Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
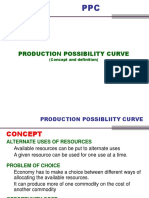
The Production Possibilities Frontiers
Transféré par
hansCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Production Possibilities Frontiers
Transféré par
hansDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
24 PART I INTRODUCTION
diagram is useful to keep in mind when thinking about how the pieces of the
economy fit together.
2-1e Our Second Model: The Production Possibilities Frontier
Most economic models, unlike the circular-flow diagram, are built using the tools
of mathematics. Here we use one of the simplest such models, called the produc-
tion possibilities frontier, to illustrate some basic economic ideas.
Although real economies produce thousands of goods and services, let’s
consider an economy that produces only two goods—cars and computers.
Together, the car industry and the computer industry use all of the economy’s
production possibilities factors of production. The production possibilities frontier is a graph that
frontier shows the various combinations of output—in this case, cars and computers—
a graph that shows the that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of pro-
combinations of output duction and the available production technology that firms use to turn these
that the economy can factors into output.
possibly produce given Figure 2 shows this economy’s production possibilities frontier. If the economy
the available factors uses all its resources in the car industry, it produces 1,000 cars and no computers.
of production and the If it uses all its resources in the computer industry, it produces 3,000 computers
available production and no cars. The two endpoints of the production possibilities frontier represent
technology these extreme possibilities.
More likely, the economy divides its resources between the two industries, pro-
ducing some cars and some computers. For example, it can produce 600 cars and
2,200 computers, shown in the figure by point A. Or, by moving some of the fac-
tors of production to the car industry from the computer industry, the economy
can produce 700 cars and 2,000 computers, represented by point B.
Because resources are scarce, not every conceivable outcome is feasible. For
example, no matter how resources are allocated between the two industries, the
economy cannot produce the amount of cars and computers represented by point C.
Given the technology available for manufacturing cars and computers, the econ-
omy does not have enough of the factors of production to support that level of
output. With the resources it has, the economy can produce at any point on or
FIGURE 2 Quantity of
Computers
The Production Possibilities Frontier Produced
The production possibilities frontier shows
the combinations of output—in this case,
cars and computers—that the economy can 3,000 F C
possibly produce. The economy can produce
any combination on or inside the frontier.
2,200 A
Points outside the frontier are not feasible B
2,000
given the economy’s resources. The slope of
Production
the production possibilities frontier measures
possibilities
the opportunity cost of a car in terms of com-
frontier
puters. This opportunity cost varies, depending 1,000 D
on how much of the two goods the economy is
producing. E
0 300 600 700 1,000 Quantity of
Cars Produced
Copyright 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. WCN 02-200-203
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- PPF , unit -1 (1)Document3 pagesPPF , unit -1 (1)tanishkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Mankiw, Chapter 1 & 2Document45 pagesReading Mankiw, Chapter 1 & 2Chris TsePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1: Introduction: Markets and PricesDocument38 pagesTopic 1: Introduction: Markets and PricesHaniff MalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking Like An EconomistDocument41 pagesThinking Like An EconomistErme Fradejas DulcePas encore d'évaluation
- Ppf-Opportunity CostDocument17 pagesPpf-Opportunity CostLeo SuingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2-2Document24 pagesChapter 2-2Faire ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Microeconomics Principles ExplainedDocument18 pagesMicroeconomics Principles ExplainedMohamed KambiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Production Possibilities FrontierDocument3 pagesThe Production Possibilities FrontierKen TuazonPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 02Document39 pagesCH 02Kenio FilhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts EconomicsDocument42 pagesBasic Concepts EconomicsJay PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 2 - Chapter 2-Thinking Like An EconomistDocument31 pagesLecture - 2 - Chapter 2-Thinking Like An Economistmubeen yamin100% (1)
- CH 2 Thinking Like An EconomistDocument44 pagesCH 2 Thinking Like An EconomistSakibPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap - 02 Thinking Like EconomistDocument21 pagesChap - 02 Thinking Like Economistsunny1236Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Concepts in EconomicsDocument19 pagesElementary Concepts in EconomicsImroz MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - MicroeconomicsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 - MicroeconomicsAustin WuebkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Economics 4th Edition Krugman Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Economics 4th Edition Krugman Solutions Manual PDFpaulettechandlerh7i9100% (8)
- Latest 004Document6 pagesLatest 004Margee PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- FS Future-Mobility RZ WEB PDFDocument6 pagesFS Future-Mobility RZ WEB PDFNET ZERO SUMMITSPas encore d'évaluation
- Production Possibilities Frontier ExplainedDocument18 pagesProduction Possibilities Frontier ExplainedRoxy Marie ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics: Sabir Ali (Mankiw) : (Original Slides Available On Demand)Document30 pagesEconomics: Sabir Ali (Mankiw) : (Original Slides Available On Demand)Nehal ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- ECO Reviewer 2-3Document6 pagesECO Reviewer 2-3Gwen Ashley Dela PenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gains from Trade ExplainedDocument6 pagesGains from Trade ExplainedIlahe MuradzadePas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Years: ROI On Digital FactoriesDocument21 pages5 Years: ROI On Digital FactoriesS raoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Production Possibilities FrontierDocument5 pagesThe Production Possibilities FrontierVenkat DevilsadvocatePas encore d'évaluation
- The Resons For Individuals, Organisations and Societies Having To Make ChoicesDocument8 pagesThe Resons For Individuals, Organisations and Societies Having To Make ChoicesMoona WahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Issues and Concepts Chapter 1Document31 pagesEconomic Issues and Concepts Chapter 1Mohit SinglaPas encore d'évaluation
- Whitepaper - Electrification and Industry TransformationDocument5 pagesWhitepaper - Electrification and Industry Transformationvikram29586Pas encore d'évaluation
- Managerial Economics Chapter 2Document17 pagesManagerial Economics Chapter 2Anonymous 1Rj80jPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction To Economics)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction To Economics)eiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking Like An EconomistDocument40 pagesThinking Like An EconomistMarcella Alifia Kuswana Putri100% (1)
- The Robotics & Automation Industry in GermanyDocument6 pagesThe Robotics & Automation Industry in GermanyAdamei AdamPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S1877050920312588 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1877050920312588 MainTình LêPas encore d'évaluation
- Limits Alternatives and Choices: Chapter 2 Thinking Like An EconomistDocument25 pagesLimits Alternatives and Choices: Chapter 2 Thinking Like An Economistdranita@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2Document22 pagesModule 2esther031216Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: (Thinking Like An Economist) +question 2,4 Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 2: (Thinking Like An Economist) +question 2,4 Chapter 3Phạm HuyPas encore d'évaluation
- ECO2424 Principles of Economics - Tutorial 1Document1 pageECO2424 Principles of Economics - Tutorial 1Ameroden LaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Production (Profit Maximization) Problem: Device Min Qnty Max Qnty Profit $ A B C DDocument1 pageProduction (Profit Maximization) Problem: Device Min Qnty Max Qnty Profit $ A B C Dkidanemariam HabtemariamPas encore d'évaluation
- Economies of Scale & ScopeDocument12 pagesEconomies of Scale & ScopeLi MoPas encore d'évaluation
- Insta Grid SummaryDocument23 pagesInsta Grid SummaryShawn Paul Boike100% (2)
- IMI Battenfeld-Wittmann CTD Application OpportunityDocument4 pagesIMI Battenfeld-Wittmann CTD Application OpportunityRandy GusmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Asm Economics 190101Document30 pagesAsm Economics 190101AnandiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 02Document29 pagesLect 02varshitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microeconomics EXAM Set 2Document10 pagesMicroeconomics EXAM Set 2Yus LindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handset Leasing and Telecommunication Operators (From Implementing To Saving An Entire Industry)Document15 pagesHandset Leasing and Telecommunication Operators (From Implementing To Saving An Entire Industry)anitaPas encore d'évaluation
- exam_Jul_13th_2022_solDocument11 pagesexam_Jul_13th_2022_solomerogolddPas encore d'évaluation
- EconomicsDocument1 pageEconomicsNISHANTH P CHOYAL 2228512Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless M Bus in Industrial IoT TechnolDocument6 pagesWireless M Bus in Industrial IoT Technolfaisal.hammad.workPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Ebook Apr21 EN v2Document22 pagesAutomotive Ebook Apr21 EN v2RAHULMISHRA1188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges For The Automotive Industry and Its Transformation Path - Andreas MeinheitDocument23 pagesChallenges For The Automotive Industry and Its Transformation Path - Andreas MeinheitHoàng Minh ChiếnPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-4 Production Possibility FrontierDocument16 pagesChapter-4 Production Possibility FrontierGMS ShopPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Tech Trends To Watch 2022 - StylusDocument18 pages10 Tech Trends To Watch 2022 - StylusMinh Dang NgocPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester-I: B.A. L.L.B. Economics - 1 Fundamentals of Economics For Lawyers Module: 1-Introduction and Basic Prerequisites Topic: Models in EconomicsDocument9 pagesSemester-I: B.A. L.L.B. Economics - 1 Fundamentals of Economics For Lawyers Module: 1-Introduction and Basic Prerequisites Topic: Models in EconomicsUtkarsh KankalPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Robot in Construction: Mallikarjuna 1ms11mcm09Document17 pagesApplication of Robot in Construction: Mallikarjuna 1ms11mcm09Bhanu Tej100% (1)
- Mobile Widget Platform Market Analysis: Understanding The Business Case and ROIDocument17 pagesMobile Widget Platform Market Analysis: Understanding The Business Case and ROILoo Chee KeongPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 02Document30 pagesLect 02yandrapragada narasimharaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking Like An Economist: Models and Trade-OffsDocument17 pagesThinking Like An Economist: Models and Trade-OffsAbid RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S1877050920323371 Main - 2Document7 pages1 s2.0 S1877050920323371 Main - 2assignment helpPas encore d'évaluation
- exam_Jul_13th_2022_textDocument8 pagesexam_Jul_13th_2022_textomerogolddPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro 2021 Syllabus W5 TasksDocument4 pagesMicro 2021 Syllabus W5 TasksVe DekPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding the Industrial Internet the $$$ Trillion Opportunities for Your EnterprisesD'EverandUnderstanding the Industrial Internet the $$$ Trillion Opportunities for Your EnterprisesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock Market Reports For The Week (23rd-27th May '11)Document7 pagesStock Market Reports For The Week (23rd-27th May '11)Dasher_No_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Saudi Pharma Market Shifts as Global Giants and Generics RiseDocument20 pagesSaudi Pharma Market Shifts as Global Giants and Generics RiseSandip Rana BallavPas encore d'évaluation
- Should I Study EconomicsDocument30 pagesShould I Study Economicsaugustrush082882Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Framework of Maruti SuzukiDocument7 pagesMarketing Framework of Maruti SuzukiRonak Parmar100% (1)
- Tmon 12-15Document1 pageTmon 12-15Sue CarterPas encore d'évaluation
- Producer's Equilibrium ExplainedDocument14 pagesProducer's Equilibrium Explainedrohitbatra100% (1)
- Distribution Competitiveness GuideDocument12 pagesDistribution Competitiveness GuideEilyn PimientaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument78 pagesCost-Volume-Profit Analysis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinSheila Jane Maderse AbraganPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Inventory Planning and ControlDocument55 pages4 Inventory Planning and ControlSandeep SonawanePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 02Document143 pagesCH 02Hassaan ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Paper - EcoDocument4 pagesSolutions Paper - Ecosanchita mukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- PPC PurchasingDocument8 pagesPPC PurchasingVarsha SriPas encore d'évaluation
- ContractDocument152 pagesContractKy Henderson0% (1)
- Financial & Statement Analysis of National Tubes Ltd.Document35 pagesFinancial & Statement Analysis of National Tubes Ltd.Aminul Karim Fahad0% (1)
- Package 5n 6d Vienna HotelDocument3 pagesPackage 5n 6d Vienna HotelHemant YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics of Strategy: Fifth EditionDocument44 pagesEconomics of Strategy: Fifth EditionSachin SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- History: Tata in IndiaDocument8 pagesHistory: Tata in IndiaSatish Kumar KPas encore d'évaluation
- Debtors SystemDocument4 pagesDebtors SystemRohit ShrivastavPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Service Sheet 129Document4 pages01 Service Sheet 129bernzikPas encore d'évaluation
- It Lab FileDocument34 pagesIt Lab FileMannu BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Contributing to Cost Overruns in Malaysian Construction ProjectsDocument9 pagesFactors Contributing to Cost Overruns in Malaysian Construction ProjectsWaleed GaberPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 11 - CF Estimation Mini Case Sols Word 1514edDocument13 pagesCH 11 - CF Estimation Mini Case Sols Word 1514edHari CahyoPas encore d'évaluation
- The New Normal Case Study TFC ScribdDocument2 pagesThe New Normal Case Study TFC ScribdTasneemPas encore d'évaluation
- Asia Amalgamated Holdings Corporation Financials - RobotDoughDocument6 pagesAsia Amalgamated Holdings Corporation Financials - RobotDoughKeith LameraPas encore d'évaluation
- Amazon Flipkart Comparision CalculatorDocument12 pagesAmazon Flipkart Comparision Calculatorshah faisalPas encore d'évaluation
- Burmah CastrolDocument13 pagesBurmah CastrolanfkrPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 Practice Questions For SL EconDocument14 pagesPaper 1 Practice Questions For SL EconKazePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Accounting For SalesDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Accounting For SalesArmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Asa - Injection Mould Component Cost EstimationDocument7 pagesAsa - Injection Mould Component Cost EstimationVenkateswaran venkateswaranPas encore d'évaluation
- COMM350: Research ProposalDocument3 pagesCOMM350: Research ProposalShayne RebelloPas encore d'évaluation