Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rate Limiting Step PDF
Transféré par
Coy Nuñez0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues1 pageTitre original
Rate-Limiting-Step (1).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues1 pageRate Limiting Step PDF
Transféré par
Coy NuñezDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
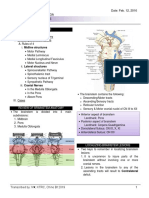
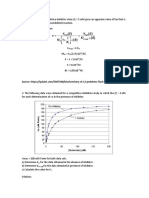
Rate
Limiting Step Enzyme Substrate Product
Glycolysis – well fed state Fructose-6-PO4 → Fructose 1,6- Phosphofructokinase-1 Use ATP Glucose 2 Pyruvate or Lactate
Cytosol Bisphosphate
Gluconeogenesis – fasting state Fructose 1,6 Bisphosphate → Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphatease Synthesis of glucose ü Intermediates from Glycolysis Glucose
and TCA
Liver(90%), kidney (10%): Fructose-6-PO4 requires: ü Glycerol, proprionyl CoA from
6 ATP TAG
ü Lactate from Cori cycle
Mitochondria, cytosol 2 NADH ü Carbon skeleton from
from B-oxidation glucogenic AA
Kreb’s Cycle Isocitrate → α-ketoglutarate Isocitrate dehydrogenase Acetyl CoA 2 CO2
Mitochonrial matrix 1 GTP
Except succinyl dehydrogenase – inner 3 NADH
mitochondrial membrane 1 FADH2
Pentose Phosphate Oxidative Phase: Glucose-6-PO4 Dehydrogenase Produce NADPH Glucose-6-Phosphate Ribose-5-PO4
Pathway/HMP Shunt Glucose-6-PO4 → NADPH
RBC and tissues that produce lipids: liver, 6-Phosphogluconate Non oxidative Phase: (not rate limiting step) Fructose-6-PO4
adipose, adrenal, thyroid, testes, lactating Enzyme: Transketolase
mammaries Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4
Co-factor: Vit B1
Cytosol
Glycogenesis – well fed state Elongation of glycogen chains Glycogen synthase α-D,Glucose Glycogen
Liver/Muscle: Cytosol α(1-4) glycosidic bonds formation
Glycogenolysis – fasting state Shortening of glycogen chains Glycogen phosphorylase Glycogen Glucose in liver
Liver/Muscle: Cytosol α(1-4) glycosidic bonds cleavage Cofactor: Vit B6 Glucose-6-Phosphate in
muscle
Lipogenesis Acetyl CoA + HCO3 → Malonyl Acetyl CoA carboxylase Use ATP Acetyl CoA Palmytoyl-CoA
Cytosol CoA Co-enzyme: BIOTIN Must be transported from the
Activated by: Citrate and mitochondria to the cytosol
insulin via citrate shuttle
Inhibited by: glucagon and EPI
Beta Oxidation Translocation of fatty-acyl CoA Carnitine-palmitoyl transferase Palmitate 8 Acetyl CoA (even) or
Mitochonria from cytosol to mitochondria Propionyl CoA+ Acetyl
FA must be activated 1st by enzyme: CoA (odd)
Fatty Acyl Coa Synthetase + 2ATP in the 7 NADH
cytosol
7 FADH2
Ketogenesis Acetoacetyl CoA + Acetyl CoA → HMG CoA Synthase Acetyl CoA Acetoacetate
Liver mitochondria HMG CoA From B oxidation Acetone
β-hydroxybutyrate
Cholesterol Synthesis HMG CoA → Mevalonate HMG CoA Reductase Requires 2 NADPH Acetyl CoA Cholesterol
Cytosol and ER
All tissues
Urea Cycle NH3 + CO2 → Carbamoyl Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthase I Use 2 Mg-ATP NH3 Urea
Liver only: mitochondri & cytosol Phosphate Activator: N-AGA Aspartate
(N-Acetylglutamate) CO2
Heme Metabolism Glycine + Succinyl CoA → δ- ALA synthase Co-factor: Pyridoxime Heme
Aminolevulinic acid
Nucleotide: PRPP + Glutamine → 5-phospho- PRPP Glutamyl Aminotransferase PRPP IMP → GMP
PURINE Synthesis B-D-ribosylamine IMP → AMP
Nucleotide: CO2 + Glutamine + ATP → Carbamoyl Phosphate II PRPP UMP → UTP → CTP
PYRIMIDINE Synthesis Carbamoyl Phosphate UMP → dUMP →TMP
Amier
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- For The Boards Summary of Metabolic Pathways BiochemDocument4 pagesFor The Boards Summary of Metabolic Pathways BiochemJaybee SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem SuperTableDocument2 pagesBiochem SuperTablePrincess MariellePas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem SuperTable PDFDocument2 pagesBiochem SuperTable PDFPrincess MariellePas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Pathways Inhibitors/Poisons of The Etc: Cytosol CytosolDocument6 pagesSummary of Pathways Inhibitors/Poisons of The Etc: Cytosol CytosolBeatrix Graecia Fernandez100% (1)
- Chart of GI SecretionsDocument2 pagesChart of GI SecretionsJordan Fernandez0% (1)
- Most CommonsDocument6 pagesMost CommonsBobet ReñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Physiology IDocument16 pagesRenal Physiology IJubilee Christiene AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycogenolysis: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesGlycogenolysis: BiochemistryManila MedPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases - BiochemDocument4 pagesDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Path Concept MapsDocument113 pagesPath Concept MapsAndleeb ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Coaching - Biochem 2022Document6 pagesFinal Coaching - Biochem 2022Jhon Paulo100% (1)
- Disorders of Cho MetabolismDocument4 pagesDisorders of Cho MetabolismJohn Christopher LucesPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycolysis and The Oxidation of Pyruvate: Clinical SignificanceDocument3 pagesGlycolysis and The Oxidation of Pyruvate: Clinical SignificanceJan JeminoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Chart-Dr.G.bhanu PrakashDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Chart-Dr.G.bhanu PrakashAsadullah YousafzaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Metabolism & The Provision of Metabolic Fuels (CHP 16 Harper) - TJLDocument6 pagesOverview of Metabolism & The Provision of Metabolic Fuels (CHP 16 Harper) - TJLMPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOCHEM-Lipid Metabolism 3Document7 pagesBIOCHEM-Lipid Metabolism 3Std DlshsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy and Lactation Flashcards - Guyton Physiology Chapter 82Document19 pagesPregnancy and Lactation Flashcards - Guyton Physiology Chapter 82MedSchoolStuffPas encore d'évaluation
- MnemonicDocument33 pagesMnemonicyanot0206Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.7 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Gluconeogenesis - Better PicturesDocument12 pages2.7 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Gluconeogenesis - Better Pictureslovelots1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Topnotch Pharma Supertable UPDATED APRIL 2017 by Yns PereyraDocument170 pages6 - Topnotch Pharma Supertable UPDATED APRIL 2017 by Yns PereyraVien CervantesPas encore d'évaluation
- GI Diarrheal Micro ChartDocument3 pagesGI Diarrheal Micro ChartEvan MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Notes For BoardsDocument35 pagesBiochemistry Notes For BoardsUjjwal PyakurelPas encore d'évaluation
- SketchyPath ChecklistDocument1 pageSketchyPath ChecklistGabriella RosinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematology-Summary My NotesDocument24 pagesHaematology-Summary My NotesToria053Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Board Exam2020 QuestionsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Board Exam2020 Questionschristinejoan100% (1)
- PleuraDocument6 pagesPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- 1.05 Biochemistry Trans - Coenzyme. Cofactors. Prosthetic Grps TRANS v2Document12 pages1.05 Biochemistry Trans - Coenzyme. Cofactors. Prosthetic Grps TRANS v2April AramPas encore d'évaluation
- HW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismDocument2 pagesHW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1Document42 pagesNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1pp100% (1)
- General Pathology 4.03 Endocrine System Super SummaryDocument15 pagesGeneral Pathology 4.03 Endocrine System Super SummaryJade MonrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesBipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomshumdingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Brainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesBrainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFVon HippoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Supertable PDFDocument70 pagesPharmacology Supertable PDFalcojonic100% (2)
- Boards' Fodder: Histologic Bodies: Benjamin A. Solky, M.D., Jennifer L. Jones, M.D., and Clare Pipkin, M.DDocument2 pagesBoards' Fodder: Histologic Bodies: Benjamin A. Solky, M.D., Jennifer L. Jones, M.D., and Clare Pipkin, M.DAreg JosephsPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycogenolysis and GlycogenesisDocument11 pagesGlycogenolysis and Glycogenesismiguel cuevas100% (2)
- Mcu-Fdt Medical Foundation College of Medicine Department of BiochemistryDocument12 pagesMcu-Fdt Medical Foundation College of Medicine Department of BiochemistryKaye bagasin100% (1)
- Physiology Summary Chapter 21Document5 pagesPhysiology Summary Chapter 21gail018Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles of The Neck PDFDocument1 pageMuscles of The Neck PDFEdreyn DellosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pancreatic Function TestDocument9 pagesPancreatic Function TestAyioKunPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)Document25 pagesCarbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)DIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology Part IDocument5 pagesPhysiology Part IrustonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Table - GonzalesDocument14 pagesPharmacology Table - GonzalesMark Angelo PonferradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz On Lipid Metabolism - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesQuiz On Lipid Metabolism - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- Character Hypertrophic Scar Keloid: Nutshell Series For FMGE/DNB/NEET-PG-General SurgeryDocument26 pagesCharacter Hypertrophic Scar Keloid: Nutshell Series For FMGE/DNB/NEET-PG-General SurgeryAbdalsalaam AbraikPas encore d'évaluation
- March 2022 Hybrid Full Course OFFICIAL Lecture Schedule - NOV-DEC UPLOADDocument3 pagesMarch 2022 Hybrid Full Course OFFICIAL Lecture Schedule - NOV-DEC UPLOADJhon PauloPas encore d'évaluation
- Trans-Out Orders: NSVD Admitting Notes Postpartum OrdersDocument7 pagesTrans-Out Orders: NSVD Admitting Notes Postpartum OrdersDre ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Board Recall Must ReadDocument8 pagesBoard Recall Must ReadSarahSalvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Coaching - Patho 2022Document6 pagesFinal Coaching - Patho 2022Jhon PauloPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial Nerves FlowchartDocument14 pagesCranial Nerves FlowchartMatthew ChristiePas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Step 1 DrugsDocument36 pagesUSMLE Step 1 DrugscougardiverPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycolysis NotesDocument2 pagesGlycolysis NotesAnsley Ellen BarfieldPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem 2.1 Introduction To MetabolismDocument5 pagesBiochem 2.1 Introduction To Metabolismlovelots1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Stimulus Effect of Hormone Inhibition PathologyDocument3 pagesEndocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Stimulus Effect of Hormone Inhibition PathologySamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Cocci Rod 4 Main Classifications: Gram Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeDocument2 pagesCocci Rod 4 Main Classifications: Gram Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeKimberly KanemitsuPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Flashcards: Microbiology and Immunology - Side by SideDocument196 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Microbiology and Immunology - Side by SideMedSchoolStuff0% (1)
- Pathway Glycolysis TCA Cycle Gluconeogenesis What Is It For?Document2 pagesPathway Glycolysis TCA Cycle Gluconeogenesis What Is It For?Rosel Ann BontiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDocument40 pagesLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- ' Biochemistry ' Biochemistry-Metabolism Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument10 pages' Biochemistry ' Biochemistry-Metabolism Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylationgksah711Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Glomerular DiseasesDocument127 pages1 Glomerular DiseasesCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 16: University of The Visayas Gullas College of Medicine Banilad, Mandaue City, CebuDocument6 pagesGroup 16: University of The Visayas Gullas College of Medicine Banilad, Mandaue City, CebuCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Berne and Levy Physiology Test BankDocument1 pageBerne and Levy Physiology Test BankCoy Nuñez0% (3)
- 2 Gram Negative Bacterial InfectionDocument89 pages2 Gram Negative Bacterial InfectionCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument55 pagesBenito K. Lim Hong III, M.DCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Renal Vascular Disease 3Document46 pages3 Renal Vascular Disease 3Coy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Obstructive UropathyDocument37 pages4 Obstructive UropathyCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho Immune System PathologyDocument7 pagesPatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- 2 Renal Tubular, Interstitial Disease 2Document94 pages2 Renal Tubular, Interstitial Disease 2Coy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammation: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument70 pagesInflammation: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Case: EndocrinologyDocument42 pagesSample Case: EndocrinologyCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Introduction To General PathologyDocument91 pages1 Introduction To General PathologyCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionDocument87 pages1 Gram Positive Bacterial InfectionCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- General Pathology - Group 9 I. Clinical Impression - ACNE II. PathophysiologyDocument1 pageGeneral Pathology - Group 9 I. Clinical Impression - ACNE II. PathophysiologyCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity of Parasitic InfectionsDocument4 pagesImmunity of Parasitic InfectionsCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooh Coo Coo NH NH NH: Function of Proteins: 2. Ionic Properties of AADocument6 pagesCooh Coo Coo NH NH NH: Function of Proteins: 2. Ionic Properties of AACoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- What Will Do If You Find Money On The Sidewalk?Document10 pagesWhat Will Do If You Find Money On The Sidewalk?Coy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 7 g6pd MedsDocument8 pagesExercise 7 g6pd MedsCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Response To Injury & Metabolic Support: Josef S. Lim, MD, FPSGS, FPCS, PalesDocument132 pagesSystemic Response To Injury & Metabolic Support: Josef S. Lim, MD, FPSGS, FPCS, PalesCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Notes 1Document10 pagesBiochem Notes 1Coy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes TableDocument3 pagesTrematodes TableCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogenesis and PathologyDocument3 pagesPathogenesis and PathologyCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cestodes NotesDocument20 pagesCestodes NotesCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Page 55 (Growth, Survival, and Death of Microorganisms)Document4 pagesPage 55 (Growth, Survival, and Death of Microorganisms)Coy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Commensal AmoebaDocument2 pagesCommensal AmoebaCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- 0.07 - 0.12 MM in Thickness But May Reach UpDocument8 pages0.07 - 0.12 MM in Thickness But May Reach UpCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Page 55 (Arrabis, Baylosis, Gudapati)Document4 pagesPage 55 (Arrabis, Baylosis, Gudapati)Coy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOC 301 ProblemSet3-2012AnswersDocument9 pagesBIOC 301 ProblemSet3-2012AnswersluoqiaoyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Enzymes and VitaminsDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Enzymes and Vitaminsvictoria cablayPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam II - Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesExam II - Review QuestionsEmmanuel JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Deber Miecoles DLDocument8 pagesPDF Deber Miecoles DLLuz pilar Nicolás delacruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Mikales Menten Great With Green Book AlsoDocument8 pagesMikales Menten Great With Green Book AlsoMOSES MILLERPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 EnzymeDocument25 pages5 EnzymeairishPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Biochemistry: Enzymes: Mr. Genaro F. Alderite JR, MsermDocument58 pagesMedical Biochemistry: Enzymes: Mr. Genaro F. Alderite JR, MsermNash DeniegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Enzymes PDFDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Enzymes PDFJenny GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tyrosinase and Superoxide Dismutase Activities of Peroxidase in The Vacuoles of Beet RootsDocument11 pagesTyrosinase and Superoxide Dismutase Activities of Peroxidase in The Vacuoles of Beet RootsEti ApriyantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Synthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument15 pagesBio Synthesis of Fatty Acidspriya19866Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topics 2023Document3 pagesTopics 2023Achraf RbPas encore d'évaluation
- Biofuel Lab CellobiaseDocument5 pagesBiofuel Lab CellobiaseDuc TranPas encore d'évaluation
- EmzymologyDocument17 pagesEmzymologySandeep AdapalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Biology Form 4: EnzymesDocument26 pagesChapter 4 Biology Form 4: EnzymesNurul Husna100% (1)
- 1.biology Oxidation 1 k19 k20Document38 pages1.biology Oxidation 1 k19 k20Darry AprilioPas encore d'évaluation
- Restriction EnzymeDocument33 pagesRestriction EnzymeFawaz MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi Sera Calibrator: Value Sheet of Mindray BS Measurement SystemDocument4 pagesMulti Sera Calibrator: Value Sheet of Mindray BS Measurement Systemtech yuva cscPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes Practice Worksheet 1Document25 pagesEnzymes Practice Worksheet 1Divyanshi VikramPas encore d'évaluation
- Step Enzyme Rationale (Why?) / Function Thermodynamics Δg°' Δg Regulation (Why/How?)Document4 pagesStep Enzyme Rationale (Why?) / Function Thermodynamics Δg°' Δg Regulation (Why/How?)Eric ChengPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas 2 BiokatalisisDocument7 pagesTugas 2 BiokatalisisKirstie ImeldaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme Part 1-5 Vikneswaran 260110132004Document7 pagesEnzyme Part 1-5 Vikneswaran 260110132004Vikneswaran VîçkýPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes: Overview Enzyme: Structure: Small Organic Molecules Inorganic IonDocument19 pagesEnzymes: Overview Enzyme: Structure: Small Organic Molecules Inorganic IonUltima PhasePas encore d'évaluation
- A.1. Competitive InhibitionDocument5 pagesA.1. Competitive InhibitionFlorecita Cabañog100% (2)
- Amboss - Enzymes and BiocatalysisDocument10 pagesAmboss - Enzymes and BiocatalysisAllysahPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymescpagente01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit C Enzyme InhibitorsDocument9 pagesUnit C Enzyme InhibitorsDulshan JayPas encore d'évaluation
- BCH 261 Midterm 2015 MTCDocument3 pagesBCH 261 Midterm 2015 MTCbecca0% (1)
- Biotransformation of DrugsDocument22 pagesBiotransformation of DrugsZaigham Hammad100% (1)
- Citric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceBiochemistry DenPas encore d'évaluation