Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Jumpover Detail of Jacketed Pipe
Transféré par
reach_arindom0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
253 vues3 pagesJACKET
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentJACKET
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
253 vues3 pagesJumpover Detail of Jacketed Pipe
Transféré par
reach_arindomJACKET
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Certificate Course
on
PIPING ENGINEERING
May 7 - 20, 2008
DESIGN OF JACKETED PIPING
T. N. Gopinath
Consultant
Organized by
Piping Engineering Cell
Computer Aided Design Centre
Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
Powai, Mumbai - 400 076
PIPING ENGINEERING CELL
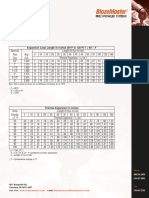
2.3. Thickness of Jacket Pipe:
Jacket pipes have to be designed for
internal pressure, which the jacket fluid
exerts. The formula given in clause
319.4.1 of the code shall be followed
with the standard procedure,
24 — Types of Jacketing:
Depending upon the criticality of the
requirement, the jacketing of the piping
system can be done:
(Only on straight pipe keeping all
bends and flange welds exposed.
eee
Fig. 22a
Gi) On straight pipes and elbows but
keeping the flange size same as that of
the core pipe
Fig. 226
(ii) On straight pipes and elbows
with flange size that of the jacket pipe.
(Reducing flanges)
JacketedPiping doc
Fig. 22€
This type is used where jacketing
requirements are critical. The slip on
type flanges are modified to get a seating
of the jacket pipe to achieve a proper
welding joint. (Refer Fig. 2.7)
2.5 Jumper Pipes:
To maintain the continuation of fluid
flow in the jacket, jumper pipes are
provided. The location of jumper pipes
on the horizontal jacketed pipe is
decided based on the type of fluid in the
jacket pipe. There can be a single jumper
‘or two jumpers and these can be placed
in one of the following pattems:
PIPING ENGINEERING CELL
k=
pa
cra
os
7 |
ha
Fig. 23
When the heating fluid is in vapor form
and no condensation is expected,
arrangement as per Patter I ean be used.
The arrangement in Pattern I makes the
vapor phase as well as the liquid phase
continuous and is ideal when steam is,
used as a heating medium in the jacket.
When the jacketing fluid is a liquid
under sufficient pressure, arrangement as
per Pattern IT or Pattern TV can be used
The arrangement for connection as per
Pattem IV is difficult to fabricate, as the
hole on the jacket pipe has to be cut to
profile. Patten =V— shows — the
arrangement in a vertical pipeline. In all
types of arrangements it should be
censured that the jumper joins the jacket
pipe at minimum distance from the
breakout flange in order to avoid cold
spots due to stagnancy. The jumper
should also be provided with
dismantling arrangement, cither flange
joints or unions, flange joint being
preferred.
JacketedPiping.doc
2.6 Spacers:
In order to keep the core pipe
concentric with the jacket pipe, supports
are provided at definite intervals. These
are done by welding flat or bar to the
core pipe called spacers. These spacers
will be stitch welded to the core pipe.
Flats. are preferred as the restrictions in
the jacket flow are minimum in this case.
The arrangement shall be as shown in
the sketch below
“psrace
pricxer
“cone DIE psTCTH
WELD
Fig. 24
NOTES: -
i) Material of spacers shall as that
of the core pipe.
ii) Spacers near to pipe bend should
be located at least 1000 mm
away from the centerline of
bend,
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1erection Drawing of DM Water Tank - T75.5AB - U-HWS - R2Document1 page1erection Drawing of DM Water Tank - T75.5AB - U-HWS - R2reach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Heat ExchangersDocument88 pages02 - Heat ExchangersDana GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Stress Strain 1Document20 pages13 Stress Strain 1Razell RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Understand The Harmonic Analysis and Ensure The Pressure Pulsation Comply With API 674 With PDFDocument11 pagesUnderstand The Harmonic Analysis and Ensure The Pressure Pulsation Comply With API 674 With PDFreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp LoopDocument37 pagesExp Loopreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Ibr Acceptable Weld JointDocument10 pagesIbr Acceptable Weld Jointreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Film Review - Chak de IndiaDocument2 pagesFilm Review - Chak de Indiareach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel-Tables 2 PDFDocument110 pagesSteel-Tables 2 PDFMahmoud AllamPas encore d'évaluation
- British Steel European Ipe Sections DatasheetDocument3 pagesBritish Steel European Ipe Sections Datasheetreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word Documentreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Arindom Kundu Language ItalianDocument1 pageArindom Kundu Language Italianreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Area Reinforcement CalculatorDocument5 pagesArea Reinforcement CalculatorAnonymous Iev5ggSR100% (1)
- Arindom Kundu Language RussianDocument1 pageArindom Kundu Language Russianreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Ramps Reflect Pragmatism After Fatal Runway Overrun IncidentsDocument8 pagesEmergency Ramps Reflect Pragmatism After Fatal Runway Overrun Incidentsreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Set Up of Day Care CentreDocument1 pageProject On Set Up of Day Care Centrereach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- IBR DetailsDocument10 pagesIBR Detailsreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Fire Water Calculation-Pol Depot, Asoj: LPM/M LPM/M LPM/M LPM/M LPM/MDocument1 pageRevised Fire Water Calculation-Pol Depot, Asoj: LPM/M LPM/M LPM/M LPM/M LPM/Mreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- IBR Thickness CalculationDocument17 pagesIBR Thickness Calculationreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Anchor / Nozzle Movements For Vertical VesselDocument17 pagesSummary of Anchor / Nozzle Movements For Vertical Vesselreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- DummyDocument12 pagesDummyrajkamal eshwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyke Sizing CalculationDocument1 pageDyke Sizing Calculationreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of anchor nozzle movementsDocument18 pagesSummary of anchor nozzle movementsreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Ows Piping Size2BLDocument3 pagesOws Piping Size2BLreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Exloop 3dimDocument69 pagesExloop 3dimreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Expansion Loop Length FormulaDocument1 pageExpansion Loop Length Formulareach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Expansion Data PDFDocument4 pagesThermal Expansion Data PDFFabio OkamotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating beam deflection and stresses using Young's modulus, moment of inertia, and applied loadDocument2 pagesCalculating beam deflection and stresses using Young's modulus, moment of inertia, and applied loadreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM material cross-reference chart for valves, fittings and flangesDocument1 pageASTM material cross-reference chart for valves, fittings and flangessgm6911Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bechtel - Use of Startup StrainerDocument17 pagesBechtel - Use of Startup Strainerreach_arindomPas encore d'évaluation
- Failure theories-IITMDocument5 pagesFailure theories-IITMsunil_patil_38Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)