Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The Body
Transféré par
Angela Reyes0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
150 vues6 pageshahahahha
Titre original
Cells and Tissues
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documenthahahahha
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
150 vues6 pagesCells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The Body
Transféré par
Angela Reyeshahahahha
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 6
CELLS AND TISSUES - Which set apart from the rest of the
part of the cell
Every living thing is made up of cells. -Barrier of Nucleus
CELLS - Building blocks of every living - consists of a double phospholipid
thing. membrane (has 2 layers)
Not all cells are the same because they - HAS HUGE nuclear pores that allow
have different functions. for exchange of material with the
TISSUES are groups of cells that are rest of the cell. Cell membrane –
similar in structure and function small nuclear pores
2.) Nucleolus (plural: nucli), nucleoli
ANATOMY OF THE CELL
- Almost spherical
Cells are not all the same - Ribosome - one of the cytoplasmic
All cells share general structures organelle just like the mito; it plays a
Cells are organized into 3 main regions : role for protein sythesis or protein
Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Plasma Membrane production
- Nucleus contains one or more
2 types of cells that are found in the body: nucleoli: sites of ribosome
1.) Gametes – sex/germ cells; specialized production; ribosomes then migrate
on reproduction to the cytoplasm through nuclear
2.) Body Cells – autosomal/somatic cells pores.
3.) Chromatin : composed of DNA and
* Gametes are cells that fuse during sexual protein; Found/scattered inside the
reproduction, germ cells are cells that give rise nucleus; Can condense to form
to gametes, and stem cells are cells that can chromosomes when the cell divides
divide through mitosis and differentiate into - Responsible for the inheritance of the
diverse specialized cell types. genes
- Derived the so called CHROMOSOMES
Spherical – most cells of the body are
- Collection of fluid inside the nuclear
spherical.
membrane called nucleoplasm
Whiplike Shapes – designed for egg cells.
Cell with no nucleus: Red Blood Cell
Cell Membrane – without it, the cell would (erythrocyte)
not be able to survive.
Multinucleated Cell (many nuclei) : Skeletal
- Most indispensable part of the cell Muscle Cell
3 REGIONS OF CELL: RIBOSOME PRODUCTION
1.) NUCLEUS Protein synthesis or Protein
Control center of the cell Formation/production
Commonly found at the center but not Travels from Nuclear membrane via
all the time pores to gain access to cytoplasm.
Contains genetic material (DNA)
3 Regions that you will find on the 2.) PLASMA MEMBRANE
nucleus : Barrier for cell contents
1.) Nuclear Membrane/Nuclear Phospholipid bilayer
Envelope
1 Phospholipid molecule is made up of 1 - Metabolic machinery of the cell
polar head and 2 tails Inclusions
Hydrophilic – heads (head have - Non-functioning units
attraction of water; polar) - Ex : Vacuole – contain pigment and
Hydrophobic – tails (fear water: non starches
polar)
DIFF CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES (vital
Also contains protein, cholesterol, and
role for the cell):
glycoproteins
Ribosomes
SPECIALIZATION:
-made of protein and RNA
Microvilli: - site of protein synthesis
Finger-like projections that increase - found at 2 locations: free In cytoplasm;
surface area for absorption of nutrients attached to rough endoplasmic
reticulum
OTHER SPECIALIZATION Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Membrane Junctions : Fluid-filled tubes for carrying
substances
1.) Tight junctions- impermeable 2 types of ER
junctions which set a parts from one 1.) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
cell to the neighboring cell Studded with ribosomes
2.) Tight junctions- impermeable Site where building materials of cellular
junctions which set a parts from one membrane are formed
cell to the neighboring cell Transports proteins which are
3.) Desmosomes – anchor junction; synthesize in the ribosome
connects the one cell to the adjacent 2.) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
lining cell Functions in cholesterol synthesis and
4.) Gap junctions – aka communicating breakdown, fat metabolism, and
junctions which can be find in the detoxification of drugs.
hard muscle No ribosomes
5.) Connexion – separate the cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus:
of one cell for the cytoplasm of the Modifies and packages proteins
adjacent lining cell
Green flatten sacs with enlarged dilated
3) CYTOPLASM
end.
- Outside the nuclear membrane but
Produces different types of packages:
inside the cell membrane
Secretory vesicles
Cell Membrane components
Lysosome - one of the cytoplasmic
organelles and one of the packages
Material outside the nucleus and inside
from the enlargement of the golgi
the plasma membrane:
apparatus
Cytosol
Lysosome
- Fluid that gel-like consistency
Contains digestive enzymes that digest
suspends/dating the organelles and
non-usable materials within the cell
inclusion bodies.
Spherical body
Organelles
“Suicidal sac”-digested lysosome
- Functioning unit
Peroxisome
- Ex : mitochondria, lysosomes and ER
Membranous sacs of contains oxidase Not found in all cells
enzymes Used for movement
Detoxify harmful substances Cilia move material across the cell
Break down free radicals (highly surface
reactive chemicals) Flagellum propels the cell
Replicate by pinching in half.
Cell Diversity
Mitochondrion
-“powerhouse” of the cell (generates Fibroblasts – cells that connect the body
ATP- which is a form of energy that is parts; acts to binds tissue together
used up by the cell of the body) Epithelial cells – cells that cover and line
- serves as the site of the cellular body organs.
respiration; involves processes that Skeletal and Smooth Muscle Cells – cells
generates ATP that move organs and body parts
- change shape continuously
Fat cell – Cell that stores nutrients
- carries out reactions where oxygen is
Lysosomes- cell that fight disease
used to break down food
- provides ATP for cellular energy
Cytoskeleton
Maintaining the char shape of the cell
Network of protein structures that
extend throughout the cytoplasm
Provides the cell with an internal
framework.
3 different types:
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments Nerve Cell – cells that gathers
Microtubules information and controls body
*differ in terms of sizes and components functions.
protein sac units Cell reproduction-sperm, nucleus and
flagellum
* take care of maintaining the shape of the cell
CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY: MEMBRANE
Centrioles TRANSPORT
Yellow structured- 2 bar like bodies and
close to the nucleus or perpendicular to Cell Membrane transport- movement of
each other substances into and out of the cell
Rod-shaped bodies made up of Transport is by 2 basic methods:
microtubules - Passive Transport
Direct formation of mitotic spindle No energy/ ATP is required
during cell division during mitosis - Active Transport
The cell must provide metabolic energy
Form of the bases of the cilia and
Rely on kinetic energy
flagella found in some cells that capable
Molecules need ATP
of movement
Solutions and Transport
Cellular Projections
Solution – homogenous mixture of 2 or - Highly polar water easily crosses the
more components plasma membrane
- Solvent – dissolving medium (water) - SOLVENT COMPONENT
- Solutes – components in smaller 3. Facilitated Diffusion
quantities within a solution (sugar, - Substances require a protein carrier
coffee granules, creamer) for passive transportation of the
molecules
Water Collection of the Cell - Larger molecules
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) – Nucleoplasm - Non lipid soluble
and cytosol; outside the cell - SOLUTE COMPONENT
- Interstitial Fluid- fluid on the ECF of Suspended in 3 diff types of solution: isotonic,
the cell hypotonic and hypertonic solutions
- Plasma found in the blood
Intracellular fluid (ICF) –inside the cell B. Filtration (relies on hydrostatic pressure
- Nucleoplasm, Cytosol gradient)
- Water and solutes are forced
Cell Membrane is Selective Permeability through a membrane by fluid, or
hydrostatic pressure.
The plasma membrane allows some
- A pressure gradient
materials to pass while excluding
-solute-containing fluid is pushed
others.
from a high pressure area to a lower
This permeability includes movement
pressure area
into and out of the cell.
Passive Transport Processes – use KE
- Molecules must move from higher
to lower pressure
A. Diffusion (relies on concentration
gradient) Active Transport Processes – use ATP
- Particles tend to distribute
- Molecules must move from lower
themselves evenly within a solution
to higher pressure
- Movement if rom high concentration
Transport substances that are unable to
to low concentration, or down a
pass by diffusion because:
concentration gradient
- They may be too large
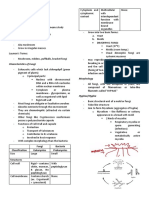
3 Types of Diffusion - They may not be able to dissolve in
the fat core(phospholipid bilayer) of
1. Simple Diffusion the membrane
- Unassisted process - They may have to move against a
- Solutes are either lipid-soluble concentration gradient(lower to
material or are small enough to pass higher concentration)
through membrane pores Two common forms of active transport
- Smaller molecules 1. Solute Pumping
- Molecules are lipid soluble to pass - Amino acids, some sugars and ions
through the phospholipid bilayer are transported by solute pumps
- SOLUTE COMPONENT - ATP energizes protein carriers, and
2. Osmosis in most cases, moves substances
- Simple diffusion of water against concentration gradients.
2. Bulk Transport - Occurs toward the end of the
a. Exocytosis interphase
- Moves materials out of the cell - DNA uncoils and each side serves as
- Material is carried in a membranous a template
vesicle S-PHASE (SYNTHESIS PHASE)
- Vesicle migrates to plasma Green – Adenine = Yellow –
membrane Thymine (DNA)
- Vesicle combines with plasma Blue – Cytosin = Red - Guanine
membrane
Stages of Mitosis
- Material is emptied to the outside
b. Endocytosis Interphase
- Extracellular substances are - No cell division occurs
engulfed by being in a membranous - The cell carries out normal
vesicle metabolic activity and growth
- Types of endocytosis - Centrioles (directors of the
Phagocytosis – cell eating formation of the spindle apparatus)
Pinocytosis – cell drinking duplicate
Cells Life Cycle Prophase
- First stage of cell division
Cells have 2 major periods: - Centrioles migrate to the poles
- Centrioles separated to form the
1. Interphase (preparatory stage)
spindle apparatus(mimcrotubules)
- Cell grows in size
- Nucleus, nuclear membrane,
- Cell carries on metabolic processes
nucleolus disappear
S-PHASE – DNA replication happens
Metaphase
2. Cell Division
- Spindle from centrioles are attached
- Cell replicates itself
to chromosomes that are aligned at
- Function is to produce more cells for
the center of the cell
growth and repair processes
Anaphase
Events of Cell Division - Daughter chromosomes are pulled
toward the poles
1. Mitosis (nuclear division) Meiosis (rise - The cell begins to elongate
from the germ cells) Telophase
- Division of the nucleus - Daughter nuclei begin forming
- Results in the formation of 2 - A cleavage furrow (for cell division)
daughter nuclei. begins to form
2. Cytokinesis - Reverse of prophase
- Divisions of the cytoplasm
- Begins with mitosis is near Nucleoplasm – chromatin material
completion
Cytosol – fluid part of cytoplasm
- Results in the formation of 2
daughter cells. Vacuole – contains pigments
DNA Replication Lysosomes
- Genetic material duplicated and Acid hydrolases
readies a cell for division into 2 cells Suicidal sack
FAT CELL – nucleus is on the side.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) - a molecule
that carries energy within cells.
INTERPHASE
Preparatory stage
Endo (inside, bringing)
Endocytosis
Exocytosis (outside)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Chapter 22 Lymphatic System Doran Mls 1 FDocument10 pagesAnaphy Chapter 22 Lymphatic System Doran Mls 1 FayenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues in AnaphyDocument8 pagesTissues in AnaphyAngela EstorninosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Iya BiancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic PDFDocument8 pagesLymphatic PDFJoydee Liza MarcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document8 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System - Free Printable TestsDocument1 pageNervous System - Free Printable TestsRayan KassamPas encore d'évaluation
- A-P Chapter 4 TissueDocument21 pagesA-P Chapter 4 TissueMONIQUE VELASCOPas encore d'évaluation
- SASDocument4 pagesSASNicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesCardiovascular System: Anatomy and PhysiologyDavid PunzalanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN Transes Midterm FRM TVCDocument18 pagesCHN Transes Midterm FRM TVCmamsh KlangPas encore d'évaluation
- Anph121lb CardiovascularDocument28 pagesAnph121lb CardiovascularDANIELA PEREZPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.Chn Definition Goals HistoryDocument48 pages1.Chn Definition Goals HistoryMarlon MeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- ANAPHY Lec Session #1 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document7 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #1 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Kinetics: Collision Theory of Reaction Rate: Emmanuel NtambiDocument21 pagesChemical Kinetics: Collision Theory of Reaction Rate: Emmanuel NtambiMoses Umaru MwesigwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Reviewer 1Document6 pagesHeart Reviewer 1tokzzPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 (The Human Organism) PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 1 (The Human Organism) PDFSebastiane SalongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 TissuesAl-Shuaib Astami Son100% (1)
- Experiments Proving That Light and Electron Behave As Wave Christian HuygensDocument2 pagesExperiments Proving That Light and Electron Behave As Wave Christian HuygensRubin RubinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Document6 pagesCell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Mark AbrazaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Nervous SystemDocument104 pages8 Nervous SystemDiana Jean Cabiente100% (1)
- Blood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDocument20 pagesBlood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewStacey CamillePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9: Skin and ITS APPENDAGES: (Vital Organs)Document4 pagesChapter 9: Skin and ITS APPENDAGES: (Vital Organs)Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- SASDocument10 pagesSASNicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 3Document8 pagesChap 3Aurora Mae AmoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Bea SeloterioPas encore d'évaluation
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial SensesmasorPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesLymphatic SystemxoxoPas encore d'évaluation
- Transes Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Document6 pagesTranses Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Reign Saplaco100% (1)
- ANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Document55 pagesANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Marcus Randielle FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- ANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASDocument10 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASFherry Mae UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study: Region 2 University of La Salette, Inc. Santiago City, IsabelaDocument11 pagesA Case Study: Region 2 University of La Salette, Inc. Santiago City, IsabelaronronPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology (10th Ed.)Document6 pagesEssentials of Anatomy & Physiology (10th Ed.)Nicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Structure and Function of Macromolecules: AP Biology Chapter 5Document48 pagesThe Structure and Function of Macromolecules: AP Biology Chapter 5iksingh78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesAnaphy Prelims ReviewerMariz Elizabeth TaytayPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Tissues: 17. The Four Major Tissue Types Are Named in Figure 3-9. For Each TissueDocument9 pagesBody Tissues: 17. The Four Major Tissue Types Are Named in Figure 3-9. For Each TissueSireRyūjinSkylerPas encore d'évaluation
- ANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Document170 pagesANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Jewell Nivera CarpioPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument61 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesJharaPas encore d'évaluation
- Macromolecules WorksheetDocument10 pagesMacromolecules WorksheetShaira BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissues, Glands and MembranesDocument68 pagesTissues, Glands and MembranesMerrylFrancisco100% (1)
- Topic 1 Learning TheoriesDocument12 pagesTopic 1 Learning Theoriesasdffasdffas asdffasdffPas encore d'évaluation
- SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument19 pagesSPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & PhysiologyLUREY JAMES A. VACALARESPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomical Descriptive Source - Integumentary Skin, Tissue, and CellsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Descriptive Source - Integumentary Skin, Tissue, and CellsGURPARABJOT KAURPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Structure and Function of Tissues: 27 January 2016 Abby R. Whittington, PHD Awhit@Mse - Vt.EduDocument23 pagesStructure and Function of Tissues: 27 January 2016 Abby R. Whittington, PHD Awhit@Mse - Vt.EduSrilekhya Meda100% (1)
- EpitheliumDocument48 pagesEpitheliumdrpankaj28100% (1)
- ANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document10 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument167 pagesReproductive System ReviewerRhyza Marie Lopez100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyDanielle AguilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Muscular System NotesDocument5 pagesAnaphy Muscular System NotesSatomi Sta AnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary System SummaryDocument94 pagesUrinary System SummaryRhyza Marie LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Intergumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntergumentary SystemAkihiro FurukawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exercise4 Tissues Hb-1 GalangDocument4 pagesLab Exercise4 Tissues Hb-1 GalangLihza May Alliah GalangPas encore d'évaluation
- ANAPHY Lec Session #14 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document8 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #14 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.Chn Introduction and FamilyDocument7 pages1.Chn Introduction and FamilyLuzie Mae SuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CELLSDocument7 pagesCELLSMaria Theresa BuscasPas encore d'évaluation
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JPas encore d'évaluation
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZPas encore d'évaluation
- MYCODocument59 pagesMYCOAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals - VirologyDocument14 pagesFinals - VirologyAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Document31 pagesHEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Angela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema 2Document35 pagesHema 2Angela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank (2 Week) : Antibody ScreensDocument5 pagesBlood Bank (2 Week) : Antibody ScreensAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema DagdagDocument1 pageHema DagdagAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Urine Sediment ConstituentsDocument12 pagesUrine Sediment ConstituentsAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument31 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument56 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Aubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityDocument38 pagesAubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedigree Analysis WorksheetDocument3 pagesPedigree Analysis WorksheetAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Coagulation Screening Procedures:: RD THDocument2 pagesCoagulation Screening Procedures:: RD THAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMA LAB-4TH WEEK-Bleeding Time and Clotting TimeDocument6 pagesHEMA LAB-4TH WEEK-Bleeding Time and Clotting TimeAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology: T. VaginalisDocument78 pagesMicrobiology: T. VaginalisAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Phagocyte System.: Innate/non-Specific Immune SystemDocument6 pagesPhagocyte System.: Innate/non-Specific Immune SystemAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals - ImmunohematologyDocument20 pagesFinals - ImmunohematologyAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Myco LQDocument37 pagesMyco LQAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterms - MycologyDocument17 pagesMidterms - MycologyAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To BB and ImmunologyDocument2 pagesIntro To BB and ImmunologyAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Hema LecDocument5 pages1 Hema LecAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Micro Bio. Lab Purposes of Staining of SpecimensDocument6 pages2 Micro Bio. Lab Purposes of Staining of SpecimensAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Hema LecDocument5 pages1 Hema LecAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Micro Bio. Lab Purposes of Staining of SpecimensDocument6 pages2 Micro Bio. Lab Purposes of Staining of SpecimensAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals - Clinical Chemistry 1 LecDocument26 pagesFinals - Clinical Chemistry 1 LecAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Hema LecDocument5 pages1 Hema LecAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology Lec 1ST Week FinalsDocument5 pagesHematology Lec 1ST Week FinalsAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod #1 Bacte Lab MicrscopeDocument4 pagesMod #1 Bacte Lab MicrscopeAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Tests: JAPAY, Princess Agatha Mei R. BS Medical Technology 3ADocument5 pagesBiochemical Tests: JAPAY, Princess Agatha Mei R. BS Medical Technology 3AAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue. 1 or 2 HoursDocument5 pagesBlue. 1 or 2 HoursAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil SSCDocument11 pagesSoil SSCvkjha623477Pas encore d'évaluation
- Libro Resumenes 2012Document735 pagesLibro Resumenes 2012fdobonat613100% (2)
- Pigeon Disease - The Eight Most Common Health Problems in PigeonsDocument2 pagesPigeon Disease - The Eight Most Common Health Problems in Pigeonscc_lawrence100% (1)
- Pioneer PDP 5071 5070pu Arp 3354Document219 pagesPioneer PDP 5071 5070pu Arp 3354Dan Prewitt100% (1)
- Given The Simulation Area For Room ServiceDocument3 pagesGiven The Simulation Area For Room ServiceRico EsponillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mil STD 792fDocument13 pagesMil STD 792fdoradoanPas encore d'évaluation
- How McDonald'sDocument2 pagesHow McDonald'spratik khandualPas encore d'évaluation
- 208-Audit Checklist-Autoclave Operation - FinalDocument6 pages208-Audit Checklist-Autoclave Operation - FinalCherry Hope MistioPas encore d'évaluation
- 2005 Harley Davidson Sportster 883 66418Document136 pages2005 Harley Davidson Sportster 883 66418Josef Bruno SchlittenbauerPas encore d'évaluation
- 41403A - Guide - Rev - 12-20-17 - With Edits - 2-16-18Document167 pages41403A - Guide - Rev - 12-20-17 - With Edits - 2-16-18Ronald KahoraPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO - TR - 15608 - 2017 (En) - Pipe Grouping SystemsDocument12 pagesISO - TR - 15608 - 2017 (En) - Pipe Grouping SystemsTeodor ProdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Yogananda Scientific HealingDocument47 pagesYogananda Scientific HealingSagar Pandya100% (4)
- Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca FinalDocument91 pagesKeratoconjunctivitis Sicca FinalJanki GajjarPas encore d'évaluation
- "Next Friend" and "Guardian Ad Litem" - Difference BetweenDocument1 page"Next Friend" and "Guardian Ad Litem" - Difference BetweenTeh Hong Xhe100% (2)
- Pay Details: Earnings Deductions Code Description Quantity Amount Code Description AmountDocument1 pagePay Details: Earnings Deductions Code Description Quantity Amount Code Description AmountVee-kay Vicky KatekaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)Document3 pagesThe Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)allovid33% (3)
- Nitric AcidDocument7 pagesNitric AcidKuldeep BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Enviroline 2405: Hybrid EpoxyDocument4 pagesEnviroline 2405: Hybrid EpoxyMuthuKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction Paper-RprDocument6 pagesReaction Paper-Rprapi-543457981Pas encore d'évaluation
- Demages Goods RecordDocument22 pagesDemages Goods Recordtariq malikPas encore d'évaluation
- PolydactylyDocument43 pagesPolydactylyWara Samsarga GedePas encore d'évaluation
- Nta855 C400 D6 PDFDocument110 pagesNta855 C400 D6 PDFIsmael Grünhäuser100% (4)
- 7 UpDocument3 pages7 UpRajeev TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element Analysis Project ReportDocument22 pagesFinite Element Analysis Project ReportsaurabhPas encore d'évaluation
- Bedwetting TCMDocument5 pagesBedwetting TCMRichonyouPas encore d'évaluation
- Iomm VFD-3 030112Document100 pagesIomm VFD-3 030112Alexander100% (1)
- TraceGains Inspection Day FDA Audit ChecklistDocument2 pagesTraceGains Inspection Day FDA Audit Checklistdrs_mdu48Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inducement of Rapid Analysis For Determination of Reactive Silica and Available Alumina in BauxiteDocument11 pagesInducement of Rapid Analysis For Determination of Reactive Silica and Available Alumina in BauxiteJAFAR MUHAMMADPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Talent MonitorDocument30 pagesGlobal Talent Monitornitinsoni807359Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Practice 6Document5 pagesReading Practice 6Âu DươngPas encore d'évaluation