Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CH 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light: Liu UCD Phy9B 07 1
Transféré par
Jaskirat0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues10 pagesillumination
Titre original
illumination
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentillumination
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
23 vues10 pagesCH 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light: Liu UCD Phy9B 07 1
Transféré par
Jaskiratillumination
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 10
Ch 33.
The Nature and
Propagation of Light
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 1
33-1. Nature of Light
Light has both wave and particle properties
Particle-like: emission, absorption…
Wave-like: propagation, interference…
Speed of light c=2.9979x108 m/s ~ 3.0x108m/s
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 2
Geometric & Physical Optics
Ray: an imaginary line along the wave traveling direction
In a particle theory of light
Light travels in straight-line paths called light rays
Rays represent the paths of particles
Branch of optics dealing with ray model – geometric optics
wave behavior – physical optics
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 3
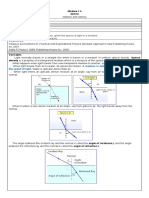
33-2. Reflection & Refraction
Angle of incidence θi
Angle of reflection θr
Law of reflection:
θi= θr
Diffusive reflection Specular reflection
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 4
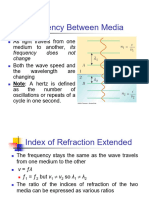
Refraction
Index of refraction of a material:
n=c/v ≥1
c=3.0x108 m/s speed of light in vacuum
v: speed of light in the medium
Light frequency doesn’t change going
from one material to another
λ= λο/n
Higher n Vacuum & air: n=1.00
slower v Water n=1.33
smaller λ Glass n=~1.4-1.6
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 5
Law of Refraction
Snell’s Law
n1sinθ1=n2sinθ2
If n1 > n2, then θ1 < θ2
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 6
General Case: Across Interface of Two
Transparent Materials
Incident, reflected, refracted rays and the
normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 7
33-3. Total Internal Reflection
nb<na
nb nb
sin θ C = sin 90° =
na na
When θ>θC, all lights are reflected, no refraction
Only happens when light goes from high n to low n material
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 8
Applications of Total Internal Reflection
Porro Prism Fiber Optics
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 9
33-4. Dispersion
n=c/v, depends on wavelength λ
Liu UCD Phy9B 07 10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyD'EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Chapter 22.1 4Document34 pagesChapter 22.1 4Richard Renz VillafuertePas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2 Refraction of LightDocument21 pages3.2 Refraction of Lighthassanoruko21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and The Principle of Ray OpticsDocument14 pagesChapter 35 The Nature of Light and The Principle of Ray Optics蘇元浚Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH - 33 - The Nature and Propagation of Light - OQP - 2016Document6 pagesCH - 33 - The Nature and Propagation of Light - OQP - 2016Snehasis DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Light EditedDocument41 pagesLight Editedmarc daniel ortizPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Principles of OpticsDocument7 pages09 Principles of OpticsedPas encore d'évaluation
- OptikaDocument14 pagesOptikaFaizCazikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Light: 3. Reflection, Refraction, PolarizationDocument11 pagesLight: 3. Reflection, Refraction, PolarizationAndré OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Light - PhysicsDocument41 pagesLight - PhysicsChristopher TigranesPas encore d'évaluation
- RefractionDocument42 pagesRefractionjanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Optics Nature of Light: Wave Nature Particle NatureDocument15 pagesOptics Nature of Light: Wave Nature Particle NatureSam BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1Document9 pagesLecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1samarthPas encore d'évaluation
- OpticsDocument51 pagesOpticsUday Kiran ChPas encore d'évaluation
- Chatper 13Document84 pagesChatper 13Adellaine Lois GreyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Interaction of Light and MatterDocument19 pagesThe Interaction of Light and MatterIbrahim MoradPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2 Snell's LawDocument11 pagesLab 2 Snell's LawSam RajibPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Engineering: by B Suresh Department of ECEDocument26 pagesOptical Engineering: by B Suresh Department of ECESatyam LalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson13 Refractive IndexDocument12 pagesLesson13 Refractive IndexGemma WrigleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Determine The Index of Refraction, Given The Speed of Light in A Medium. State Snell's Law (Law of Refraction)Document4 pagesDetermine The Index of Refraction, Given The Speed of Light in A Medium. State Snell's Law (Law of Refraction)alleaheunice29Pas encore d'évaluation
- As 23b OpticsDocument57 pagesAs 23b OpticsHany ElGezawyPas encore d'évaluation
- FAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 18-Aug-2021 Wave Optics-InterferenceDocument53 pagesFAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 18-Aug-2021 Wave Optics-Interferencetejas paiPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Enzo Nathan - FA#8 - Activity 1.8 - Reflection and RefractionDocument8 pagesGo Enzo Nathan - FA#8 - Activity 1.8 - Reflection and Refractionenzonathan.goPas encore d'évaluation
- Optics: The Science of Light Imaging: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimDocument16 pagesOptics: The Science of Light Imaging: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimjohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection RefractionDocument17 pagesReflection RefractionDhira GunawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment #17: Refraction: BjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment #17: Refraction: BjectivesAref DahabrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Sub-CPMK 2 Hukum Dasar CahayaDocument24 pagesSub-CPMK 2 Hukum Dasar CahayaRonald SuciptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Humara Nam Ravi HaiDocument8 pagesHumara Nam Ravi HaiRavi ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- 12-Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument10 pages12-Reflection and Refraction of LightGIEPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175) : Ray TheoryDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175) : Ray TheorySaikat MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Optics PHY F213: Dr. Manjuladevi.V Assistant Professor Department of Physics BITS Pilani 333031Document36 pagesOptics PHY F213: Dr. Manjuladevi.V Assistant Professor Department of Physics BITS Pilani 333031Araman Tanvir0% (1)
- P3T1 Stud NotesDocument66 pagesP3T1 Stud Notesyash bhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts and Units in Illumination EngineeringDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts and Units in Illumination EngineeringRajendranbehappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Refraction of LightDocument22 pagesRefraction of Lightsuersh1_srivaiPas encore d'évaluation
- UP3 - 1.4. Total Internal Reflection - pg19-24Document6 pagesUP3 - 1.4. Total Internal Reflection - pg19-24mohmmadaliawadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document70 pagesChapter 6mrsm fizik100% (1)
- Ray Obtics PhysicsDocument150 pagesRay Obtics Physicshazem ab2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture (Optics and Laser)Document40 pagesLecture (Optics and Laser)Salama NaumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection, Refraction, and DiffractionDocument18 pagesReflection, Refraction, and Diffractionjaymart villartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometrical OpticsDocument30 pagesGeometrical Opticsdildar123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture (Optics and Laser)Document32 pagesLecture (Optics and Laser)Muhammad MoizPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Refraction and ReflectionDocument24 pages2nd Refraction and ReflectionSahmi Abdulqahar NizoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection, Refraction, and DiffractionDocument18 pagesReflection, Refraction, and DiffractionImmanuel Suman ShijuPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 RefractionDocument29 pages5 RefractionAananth BalachandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three Light As Wave MotionDocument11 pagesChapter Three Light As Wave MotionSabrina NevilleLongbottom RitterPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 22: Optical Properties: Issues To Address..Document32 pagesChapter 22: Optical Properties: Issues To Address..Qaz ZaqPas encore d'évaluation
- OC - Lect - 02 Aziz AlhaidariDocument21 pagesOC - Lect - 02 Aziz Alhaidariabdulaziz saif ali mansoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Photonics 02 Light PropertiesDocument39 pagesPhotonics 02 Light PropertiesVandana SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Compare The Rival Theories of Light Held by ScientistsDocument12 pagesLight Compare The Rival Theories of Light Held by ScientistsPhilip MoorePas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Refraction IndexDocument3 pagesDetermination of Refraction IndexDrakalopPas encore d'évaluation
- Dutch Physicist Christian Huygens Captured This Propagation Mechanism MATHEMATICALLYDocument16 pagesDutch Physicist Christian Huygens Captured This Propagation Mechanism MATHEMATICALLYAijaz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ray Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexDocument7 pagesRay Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexranjithPas encore d'évaluation
- WAVES NOTES Total Internal ReflectionDocument2 pagesWAVES NOTES Total Internal ReflectionDink MemesPas encore d'évaluation
- RefractionDocument4 pagesRefractionJOSHUA CINCOPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics Laboratory Course Code: PHY119Document26 pagesEngineering Physics Laboratory Course Code: PHY119Dhruva is livePas encore d'évaluation
- Serat OptikDocument100 pagesSerat OptikNur Moh. Alif Al-wahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics Optics MainDocument87 pagesEngineering Physics Optics MainHasan ZiauddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Universidad Nacional Abierta Y A Distancia UnadDocument18 pagesUniversidad Nacional Abierta Y A Distancia UnadJarin cruz herreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Filmetrics Tutorial - Thickness Metrology Guide v3NDocument12 pagesFilmetrics Tutorial - Thickness Metrology Guide v3NsaranyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8Document52 pagesLecture 8Ashraf maghPas encore d'évaluation
- Curtain Wall (Jaskirat)Document29 pagesCurtain Wall (Jaskirat)JaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Case StudyDocument49 pagesBuilding Case StudyJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Commercial Kitchen (Ass. 2)Document21 pagesCommercial Kitchen (Ass. 2)JaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Construction Bachelor of Architecture: Submitted byDocument7 pagesBuilding Construction Bachelor of Architecture: Submitted byJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument29 pagesQuestion BankJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Petronas Tower and Ritz TowerDocument28 pagesPetronas Tower and Ritz TowerJaskirat100% (1)
- Facade ConstructionDocument16 pagesFacade ConstructionJaskirat100% (1)
- Comm Kitchen Case StudyDocument2 pagesComm Kitchen Case StudyJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Housing Assignment - Ii Census DataDocument6 pagesHousing Assignment - Ii Census DataJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 - 2021Document1 pageAssignment 1 - 2021JaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- High Rise Building.-Fire Safety ServicesDocument10 pagesHigh Rise Building.-Fire Safety ServicesJaskirat100% (1)
- Building Services PPT PlumbingDocument26 pagesBuilding Services PPT PlumbingJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- I.K.G. P.T.U Campus Mohali-Ii: Report On Pre-FaricationDocument12 pagesI.K.G. P.T.U Campus Mohali-Ii: Report On Pre-FaricationJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment I - Housing QuestionDocument4 pagesAssignment I - Housing QuestionJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Economics - IIIDocument34 pagesBuilding Economics - IIIJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Economics - IDocument4 pagesBuilding Economics - IJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics of LR and HRBDocument4 pagesEconomics of LR and HRBJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Components of PrefabricationDocument18 pagesComponents of PrefabricationJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Prefabricated StructuresDocument30 pagesStudy of Prefabricated StructuresJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Economic Analysis of Low Rise High Rise BuildingDocument4 pagesComparative Economic Analysis of Low Rise High Rise BuildingJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - IiiDocument11 pagesAssignment - IiiJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Economics - IIDocument4 pagesBuilding Economics - IIJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Traffic and Transportation Assignment-1: Bachelor of ArchitectureDocument8 pagesTraffic and Transportation Assignment-1: Bachelor of ArchitectureJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - IiDocument6 pagesAssignment - IiJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Housing Survey CensusDocument16 pagesHousing Survey CensusJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems Related To TrafficDocument13 pagesProblems Related To TrafficJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Housing Typologies: United Kingdom, Europe and AfricaDocument26 pagesHousing Typologies: United Kingdom, Europe and AfricaJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - IDocument7 pagesAssignment - IJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Housing Typologies-Us, Europe, AfricaDocument31 pagesHousing Typologies-Us, Europe, AfricaJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- QnA ASSIGNMENTDocument26 pagesQnA ASSIGNMENTJaskiratPas encore d'évaluation
- Morning Star (Red Rising Trilogy, #3)Document12 pagesMorning Star (Red Rising Trilogy, #3)Johnathon Beskine0% (4)
- Al Aqwal Al RajihaDocument265 pagesAl Aqwal Al RajihaАбу ЯхьяPas encore d'évaluation
- Biserici Lemn Ucraina Polonia UNESCO 2011Document451 pagesBiserici Lemn Ucraina Polonia UNESCO 2011App Protecţia Patrimoniului100% (1)
- Annotated Bibliography VPPDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliography VPPapi-340935317Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation - Dialogues Grammar Point Grammar Exercises 1 Grammar Exercises 2 Dialogue ExercisesDocument6 pagesPresentation - Dialogues Grammar Point Grammar Exercises 1 Grammar Exercises 2 Dialogue ExercisesHAPPY ARIFIANTOPas encore d'évaluation
- Daria TV ScriptsDocument1 018 pagesDaria TV ScriptsFrater Bier100% (5)
- Microsoft Project - Guided Tour - StartDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Project - Guided Tour - StartcaonibetPas encore d'évaluation
- Taj MahalDocument8 pagesTaj MahalSumayya KareemPas encore d'évaluation
- OPTICAL MINERALOGY PP Presentation Upto 075 BatchDocument82 pagesOPTICAL MINERALOGY PP Presentation Upto 075 BatchSuman TimalsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 1 Art - HumanitiesDocument96 pagesMODULE 1 Art - HumanitiesRejaelSenoro67% (9)
- Freehand SketchingDocument14 pagesFreehand SketchingJustine WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequence of Works For Building ConstructionDocument2 pagesSequence of Works For Building ConstructionBoni Amin76% (34)
- The Satire in 'Gulliver's Travels'Document6 pagesThe Satire in 'Gulliver's Travels'Sarbojeet Poddar100% (1)
- Aspie Quiz CorrectedDocument16 pagesAspie Quiz CorrectedKeplerPyePas encore d'évaluation
- A 0308003Document196 pagesA 0308003Kissy De Las Mercedes Pérez Bustamante0% (3)
- Operation ID - 201312020932562727Document1 pageOperation ID - 201312020932562727n0nt0nPas encore d'évaluation
- Neighbourhood PlanningDocument11 pagesNeighbourhood PlanningVidhu Krishna VsPas encore d'évaluation
- Burke Cursing ApostlesDocument25 pagesBurke Cursing ApostlesFolarin AyodejiPas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Workbook Answer Key 1Document16 pagesA2 Workbook Answer Key 1samuel54% (13)
- Literature and Poetry ArtDocument29 pagesLiterature and Poetry ArtAspiringInstruc2rPas encore d'évaluation
- Art of Scroll SawDocument130 pagesArt of Scroll Sawwasflo92% (50)
- EDCI 517 F17 Reaves SyllabusDocument9 pagesEDCI 517 F17 Reaves Syllabusfostersds1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Voz Pasiva: ProfesorDocument3 pagesVoz Pasiva: ProfesorAnderson CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Dieter Rams 10 Principles of Good Design 2Document87 pagesDieter Rams 10 Principles of Good Design 2PonHarshavardhanan100% (1)
- The Three Important Facts Which Influence The Literature of Victorian AgeDocument6 pagesThe Three Important Facts Which Influence The Literature of Victorian Agerisob khanPas encore d'évaluation
- FlamingoDocument9 pagesFlamingoprakhar153Pas encore d'évaluation
- Script For Literary NightDocument4 pagesScript For Literary NightJoezer Gumangan VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Drama Conventions and StylesDocument2 pagesElements of Drama Conventions and StylesAngelo DonatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cruise Ship Song List (2021)Document7 pagesCruise Ship Song List (2021)EntonyKarapetyan100% (4)
- RawPedia BookDocument187 pagesRawPedia BookMike Ignatius Nelson100% (1)