Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Material Downloaded From - 1 / 7
Transféré par
HemantTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Material Downloaded From - 1 / 7
Transféré par
HemantDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
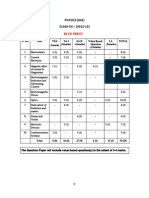
ISC
Class 12
Previous Year Paper 01 (2018)
Physics
Maximum Marks: 70
Time allowed: Three hours
Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT
start writing during this time.
All questions are compulsory.
This question paper is divided into 4 Sections, A, B, C and D as follows:
Section A : Question number 1 is of twelve marks. All parts of this question are compulsory.
Section B : Question numbers 2 to 12 carry 2 marks each with two questions having internal
choice.
Section C : Question numbers 13 to 19 carry 3 marks each with two questions having
internal choice.
Section D : Question numbers 20 to 22 are long-answer type questions and carry 5 marks
each.
Each question has an internal choice.
The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [ ].
All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as and adjacent to the
rest of the answer.
Answers to sub parts of the same question must be given in one place only. A list of useful
physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
A simple scientific calculator without a programmable memory may be used for calculations.
Section A
Answer all questions.
1. A. Choose the correct alternative (a), (b), (c) or (d) for each of the questions given below:
i. The order of coloured rings in a carbon resistor is red, yellow, blue and silver. The
resistance of the carbon resistor is:
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 7
a. 24×106 Ω ± 5%
b. 24×106 Ω ± 10%
c. 34×104 Ω ± 10%
d. 26×104 Ω ± 5%
ii. A circular coil carrying a current I has radius R and number of turns N. If all the
three, i.e. the current I, radius R and number of turns N are doubled, then,
magnetic field at its centre becomes:
a. Double
b. Half
c. Four times
d. One fourth
iii. An object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm, at
a distance of 15 cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
a. Virtual and magnified
b. Virtual and diminished
c. Real and magnified
d. Real and diminished
iv. Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
a. Emax = hλ –
b. Emax =
c. Emax = hv +
d. Emax =
v. In Bohr's model of hydrogen atom, radius of the first orbit of an electron is r0
Then, radius of the third orbit is:
a.
b. r0
c. 3r0
d. 9r0
B. Answer the following questions briefly and to the point.
i. In a potentiometer experiment, balancing length is found to be 120 cm for a cell E1
of emf 2V. What will be the balancing length for another cell E2 of emf 1·5V? (No
other changes are made in the experiment.)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 7
ii. How will you convert a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter?
iii. A moving charged particle q travelling along the positive x-axis enters a uniform
magnetic field B. When will the force acting on q be maximum?
iv. Why is the core of a transformer laminated?
v. Ordinary (i.e. unpolarised) light is incident on the surface of a transparent
material at the polarising angle. If it is partly reflected and partly refracted, what
is the angle between the reflected and the refracted rays?
vi. Define coherent sources of light.
vii. Name a material which is used in making control rods in a nuclear reactor.
Section B
Answer all questions.
2. Define current density. Write an expression which connects current density with drift
speed.
3. a. A long horizontal wire P carries a current of 50A. It is rigidly fixed. Another wire Q is
placed directly above and parallel to P, as shown in Figure 1 below. The weight per
unit length of the wire Q is 0·025 Nm-1 and it carries a current of 25A. Find the
distance ‘r’of the wire Q from the wire P so that the wire Q remains at rest.
OR
b. Calculate force per unit length acting on the wire B due to the current flowing in the
wire A. (See Figure 2 below)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 7
4. i. Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
ii. A rectangular coil having 60 turns and area of 0·4m2 is held at right angles to a
uniform magnetic field of flux density 5×10-5T. Calculate the magnetic flux passing
through it.
5. What is motional emf ? State any two factors on which it depends.
6. i. What is the ratio of the speed of gamma rays to that of radio waves in vacuum?
ii. Name an electromagnetic wave which is used in the radar system used in aircraft
navigation.
7. A biconvex lens made of glass (refractive index 1·5) has two spherical surfaces having
radii 20 cm and 30 cm. Calculate its focal length.
8. State any two differences between primary rainbow and secondary rainbow.
9. i. State de Broglie hypothesis.
ii. With reference to photoelectric effect, define threshold wavelength.
10. Calculate the minimum wavelength of the spectral line present in Balmer series of
hydrogen.
11. a. What is meant by pair annihilation? Write a balanced equation for the same.
OR
b. What is meant by the terms half-life of a radioactive substance and binding energy of
a nucleus?
12. In a communication system, what is meant by modulation? State any two types of
modulation.
Section C
Answer all questions.
13. Obtain an expression for intensity of electric field at a point in end on position, i.e. axial
position of an electric dipole.
14. Deduce an expression for equivalent capacitance C when three capacitors C1, C2 and C3
are connected in parallel.
15. a. and are two batteries having emf of 34V and 10V respectively and internal
resistance of 1Ω and 2Ω respectively. They are connected as shown in Figure 3 below.
Using Kirchhoff’s’ Laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 7
OR
b. An electric bulb is marked 200V, 100W. Calculate electrical resistance of its filament.
If five such bulbs are connected in series to a 200V supply, how much current will
flow through them?
16. a. For any prism, prove that:
where the terms have their usual meaning.
OR
b. When two thin lenses are kept in contact, prove that thier combined or effective focal
length F is given by:
where the terms have their usual meaning.
17. i. In Young’s double slit experiment, show graphically how intensity of light varies with
distance.
ii. In Fraunhofer diffraction, how is the angular width of the central bright fringe
affected when slit separation is increased?
18. Write one balanced equation each to show:
i. Nuclear fission
ii. Nuclear fusion
iii. Emission of β− (i.e. a negative beta particle)
19. With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener
diode. What is the use of a Zener diode?
20. a. An alternating emf of 220V is applied to a circuit containing a resistor R having
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 7
resistance of 160Ω and a capacitor ‘C’ in series. The current is found to lead the supply
voltage by an angle .
i. Calculate: (1) The capacitive reactance (2) Impedance of the circuit (3) Current
flowing in the circuit
ii. If the frequency of the applied emf is 50 Hz, what is the value of the capacitance of
the capacitor ‘C’?
OR
b. An A.C. generator generating an emf of = 300 sin (100 ) V is connected to a series
combination of 16 capacitor, 1H inductor and 100 Ω resistor. Calculate:
i. Impedance of the circuit at the given frequency.
ii. Resonant frequency fo.
iii. Power factor at resonant frequency fo.
21. a. Draw a labelled ray diagram of an image formed by a refracting telescope with final
image formed at infinity. Derive an expression for its magnifying power with the final
image at infinity.
OR
b. i. Using Huygen’s wave theory, derive Snell’s law of refraction.
ii. With the help of an experiment, state how will you identify whether a given beam
of light is polarised or unpolarised.
22. a. i. The forward characteristic curve of a junction diode is shown in Figure 4 below:
Calculate the resistance of the diode at:
(1) V = 0·5 V
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 7
(2) I = 60 mA
ii. Draw separate energy band diagrams for conductors, semi-conductors and
insulators and label each of them.
OR
b. i. The arrangement given below represents a logic gate:
A B C D
0 0
1 0
0 1
1 1
Copy the following truth table in your answer booklet and complete it showing
outputs at C and D.
ii. Draw a labelled diagram of a common emitter amplifier, showing waveforms of
signal voltage and output voltage.
Useful Constants and Relations:
1. Permeability of Vaccum ( ) =
2. Rydberg's constant (R) = 1.097 x 107 m-1
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 7 / 7
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics sp02 PDFDocument25 pages12 Physics sp02 PDFaditya prabhakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFDocument9 pagesCbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFIshika SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFDocument8 pages12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFAshish ChaharPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Sunaina RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24Document3 pagesClass 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24PrincePas encore d'évaluation
- BP&QP 1Document6 pagesBP&QP 1Akash AchuPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physics SP CbseDocument20 pages12 Physics SP CbsePrachi DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 PDFDocument7 pages2013 PDFnandagopanPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Lyp Physics s1Document7 pages12 Lyp Physics s1jashwanth kumar58Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12th Physics B-5Document10 pages12th Physics B-5Riya KakaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CbseDocument5 pagesCbserockstar104Pas encore d'évaluation
- FLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsDocument4 pagesFLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsChetanPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper-01: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20Document20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper-01: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20ANUP KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Xii SQPDocument9 pagesPhysics Xii SQPAYUSHI MANDALPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022-23. 12 FinalDocument5 pages2022-23. 12 FinalSrushti ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-1Document8 pagesClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-1kamali.v777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 Indore Class Xii Physics Assignment For Summer Vacation 2019-20 ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya No.2 Indore Class Xii Physics Assignment For Summer Vacation 2019-20 ElectrostaticsRahul SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy 2015Document5 pagesPhy 2015ANASPas encore d'évaluation
- QP Xii Phy PB1 2023-24Document7 pagesQP Xii Phy PB1 2023-24Puskar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsDocument53 pagesSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2010 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Document30 pagesCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2010 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4zelPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 SQPDocument7 pages7 SQPlanfury45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PHYSICS (Theory)Document7 pagesSample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PHYSICS (Theory)Abhimanyu MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Apeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsDocument4 pagesApeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsabhilashagoelPas encore d'évaluation
- 12TH PHYSICS FTDocument10 pages12TH PHYSICS FTABHISHEK PANDAPas encore d'évaluation
- SBR Pu Ii Model PapersDocument39 pagesSBR Pu Ii Model Paperstechwithtarun477Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Spectrum - PsDocument46 pagesPhysics Spectrum - PsiitforumPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Physics PB I 2023-24Document6 pagesQuestion Paper Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics2015 16Document6 pagesPhysics2015 16tranquil_452889939Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Code No. 1/2 Set: 2 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsDocument5 pagesPhysics Code No. 1/2 Set: 2 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsChandan PatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physice 2013 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFDocument6 pagesPhysice 2013 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Ii Pu Physics QPDocument5 pagesIi Pu Physics QPHarshith HachhuPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentRuprabh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- XII-Physics SQP 2018-19 PDFDocument8 pagesXII-Physics SQP 2018-19 PDFNikhil singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFDocument14 pagesSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorPas encore d'évaluation
- PB - I Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - I Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics SQPDocument108 pagesPhysics SQPS. BALA MURALI KRISHNAPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Annual Examination Question Paper 2013: CSBE Sample Papers, Question, Papers, Notes For Class 6 To 12Document7 pagesCBSE Annual Examination Question Paper 2013: CSBE Sample Papers, Question, Papers, Notes For Class 6 To 12arjunPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Most Imp Derivation and Long Answer Questions in Physics 1Document23 pagesList of Most Imp Derivation and Long Answer Questions in Physics 1Aham GtyPas encore d'évaluation
- HSSC 2 Phy Paper PreboardDocument4 pagesHSSC 2 Phy Paper PreboardEman AliPas encore d'évaluation
- KSEEB II PU PHYSICS Model Question Paper 2020 21 Set 2Document2 pagesKSEEB II PU PHYSICS Model Question Paper 2020 21 Set 2kumbarprajwal24Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Special Physics 12Document6 pagesCBSE Special Physics 12Arnab ChakrabartiPas encore d'évaluation
- 13122023013802physics Practice Paper 1Document8 pages13122023013802physics Practice Paper 1Srushti ChougulePas encore d'évaluation
- SAMPLE PAPER-09 (Unsolved)Document3 pagesSAMPLE PAPER-09 (Unsolved)ShantanuSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Physics Set 3: All Questions Are Compulsory. There Are 27 Questions in AllDocument4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Physics Set 3: All Questions Are Compulsory. There Are 27 Questions in AllI dont have a NamePas encore d'évaluation
- General Instructions: Sample Question Paper Class XII - Physics (Applicable For March 2016 Examination)Document12 pagesGeneral Instructions: Sample Question Paper Class XII - Physics (Applicable For March 2016 Examination)Anshuman GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Class 12th Board Question Bank PDFDocument743 pagesPhysics Class 12th Board Question Bank PDFVineet sharma100% (1)
- Physice 2010 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFDocument6 pagesPhysice 2010 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFSunita AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- ISC Class 12 Physics Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesISC Class 12 Physics Important QuestionsdhinchakclashersPas encore d'évaluation
- Ii Puc Phy 28.04.2021Document2 pagesIi Puc Phy 28.04.2021Bharatesha Gouda M PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- II PUC Physics Paper 1Document2 pagesII PUC Physics Paper 1narayanammagnarayanamma90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 UT Set 2Document5 pagesClass 12 UT Set 2garvit1223Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesD'EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields ID'EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisD'EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- ISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 02 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 02 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- ISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18Document18 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- ISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 01 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Document5 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Question Paper 01 (2018) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Isc Lyp Geography 01 2017Document5 pages12 Isc Lyp Geography 01 2017HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry For B.SC - 1st YearDocument7 pagesChemistry For B.SC - 1st YearHemantPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mountain Dog Diet PDFDocument11 pagesThe Mountain Dog Diet PDFHemantPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 2Document2 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 2HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class-VIII Mathematics: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 6Document6 pagesCBSE Class-VIII Mathematics: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 6HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry For B.SC - 1st YearDocument7 pagesChemistry For B.SC - 1st YearHemantPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 2Document2 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 2HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 2Document2 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 2HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Maths Ncert CH 08 Mapping Your Way QuesDocument9 pages05 Maths Ncert CH 08 Mapping Your Way QuesHemant100% (1)
- 05 Maths Ncert CH 07 Can You See The Pattern QuesDocument12 pages05 Maths Ncert CH 07 Can You See The Pattern QuesHemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Maths Ncert CH 01 The Fish Tale QuesDocument5 pages05 Maths Ncert CH 01 The Fish Tale QuesHemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Social Science SP 01Document13 pages10 Social Science SP 01HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Eng Comm SP Sa1 02Document11 pages9 Eng Comm SP Sa1 02Hemant0% (1)
- 10 Icse Chemistry Lyp 01 2017Document6 pages10 Icse Chemistry Lyp 01 2017HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Eng Comm SP Sa1 01 PDFDocument10 pages9 Eng Comm SP Sa1 01 PDFHemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Lyp Science Set3Document21 pages10 Lyp Science Set3HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2016 Set 1: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 8Document8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2016 Set 1: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 8HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Lyp Science Set1Document25 pages10 Lyp Science Set1HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 7Document7 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 7HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- KP KCDocument11 pagesKP KCHussain AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- (C. Grosche F. Steiner) Handbook of Feynman Path I (B-Ok - Xyz)Document459 pages(C. Grosche F. Steiner) Handbook of Feynman Path I (B-Ok - Xyz)gog100% (1)
- +Fall+MASC551 Syllabus+2017+Document3 pages+Fall+MASC551 Syllabus+2017+Amit JainPas encore d'évaluation
- NRQCDDocument106 pagesNRQCDMuhammadArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- EC312 Lesson 15 Antenna Fundamentals-StudentsDocument14 pagesEC312 Lesson 15 Antenna Fundamentals-StudentsDonnPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-Beginning Vibration AnalysisDocument153 pages01-Beginning Vibration AnalysisAnonymous ffje1rpa100% (1)
- Fermi Theory of Beta Decay (Contd.) : Dr. Sanjay KumarDocument13 pagesFermi Theory of Beta Decay (Contd.) : Dr. Sanjay KumarnjhgffyfPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 3 - Electric Field-Electric Flux-Gauss's LawDocument9 pagesMODULE 3 - Electric Field-Electric Flux-Gauss's LawPatrick CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration of High Voltage Resistor DividersDocument2 pagesCalibration of High Voltage Resistor DividersLina Muñoz CantilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Properties Testing and Powder Flowability - Powder & Bulk Solids Solutions PDFDocument3 pagesFlow Properties Testing and Powder Flowability - Powder & Bulk Solids Solutions PDFSukaran SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- AISC Properties MMDocument31 pagesAISC Properties MMManuel JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrónica Análogo Digital: E.P. de Física - Facultad de Ciencias Físicas - UNMSMDocument16 pagesElectrónica Análogo Digital: E.P. de Física - Facultad de Ciencias Físicas - UNMSMMartin AbPas encore d'évaluation
- OptistructDocument85 pagesOptistructSahithyananda ShashidharPas encore d'évaluation
- Electron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3Document63 pagesElectron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3younessinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Year 2020 - 2021 - ODD Semester PH8151 - Engineering Physics Unit-V Crystal PhysicsDocument10 pagesAcademic Year 2020 - 2021 - ODD Semester PH8151 - Engineering Physics Unit-V Crystal PhysicsBala NandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gr12 MCQDocument87 pagesGr12 MCQkaaviya.mksasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument36 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matterggle82338Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Critical Review On The Shear Lag Effect of Steel Channel Sections Subject To Tensile LoadingDocument9 pagesA Critical Review On The Shear Lag Effect of Steel Channel Sections Subject To Tensile LoadingGRENZE Scientific Society100% (2)
- Optical Properties of SemiconductorsDocument66 pagesOptical Properties of SemiconductorsCarolina UntilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexural Design of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Soranakom Mobasher 106-m52Document10 pagesFlexural Design of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete Soranakom Mobasher 106-m52Premalatha JeyaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Test PhysicsDocument56 pagesRevision Test PhysicsAkshay Khanzode100% (4)
- Chapter 16 - Solubility and Complex Ion EquilibriaDocument17 pagesChapter 16 - Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibriar1meshb1lla1969Pas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL4596 SyllabusDocument2 pagesBIOL4596 SyllabusmbrylinskiPas encore d'évaluation
- SHS General Chemistry 2Document350 pagesSHS General Chemistry 2John Luis Reyes90% (20)
- Std12 Phy Vol 1Document237 pagesStd12 Phy Vol 1Aaron Merrill50% (2)
- KKMehta-Pilot Plant Scale Up TechniqueDocument84 pagesKKMehta-Pilot Plant Scale Up TechniqueAnkit PokarPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation Structure With SW Motion-Remote LoadDocument21 pagesSimulation Structure With SW Motion-Remote LoadAlexDiazPas encore d'évaluation
- A World Without Cause and Effect: Logic-Defying Experiments Into Quantum Causality Scramble The Notion of Time ItselfDocument3 pagesA World Without Cause and Effect: Logic-Defying Experiments Into Quantum Causality Scramble The Notion of Time ItselfWalterHuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics, Lecture 3Document22 pagesFluid Mechanics, Lecture 3Adhi FebrianPas encore d'évaluation