Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pe Geo
Transféré par
ThaungMyintTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pe Geo
Transféré par
ThaungMyintDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
P
PRRO
OFFE
ESSS
SIIO
ONNA
ALL E
ENNG
GIIN
NEEE
ERRS
SSSP
PEEC
CIIA
ALLIIS
STT R
REEG
GIIS
STTR
RAATTIIO
ONNE
EXXA
AMMIIN
NAATTIIO
ONN
Geotechnical
Engineering
2010
Information for Applicants
professional engineers board singapore
Professional
5 Maxwell Road 1stExamination
Engineers Registration FEE 2010
storey Tower Block MND Complex Singapore 069110
Page 1
Professional Engineers Specialist Registration Examination
On Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Information for Applicants
Contents Page
1 Introduction ....................................................................................... 2
2 Eligibility To Sit For Examination........................................................... 2
3 Fees .................................................................................................. 2
4 Dates of Examination .......................................................................... 2
5 Venue ................................................................................................ 3
6 Application Forms ............................................................................... 3
7 Structure Of Examination..................................................................... 3
8 Final Results and Notification …………..…………………………………………………4
9 Examination Appeals…………………………………………………………………..……..4
10 Review Courses ................................................................................. .4
11 Refund Of Fees................................................................................... 4
Annex A: FORMAT AND SYLLABUS
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 2
Professional Engineers Specialist Registration Examination
On Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Information for Applicants
1 INTRODUCTION
The Professional Engineers Act provides for the registration of specialist
professional engineer. In particular, a professional engineer registered in the
branch of civil engineering may apply to the Professional Engineers Board to
be registered as a specialist professional engineer in geotechnical
engineering.
To apply for registration, the applicant must have in force a valid practicing
certificate. He must possess the requisite number of years of recognised
practical experience, a certain number of which must be in geotechnical
engineering. He is also required to have a post-graduate engineering degree
(such as M.Sc or PhD) majoring in geotechnical engineering or sat and
passed a specialist registration examination on geotechnical
engineering conducted by the Board.
The following sections set out the requirements and details for the specialist
registration examination on geotechnical engineering while details on other
application requirements are available on the PEB website at
www.peb.gov.sg.
2 ELIGIBILITY TO SIT FOR EXAMINATION
A professional engineer registered in the branch of civil engineering may
apply to sit for the specialist registration examination on geotechnical
engineering conducted by the Board.
3 FEES
The fees for an application to sit for the specialist registration examination on
geotechnical engineering is $1200.
4 DATES OF EXAMINATION
The date for the specialist registration examination on geotechnical
engineering is 28 Sep 2010.
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 3
5 VENUE
Details of the venue would be given to successful applicants at a later date.
6 APPLICATION FORMS
Application forms can be downloaded from the PEB website at
http://www.peb.gov.sg. All applications are to be submitted to PEB with
applicable fees and documents by 15 Jul 2010 latest. Applicants are advised
to send in their applications early to allow time for processing. They would be
informed of the status of their applications and other details by post at least
two weeks before the examinations.
7 STRUCTURE OF EXAMINATION
A summary of the structure of the examination is shown in the table below.
The examination is ‘open book’ and further details are given in Annex A:
Format and Syllabus.
Subjects Time Allocated Format
Part 1
Covers almost all disciplines
of geotechnical engineering Multiple Choice
2 hours
involving both soil and rock Questions ( MCQ)
(9 am - 11 am)
mechanics as well as
Singapore geology
Part 2 Answer 2 compulsory
Covers two compulsory questions on site
topics on site investigation investigation and soil
and soil properties plus four 4 hours properties
specific topics on excavation, (1 pm – 5 pm)
building foundations, Answer 2 out of 4
tunneling and slope stability questions on specific
topics
8 FINAL RESULTS AND NOTIFICATION
Examination results will be given to candidates on a Pass/Fail basis. No
examination scores or marks will be given to candidates. Examination results
are mailed to the candidates within twelve weeks after the examination.
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 4
9 EXAMINATION APPEALS
A candidate who has failed the examination may submit a written appeal to
review his/her performance together with a payment of $25. The appeal is to
be made within 2 weeks after the receipt of results and late appeals would
not be considered. The result of the appeal/review will be sent by written mail
to the appeal candidate.
10 REVIEW COURSES
The Board does not endorse any review course or material provided as study
aides.
11 REFUND OF FEES
Where an applicant who has been accepted is unable to sit for the
examination subsequently, the Board may, at its discretion, refund part of the
fees that the applicant has paid.
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 5
Annex A: FORMAT AND SYLLABUS
I Geotechnical Engineering Examination Part 1
This paper aims to examine the candidates on their understanding of the
fundamentals and practice of geotechnical engineering. Candidates are
expected to have a broad understanding of the concepts, theories, modes of
failure, assumptions and design concerns in various disciplines within
geotechnical engineering. This paper is catering for breadth covering topics
stipulated in the syllabus.
Format
This is a 2-hour paper with multiple choice questions. The candidates may
bring along their own reference materials and calculators as necessary.
II Geotechnical Engineering Examination Part 2
This paper aims to examine the candidates on their proficiency in the practice,
application and design aspects of geotechnical engineering at the professional
level. Candidates are expected to have a good working knowledge and
experience of design, construction and regulatory requirements in
geotechnical engineering in Singapore. This paper is catering for depth. It
places emphasis on the role of the specialist professional engineer in
geotechnical engineering in construction projects in the local context.
Format
This is a 4-hour paper. Section A has two questions covering site investigation
and evaluation of soil parameters. Both questions are compulsory. Section B
has four questions. The candidates are required to choose two out of the four
which can be in the areas of building foundation, earth retaining structure,
tunneling, soil improvement and slope stability. The candidates may bring
along their own reference materials and calculators as necessary.
III Syllabus
Geology of Singapore
o Basic geological formations of Singapore and their distribution
o Weathering classification and description of rocks for engineering
purposes
o Classification of recent deposits and their characteristic soil properties
Soil Mechanics Fundamentals
o Index properties
o Soil classification
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 6
o Mechanical properties - shear strength, compressibility and
permeability
o Concepts of effective stress versus total stress
o Soil compaction
o Bearing capacity of soil
o Seepage and ground water flow
o Settlement and consolidation
o Stress distribution
Rock Mechanics Fundamentals
o Intact rock properties, Influence of sample size
o Factors defining the behavior of rock mass versus intact rock; types
of discontinuities
o Rock tests: unconfined compression test, point load test, durability
test
o Rock mass properties; Mohr-Coulomb parameters; Hoek and Brown
empirical failure criteria, deformation modulus
o Shear strength of discontinuities
o Rock mass classification, RMR and Q
o Cross-section shapes of underground excavations in rock
o Typical failure mechanisms in rock excavations and post-failure
behavior
o Design of rock support
o Interaction of rock support with deformation behavior of rock mass
Site investigation
o Types of drilling (rotary drilling, wash boring, flight auger, etc)
o Types of in-situ testing including standard penetration test (SPT),
vane shear test (FVT), cone penetration test (CPT), pressuremeter
test (PMP), permeability test, Packer test
o Types of sampling method such as Shelby tube, open drive sampler,
piston sampler, Mazier sampler, diamond coring for rocks, etc.
o Ground water hydrology, such as the source of ground water or pore-
pressure which may affect the geotechnical design
o Significance of soil sample and rock core recovery rate and RQD
o Planning requirements such as number of borehole and their
locations, depth of drilling, types and frequencies of sampling and in-
situ testing and types of laboratory tests, etc.
o Significance of desk top study such as knowing the geological
formation and topography, searching for available data from various
sources on soil conditions, knowing the presence and types of
surrounding structures, etc.
o Significance of site reconnaissance before drilling and visits during
drilling to understand the site conditions, observing the performance
of surrounding structures and checking the progress and quality of
drilling works, etc.
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 7
Field and laboratory testing
o Principles of various in-situ tests (SPT, FVT, CPT, PMT, permeability
test and Packer test) and the interpretation of test results, sources of
errors and the range of applications in geotechnical design
o Principles of common laboratory tests to obtain index properties,
shear strength and modulus (drained and undrained with or without
pore-water measurements), consolidation test, permeability test, uni-
axial compression test on rock, point load test on rock, etc;
interpretation of test results and their range of applications
Soil Properties
o Physical properties and their inter-relationships and significance in
geotechnical design
o Mechanical properties such as strength (drained and undrained),
compressibility and permeability
o Chemical properties which may affect the design of foundation
Constitutive Soil Models
o Understand limitations and range of applications of Mohr-Coulomb
model and other advanced soil models
o Understand the significance of each soil parameter
o Know how to evaluate soil parameters for each soil model
o Understand the significance of total and effective stress analysis as
well as undrained, drained and consolidation analysis
Instrumentation
o Types of geotechnical instruments and their engineering purposes,
o Principles of each instrument, method of installation, potential
sources of errors in installation and measurement
o Planning of instrumentation program (location and depth of
installation, monitoring frequency, review levels, etc)
o Interpretation of readings and their implications; potential sources of
errors
Foundation Engineering
o Shallow foundations – footings and rafts
o Deep foundations – driven piles, bored piles and caissons
o Chin’s method and Hiley formula
o Wave equation analysis - PIT, PDA and CAPWAP
o Pile load tests and interpretation of results
o Group piles; capacity and settlement
o Lateral loads on piles
o Underpinning
Earth Retaining Structures
o Earth pressure on walls (Rankine, Coulomb and log-spiral method)
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 8
o RC retaining wall
o Gravity retaining wall – crib wall, reinforced soil, gabion wall
o Embedded retaining wall – cantilever, propped and anchored
o Seepage and pore pressure considerations
Tunnelling
o Excavation methods in soil and rock
o Ground support methods in soil (temporary & permanent)
o Rock support methods (temporary & permanent)
o Excavation sequencing
o Staging of rock support application
o Maintaining stability of the excavation face
o Dealing with groundwater during excavation
o Rock mass improvement
Slope Stability
o Taylor’s chart, Infinite slope, Swedish method and various
approaches utilizing the method of slices, circular and non-circular
slip analysis
o Effect of soil suction on slope stability
o Total and effective stress analysis as well as drained and undrained
analysis, cut slopes and embankment slopes
o Evaluation of soil strength and ground water regime
o Preventive works and remedial measures
Soil Improvement
o Surface compaction
o Pre-loading and surcharging
o Pre-fabricated vertical drains, sand drains
o Stone columns
o Dynamic and vibro compaction
o Deep mixing and jet grouting
o Chemical grouting
o De-watering
o Seepage cut-offs
o Soil reinforcement – geosynthetics, soil nails
Ground Anchors
o Element of ground anchors
o Load deriving zones
o Fixed length design
o Load and creep tests
o Pre-loading of anchors
o Corrosion protection
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Page 9
References
Reference materials include but not limited to:
Codes and Standards under Building Control Act and Regulations, e.g.
CP4, CP18, BS5930, BS8002, BS8004, BS8081, CIRIA C580, CIRIA
140, etc.
Codes and Standards for Roads and Transit Systems to LTA’s
requirements
Textbooks and handbooks on soil mechanics, foundation engineering,
rock mechanics, tunneling, soil improvement and slope stability
Specialist Registration Examination Geotechnical Engineering 2010
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Geotechnical Earthquake Eng For HW PDFDocument210 pagesGeotechnical Earthquake Eng For HW PDFJose LuisPas encore d'évaluation
- Specifications of Test Adit TunnelDocument87 pagesSpecifications of Test Adit TunnelSushmit SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsD'EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovation in Bored Tunnel Segmental Lining Design in Singapore - Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC)Document9 pagesInnovation in Bored Tunnel Segmental Lining Design in Singapore - Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete (SFRC)SeasonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bill of Quantity For Drilling of Twenty BoreholesDocument1 pageBill of Quantity For Drilling of Twenty BoreholesAnonymous OeoeVBmwPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Construction of Microtunneling ProjectsDocument3 pagesDesign and Construction of Microtunneling ProjectsMahmood AliPas encore d'évaluation
- First Revision-15 Aug 2017 - DESIGN GUIDELINES PDFDocument277 pagesFirst Revision-15 Aug 2017 - DESIGN GUIDELINES PDFБ. СайнболдPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 ITATech Sprayed Membranes CelestinoDocument60 pages2 ITATech Sprayed Membranes CelestinoMarcelo ApoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Culvert ThicknessDocument23 pagesCulvert ThicknessNilaAbubakarPas encore d'évaluation
- GEESS - 22nd Minutes - Nurul - Yee TS Edit 28 Feb 2021-Tao (FINAL)Document13 pagesGEESS - 22nd Minutes - Nurul - Yee TS Edit 28 Feb 2021-Tao (FINAL)Ismacahyadi Mohamed Jais100% (1)
- Trief KerbDocument8 pagesTrief KerbMurthyThendelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ground Improvement Using Jet GroutingDocument41 pagesGround Improvement Using Jet GroutingArnab SurPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 Poulos Settlement Prediction PDFDocument22 pages2006 Poulos Settlement Prediction PDFSantosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Channeline BrochureDocument32 pagesChanneline BrochureAlexandru IgnatPas encore d'évaluation
- Unified Facilities Criteria (Ufc) : Dewatering and Groundwater ControlDocument161 pagesUnified Facilities Criteria (Ufc) : Dewatering and Groundwater ControlManiko ManikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Microtunneling and Tunneling in Cobbles and Boulders References, 2019-08-11Document35 pagesMicrotunneling and Tunneling in Cobbles and Boulders References, 2019-08-11swhuntPas encore d'évaluation
- GT1R1A - Caracterisation of Rock Masses PDFDocument48 pagesGT1R1A - Caracterisation of Rock Masses PDFfededaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compendium of Ground Modification FDOT - BC354 - 64 - RPTDocument371 pagesCompendium of Ground Modification FDOT - BC354 - 64 - RPTBluebelgianPas encore d'évaluation
- Water StopperDocument6 pagesWater StopperMF YousufPas encore d'évaluation
- Code of Practice For Reinforcement of Rock Slopes With Plane Wedge FailureDocument16 pagesCode of Practice For Reinforcement of Rock Slopes With Plane Wedge FailurePabloPas encore d'évaluation
- DFDocument22 pagesDFPK100% (1)
- Advances in Rockfill StructuresDocument27 pagesAdvances in Rockfill StructuresHesbon MoriasiPas encore d'évaluation
- EMP Transmission Line-EnGDocument58 pagesEMP Transmission Line-EnGMin Chan MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- IBC Site ClassificationDocument1 pageIBC Site ClassificationAnonymous mZUchvhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Shotcrete Lining in A TunnelDocument13 pagesShotcrete Lining in A TunnelNaveen R100% (1)
- E Ect of Building Sti Ness On Tunnelling-Induced Ground Movement-MAIRDocument13 pagesE Ect of Building Sti Ness On Tunnelling-Induced Ground Movement-MAIRSérgio BernardesPas encore d'évaluation
- G&P Digest Issue 6Document8 pagesG&P Digest Issue 6Chua Chim HueePas encore d'évaluation
- Nilex Woven Geotextile SpecificationsDocument1 pageNilex Woven Geotextile SpecificationsAbdullah BasalamahPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Between 2d and 3d Behaviour of Sheet Piles by Finite Element MethodDocument16 pagesComparison Between 2d and 3d Behaviour of Sheet Piles by Finite Element MethodtavialimPas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Gravel Wearing Course Design PDFDocument10 pages11-Gravel Wearing Course Design PDFjohn_d_thirdPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 5228-4 1992 Piling Noise & VibrationDocument70 pagesBS 5228-4 1992 Piling Noise & VibrationbarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Institution of Civil Engineers (1988) Specification For Piling - Contract Documentation and MeasurementDocument35 pagesInstitution of Civil Engineers (1988) Specification For Piling - Contract Documentation and MeasurementBobPas encore d'évaluation
- Issues in Evaluating Capacity of Rock Socket FoundationsDocument11 pagesIssues in Evaluating Capacity of Rock Socket FoundationspaducoPas encore d'évaluation
- Jet Grouting PDFDocument8 pagesJet Grouting PDFDani JoePas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Construction of Grouted RiprapDocument16 pagesDesign and Construction of Grouted Ripraptomaustin100% (1)
- David Muir Wood Slides PDFDocument118 pagesDavid Muir Wood Slides PDFserçinPas encore d'évaluation
- Immersed Tunnels: in The Permanent Stage Is Kept at ADocument1 pageImmersed Tunnels: in The Permanent Stage Is Kept at AmaherelabdPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Construction of MRT Project Contract 825 of CCL1 in SingaporeDocument8 pagesDesign and Construction of MRT Project Contract 825 of CCL1 in SingaporeSABEASNPas encore d'évaluation
- NSW Transport PDFDocument21 pagesNSW Transport PDFIzam FatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wbi Print6 0Document13 pagesWbi Print6 0milan_popovic_2100% (1)
- Time Dependent Movements On The Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport Pedestrian Tunnel, Ontario, CanadaDocument15 pagesTime Dependent Movements On The Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport Pedestrian Tunnel, Ontario, CanadaAndrew CushingPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretive Flood Report RevA FinalDocument40 pagesInterpretive Flood Report RevA FinalSanjoy SanyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Thewes2016 - Clogging EvaluationDocument7 pagesThewes2016 - Clogging EvaluationMoez SelmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 15835 1 2018Document14 pagesIso 15835 1 2018yyk comPas encore d'évaluation
- DFI 2011 - The Use of Polymer As Drilling Fluid and Its Impact On Pile Shaft Friction CharacteristicsDocument21 pagesDFI 2011 - The Use of Polymer As Drilling Fluid and Its Impact On Pile Shaft Friction CharacteristicsAndrés MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- I-System Classification Provides Comprehensive Design SupportDocument24 pagesI-System Classification Provides Comprehensive Design SupportDebasis BarmanPas encore d'évaluation
- ..-HKIE-download-Tunnel Related Failures PDFDocument11 pages..-HKIE-download-Tunnel Related Failures PDFAbdelali SolPas encore d'évaluation
- Wekiva 7A (240200-2!52!01) Final Report of GEI For Misc Structures 7-13-17Document92 pagesWekiva 7A (240200-2!52!01) Final Report of GEI For Misc Structures 7-13-17Oanh PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Geotechnical Investigation of Bridge StructuresDocument14 pagesGuidelines For Geotechnical Investigation of Bridge StructuresadeolaodukoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- XYPEX TESTING SUMMARYDocument18 pagesXYPEX TESTING SUMMARYSamrerng KriengprathanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Layout and Design Techniques of Cross Section For The Large Immersed Tunnel PDFDocument8 pagesLayout and Design Techniques of Cross Section For The Large Immersed Tunnel PDFSEDIMPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Shaft Lining and Stations for Deep Ore DepositsDocument20 pagesDesign of Shaft Lining and Stations for Deep Ore DepositsManish Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- BBA Cert For ReCo High Adherence Strip and Panel Lug System For Ret Walls & Bridge Abuts (2003)Document8 pagesBBA Cert For ReCo High Adherence Strip and Panel Lug System For Ret Walls & Bridge Abuts (2003)sandycastlePas encore d'évaluation
- Impact and Management of Stray Current On DC Rail SystemsDocument8 pagesImpact and Management of Stray Current On DC Rail Systems曾乙申100% (1)
- A New Method For Single Pile Settlement Prediction and AnalysisDocument5 pagesA New Method For Single Pile Settlement Prediction and AnalysisCesar Felipe Jimenez SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Procedure For Liquefaction Mitigation Using Dynamic CompactionDocument7 pagesDesign Procedure For Liquefaction Mitigation Using Dynamic CompactionLivian TeddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For The Use of Steel Piling For Bridge FoundationsDocument21 pagesGuidelines For The Use of Steel Piling For Bridge FoundationsHermann PankowPas encore d'évaluation
- Rerto Faq 110121Document5 pagesRerto Faq 110121ThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Communications in Computer and Information Science 781: Editorial BoardDocument10 pagesCommunications in Computer and Information Science 781: Editorial BoardThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- SP012Document5 pagesSP012Lim ChintakPas encore d'évaluation
- Drained Cavity Expansion Analysis With A Unified State Parameter Model For Clay and Sand-Cgj-2016-0695Document29 pagesDrained Cavity Expansion Analysis With A Unified State Parameter Model For Clay and Sand-Cgj-2016-0695ThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- CommentsDocument1 pageCommentsThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- BH - 01 PDFDocument2 pagesBH - 01 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Interim Report 1Document11 pagesInterim Report 1ThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- T&C2Document6 pagesT&C2ThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- SP012Document5 pagesSP012Lim ChintakPas encore d'évaluation
- Documents - Pub Stability Analysis For Diaphragm Walls To Din 4126 Ggu TrenchDocument43 pagesDocuments - Pub Stability Analysis For Diaphragm Walls To Din 4126 Ggu TrenchThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Displacementbased Seismic Design of Structures Calvi 205Document24 pagesDisplacementbased Seismic Design of Structures Calvi 205oneakshayPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem 17 Nov 15Document1 pageSem 17 Nov 15ThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Output Version 2017.1.0.0: Min MaxDocument1 pageOutput Version 2017.1.0.0: Min MaxThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Pressure Calculation For The Shoring Plate: New Bridge Centre, BLK 336, Smith Street #06-305, SINGAPORE 050336Document13 pagesActive Pressure Calculation For The Shoring Plate: New Bridge Centre, BLK 336, Smith Street #06-305, SINGAPORE 050336ThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
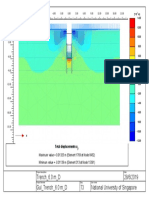
- Trench - 6.0 M - D 28/6/2019 Gul - Trench - 6.0 M - D 73 National University of SingaporeDocument1 pageTrench - 6.0 M - D 28/6/2019 Gul - Trench - 6.0 M - D 73 National University of SingaporeThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Output Version 2017.1.0.0: Unsat SatDocument9 pagesOutput Version 2017.1.0.0: Unsat SatThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3.0 M - UD - COM2 PDFDocument2 pages19 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3.0 M - UD - COM2 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Output Version 2017.1.0.0: Unsat SatDocument9 pagesOutput Version 2017.1.0.0: Unsat SatThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
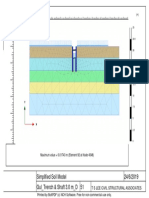
- 01 Simplified Soil Model PDFDocument1 page01 Simplified Soil Model PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Bending of PlatesDocument4 pages12 Bending of PlatesRavi SalimathPas encore d'évaluation
- Resource Piling: Large Load Tests Using A Reaction SystemDocument38 pagesResource Piling: Large Load Tests Using A Reaction SystemThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Aijrstem19 PDFDocument5 pagesAijrstem19 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3.0 M - UD - COM2 PDFDocument2 pages19 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3.0 M - UD - COM2 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertical Equipment FoundationDocument15 pagesVertical Equipment FoundationThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet PilesDocument20 pagesSheet PilesBryan AlmodovarPas encore d'évaluation
- 09-1 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3.0 M - D - COM1 PDFDocument2 pages09-1 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3.0 M - D - COM1 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 01 StaticPileLoadTest PDFDocument23 pages02 01 StaticPileLoadTest PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- Content Cover Page - Standard PDFDocument1 pageContent Cover Page - Standard PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3 PDFDocument1 page14 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3 PDFDocument1 page10 Gul - Trench & Shaft 3 PDFThaungMyintPas encore d'évaluation
- BUMANGLAG - CLASS D - JEL PlanDocument3 pagesBUMANGLAG - CLASS D - JEL PlanMAUREEN BUMANGLAGPas encore d'évaluation
- Historyofluthera01morg PDFDocument420 pagesHistoryofluthera01morg PDFJhonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhaktisiddhanta Appearance DayDocument5 pagesBhaktisiddhanta Appearance DaySanjeev NambalatePas encore d'évaluation
- Progress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalDocument7 pagesProgress Test 5 (Units 13-15) : Complete All Seven Sections. There Are Seventy Marks in TotalIlia GviniashviliPas encore d'évaluation
- GWP - Unicef - Guidance Note Risk Assessments For Wash PDFDocument56 pagesGWP - Unicef - Guidance Note Risk Assessments For Wash PDFyomifPas encore d'évaluation
- Adina CFD FsiDocument481 pagesAdina CFD FsiDaniel GasparinPas encore d'évaluation
- June 2016 - QuestionsDocument8 pagesJune 2016 - Questionsnasir_m68Pas encore d'évaluation
- The City - Populus' As A Self-Governing CorporationDocument24 pagesThe City - Populus' As A Self-Governing Corporation马寅秋Pas encore d'évaluation
- Handout of English For PsychologyDocument75 pagesHandout of English For PsychologyRivan Dwi AriantoPas encore d'évaluation
- 50 Cool Stories 3000 Hot Words (Master Vocabulary in 50 Days) For GRE Mba Sat Banking SSC DefDocument263 pages50 Cool Stories 3000 Hot Words (Master Vocabulary in 50 Days) For GRE Mba Sat Banking SSC DefaravindPas encore d'évaluation
- Levenbach Causal2017Document15 pagesLevenbach Causal2017Jenna GrantPas encore d'évaluation
- Merry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)Document6 pagesMerry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)gmit92Pas encore d'évaluation
- DirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideDocument5 pagesDirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideTempest JannaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Research TeamDocument4 pagesThe Research Teamapi-272078177Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Pantheon of Greek Gods and GoddessesDocument2 pagesThe Pantheon of Greek Gods and Goddessesapi-226457456Pas encore d'évaluation
- New Democracy June-August 2017Document32 pagesNew Democracy June-August 2017Communist Party of India - Marxist Leninist - New DemocracyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vadiyanatha AstakamDocument4 pagesVadiyanatha AstakamRaga MalikaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case of DrowningDocument16 pagesA Case of DrowningDr. Asheesh B. PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Marwar Steel Tubes Pipes StudyDocument39 pagesMarwar Steel Tubes Pipes Studydeepak kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Music Really Means To ChildrenDocument5 pagesWhat Music Really Means To ChildrenMara Sofia ValentePas encore d'évaluation
- Christian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Document78 pagesChristian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Nwaozuru JOHNMAJOR ChinecheremPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEST 6. Chest Trauma 2022 YismawDocument61 pagesCHEST 6. Chest Trauma 2022 YismawrobelPas encore d'évaluation
- New Text DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Text DocumentDhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Table Topics Contest Toastmaster ScriptDocument4 pagesTable Topics Contest Toastmaster ScriptchloephuahPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Deuteronomy On Its Own TermsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Deuteronomy On Its Own TermsAlberto RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Urban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniDocument1 pageUrban Process Design - Hamid ShirvaniCaramel LattePas encore d'évaluation
- Corporation Law Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesCorporation Law Quiz AnswerswivadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Test, Part 2: Literature With A Purpose: Total Score: - of 40 PointsDocument3 pagesUnit Test, Part 2: Literature With A Purpose: Total Score: - of 40 PointsAriana Stephanya Anguiano VelazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- A Cautionary Tale of Psychoanalysis and SchizophreniaDocument30 pagesA Cautionary Tale of Psychoanalysis and SchizophreniaJona JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Quiz Corrections ADocument4 pagesChapter 5 Quiz Corrections Aapi-244140508Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansD'EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignD'EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (137)
- Summary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathD'EverandSummary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetD'EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (10)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsD'EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationD'EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (18)
- Cable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignD'EverandCable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeD'EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (59)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressD'EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Produced Water Treatment Field ManualD'EverandProduced Water Treatment Field ManualÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationD'EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationPas encore d'évaluation
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansD'EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentD'EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentPas encore d'évaluation
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignD'EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisD'EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Guidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaD'EverandGuidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Methodology for Estimating Carbon Footprint of Road Projects: Case Study: IndiaD'EverandMethodology for Estimating Carbon Footprint of Road Projects: Case Study: IndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines for Siting and Layout of FacilitiesD'EverandGuidelines for Siting and Layout of FacilitiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyD'EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyPas encore d'évaluation