Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CH 28 Nausea/Vomiting
Transféré par
kandee0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
58 vues2 pagesThis document summarizes different drug classes used to treat nausea and vomiting, including their mechanisms of action and clinical use. It discusses:
1. Anticholinergics, antihistamines, cannabinoids, benzodiazepines, dopamine antagonists, glucocorticoids, and substance P/neurokinin-1 antagonists - their mechanisms for treating nausea/vomiting.
2. Considerations for choosing antiemetics based on chemotherapy regimen and preventing acute/delayed nausea and vomiting.
3. Adverse effects, drug interactions, and important clinical pearls regarding use of dopamine antagonists, cannabinoids, and substance P/neurokinin-1
Description originale:
n/v
Titre original
N:Vquizlet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document summarizes different drug classes used to treat nausea and vomiting, including their mechanisms of action and clinical use. It discusses:
1. Anticholinergics, antihistamines, cannabinoids, benzodiazepines, dopamine antagonists, glucocorticoids, and substance P/neurokinin-1 antagonists - their mechanisms for treating nausea/vomiting.
2. Considerations for choosing antiemetics based on chemotherapy regimen and preventing acute/delayed nausea and vomiting.
3. Adverse effects, drug interactions, and important clinical pearls regarding use of dopamine antagonists, cannabinoids, and substance P/neurokinin-1
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
58 vues2 pagesCH 28 Nausea/Vomiting
Transféré par
kandeeThis document summarizes different drug classes used to treat nausea and vomiting, including their mechanisms of action and clinical use. It discusses:
1. Anticholinergics, antihistamines, cannabinoids, benzodiazepines, dopamine antagonists, glucocorticoids, and substance P/neurokinin-1 antagonists - their mechanisms for treating nausea/vomiting.
2. Considerations for choosing antiemetics based on chemotherapy regimen and preventing acute/delayed nausea and vomiting.
3. Adverse effects, drug interactions, and important clinical pearls regarding use of dopamine antagonists, cannabinoids, and substance P/neurokinin-1
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Ch 28 Nausea/Vomiting
Study online at quizlet.com/_6iqw6y
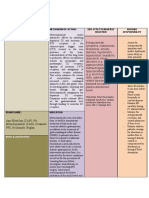
1. Anticholinergics - Motion sickness 9. Cannabinoids efficacy - CINV (2nd line agent)
(Scopolamine) - Block muscarinic receptors (inner ear
10. Classification of Chemo - Low: <10%
Antiemetic Use & to vomiting center)
Drugs and Patients - Low-Moderate: 10-30%
MOA
- Moderate: 30-60%
2. Antihistamines - Motion sickness - Moderate-High: 60-90%
(Dimenhydrinate) - Block histamine type 1 receptors (inner - High >90%
Antiemetic Use & ear to vomiting center)
MOA • Acute Emesis
• Anticipatory Emesis
3. Basic Principles of - Consider emetogenic potential of
• Delayed Emesis
Chemotherapy chemotherapy regimen.
Antiemetic - Give appropriate antiemetics to prevent 11. Dopamine Antagonists - EPS
Therapy nausea and vomiting at least 30 minutes adverse effects - QT prolongation/dysrhythmia
before emetogenic chemotherapy. - Anticholinergic effects
- Schedule antiemetics throughout (hypotension/sedation)
anticipated period of nausea and - Promethazine: respiratory
vomiting risk. depression in children <2 yo,
- Always prescribe PRN antiemetics for extravasation
breakthrough nausea and vomiting
12. Dopamine Antagonists - Phenothiazines: BBW: dementia
between scheduled doses.
Agents (drugs) pt with psych = EPS/QT
- Use antiemetic combinations with non
prolongation
overlapping MOA when possible.
- Butyrophenones (haloperidol)
- Consider patient-specific variables
- Metoclopramide (avoid in
when choosing a regimen
elderly/antipsychotics)
- Re-evaluate patients frequently during
and between chemotherapy courses for 13. Dopamine Antagonists - CINV
efficacy and toxicity of antiemetic Agents efficacy - PONV
regimen. - Other
- Consider nonpharmacologic 14. Dopamine Antagonists - IM preferred
interventions, especially in patients with clinical pearls - SC contraindicated
anticipatory nausea and vomiting. (Promethazine) - IV through large bore <25
4. Benzodiazepines - unknown mg/min
(Lorazepam) - Unknown: maybe activate GABA 15. Dopamine Antagonists - Chemotherapy, postoperative,
Antiemetic Use & leading (Prochlorperazine) general
MOA to inhibition of pathways Antiemetic Use & MOA - Block dopamine 2 receptors in
5. Cannabanoids - Chemotherapy the CTZ
(Dronabinol) - Unknown: maybe activate cannabinoid 16. Glucocorticoids - Chemotherapy
Antiemetic Use & receptors in the vomiting center (Dexamethasone) - Unknown: maybe prostaglandin
MOA Antiemetic Use & MOA synthesis
6. Cannabinoids - Temporal disintegration 17. Motion Sickness tx - Most Effective: scopolamine (2-
adverse effects - Dissociation 4 hr to see effects) patch = less
- Depersonalization anticholinergic effects
- Dysphoria - Antihistamines: dimenhydrinate,
- Hypotension cyclizine
- Sedation/drowsiness
18. Nausea/Vomiting drugs - Serotonin Antagonists
7. Cannabinoids - Dronabinol - Glucocorticoids
Agents (drugs) - Nabilone - Substance P/Neurokinin-1
8. Cannabinoids - contraindicated in patents with psych Antagonists
clinical pearls disorders - Dopamine Antagonists
- caution in CV disorders - Cannabanoids
- Abuse potential - Anticholinergics
- Antihistamines
- Benzodiazepines
19. Pregnancy and - 1st line: Nonpharmacologic 27. Substance P/Neurokinin-1 - Chemotherapy
Nausea/Vomiting therapy *avoid iron Antagonists (Aprepitant ) - Block substance
- 1st line pharmacologic: Antiemetic Use & MOA P/Neurokinin 1 receptors in
Doxylamine + Vitamine B (↓ by the brain
70%, safe on fetus)
28. Substance P/Neurokinin - fatigue
- 2nd line: Prochlorperazine,
Inhibitors adverse effects - asthenia
metoclopramide, ondansetron
- hiccups
20. Pregnancy and - Vitamin B6 = pyridoxine - diarrhea
Nausea/Vomiting extra - Delayed release combo = - mild transaminitis
info diclegis - drug interactions (inhibits
- Methylprednisolone is last 3A4 + metabolized by 3A4)
resort: risk of cleft lip/palate if
29. Substance P/Neurokinin - aprepitant
before 10 weeks
Inhibitors Agents (drugs) - fosaprepitant → aprepitant
21. Prevention of ACUTE and - High: 5-HT3 + DEX + NK1 + (prodrug)
Delayed N/V OLZ - rolapitant
- Moderate: 5-HT3 + DEX - netupitant
- Low: 5-HT3 or DEX
30. Substance P/Neurokinin - Fos/Aprepitant: effective
- Minimal: none
Inhibitors clinical pearls against delayed and acute
N/V
5-HT3: serotonin receptor
- Fosaprepitant: only IV to
antagonist
replace 1st dose of 3 does
DEX: dexamethasone
regimen aprepitant
NK1: neurokinin receptor
- Netupitant: combo product
antagonist
(effective for delayed N/V)
OZL: olanzapine
31. Substance P/Neurokinin - CINV: moderate efficacy
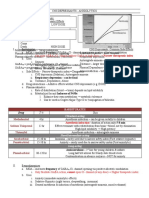
22. Serotonin 5HT-3 - Headache, dizziness, diarrhea
Inhibitors Efficacy (combo with glucocorticoids
Receptor Antagonists - Ondansetron: QT prolongation
and 5HT antagonist)
Adverse Effects - Dolasetron: fatal arrhythmia
- PONV
(IV @ high dose)
23. Serotonin 5HT-3 - Ondansetron
Receptor Antagonists - Granistron
Agents (drugs) - Palonosetron
- Dolasetron
24. Serotonin 5HT-3 - Palosetron: effective against
Receptor Antagonists delayed and acute N/V
Clinical Pearls - Zofran better at tx anti
vomiting vs tx anti nausea
25. Serotonin 5HT-3 - Pregnancy
Receptor Antagonists - Viral gastritis
Efficay: High - Cisplatin/other emetic chemo
agents (efficacy increased with
glucocorticoids)
- Radiation therapy
- Anesthesia
26. Serotonin Antagonists - Chemotherapy, postoperative,
(Ondansetron) general
Antiemetic Use & MOA - Block 5HT receptors in vagal
afferent and CTZ
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ADocument4 pagesAkandee100% (3)
- ADocument4 pagesAkandee100% (3)
- Med Notes Pocket Drug Guide PDFDocument208 pagesMed Notes Pocket Drug Guide PDFIdalís DmgzPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiemetic Drug - PresentationDocument14 pagesAntiemetic Drug - PresentationYue Chen100% (1)
- Antiemetic Prophylaxis For CINV NEJM 2016Document12 pagesAntiemetic Prophylaxis For CINV NEJM 2016tcd_usaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: TramadolDocument5 pagesDrug Study: TramadolOmyl-Khayr M. SulogPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesI. Drug Study: Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Considerationscyn yana0723Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anti EmesisDocument16 pagesAnti EmesisTalitha AmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Abuse & DependenceDocument3 pagesDrug Abuse & DependenceJustin HulinPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyZia CaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyZia CaldozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Managing Hiccups in A Cancer PatientDocument3 pagesApproach To Managing Hiccups in A Cancer Patientadri20121989Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anti DepressantDocument6 pagesAnti Depressantyahyaahmed152000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisPas encore d'évaluation
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyDocument8 pagesMetaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyFrauline GagaracruzPas encore d'évaluation
- TramadolDocument2 pagesTramadoldwightciderPas encore d'évaluation
- LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesLevetiracetamGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- CNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsDocument4 pagesCNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsJustin HulinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument3 pagesCholinergic Antagonistszkhan260Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metocloprramide HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesMetocloprramide HydrochlorideBeatrizz P GellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Histamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCDocument57 pagesHistamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCFaisal 'arifPas encore d'évaluation
- Adiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Document5 pagesAdiel Joy P. Calsa Drug Study March 9, 2022Adiel CalsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Document5 pagesTramadol, Paracetamol, Calmoseptine, B12Denise EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia PharmacologyDocument12 pagesAnesthesia PharmacologyMagy SnowPas encore d'évaluation
- MeclizineDocument2 pagesMeclizineGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- PDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateDocument3 pagesPDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateCrishelPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Midazozalam Drug StudyDocument3 pages7 Midazozalam Drug Studyshadow gonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs W/ Important Action On Smooth Muscle (Autacoids)Document3 pagesDrugs W/ Important Action On Smooth Muscle (Autacoids)Liezel Dejumo Bartolata100% (1)
- Drug Study 2Document37 pagesDrug Study 2Keir Mrls ForcadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study 2Document38 pagesDrug Study 2Keir Mrls Forcadilla100% (1)
- Drug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingDocument1 pageDrug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingRoland YustePas encore d'évaluation
- Antipsychotic Drugs - Pharmacology - An Illustrated ReviewDocument5 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs - Pharmacology - An Illustrated ReviewDragutin PetrićPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCNS Drug StudyNicole PajaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugstudy Liver CirrhosisDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Liver CirrhosisBunnie AlphaPas encore d'évaluation
- Garate Aubreydrug Studyns6 01 21 23Document6 pagesGarate Aubreydrug Studyns6 01 21 23AUBREY GARATEPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat Presentation ProvidersDocument13 pagesMat Presentation Providersapi-649066372Pas encore d'évaluation
- TramadolDocument3 pagesTramadolKaren Viviene Aberilla CincoPas encore d'évaluation
- AntiemeticsDocument33 pagesAntiemeticsSaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Opioid-BenzosTapering FlowchartDocument1 pageOpioid-BenzosTapering FlowchartjuanchibarberoismPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7 Course TaskDocument13 pagesWeek 7 Course TaskRachelle CambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study of AminoglycosidesDocument4 pagesDrug Study of AminoglycosidesJessica GlitterPas encore d'évaluation
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanis MOF Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanis MOF Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaPas encore d'évaluation
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneAya EssamriPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabije, Arvie Jayselle P. Ncenhl07: Drug Data Drug Action Nursing InterventionsDocument3 pagesTabije, Arvie Jayselle P. Ncenhl07: Drug Data Drug Action Nursing InterventionsJaysellePuguonTabijePas encore d'évaluation
- ParacetamolDocument3 pagesParacetamolTRISHA NERIPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG NAME DepressionDocument3 pagesDRUG NAME DepressionLord Allen B. GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study AntipsychoticDocument9 pagesDrug Study AntipsychoticAMAL ALI HASSANPas encore d'évaluation
- Forcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyDocument12 pagesForcadilla Medsurg Drug StudyKeir Mrls ForcadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychopharma 1Document7 pagesPsychopharma 1Mitchee Zialcita100% (1)
- TramadolDocument2 pagesTramadolAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganPas encore d'évaluation
- PharmaDocument20 pagesPharmaMary Roan RonatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Forcadilla - Drug Study orDocument31 pagesForcadilla - Drug Study orKeir Mrls ForcadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study of OpioidDocument3 pagesDrug Study of OpioidGerrahPas encore d'évaluation
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideJack SolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaPas encore d'évaluation
- ERDrug Study DimayugaDocument25 pagesERDrug Study DimayugaSophia DimayugaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyAbigail Basco100% (3)
- Insomnia PDFDocument2 pagesInsomnia PDFkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- EKGquizlet PDFDocument9 pagesEKGquizlet PDFkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- HTNDocument3 pagesHTNkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- GERDDocument3 pagesGERDkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 38 HeadacheDocument3 pagesCH 38 HeadachekandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch41Geeaiedaie Di de (Gad)Document2 pagesCh41Geeaiedaie Di de (Gad)kandeePas encore d'évaluation
- NeuroDocument48 pagesNeurokandeePas encore d'évaluation
- CPRDocument2 pagesCPRkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4Document3 pagesCH 4kandeePas encore d'évaluation
- CH9 BatesDocument4 pagesCH9 BateskandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Steroids Quiz LetDocument1 pageSteroids Quiz LetkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- NeuroDocument48 pagesNeurokandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Steroids Quiz LetDocument1 pageSteroids Quiz LetkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- HyperlipidemiaQuizlet PDFDocument2 pagesHyperlipidemiaQuizlet PDFkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Bates CH 17 NeuroDocument11 pagesBates CH 17 NeurokandeePas encore d'évaluation
- WeeklyCalender PDFDocument2 pagesWeeklyCalender PDFkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperlipidemia QuizletDocument2 pagesHyperlipidemia QuizletkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Seizures Quiz LetDocument3 pagesSeizures Quiz LetkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Pain Quiz LetDocument5 pagesPain Quiz LetkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- PathoQuizlet PDFDocument15 pagesPathoQuizlet PDFkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- PathoDocument15 pagesPathokandeePas encore d'évaluation
- BBDocument1 pageBBkandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageSunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdaykandeePas encore d'évaluation
- DM NotesDocument5 pagesDM NoteskandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 19 Final NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 19 Final NoteskandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 23 Final NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 23 Final NoteskandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Mascc Antiemetic Guidelines English v.1.2.1Document55 pagesMascc Antiemetic Guidelines English v.1.2.1cricriPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerpointDocument20 pagesPowerpointJoel MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Nausea and Vomiting: Key ConceptsDocument35 pagesNausea and Vomiting: Key ConceptsMila ErnilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacological Mechanisms of 5-HT3 and Tachykinin NK1 Receptor Antagonism ToDocument7 pagesPharmacological Mechanisms of 5-HT3 and Tachykinin NK1 Receptor Antagonism TocricriPas encore d'évaluation
- ASCO Anti Emetics in OncologyDocument18 pagesASCO Anti Emetics in OncologyUswatun KhasanahPas encore d'évaluation
- CINV Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesCINV Guidelines PDFagilPas encore d'évaluation
- An Approach To Evaluating Drug-Nutrient InteractionsDocument12 pagesAn Approach To Evaluating Drug-Nutrient InteractionsEleonora ComucciPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiemetic Medications: Agents, Current Research, and Future DirectionsDocument8 pagesAntiemetic Medications: Agents, Current Research, and Future DirectionsNusieba IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence-Based Prevention of CINV: What's New in ASCO Guidelines?Document2 pagesEvidence-Based Prevention of CINV: What's New in ASCO Guidelines?robyalfPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Consensus Guidelines For The Management of PonvDocument29 pages2014 Consensus Guidelines For The Management of PonvHumaira Azmi100% (1)
- NCCN Antiemesis Guideline 2018 v3 PDFDocument68 pagesNCCN Antiemesis Guideline 2018 v3 PDFholdonpainendsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacotherapy of CancerDocument166 pagesPharmacotherapy of Canceryeni62100% (1)
- Government of Canada Report On Emend (Aprepitant)Document6 pagesGovernment of Canada Report On Emend (Aprepitant)jennabushPas encore d'évaluation
- Aprepitant - FosaprepitantDocument11 pagesAprepitant - Fosaprepitantfefy74Pas encore d'évaluation
- 13 OncologyDocument30 pages13 Oncologyandirio7486Pas encore d'évaluation
- Guidline Mual Muntah Kemotrapi PDFDocument10 pagesGuidline Mual Muntah Kemotrapi PDFTyas TyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiemetic DrugsDocument8 pagesAntiemetic DrugsAyesha LiaqatPas encore d'évaluation
- AntiemeticsDocument37 pagesAntiemeticsAriel OlshevskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aprepitant - 125mg CapsuleDocument9 pagesAprepitant - 125mg CapsuleMd. Abdur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Audit PresentationDocument68 pagesNausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care Audit PresentationGonzalo MaldonadoPas encore d'évaluation