Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Human Respiration Model Analysis
Transféré par
khairul afzal mokhtarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Human Respiration Model Analysis
Transféré par
khairul afzal mokhtarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SOLAF BIOLOGI SPM RESPIRASI
SOALAN STRUKTUR RESPIRASI
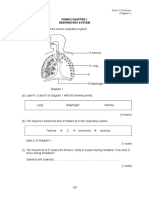
1 Diagram1.1 represents a model of the human lungs in the respiratory mechanism.
Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan model yang mewakili peparu manusia dalam mekanisma
pernafasan.
Diagram 1.1/ Rajah 1.1
(a) Based on the model of the lungs in Diagram , what are the equivalent structures
F to the glass tube and the bell jar in the human respiratory system?
R Berdasarkan model peparu dalam Rajah , apakah struktur setara antara salur
kaca dan serkup kaca dalam sistem pernafasan manusia?
Glass tube/ salur kaca:
……………………………………………………………………………………....................
Bell jar/ serkup kaca
……………………………………………………………………………………….................
[2 m]
(b)(i) The thin rubber sheet represents the diaphragm in the human respiratory system.
F What is the function of the thin rubber sheet in the model of the lungs?
R Kepingan getah nipis mewakili diaphragm dalam sistem pernafasan manusia.
Apakah fungsi kepingan getah nipis dalam model peparu?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 m]
(ii) The balloons represent the human lungs.
A Explain one characteristic of the balloons which is similar to the human lungs.
R Belon-belon mewakili peparu manusia.
Jelaskan satu ciri belon yang menyamai peparu manusia.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2m]
(c)(i) The strings in the model of the lungs is pulled down.
JPN PERAK Page 1
SOLAF BIOLOGI SPM RESPIRASI
F Draw the changes to the thin rubber sheet and the balloons in Diagram 4.2 below.
S
Tali dalam model peparu ditarik ke bawah.
Lukiskan perubahan kepada kepingan getah nipis dan belon-belon dalam Rajah 4.2
Diagram 4.2 / Rajah 4.2
[1 m]
(ii) Observe your drawing in (c)(i).
F Explain the relationship between the changes in the model of the lungs you have
T drawn and the real human respiratory system.
Perhatikan lukisan anda di (c)(i).
Huraikan perkaitan antara perubahan-perubahan dalam model peparu yang anda
lukis dengan sistem pernafasan manusia yang sebenarnya.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………..……………………………………………
[3 m]
(d)(i) The percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide gases in inspired and expired air is
A Determined by using J-tube.Why is the end of the J-tube dipped in potassium
T hydroxide solution and then followed by potassium pyrogallol solution.
Peratus oksigen dan karbon dioksida dalam udara sedutan dan udara hembusan
ditentukan menggunakan salur-J. Mengapakah hujung salur-J dibenam dalam
larutan kalium hidroksida dan kemudian dibenam pula dalam larutan kalium
piragalol.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[1 m]
(ii) Table 4.3 shows the result of a study on the content of inspired and expired air.
AN Jadual 4.3 menunjukkan keputusan kajian ke atas kandungan udara sedutan dan
R udara hembusan.
Type of gas Inspired gas/% Expired gas / %
Jenis gas Udara sedutan / % Udara hembusan/ %
JPN PERAK Page 2
SOLAF BIOLOGI SPM RESPIRASI
Oxygen 21.0 16.0
Oksigen
Carbon dioxide 0.04 4.0
Karbon dioksida
Nitrogen gas 78.0 78.0
Gas nitrogen
Water vapour Vary Saturated
Wap air Berubah-ubah Tepu
Table 3.3/ Jadual 4.3
Explain why there is an increase in percentage of carbon dioxide in the expired air.
Jelaskan mengapa terdapat pertambahan peratusan karbon dioksida dalam udara
hembusan?
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
.……………………………………………………………………………………………........
[2 m]
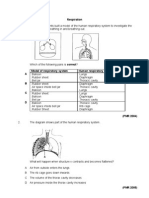
2 Diagram shows human respiratory system.
Rajah menunjukkan sistem respirasi manusia
(a) Label the structure P, Q and R.
P Labelkan struktur P,Q dan R
R [3m]
(b)(i) What happen to structure labelled Q and R during when we inhale air?
P Apakah yang berlaku kepada struktur Q dan R apabila kita menarik nafas?
R
Q : .................................................................................................................................
R : .................................................................................................................................
[2m]
(ii) What is the effect of the activity in (b)(i) to the thoracic cavity?
F Apakah kesan ke atas rongga toraks apabila keadaan di (b)(i) berlaku?
R
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………….........
.......................................................................................................................................
JPN PERAK Page 3
SOLAF BIOLOGI SPM RESPIRASI
[2 m]
(c)(i) Inhalation air enter S. Name S.
P Udara yang disedut berkumpul di S.
T Namakan S.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[1m]
(ii) Draw the arrow to show direction of oxygen and carbon dioxide moving during gases
P exchange.
R Lukiskan pada rajah di bawah arah pergerakan oksigen dan karbon dioksida
semasa proses pertukaran gas.
[1m]
(iii) State one characteristic of S to enable the process of gases exchange take place
P efficiently.
R Berikan SATU ciri struktur S yang membolehkan gas melaluinya
dengan cekap
.......................................................................................................................................
[1m]
(d) Explain how oxygen in the blood transport to all body cell.
F Terangkan bagaimana oksigen yang berada di dalam darah diangkut ke semua sel
T tubuh.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[3m]
3 Diagram shows concentration of substance Y in student’s blood during and after
AN vigorous activity
Rajah menunjukkan kepekatan bahan Y dalam darah seorang pelajar semasa dan
selepas melakukan senaman cergas.
JPN PERAK Page 4
SOLAF BIOLOGI SPM RESPIRASI
(a)(i) Name substance Y.
P Namakan bahan Y
T
…….…………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1m]
(ii) Name type of respiration process which caused accumulation of substance Y in the
P muscle cells of the student.
S Nyatakan jenis respirasi yang menyebabkan bahan Y terkumpul di dalam sel-sel
otot pelajar tersebut.
….……………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1m]
(iii) Explain how substance Y produce from the process you named in (a)(ii).
F Terangkan bagaimana bahan Y terhasil daripada jenis respirasi yang anda
T nyatakan di (a)(ii).
..………………………………………………………………………………………………..
..………………………………………………………………………………………………
..………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2m]
(b) Base on the graph above, explain what happen to oxygen intake along time taken P
ST and Q.
S Berdasarkan graf pada Rajah 3, terangkan apa yang berlaku kepada pengambilan
oksigen disepanjang tempoh P dan Q ?
P :..……………………………………………………………………………………………...
JPN PERAK Page 5
SOLAF BIOLOGI SPM RESPIRASI
..……………………………………………………………………………………………….
..……………………………………………………………………………………………….
[2m]
Q: ...………………………………………………………………………………………….…
…..……………………………………………………………………………………………..
…..……………………………………………………………………………………………..
[2m]
(c)(i) The process you named in (a)(ii) also can take place in yeast.
F State one difference between both process
T Respirasi yang anda nyatakan dalam (a)(ii) juga berlaku dalam yis.
Berikan satu perbezaan antara kedua-dua proses.
…..……………………………………………………………………………………………..
……..……………………………………………………………………………………………
[1m]
(ii) Yeast needed in food industry. Explain the statement.
ST Yis diperlukan dalam industri makanan. Terangkan pernyataan tersebut.
S
…..……………………………………………………………………………………………..
……..……………………………………………………………………………………………
…..……………………………………………………………………………………………..
……..……………………………………………………………………………………………
[3m]
JPN PERAK Page 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Force and Pressure Concepts ExplainedDocument4 pagesForce and Pressure Concepts ExplainedpinocchioPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Kimia K2 Trial SPM MRSM 2019 PDFDocument18 pagesSkema Kimia K2 Trial SPM MRSM 2019 PDFFarhalina Nazira0% (1)
- Analisis Item Bio SPM 2003-2019Document4 pagesAnalisis Item Bio SPM 2003-2019Caryn YeapPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon Compounds (Good)Document6 pagesForm 5 Chapter 2 Carbon Compounds (Good)Everest Lim Yong KeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4Document11 pagesSkema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4jeglila50% (4)
- Topical Test Chapter 4 Periodic Table of ElementsDocument3 pagesTopical Test Chapter 4 Periodic Table of ElementsIVAN TIONG WEI JUN MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work and Activities for Science Form 2 Biodiversity and EcosystemDocument20 pagesScheme of Work and Activities for Science Form 2 Biodiversity and EcosystemBestah Joewellster Teo100% (1)
- Bahagian BDocument6 pagesBahagian BNik ZakiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Soalan SPM Links (12!5!6)Document43 pagesBank Soalan SPM Links (12!5!6)newdirextion50% (2)
- SPM EST TRIAL 3 1 Soalan Kertas 1Document6 pagesSPM EST TRIAL 3 1 Soalan Kertas 1Fhatin Nor Nashlin100% (1)
- 7 Transfer of Electrons at A DistanceDocument15 pages7 Transfer of Electrons at A DistancenamikPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Perfect Score Module Form 5Document48 pagesPhysics Perfect Score Module Form 5jemwesleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Theme: Waves, Light and Optics Chapter 5: WavesDocument17 pagesTheme: Waves, Light and Optics Chapter 5: WavesJacqueline Lim100% (1)
- Tanjung Rhu NotesDocument5 pagesTanjung Rhu NotesEfa Natrah NordinPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry: Course Code: SKO 3033 Semester 2 Sessions 2020/2021 Id Number and NameDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Course Code: SKO 3033 Semester 2 Sessions 2020/2021 Id Number and NameSITI HUMAIRAH BINTI HAMZAHPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK CONVENT BUKIT NANAS PHYSICS YEARLY LESSON PLANDocument12 pagesSMK CONVENT BUKIT NANAS PHYSICS YEARLY LESSON PLANSazlinAinaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Chemistry Answering Technique PDFDocument12 pagesSPM Chemistry Answering Technique PDFAriss LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Document16 pagesTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1ST Mid Term Form 4 2020 (Answer)Document4 pages1ST Mid Term Form 4 2020 (Answer)Nurul SalwanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kertas Sebenar 2012 Bahasa Inggeris 1119/1Document3 pagesKertas Sebenar 2012 Bahasa Inggeris 1119/1Pete Wang100% (1)
- SPM Biology Perlis 2010Document0 pageSPM Biology Perlis 2010Clement TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Jawapan Kimia p2Document12 pagesSkema Jawapan Kimia p2HenrySeow50% (8)
- (Spmsoalan) Soalan KBAT Bio 8Document8 pages(Spmsoalan) Soalan KBAT Bio 8Felicia Ling0% (1)
- Modul Cemerlang Kimia JPNDocument86 pagesModul Cemerlang Kimia JPNA9951983% (6)
- Fizik K2Document29 pagesFizik K2qq235100% (2)
- Biology Paper 2 & 3 (SPM 2009)Document10 pagesBiology Paper 2 & 3 (SPM 2009)Kar Wah0% (2)
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistryyoga nayagi punichelvanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul TermokimiaDocument27 pagesModul Termokimianoorkeyo100% (1)
- SPM Kimia Tingkatan 4,5 - Paper3 - 20170420112820Document4 pagesSPM Kimia Tingkatan 4,5 - Paper3 - 20170420112820nurzatilPas encore d'évaluation
- ModulDocument39 pagesModulThanabalan MunuswamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Module & More Kimia TG 4Document203 pagesModule & More Kimia TG 4Pinky Ong Woan Fei Ong100% (1)
- 2015 PSPM Kedah Fizik2 W AnsDocument32 pages2015 PSPM Kedah Fizik2 W Ansjee2kk90% (10)
- Rajah 1.1 Dan Rajah 1.2 Menunjukkan Satu Eksperimen Untuk Mengkaji Kekonduksian Elektrik Bagi Plumbum (II) BromidaDocument5 pagesRajah 1.1 Dan Rajah 1.2 Menunjukkan Satu Eksperimen Untuk Mengkaji Kekonduksian Elektrik Bagi Plumbum (II) BromidaMohd Aswad Abd RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocument12 pagesChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiEmily VinciPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Melaka Biologi Kertas 2Document17 pages2016 Melaka Biologi Kertas 2Hemanathan HarikrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFDocument22 pages03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFSitiRohaizaMatYusoffPas encore d'évaluation
- Skema Biologi k3 SPM 2010Document11 pagesSkema Biologi k3 SPM 2010fatimahmni100% (1)
- Addmath Exercise Form 4Document2 pagesAddmath Exercise Form 4Ainun SyakirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Chapter 3 EssayDocument8 pagesForm 4 Chapter 3 EssaykiongocPas encore d'évaluation
- F2 Science Chapter Summary Form 2Document12 pagesF2 Science Chapter Summary Form 2Cerdik CekapPas encore d'évaluation
- Peraturan Pemarkahan Percubaan SBP Pt3 2015 - SainsDocument13 pagesPeraturan Pemarkahan Percubaan SBP Pt3 2015 - Sainsfira100% (3)
- Latihan Linear MotionDocument3 pagesLatihan Linear MotionLily Suhany MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- WAJA CHP.2 Carbon Compounds 2Document35 pagesWAJA CHP.2 Carbon Compounds 2Safwan MazlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Information: 1.0 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon Completion of This Course, Students Should BeDocument2 pagesCourse Information: 1.0 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon Completion of This Course, Students Should BeaisyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 P2Document20 pagesChapter 7 P2siewkiemPas encore d'évaluation
- Elasticity QuizDocument5 pagesElasticity QuizTuck Diery0% (1)
- SPM Form 4 Notes - Introduction to ChemistryDocument1 pageSPM Form 4 Notes - Introduction to ChemistryMimie Yasmin KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- RPH Science ExperimentDocument5 pagesRPH Science ExperimentNorzilah MazaharPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Bio P2 SMART 2018Document179 pagesSeminar Bio P2 SMART 2018zulkarnain100% (1)
- SVM Semester 1 and 2 Scheme of WorkDocument24 pagesSVM Semester 1 and 2 Scheme of WorkFatin Farhana100% (1)
- LESSON PLAN YEAR 1 (Minggu Transisi)Document24 pagesLESSON PLAN YEAR 1 (Minggu Transisi)maxallen890Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document32 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (3)
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Document22 pagesSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Document6 pagesIT Chem F5 Topical Test 5 (BL)Titim MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector SPM 2003 - 2007Document4 pagesVector SPM 2003 - 2007Rosmizar AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1naza977590% (29)
- Checkpoint 1Document5 pagesCheckpoint 1Eunice Xiiao WennPas encore d'évaluation
- T3 Bab 1Document8 pagesT3 Bab 1myraePas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 Chapter 1 (1) FarhanaDocument5 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 (1) FarhanaParamasivam Kandasamy100% (2)
- Form 2 Chapter 1Document7 pagesForm 2 Chapter 1ziePas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophy of Disciple Making PaperDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of Disciple Making Paperapi-665038631Pas encore d'évaluation
- Frozen DessertDocument3 pagesFrozen DessertcsqueilPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study On Maruti 800Document4 pagesCase Study On Maruti 800Nizar MesaniPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC of MaggiDocument19 pagesPLC of Maggikrati agarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Hong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3ADocument69 pagesHong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3AMARENG BERNABEPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 2 Curriculum GuideDocument19 pagesMath 2 Curriculum GuideMichelle Villanueva Jalando-onPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat IQ TestDocument3 pagesCat IQ TestBrendan Bowen100% (1)
- 2009 GCSE PE SpecificationsDocument225 pages2009 GCSE PE SpecificationsAdstasticPas encore d'évaluation
- LP IV Lab Zdvzmanual Sem II fbsccAY 2019-20z 20-ConvxvzzertedDocument96 pagesLP IV Lab Zdvzmanual Sem II fbsccAY 2019-20z 20-ConvxvzzertedVikas GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Absolute Value - WikipediaDocument10 pagesAbsolute Value - WikipediaVenu GopalPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are Your Observations or Generalizations On How Text/ and or Images Are Presented?Document2 pagesWhat Are Your Observations or Generalizations On How Text/ and or Images Are Presented?Darlene PanisaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4900 DatasheetDocument2 pages4900 DatasheetMakam Raghu100% (1)
- EA Flora 1Document3 pagesEA Flora 1A. MagnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mohammad R. Mestarihi: About Me ObjectiveDocument1 pageMohammad R. Mestarihi: About Me ObjectiveMhmd MsttPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11Document90 pages2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11eko sulistyo75% (4)
- Optitex Com Products 2d and 3d Cad SoftwareDocument12 pagesOptitex Com Products 2d and 3d Cad SoftwareFaathir Reza AvicenaPas encore d'évaluation
- My ResumeDocument4 pagesMy Resumeapi-216740002Pas encore d'évaluation
- NetworkingDocument1 pageNetworkingSherly YuvitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Manual: Semester: - ViiiDocument15 pagesLaboratory Manual: Semester: - Viiirsingh1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 API 653 Exam Mar 2015 MemoryDocument12 pages1 API 653 Exam Mar 2015 MemorymajidPas encore d'évaluation
- 60Hz Axial-Fan Centrifugal-Fan AC EN (2009) PDFDocument136 pages60Hz Axial-Fan Centrifugal-Fan AC EN (2009) PDFRodrigo GonçalvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer MethodsDocument91 pagesLinear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer MethodsFaith Reyna TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Revisited: Understanding Key Concepts and Applying Analytical SkillsDocument31 pagesLiterature Revisited: Understanding Key Concepts and Applying Analytical SkillsMuhammad Furqan Aslam Awan100% (2)
- Automated Crime Reporting SystemDocument101 pagesAutomated Crime Reporting SystemDeepak Kumar60% (10)
- Laser Engrave Co2 System BJ-1390Document5 pagesLaser Engrave Co2 System BJ-1390Sasa TodorovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Utilization of Wood WasteDocument14 pagesUtilization of Wood WasteSalman ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Penilaian Risiko Kerja Menggunakan Metode Hirarc Di Pt. Sinar Laut Indah Natar Lampung SelatanDocument7 pagesPenilaian Risiko Kerja Menggunakan Metode Hirarc Di Pt. Sinar Laut Indah Natar Lampung SelatanIndun InsiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Compabloc Manual NewestDocument36 pagesCompabloc Manual NewestAnonymous nw5AXJqjdPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Starter WBDocument88 pages1 Starter WBHYOPas encore d'évaluation
- EVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFDocument80 pagesEVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFgibonulPas encore d'évaluation