Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
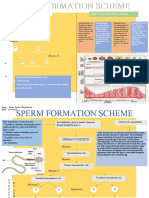
Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation Structures
Transféré par
Jason Mark MayorDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation Structures
Transféré par
Jason Mark MayorDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NAME:______________________________________
Complete the Fetal Circulation diagram by filling up the blanks. Write the letter of the correct answer on your
answer sheet.
Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation Structures
A. Umbilical Artery
Placenta
B. Umbilical Vein
1)
Ductus Venosus C. Left Ventricle
D. Foramen Ovale
2)
E. Hepatic Vein
IVC
RA
3)
LA
4)
Aorta
5)
MATCHINGPlacenta
TYPE: Match Column A with Column B. Choices can be used more than once. Write the letter
of your choice on the answer sheet.
SET A:COLUMN A – Functions COLUMN B – Fetal/Embryotic Structure
______1. Forms the oocytes and spermatocytes. A. Chorion
______2.Serves as a repository for fetal waste. B. Umbilical cord
______3. Serves as a lifeline from the embryo to the placenta. C. Yolk sac
______4. Source of oral fluid of the fetus. D. Amniotic fluid
______5. It gives rise to the placenta. E. Placenta
______6. Produces HCG, estrogen and progesterone.
SET B: COLUMN A – Developmental Milestone COLUMN B – Age of Gestation
_______7. Placental formation is complete. A. 12 weeks
_______8. Fetal heart sounds are audible with stethoscope. B. 16 weeks
_______9. Lower extremities are fully formed. C. 20 weeks
_______10. Lanugo begins to decrease in amount. D. 36 weeks
_______11. Testes descend fully into the scrotal sac. E. 40 weeks
SET C : Terminologies
______12. A process that takes about 264 days A. Ballottment
from the date of fertilization of the egg
______13. The term used for the developing fertilized B. Hegar’s sign
egg during the first 9 weeks of pregnancy
______14. The softening of the lower uterine segment C. Souffle
______15. The use of a finger to push sharply against D. Flatulence
the uterus and detect the presence or
position of a fetus by its return impact.
______16. A low murmuring or blowing sound E. Striae gravidarum
heard through a stethoscope.
______17. Reddish slightly depressed streaks F. Spinnnbarkheit
in the abdominal wall, breast and thighs
______18. “Mask of Pregnancy” which are brownish G. Pregnancy
patches on the face
______19. Excessive gas during pregnancy which is H. Chloasma
caused by hormone progesterone
______20. Compression of the vena cava by enlarged uterus I. Embryo
_____21. The strecthability of the cervical mucus J. Supine hypotensive
syndrome
Identification. Indicate what month in the pregnancy does each described fetal development occurs. Write the
answer on the space provided before the number.
______1. Quickening present
______2. Capable of hearing sounds
______3. Organogenesis is completed
______4. Functional liver and pancreas
______5. Heart beat audible by doppler
______6. Sex can be determined whether it's a boy or a girl
______7. Alveoli matures/ surfactant present in amniotic fluid
______8. Presence of 1-2 creases on sole of foot/ Decrease in lanugo
______9. Rudimentary heart appears as a bulge on the anterior surface
_____10. Fetus kicks actively/ Start of conversion of fetal hemoglobin to adult
The menstrual phase is the first stage of the menstrual cycle. This phase starts when an egg from the previous
cycle is not fertilized. Because pregnancy has not taken place, levels of the hormones 1)
__________________________ and 2)_______________________________ drop. The thickened lining of the
uterus, which would support a pregnancy, is no longer needed, so it sheds through the vagina. Follicular phase.
The follicular phase starts on the first day of the menstrual period and ends during ovulation. It starts when the
hypothalamus sends a signal to the pituitary gland to release3) __________________________________. This
hormone stimulates the ovaries to produce around 5 to 20 small sacs called follicles. Each follicle contains an
immature egg. Only the healthiest egg will eventually mature. (On rare occasions, a woman may have two eggs
mature.) The rest of the follicles will be reabsorbed into the body. The maturing follicle sets off a surge in
estrogen that thickens the lining of the uterus. This creates a nutrient-rich environment for an embryo to grow.
Ovulation phase. The rising estrogen levels during the follicular phase trigger the pituitary gland to release
4)_______________________________. This is what starts the process of ovulation. Ovulation is when the
ovary releases a mature egg. The egg travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus to be fertilized by sperm.
The ovulation phase is the only time during the menstrual cycle when a woman can get pregnant. Symptoms
during ovulation include: a slight rise in basal body temperature, abdominal pain in the ovarian region or
5)_______________________________ sign and thicker discharge that has the texture of egg whites or
6)_______________________________ sign. Ovulation happens at around day 14 in a 28-day cycle — right in
the middle. It lasts about 24 hours. After a day, the egg will die or dissolve if it is not fertilized. Luteal phase.
After the follicle releases its egg, it changes into the 7)________________________________. This structure
releases hormones, mainly 8)__________________________________ and some estrogen. The rise in
hormones keeps the uterine lining thick and ready for a fertilized egg to implant. If pregnancy takes place, the
body will produce 9)__________________________________. This is the hormone pregnancy tests detect. It
helps maintain the 10)______________________________ and keeps the uterine lining thick. If pregnancy
does not occur, the corpus luteum will shrink away and be resorbed. This leads to decreased levels of estrogen
and progesterone, which causes the onset of your period. The uterine lining will shed during your period and
back to menstrual phase of the cycle.
True or False. Write A if the statement is correct and B if not on the space provided before the number.
______1. A woman’s reproductive lifespan begins after menarche and terminates with menopause.
______2. Ovulation refers to the attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine lining.
______3. Implantation occurs 8-10 days after fertilization.
______4. Placentation refers to the formation, type and structure or arrangement of the placenta.
______5. Excitement is an involuntary climax experienced by both men and women involving a series of
muscular contractions profound physiologic bodily response and intense sexual pleasure.
______6. The male’s capacity to reproduce is associated with sexual excitement, penile erection and
ejaculation.
______7. Males have three identifiable sexual response patterns with wider range of duration and intensity of
orgasms.
______8. Females have one basic sexual response pattern; excitement progresses steadily to plateau, orgasm
and resolution.
______9. The woman should report fetal movement of three or less in one hour period after 20 weeks of
pregnancy.
______10. The fetal heart sound can be heard using the stethoscope by 18-20 weeks of gestation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornD'EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 5: Department of EducationDocument10 pagesScience 5: Department of EducationJulien PitogoPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test in SCIENCE V Name: - Date: - Grade and Section: - ScoreDocument1 pageSummative Test in SCIENCE V Name: - Date: - Grade and Section: - ScoreMhafolz Arong BardosPas encore d'évaluation
- Dental Management of the Pregnant PatientD'EverandDental Management of the Pregnant PatientChristos A. SkouterisPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test in SCIENCE V Name: - Date: - Grade and Section: - ScoreDocument1 pageSummative Test in SCIENCE V Name: - Date: - Grade and Section: - ScoreMaryflor MoratoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaD'EverandThe Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Document4 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Anatomy of the Human Peritoneum and Abdominal Cavity: Considered from the Standpoint of Development and Comparative AnatomyD'EverandThe Anatomy of the Human Peritoneum and Abdominal Cavity: Considered from the Standpoint of Development and Comparative AnatomyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Summative Test in Science 5Document3 pages1 Summative Test in Science 5Ailex Store67% (3)
- Science5 q2 Mod2 Menstrual-Cycle v4Document14 pagesScience5 q2 Mod2 Menstrual-Cycle v4pot pooot85% (20)
- Hinanay - SSG 3 CmcaDocument3 pagesHinanay - SSG 3 CmcaHenie Louise HinanayPas encore d'évaluation
- Midwifery Revision Questions-1Document8 pagesMidwifery Revision Questions-1kariuki90406978Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science 5 2nd Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesScience 5 2nd Quarter ExamLouie Ric FiscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cot First QuarterDocument15 pagesCot First QuarterRowena Torres DahiligPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2 Scie5 Ist SumTestDocument2 pagesQ2 Scie5 Ist SumTestCharmie Tigoy Baynos PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- HINANAY SSG 4 Antepartum CareDocument4 pagesHINANAY SSG 4 Antepartum CareHenie Louise HinanayPas encore d'évaluation
- The Developing Human Clinically Oriented Embryology 9th Edition Test BankDocument15 pagesThe Developing Human Clinically Oriented Embryology 9th Edition Test BanktestbanklooPas encore d'évaluation
- Science and Health: FertilizationDocument8 pagesScience and Health: FertilizationPauline Leon-Francisco LeongPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 5 DLP 2 - FetilizationDocument8 pagesScience 5 DLP 2 - FetilizationAldrin PaguiriganPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative 1 - Quarter 3Document6 pagesSummative 1 - Quarter 3Diane Tayab MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- TJS Matungao, Bulakan, Bulacan: Name: Grade and Section: I. Matching TypeDocument3 pagesTJS Matungao, Bulakan, Bulacan: Name: Grade and Section: I. Matching Typenina lykka calaraPas encore d'évaluation
- ST Science 5 Q2Document5 pagesST Science 5 Q2donna kristine delgado100% (2)
- ST SCI 10 wk1-2Document3 pagesST SCI 10 wk1-2Ivygrace NabitadPas encore d'évaluation
- Read and Choose The Correct Answer From The Box Below.: Boys GirlsDocument1 pageRead and Choose The Correct Answer From The Box Below.: Boys GirlsjekjekPas encore d'évaluation
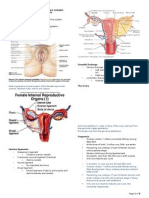
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJonalyn Brozula CapobresPas encore d'évaluation
- Science5 - q2 - Mod2 - Menstrual Cycle - v4Document20 pagesScience5 - q2 - Mod2 - Menstrual Cycle - v4Nellen Grace Ortiz86% (7)
- ST1 ScienceDocument1 pageST1 SciencePhilip YansonPas encore d'évaluation
- Male and Female Reproductive LONG TESTDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive LONG TESTfe jandugan100% (1)
- First Summative Test Science 5Document3 pagesFirst Summative Test Science 5Gil Arriola100% (2)
- Reproduction: Test B 1. Complete The DefinitionsDocument2 pagesReproduction: Test B 1. Complete The DefinitionsMariaPas encore d'évaluation
- CA RationaleDocument8 pagesCA RationaleNursing LecturePas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesReproductive SystemRogelia condes floresPas encore d'évaluation
- Remedial Worksheet 2Document1 pageRemedial Worksheet 2michelle.baguioPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesFetal DevelopmentBela MillenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test in ScienceDocument4 pagesSummative Test in ScienceMK PeolloPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Quarterly Exam Science 5Document6 pages2nd Quarterly Exam Science 5Reshiele FalconPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSE Project Final ExamDocument7 pagesASSE Project Final ExamMycz DoñaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2ND Quarter WS in ScienceDocument2 pages2ND Quarter WS in Sciencemarion ildefonso0% (1)
- Reproductive system - Ôn tậpDocument16 pagesReproductive system - Ôn tập03. Nguyễn Đặng Thiên BảoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 5 ST 2Document1 pageScience 5 ST 2jekjek100% (1)
- Score: Answer This Test in One Hour.: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesScore: Answer This Test in One Hour.: Multiple ChoiceMara LabanderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument5 pagesIdentify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMara LabanderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam2 98Document8 pagesExam2 98ramadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz No. 1 Science 5 Second Quarter Name: - GradeDocument2 pagesQuiz No. 1 Science 5 Second Quarter Name: - GradeCecilia Guevarra Dumlao100% (4)
- First Summative Test in Science 5 (Quarter 2) : Uterus Vagina Cervix Vulva Ovary Fallopian TubeDocument4 pagesFirst Summative Test in Science 5 (Quarter 2) : Uterus Vagina Cervix Vulva Ovary Fallopian TubeJennet Perez100% (2)
- June 9-13 June 4-8 June 14-21Document2 pagesJune 9-13 June 4-8 June 14-21Whenna Mailom MacahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive System Answer KeyDocument7 pagesReproductive System Answer Keyapi-209542414Pas encore d'évaluation
- LAS Chapter 3 2nd Grading Science 5Document1 pageLAS Chapter 3 2nd Grading Science 5monica.mendoza001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Male and Female Reproductive System TestDocument2 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System TestRoana Marie Tapia100% (5)
- Grade 9 Biology-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Biology-WPS OfficealemnehzelekePas encore d'évaluation
- Quarter 2 Week 2 in Science-For COTDocument32 pagesQuarter 2 Week 2 in Science-For COTRhona Liza CanobasPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 Case Study PresentationDocument93 pagesModule 5 Case Study PresentationEDULLANTES ANA MAEPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 Q3 Summative TestDocument9 pagesScience 10 Q3 Summative Testpedro braulioPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal QuizzesDocument8 pagesMaternal QuizzesJhaji Mei Margarete CasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Marks Wise Questions CH-2Document22 pagesMarks Wise Questions CH-2lakshshah5116Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study GD - UpdatedDocument3 pagesStudy GD - UpdatedSolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3RD Q Module 1 Quiz 1 Reproductive SystemDocument1 page3RD Q Module 1 Quiz 1 Reproductive Systemsinunuc nhs100% (1)
- Science V - Worksheets - 1st QuarterDocument19 pagesScience V - Worksheets - 1st QuartergalonowelmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Pre TestDocument3 pagesUnit Pre Testapi-376200062Pas encore d'évaluation
- Women Health Presentation (Ovarian Cyst)Document17 pagesWomen Health Presentation (Ovarian Cyst)Lim Su-WeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mind Map Sceme Formulation Spem and EggDocument2 pagesMind Map Sceme Formulation Spem and EggFuzna DahliaPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Asdala TransDocument8 pagesDR - Asdala TransthorheavenPas encore d'évaluation
- Tndlive Gynaecology 1 PDFDocument35 pagesTndlive Gynaecology 1 PDFZala pratiksha BhagvatsinhPas encore d'évaluation
- HUMAN EXCRETORY AND Reproductive SystemDocument35 pagesHUMAN EXCRETORY AND Reproductive SystemShilpa Born To LovePas encore d'évaluation
- Ipi131357 PDFDocument10 pagesIpi131357 PDFrizky rachmatullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Labiaplasty: A Guide For WomenDocument3 pagesLabiaplasty: A Guide For WomenBudi Iman SantosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Endometriosis & AdenomyosisDocument54 pagesEndometriosis & AdenomyosisKapil StaleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Endometriosis LirDocument32 pagesEndometriosis LirFellita Ratri APas encore d'évaluation
- Postmenopausal BleedingDocument36 pagesPostmenopausal BleedingANJU S BPas encore d'évaluation
- Infertility, Investigation and Management: Dr. Raedah Al-FadhliDocument64 pagesInfertility, Investigation and Management: Dr. Raedah Al-Fadhliapi-3703352Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cervix InformationDocument4 pagesCervix InformationEdrea Aquino MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Pengajaran Harian (RPH) : Toolkit LS 2Document3 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Harian (RPH) : Toolkit LS 2Rubiah BasriPas encore d'évaluation
- Family PlanningDocument4 pagesFamily PlanningsekwetPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Apporoach To UttarbastiDocument19 pagesPractical Apporoach To UttarbastiMadhura PhadtarePas encore d'évaluation
- HSG Di RS Rumkital Hang TuahDocument14 pagesHSG Di RS Rumkital Hang TuahC. B. PatandiananPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesPhysiology of Female Reproductive Systemswera zainabPas encore d'évaluation
- Female AnatomyDocument11 pagesFemale AnatomyBARRIENTOS, RITCHELLE C.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Final Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesMaternal Final Exam Reviewercassy SadiePas encore d'évaluation
- Hotpantz: Herbal GynecologyDocument28 pagesHotpantz: Herbal GynecologyMandy M.100% (20)
- Genital ProlapseDocument40 pagesGenital ProlapseDIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Wins ProgramDocument2 pagesWins ProgramMaresa BernidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Vaginal Discharge in ChildrenDocument12 pagesApproach To Vaginal Discharge in ChildrensujataPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual Cycle and HormonesDocument30 pagesMenstrual Cycle and HormonesGALPAO MELISSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Case StudyDocument38 pagesEctopic Case StudyMicah LangidenPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetri: Uswatul Khoirot, S. KedDocument19 pagesObstetri: Uswatul Khoirot, S. KedNovia RizqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetrics by Ten Teachers, 20th Edition 2017Document33 pagesObstetrics by Ten Teachers, 20th Edition 2017salah subbah100% (1)
- Q2 - First Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ2 - First Summative TestMilagros ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- IUD Insertion Consent FormDocument2 pagesIUD Insertion Consent FormShelly PiercePas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation 3Document3 pagesEvaluation 3Cyril CauilanPas encore d'évaluation
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessD'Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (33)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseD'EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsD'EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainD'EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (65)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (393)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeD'EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceD'EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (18)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedD'EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldD'EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (597)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainD'EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (111)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouD'EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (62)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveD'EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorD'EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionD'EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (812)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessD'EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesD'EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (397)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceD'EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (517)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsD'EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (3)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignD'EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (19)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemD'EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (116)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomD'EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (216)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindD'EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (93)
- Civilized To Death: The Price of ProgressD'EverandCivilized To Death: The Price of ProgressÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (215)