Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Child or Learner-Centred Approach: Approaches Principles/Characteristics/Views
Transféré par
Syrel SerranoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Child or Learner-Centred Approach: Approaches Principles/Characteristics/Views
Transféré par
Syrel SerranoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
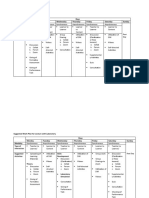
APPROACHES PRINCIPLES/CHARACTERISTICS/VIEWS
Child or Learner- Centred - Learner-centred approach do not employ a single method. This approach emphasizes a variety
Approach of types of method that focuses on what the students are learning, it changes the role of the
teachers from a provider of information to facilitating student learning.
- Learner-Centred teaching focuses on the process of learning.
- Student learning methods include:
o Active learning in which students solve problems, answer questions, formulate questions
of their own, discuss, explain, debate, or brainstorm during class.
o Cooperative learning, in which students work in terms on problems and projects under
conditions that assure both positive independence and individual accountability.
o Inductive teaching and learning, in which students are fist presented with challenges
Subject-Centred Approach - In a subject-centred approach to curriculum, each content area contains its own set of skills
and concepts for mastering the concepts,
- The teacher presents content and skills to students in a logical sequence.
- The focus is on the delivery of the subject content by the teacher for students to acquire.
- Importance is laid on topics or concepts included in the subject around which all the teaching
and learning revolve.
- Textbook is the only source and main source of the teacher
- Word by word, phrase by phrase, the matters are presented before the teacher.
- The content or the subject matter of the textbook is itself a guide to the teachers to divide his or
her methodology.
- Insistence on the students to memorize the facts by repeated reading.
- Questions given at the end of the chapter are to be asked to the students for assessment of
learning.
- The students answer the questions both orally and in written form by occupying from the
textbook.
- They may produce the answers orally and in written form by reproducing the exact content.
Problem-Centred Approach - Problem-centred approach provides a vehicle to achieve goals and objectives identified in the
curriculum
o Evidence from research and international studies suggests that are students are proficient
in procedures but do not have the conceptual understanding to solve problems.
- Problem-based curricula provide a learning environment in which competencies is fostered not
primarily by teaching to impart knowledge but through encouraging an inquisitive style of
learning
o Preliminary discussion in small groups, contextual learning, integration of knowledge and
an emphasis on patient problems, have several cognitive effects on student learning,
these effects are increased retention of knowledge, enhancement of integration of
basics sciences concepts into chemical problems , the development of self-directed
learning skills and the enhancement of students’ intrinsic interest in the subject matter.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 10 Heartmath PracticesDocument52 pages10 Heartmath PracticesPatPas encore d'évaluation
- SPMM 2015 FullDocument1 610 pagesSPMM 2015 FullAnamika Sinha100% (4)
- NCP SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesNCP Schizophreniajoshua canja100% (5)
- Proposal AssignmentDocument24 pagesProposal AssignmentSamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- My Vocabulary BookDocument2 pagesMy Vocabulary BookHanna NannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Approaches, Methods, TechniquesDocument34 pagesTeaching Approaches, Methods, TechniquesJohn Lloyd Generoso100% (1)
- Motivation and The Meaning of WorkDocument4 pagesMotivation and The Meaning of WorkRodrick WilbroadPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Vicarious TraumaDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Vicarious TraumavacantboxPas encore d'évaluation
- Lapproaches To Curriculum Designing: Obenita, Mary Ann Ortizano, Ritchelle Nadela, Dorothy JoyDocument39 pagesLapproaches To Curriculum Designing: Obenita, Mary Ann Ortizano, Ritchelle Nadela, Dorothy JoyDorothy Joy Nadela100% (1)
- Nature of LearningDocument2 pagesNature of LearningFlorens Genoves BagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding the Disciplines of CounselingDocument9 pagesUnderstanding the Disciplines of CounselingMarjorie B. BaskiñasPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Approaches and Methods GuideDocument3 pagesTeaching Approaches and Methods GuideKenneth Delos SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Episode 9 Preparing For Teaching An LearningDocument5 pagesLearning Episode 9 Preparing For Teaching An LearningCrizel Mae EnovisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of 20th and 21st Century EducationDocument9 pagesComparison of 20th and 21st Century EducationHermie RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- FS1 - Learning Episode 9Document7 pagesFS1 - Learning Episode 9DANIELA GALINGANPas encore d'évaluation
- Approaches and Methods of Teaching: Prof. Jovar G. Pantao Faculty, Mindanao State University Fatima, General Santos CityDocument75 pagesApproaches and Methods of Teaching: Prof. Jovar G. Pantao Faculty, Mindanao State University Fatima, General Santos Citykathy lapid100% (1)
- Tpack - FrameworkDocument9 pagesTpack - Frameworkapi-514537755Pas encore d'évaluation
- Methods and Techniques: The K-12 ApproachDocument45 pagesMethods and Techniques: The K-12 Approachlaren100% (1)
- Explaining The Dialogic Processes of Teaching and Learning (Mercer & Howe, 2012)Document10 pagesExplaining The Dialogic Processes of Teaching and Learning (Mercer & Howe, 2012)Claudia Albuccó AriztíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloPas encore d'évaluation
- P Based LearningDocument8 pagesP Based LearningPdianghunPas encore d'évaluation
- Output 1Document3 pagesOutput 1jeanly famat patatagPas encore d'évaluation
- Approaches NotesDocument2 pagesApproaches NotesLaarnie Blessful SucalPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Approaches and MethodsDocument4 pagesDifferent Approaches and Methodsbonifacio gianga jr100% (2)
- EPP W ENTREP-LPDocument7 pagesEPP W ENTREP-LP202100133Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem-Solving vs. Problem-Based Learning - Different But Inter-RelatedDocument2 pagesProblem-Solving vs. Problem-Based Learning - Different But Inter-RelatedMiftah AltintopPas encore d'évaluation
- TEACHING APPROACHES AND METHODSDocument1 pageTEACHING APPROACHES AND METHODSCariza AndaPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Approaches & Methods: Presented By: Kirk John TonidoDocument53 pagesTeaching Approaches & Methods: Presented By: Kirk John Tonidoanalyn100% (2)
- Principles of LCT (SCT)Document4 pagesPrinciples of LCT (SCT)Chaé RiPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Teaching 2 Report 1Document16 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 2 Report 1Michelle AmogPas encore d'évaluation
- FLCT Review Material for Distribution 2024 2Document9 pagesFLCT Review Material for Distribution 2024 2danllyodangelo.sambajonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bpe 114Document3 pagesBpe 114Dawnald Fortin PepitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem-Based Learning: Sri Sundari Medu Fkik UmyDocument25 pagesProblem-Based Learning: Sri Sundari Medu Fkik UmyArio Anindito PPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Centered Design: V. Crafting The CurriculumDocument9 pagesProblem Centered Design: V. Crafting The CurriculumKarole Niña MandapPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Teaching Method: Health Education Methods/StrategiesDocument18 pagesTraditional Teaching Method: Health Education Methods/StrategiesNichole ShainePas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Strategies:-: IntroductionDocument10 pagesInstructional Strategies:-: IntroductionSnehaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - 1.1 and 1.2 - Introduction and Approaches To Learner-Centered Teaching - PANOPIO, LACERNA, PALAYADocument11 pagesModule 1 - 1.1 and 1.2 - Introduction and Approaches To Learner-Centered Teaching - PANOPIO, LACERNA, PALAYAMarlyn Dimatatac PanopioPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Teaching: Different Methods and ApproachesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Teaching: Different Methods and ApproachesFaithful FighterPas encore d'évaluation
- Fs-1-Learning-Episode-4 2Document5 pagesFs-1-Learning-Episode-4 2Lapiz SheilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachiingDocument3 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered TeachiingAnne RaycoPas encore d'évaluation
- K-12 Learner-Centered ApproachDocument14 pagesK-12 Learner-Centered ApproachJemmuel SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Report FlowDocument11 pagesReport FlowMarlyn Dimatatac Panopio100% (1)
- BPS Teacher Rubrics PDFDocument50 pagesBPS Teacher Rubrics PDFFazal NiaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach and MethodDocument2 pagesApproach and MethodShenna Mae GosanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Profed 4 ReviewerDocument7 pagesProfed 4 ReviewerCarl Anthony Miguel AlcazarPas encore d'évaluation
- REVIEWER Profed102 Module1&2Document5 pagesREVIEWER Profed102 Module1&2ROSETHEL PEDROSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Centred InstructionDocument16 pagesLearning Centred Instructioncalvin matePas encore d'évaluation
- Subject/Teacher Centered DesignDocument5 pagesSubject/Teacher Centered DesignDr. Rehmat Shah /AP/TTS/Education/JBDPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Effective Procedures in Teaching Science FinalDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Effective Procedures in Teaching Science FinalJasmine Nicole OsallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Design Curriculum Mapping and AuditDocument5 pagesCurriculum Design Curriculum Mapping and AuditLoreijane LimpiadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity # 1: Donna Joyce R. Magdaong Iii Beed/Block-12Document3 pagesActivity # 1: Donna Joyce R. Magdaong Iii Beed/Block-12Donna Joyce MagdaongPas encore d'évaluation
- Student-centered teaching shifts focus from instructors to active learningDocument6 pagesStudent-centered teaching shifts focus from instructors to active learningJames Tyler BayalanPas encore d'évaluation
- with-Answers-TEACHING PROFESSION - MODULE1Document12 pageswith-Answers-TEACHING PROFESSION - MODULE1Aeron Chester DinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer Sir GlennDocument6 pagesReviewer Sir GlennGenevie ManimtimPas encore d'évaluation
- PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING STRATEGIESDocument41 pagesPROBLEM-BASED LEARNING STRATEGIESahmad nabilPas encore d'évaluation
- Master of Arts in EducationDocument19 pagesMaster of Arts in EducationJohn Lewis SuguitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Language Teaching Methods Course - Docx1Document41 pagesLanguage Teaching Methods Course - Docx1mouminomarmoumin1Pas encore d'évaluation
- College of St. John-Roxas: Online and Modular Home-Based Learning Modalities Overview RationaleDocument10 pagesCollege of St. John-Roxas: Online and Modular Home-Based Learning Modalities Overview RationaleMichael Vincent BarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Mckimmie Ept436 Goals v2Document4 pagesMckimmie Ept436 Goals v2api-661969425Pas encore d'évaluation
- 001 Thoughts and Actions of Teachers 05 12 2020 23 38Document6 pages001 Thoughts and Actions of Teachers 05 12 2020 23 38asmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study GuideDocument2 pagesStudy Guideanthony100% (3)
- Stakeholder Roles in Curriculum DevelopmentDocument6 pagesStakeholder Roles in Curriculum DevelopmentTamayo HelbertPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 AN OVERVIEW OF TASK-BASED LANGUAGE TEACHINGDocument4 pagesChapter 1 AN OVERVIEW OF TASK-BASED LANGUAGE TEACHINGdiemquynh210922Pas encore d'évaluation
- Syukurmanlaia J 23 24 ENGLISFORPHYSICS A RekayasaideDocument4 pagesSyukurmanlaia J 23 24 ENGLISFORPHYSICS A Rekayasaideimam daulayPas encore d'évaluation
- edu542 Lesson 11-16Document2 pagesedu542 Lesson 11-16Jo MomPas encore d'évaluation
- Team A - Discovery-Inquiry Based ApproachDocument32 pagesTeam A - Discovery-Inquiry Based ApproachJemuel LuminariasPas encore d'évaluation
- Approiaches To CurrDocument27 pagesApproiaches To CurrEsmeralda EgePas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument22 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJessie MaldeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Lesson 1 2 3 SocStEd 311Document41 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1 2 3 SocStEd 311Miguel Maribao Aquino Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 25. EFLDocument13 pagesTopic 25. EFLAntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- The Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013Document1 pageThe Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013Syrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- MACOSDocument6 pagesMACOSSyrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Geographical TermsDocument2 pagesGeographical TermsSyrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- History in The Development of Educational MeasurementDocument5 pagesHistory in The Development of Educational MeasurementSyrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Geography: Center of Excellence in Teacher EducaDocument2 pagesHuman Geography: Center of Excellence in Teacher EducaSyrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Terms: Domains of Learning Cognitive Domain (HEAD)Document2 pagesTerms: Domains of Learning Cognitive Domain (HEAD)Syrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Involves: A Is A Particular Method of Doing An, Usually A Method That Practical SkillsDocument10 pagesActivity Involves: A Is A Particular Method of Doing An, Usually A Method That Practical SkillsSyrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- History in The Development of Educational MeasurementDocument4 pagesHistory in The Development of Educational MeasurementSyrel SerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative Report (MatthewP.)Document4 pagesNarrative Report (MatthewP.)Matthew John PalenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Purpose, Problem StatementsDocument4 pagesResearch Purpose, Problem StatementsManish Kohli100% (1)
- Activity Completion Report: Prepared byDocument6 pagesActivity Completion Report: Prepared byBoboy BerlsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher's IPPD for Professional DevelopmentDocument1 pageTeacher's IPPD for Professional DevelopmentAngel Nicolin SuymanPas encore d'évaluation
- Position and Competency Profile: Teacher IDocument13 pagesPosition and Competency Profile: Teacher Iangge28Pas encore d'évaluation
- MGT162 (Chapter 6 - Leading)Document23 pagesMGT162 (Chapter 6 - Leading)Nur Syahidah50% (4)
- Effects OF Test Anxiety, Distance Education ON General Anxiety AND Life Satisfaction OF University StudentsDocument11 pagesEffects OF Test Anxiety, Distance Education ON General Anxiety AND Life Satisfaction OF University StudentsJorge Gamboa VelasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Managerial Decision-MakingDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Managerial Decision-Makingp.sankaranarayananPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Domains of Teacher CompetenciesDocument3 pages7 Domains of Teacher CompetenciesNelson Deangkinay100% (1)
- Problems of Psychology in The 21st Century, Vol. 2, 2012Document83 pagesProblems of Psychology in The 21st Century, Vol. 2, 2012Scientia Socialis, Ltd.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Executive Expression Function PDF WritingDocument2 pagesExecutive Expression Function PDF WritingJosePas encore d'évaluation
- ELICIT (Access Prior Knowledge) Materials: S3ES - IV-g-h-4-5Document2 pagesELICIT (Access Prior Knowledge) Materials: S3ES - IV-g-h-4-5Richie MacasartePas encore d'évaluation
- Career Development Plan For Shs Students (Sy 2019 - 2020) General ObjectivesDocument3 pagesCareer Development Plan For Shs Students (Sy 2019 - 2020) General ObjectivesBeryl AbucejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Personality Report by IMXDocument22 pagesSample Personality Report by IMXJohn Elbert FalsisPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding The Self 1Document18 pagesUnderstanding The Self 1DANE PIAMONTEPas encore d'évaluation
- Students' Motivation in Learning English: Neng Aprilia Purmama, Neng Sri Rahayu, Rasi YugafiatiDocument6 pagesStudents' Motivation in Learning English: Neng Aprilia Purmama, Neng Sri Rahayu, Rasi Yugafiatiadinda febiPas encore d'évaluation
- DMC Language LearningDocument12 pagesDMC Language LearningCari GonzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggested Weekly Work Plan For Lecture and Lab1Document2 pagesSuggested Weekly Work Plan For Lecture and Lab1Alexie Carvajal100% (1)
- Edtpa Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan Templateapi-338289862Pas encore d'évaluation