Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Heart Pharmacy
Transféré par
Libido Moka0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues1 pageAll about the heart
Titre original
The heart pharmacy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAll about the heart
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues1 pageThe Heart Pharmacy
Transféré par
Libido MokaAll about the heart
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
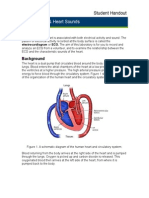
Cardiovascular Drugs Based on stage/onset:
1. Normal - <120/80
2. Prehypertensive – 120-135/80-89
3. Stage I – 140-159/90-99
4. Stage II - >160/100
Special Cases of Hypertension
1. Hypertension in Pregnancy
Basics of the Cardiac Cycle:
a. Gestational – 140/90 after 20 weeks
Systole – period of time when the heart
age of gestation
muscle is contracting
b. Preeclampsia – characterized by
Preload – at the end of atrial systole, the
proteinuria and severe signs and
ventricles will expand to accommodate the
symptoms
incoming volume of blood from the atrium
c. Eclampsia – characterized by
Afterload – the amount of resistance the generalized tonic-clonic seizures
heart must overcome to open the aortic 2. Severe Hypertension
valve and push the blood volume out into a. Hypertensive emergency
the systemic circulation. Characteristics:
Diastole – period of time when the heart i. 180/120 BP
muscle is relaxed and the chambers fill with ii. Presence of end organ
blood damage
b. Hypertensive urgency
Determinants of Blood Pressure Characteristics:
1. Cardiac Output (ml/minute) i. 160/100 BP
Factors that affect: ii. No end organ damage
a. Heart rate (bpm) – directly
proportional
b. Stroke Volume (ml/beat)
Factors that affect:
i. Inotropy – directly
proportional
ii. Preload – directly
proportional
Factors that affect preload:
1. Blood volume
2. Venous tone
2. Total peripheral resistance
Factors that affect:
a. Arterial tone
Hypertension
The condition described as repeated, reproducible
elevation of blood pressure.
Classifications
Based on Etiology:
1. Primary – no discernable cause
2. Secondary – with specific etiology
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Anatomy MCQDocument10 pagesAnatomy MCQnistaraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart As A PumpDocument25 pagesThe Heart As A Pumpمحمد القدوميPas encore d'évaluation
- 02page SageDocument140 pages02page SageSergio MontesPas encore d'évaluation
- WFTF Chamber Quantification Summary Doc Final July 18Document18 pagesWFTF Chamber Quantification Summary Doc Final July 18Saloum Muhammed IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulation of Heart Rate, Stroke Volume, Cardiac Output, Blood FlowDocument20 pagesRegulation of Heart Rate, Stroke Volume, Cardiac Output, Blood FlowShveta MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Echo Pocket 2014Document18 pagesEcho Pocket 2014abbouamine100% (2)
- Cardiogenic Shock NCLEX Review QuizDocument6 pagesCardiogenic Shock NCLEX Review QuizRegie Marie EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- DCRV PPT NowDocument22 pagesDCRV PPT NowKarthik RamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure) FINALDocument6 pagesHeart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure) FINALKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isPas encore d'évaluation
- CVS PhysiologyDocument43 pagesCVS Physiologyapi-3705050100% (1)
- American Muscle & Fitness Kick Boxing Aerobics ManualDocument37 pagesAmerican Muscle & Fitness Kick Boxing Aerobics Manualfavoloso1Pas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Green Road Term 2 Trial Exam 2019 MSDocument4 pagesSMK Green Road Term 2 Trial Exam 2019 MSvoon sjPas encore d'évaluation
- L. A. Geddes ME, PHD Auth. Handbook of Blood Pressure MeasurementDocument171 pagesL. A. Geddes ME, PHD Auth. Handbook of Blood Pressure MeasurementYashPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsRasendria FirdiansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Pressure and SoundDocument45 pagesBlood Pressure and SoundRamanathan SunderPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Download Book Ecg in 10 Days PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Ecg in 10 Days PDFdeborah.arnaud284100% (14)
- Cvs MnemonicsDocument3 pagesCvs MnemonicsSuneel Kaushik KPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg Heart Sounds Laboratory HandoutDocument7 pagesEcg Heart Sounds Laboratory HandoutShashank SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Document89 pages3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Sheryl Layne Lao-SebrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz Cardiovascular Part 1 of 3Document30 pagesQuiz Cardiovascular Part 1 of 3MedShare90% (10)
- Blood Flow Mechanics in Cardiovascular DevelopmentDocument15 pagesBlood Flow Mechanics in Cardiovascular Developmentromane gaston bretonPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument64 pagesCongestive Heart FailureBentoys StreetPas encore d'évaluation
- Shocks MCQDocument6 pagesShocks MCQJaya Krishna Naidu100% (1)
- A Practical Approach To Clinical Echocardiography (2014) (PDF) PDFDocument423 pagesA Practical Approach To Clinical Echocardiography (2014) (PDF) PDFDiana Loloiu67% (3)
- CDI Physician Query For CHFDocument1 pageCDI Physician Query For CHFMuskegPressPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/21 October/November 2021Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/21 October/November 2021lllllisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gambaran - Ekg - Infark - Miokard (Dr. Erwin A)Document39 pagesGambaran - Ekg - Infark - Miokard (Dr. Erwin A)Lingga GumelarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Nursing Review NleDocument46 pagesPediatric Nursing Review NleClarissa GuifayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Heart BlockDocument59 pagesComplete Heart BlockJoan Rae Tan71% (7)
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesBlood Circulatory SystemAathifa ThowfeekPas encore d'évaluation