoring in adjacent buildings; and determine the face displacement during open SEM
tunnelling and underground need and timing for corrective measures. tunnelling, ground convergence
projects provides data that and swelling, soil pressure at certain
helps engineers and contractors Traversing probe inclinometer: One of depths, pore pressure, horizontal
in every stage of a project. Instruments the most commonly used for monitoring ground deformations, vertical ground
are used to characterize initial site lateral subsurface deformations. movements at surface or in various
conditions, verify design assumptions and Consisting of a portable wheeled probe, depths (settlement), load in anchored
to monitor the effects of construction. graduated control cable, and a portable elements, strain in compressed or
Each project presents a unique set of readout, the operator makes a survey tensioned structural elements, structural
critical parameters, and the designer of the borehole, taking tilt readings at deformations (buildings, utilities, bridges),
must identify those parameters and select intervals, from the bottom to the top. construction-induced vibrations, and
instruments to measure them. The resulting data provides a detailed groundwater levels near the dewatered
profile of the casing. If ground movement areas during tunnelling.
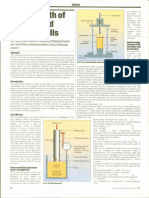
Pore-water pressure: This parameter occurs, subsequent surveys will reveal
helps establish initial site conditions; changes in the profile, which can be WHAT ARE COMMON LOCATIONS FOR
predict slope stability; design and build plotted to determine the magnitude, INSTRUMENTS?
for lateral earth pressures and monitor the depth, direction, and rate. At tunnel face, on the perimeter of the
effectiveness of drainage schemes. tunnel, on the ground surface, at various
Vertical deformation: Measurements depths above the tunnel, on the adjacent
Standpipe piezometers: Sometimes help verify soil consolidation is structures and buildings, in the launch
referred to as an open-hydraulic proceeding as predicted; monitor heave and extraction shafts where the tunnel
piezometer or a Casagrande piezometer, in floor of excavation; monitor settlement meets the excavation, on support of
it consists of a porous water-intake due to ground loss or heave outside excavation elements such as tie-backs,
element connected to a riser pipe. Water of excavation; monitor for settlements struts, and piles, on utilities (water-mains,
enters the riser pipe through the intake that may damage buildings or service sewers), on existing building cracks, and
element, which is normally sealed in the connections and determine the need adjacent to the sources of vibration.
borehole at a specified depth. As pore- and timing for corrective measures.
water pressure increases or decreases, the Important instruments to measure vertical WHAT ARE THE FREQUENCIES OF
water level inside the standpipe rises or deformation are: Settlement Cells (to DATA ACQUISITION?
falls. Readings are usually obtained with monitor a single, subsurface point); Frequencies vary depending on the
a water level indicator, which provides a Settlement Extensometers (to monitor importance of the parameter that is
depth-to-water measurement. large settlements in soft ground below being monitored and the construction
fills); MultiPoint Rod Extensometers stage. Usually, the highest frequencies
Vibrating wire piezometers: These (provide high resolution multipoint are during active tunnelling and after
instruments consist of a tensioned steel measurements of vertical deformation) completion of a section, the frequencies
wire, one end of which is anchored and and Horizontal Inclinometers. can be reduced and continued for a
the other end fixed to a diaphragm. The defined period as a confirmatory measure.
diaphragm deflects in response to applied An automatic data acquisition system While some parameters, such as ground
pore water pressure, changing the tension may be required when there is a need surface or building movements, may
in the wire and its resonant frequency. for real-time monitoring and automatic require at least one round of reading
They are typically used for continuous alarms; sensors are located at a remote during the tunnelling shift, some
and long-term pore pressure monitoring, site or in a location that prevents easy parameters may require more frequent
specifically in fine-grained soils where access; there are too many sensors for or even continuous monitoring using
the use of conventional standpipe timely manual readings; or qualified automatic data loggers or remote data
piezometers is not recommended. technicians are not available. acquisition systems
Lateral Deformation: Measurements of
this parameter evaluate the stability of
slopes; monitor deformation of laterally Agree or disagree?
loaded pile; monitor the magnitude and Let us know what your experience has taught you. Or let us know what topic should be
rate of movements in rock masses; check included in future Rules of Thumb columns. editor@tunnelsandtunnelling.com
for ground movement that may affect
40 | February ~ March 2017 | www.tunnelsandtunnelling.com
040tunNA0217_ROT.indd 40 10/02/2017 11:26
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ground Freezing 1980: Selected Papers from the Second International Symposium on Ground Freezing, Trondheim, Norway, 24-26 June 1980D'EverandGround Freezing 1980: Selected Papers from the Second International Symposium on Ground Freezing, Trondheim, Norway, 24-26 June 1980Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geomorphological Roulette For EngineersDocument42 pagesGeomorphological Roulette For EngineersNathan VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Expansive Soils PaperDocument7 pagesExpansive Soils PaperM Ramzan QadirPas encore d'évaluation
- Slope Stability Guidelines For Devt ApplicationsDocument24 pagesSlope Stability Guidelines For Devt ApplicationsJose Leo MissionPas encore d'évaluation
- May 2017 HCTRA Standard Specifications PDFDocument1 270 pagesMay 2017 HCTRA Standard Specifications PDFLiliana RibeiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Settlement Settlement of Shallow Footings On Layered Soil State of The Art of Shallow Footings On Layered Soil State of The ArtDocument8 pagesSettlement Settlement of Shallow Footings On Layered Soil State of The Art of Shallow Footings On Layered Soil State of The ArtAnshuman SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Compression Behavior in One-Dimensional Consolidation TestsDocument6 pagesSecondary Compression Behavior in One-Dimensional Consolidation TestsBookAncestorPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Pore Water Pressures in Embankment Stability PDFDocument6 pagesRole of Pore Water Pressures in Embankment Stability PDFfaroeldrPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Peat Strength, Peat Characterisation and Constitutive Modelling of Peat With Reference To LandslidesDocument24 pagesReview of Peat Strength, Peat Characterisation and Constitutive Modelling of Peat With Reference To LandslidesAnbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mayne & Peuchen (2018) - CPTu NKT For Su in ClaysDocument6 pagesMayne & Peuchen (2018) - CPTu NKT For Su in Clayschin_kbPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comparative Evaluation of Various AdditivesDocument11 pagesA Comparative Evaluation of Various Additivesagus_ip3808Pas encore d'évaluation
- British Standard: A Single Copy of This British Standard Is Licensed ToDocument29 pagesBritish Standard: A Single Copy of This British Standard Is Licensed TodamithPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Admixtures: Specification Accelerating and Retarding Water-Reducing AdmixturesDocument22 pagesConcrete Admixtures: Specification Accelerating and Retarding Water-Reducing AdmixtureskushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hoek - Characterisation Andengineering Properties of Tectonically Undisturbed But Lithologically Varied Sedimentary Rock MassesDocument9 pagesHoek - Characterisation Andengineering Properties of Tectonically Undisturbed But Lithologically Varied Sedimentary Rock Massesecossich123100% (1)
- Friction Capacity of SoilDocument8 pagesFriction Capacity of SoilkushaljpPas encore d'évaluation
- Piling Good Practice Guide (LABC Warranty, 2014)Document3 pagesPiling Good Practice Guide (LABC Warranty, 2014)sandycastlePas encore d'évaluation
- (Extract) Ch. 6 Interpretation of Rock Properties - From FHWA-If-02-034 Evaluation of Soil and Rock PropertiesDocument98 pages(Extract) Ch. 6 Interpretation of Rock Properties - From FHWA-If-02-034 Evaluation of Soil and Rock PropertiesO SPas encore d'évaluation
- Horizontal DrainDocument8 pagesHorizontal DrainHariprasath TPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Stabilizing TechniquesDocument8 pagesSoil Stabilizing TechniquesSaurabh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compression IndexDocument3 pagesCompression IndexTran Nguyen100% (3)
- The Direct Shear Strength and Dilatancyof Sand-Gravel MixturesDocument27 pagesThe Direct Shear Strength and Dilatancyof Sand-Gravel MixturesPipatpong NookhaoPas encore d'évaluation
- CFEM 4th Ed Errata (April 2018)Document10 pagesCFEM 4th Ed Errata (April 2018)DudePas encore d'évaluation
- Permeability From Grain Size Distribution PDFDocument137 pagesPermeability From Grain Size Distribution PDFDelvin JacobsPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment Load in WallapDocument3 pagesMoment Load in WallapSajjad AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1998-03 Pages 38-41 PDFDocument4 pages1998-03 Pages 38-41 PDFMu Hardi100% (1)
- Cambridge INSITU - Pressuremeters - Web PDFDocument28 pagesCambridge INSITU - Pressuremeters - Web PDFChristian ValerioPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of A One-Dimensional Large-Strain Consolidation Model To A Fullscale Tailings Storage Facility PDFDocument11 pagesApplication of A One-Dimensional Large-Strain Consolidation Model To A Fullscale Tailings Storage Facility PDFchenPas encore d'évaluation
- 5075 1 1982 PDFDocument23 pages5075 1 1982 PDFhz135874Pas encore d'évaluation
- Groundwater Control For ConstructionDocument22 pagesGroundwater Control For ConstructionkrainajackaPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Ground Movements Induced by ExcavationsDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Ground Movements Induced by ExcavationsNaveen BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Asadzadeh - Direct Shear Testing On A Rockfill MaterialDocument18 pagesAsadzadeh - Direct Shear Testing On A Rockfill MaterialDavid CastañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Settlement of Circular Footing On SandDocument26 pagesSettlement of Circular Footing On SandninoronaldPas encore d'évaluation
- Studies On Correlation Between Flexural Strength and Compressive Strength of ConcreteDocument6 pagesStudies On Correlation Between Flexural Strength and Compressive Strength of ConcreteTim Lin50% (2)
- Shear Strength Reduction at Soil Structure InterfaceDocument10 pagesShear Strength Reduction at Soil Structure InterfaceKasim BaručijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Embankment SlopeDocument16 pagesEmbankment SlopeFlorentina SuduPas encore d'évaluation
- Hunt Del Nero 2012 - Microunneling in Cobbles and Boulders PaperDocument36 pagesHunt Del Nero 2012 - Microunneling in Cobbles and Boulders PaperswhuntPas encore d'évaluation
- Siegel Et Al 2014 Neutral Plane Method For Drag Force of Deep Foundations and The AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design SpecificatiDocument10 pagesSiegel Et Al 2014 Neutral Plane Method For Drag Force of Deep Foundations and The AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design SpecificatirotkvicePas encore d'évaluation
- Processing Mixtures of Lime, Fly Ash, and Heavy Metal Wastes in Structural Fills and Other Construction ApplicationsDocument4 pagesProcessing Mixtures of Lime, Fly Ash, and Heavy Metal Wastes in Structural Fills and Other Construction ApplicationsROHITPas encore d'évaluation
- Seepage and Contraction Joints in Concrete Canal LiningDocument25 pagesSeepage and Contraction Joints in Concrete Canal LiningRohan ShivasundarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pinhole Erosion Test For Identification of Dispersive ClaysDocument28 pagesPinhole Erosion Test For Identification of Dispersive ClaysAndyra Jaiz Baddu100% (1)
- Analysis of Plate Load Test ResultsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Plate Load Test Resultssaranga adeeshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil Mechanics LecturesDocument117 pagesSoil Mechanics LecturesEhtesham MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Advances in Soil Liquefaction Engineering and Seismic Site Response EvaluationDocument46 pagesRecent Advances in Soil Liquefaction Engineering and Seismic Site Response Evaluationv100% (2)
- In-Situ Test Calibrations For Evaluating Soil Parameters: P.W. MayneDocument52 pagesIn-Situ Test Calibrations For Evaluating Soil Parameters: P.W. MayneMayoo LaxmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Barton-High Pressure Pre-Grouting. TTI Sept 2004 p28-30 PART IDocument3 pagesBarton-High Pressure Pre-Grouting. TTI Sept 2004 p28-30 PART Icastille1956Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prediction of The Axial Bearing Capacity of PilesDocument6 pagesPrediction of The Axial Bearing Capacity of PilesNicole CarrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Collapse of A Reiinforced Soil Segmental Retainign WallDocument9 pagesCollapse of A Reiinforced Soil Segmental Retainign WallrfingePas encore d'évaluation
- 300 Solved Problems Soil / Rock Mechanics and Foundations EngineeringDocument1 page300 Solved Problems Soil / Rock Mechanics and Foundations EngineeringAkash Ashish GautamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Lateral Earth PressureDocument23 pagesSeismic Lateral Earth PressuremrnaeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Dips v7 Manual (081-100)Document20 pagesDips v7 Manual (081-100)Karina CarmonaPas encore d'évaluation
- AttD6 - 225 Roy Geotech ReportDocument128 pagesAttD6 - 225 Roy Geotech ReportEmerson SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Silt From CPTu - Shuttle-Jefferies PDFDocument29 pagesDetermining Silt From CPTu - Shuttle-Jefferies PDFRaúl Bernal LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile Behavior-Consequences of Geological and Construction ImperfectionsDocument26 pagesPile Behavior-Consequences of Geological and Construction ImperfectionsIvan MojicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactive Soils Can Be Vicious: Paper Presented byDocument6 pagesReactive Soils Can Be Vicious: Paper Presented byJohn Dakota100% (1)
- Lecture 10 - Natural Terrain Landslide Risk Management (19 Nov 2020) FinalDocument99 pagesLecture 10 - Natural Terrain Landslide Risk Management (19 Nov 2020) FinalYUK LAM WONGPas encore d'évaluation
- Eerc-75-29Document40 pagesEerc-75-29Hector Haches100% (1)
- Triaxial Testing of Granular Soil (Colliat-Dangus, 1988)Document21 pagesTriaxial Testing of Granular Soil (Colliat-Dangus, 1988)Abraham FIgueroa ARevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Roberson 2012 PDFDocument22 pagesRoberson 2012 PDFAdy NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hunt&Angulo 1999 Base Lining BouldersDocument16 pagesHunt&Angulo 1999 Base Lining BouldersswhuntPas encore d'évaluation
- Bomba de Vácuo Sotorbilt 4mrDocument12 pagesBomba de Vácuo Sotorbilt 4mrWormInchPas encore d'évaluation
- Retrofit of Water Mist Catcher: WMC For L23/30 (H) and L28/32 (H) GensetsDocument2 pagesRetrofit of Water Mist Catcher: WMC For L23/30 (H) and L28/32 (H) GensetsMichael GorobaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 GeosyntheticsDocument315 pagesUnit 5 Geosyntheticskowshik1737551Pas encore d'évaluation
- 101.S-4501 Steamer Cyclone Cleaning ProcedureDocument6 pages101.S-4501 Steamer Cyclone Cleaning ProcedureTRONGKIMPas encore d'évaluation
- 20W40 MSDSDocument2 pages20W40 MSDSAbhinav SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics - AC - DC PDFDocument20 pagesBasic Electronics - AC - DC PDFRowena ResurreccionPas encore d'évaluation
- PDRXDocument4 pagesPDRXNeel AdwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- nRF24LU1 - NordicDocument187 pagesnRF24LU1 - NordicEdward SURIELPas encore d'évaluation
- Entreprise Programming Lab - Skill WorkbookV1.0Document198 pagesEntreprise Programming Lab - Skill WorkbookV1.0Dhanush Parasa40% (5)
- Supercontryx®: Innovative Glass For X - Ray ProtectionDocument2 pagesSupercontryx®: Innovative Glass For X - Ray ProtectionUsman AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercruiser Service Manual #14 Alpha I Gen II Outdrives 1991-NewerDocument715 pagesMercruiser Service Manual #14 Alpha I Gen II Outdrives 1991-NewerM5Melo100% (10)
- A Study On The Design Optimization of An AUV by Using Computational Fluid Dynamic AnalysisDocument7 pagesA Study On The Design Optimization of An AUV by Using Computational Fluid Dynamic AnalysisSalma SherbazPas encore d'évaluation
- Tension Capacity of PileDocument8 pagesTension Capacity of Pilenimal179100% (1)
- Data SheetDocument2 pagesData SheetAsalamEilujPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Ee 1991Document7 pagesGate Ee 1991Bhavani Chandra UniquePas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 VGP Checklist - Rev0Document9 pages2015 VGP Checklist - Rev0Takis RappasPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Review 1 ScheduleDocument1 pageProject Review 1 ScheduleH R VALAPas encore d'évaluation
- (Communication) (English E-Book) Scientific Writing PDFDocument5 pages(Communication) (English E-Book) Scientific Writing PDFIrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- C32 Electronic Unit Injector - Adjust PDFDocument4 pagesC32 Electronic Unit Injector - Adjust PDFmanu luvunga100% (2)
- WS500 Operator WorkstationDocument2 pagesWS500 Operator WorkstationNayants GuzmánPas encore d'évaluation
- SensoNODE Catalog 3864 Feb 2015Document28 pagesSensoNODE Catalog 3864 Feb 2015btsgr parkerPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 Free Data Science Projects To Boost Your Knowledge & SkillsDocument18 pages17 Free Data Science Projects To Boost Your Knowledge & SkillshamedfazelmPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB LMU 574 - mcd80Document12 pagesABB LMU 574 - mcd80gadware2011bplPas encore d'évaluation
- Maison À BordeauxDocument5 pagesMaison À BordeauxSpam TestPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Deus II UkDocument52 pagesManual Deus II UkMariusPas encore d'évaluation
- Extended End-Plate Stiffener PDFDocument2 pagesExtended End-Plate Stiffener PDFaams_sPas encore d'évaluation
- Chrony Beta and GammaDocument36 pagesChrony Beta and GammaÁdám MajorPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Questions and Answers - 2011Document10 pagesTutorial Questions and Answers - 2011Jan ScarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cfw300 Manual 1Document124 pagesCfw300 Manual 1maurilioPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Force CANADA Code - CNBC2005-V421Document7 pagesSeismic Force CANADA Code - CNBC2005-V421Niko NištićPas encore d'évaluation