Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Quarter Final 10 Mercury
Transféré par
Joram Ray Obiedo100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
168 vues2 pagesexam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentexam
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
168 vues2 pages2nd Quarter Final 10 Mercury
Transféré par
Joram Ray Obiedoexam
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Madrid National High School
Nat’l Highway, Linibunan, Madrid, Surigao del Sur
Second Quarter Midterm Examination
Science 10 LRN:
09.22.2017
I. Multiple Choice Test.
Direction(s): Read the following items carefully. Choose the correct answer, write the letter of your choice in your answer sheet.
1. In which case or cases is electric field present?
I. A spark jumping between two nearby rods. II. A charge that sis momentarily at rest. III. A rotating bar magnet.
a. I only b. I and II only c. II and III only d. I, II and III
2. Which statement about electromagnet is TRUE?
a. The electric field surrounding a battery-powered electromagnet alternates constantly.
b. The current in the electromagnet coil temporarily magnetizes the iron core.
c. The electric field strength is inversely proportional to the current,
d. The magnetic field line produced are all straight.
3. Which arrangement of three bar magnets results to an attraction between the first and the second, and a repulsion between the second and the third magnet?
MAGNET 1 MAGNET 2 MAGNET 3
a.
N S N S S N
b. N S S N N S
c. S N N S N S
d. S N S N S N
4. Which set ups model the working principle of a transformer and an electric generator respectively?
b. c.
a.
d.
5. What transformation can take place in a ceiling fan’s electric motor?
a. Electrical energy into mechanical energy
b. Mechanical energy into electrical energy
c. Alternating current into direct current
d. Direct current into alternating current
6. What basic principle enables ALL electric generators to operate?
a. Iron is the only element that is a magnetic
b. Opposite electric charges attract and like charges repel.
c. A closed-loop conductor within a changing magnetic field will have an induced emf.
d. A current-carrying conductor placed within a magnetic field will experience a magnetic force.
7. Which EM wave has the highest frequency?
a. Infrared b. Radio waves c. X-rays d. Gamma rays
8. Which property spells the difference between radio waves and visible light radiation?
a. Color b. Speed in vacuum c. Wavelength d. None of the choices
9. What type of electromagnetic waves is used in radar?
a. Infrared rays b. Microwaves c. Radio waves d. Ultra-violet rays
10. Which two waves lie at the ends of the visible spectrum?
a. Infrared and Ultra-violet rays b. Radio waves and Microwaves c. Radio waves and X-rays d. X-rays and Gamma rays
11. In the visible spectrum, which color has the longest wavelength?
a. Blue b. Green c. Red d. Violet
12. Which property spells the difference between infra-red and ultra-violet radiation?
a. Color b. Speed in vacuum c. Wavelength d. None of the choices
13. A certain radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 675 kHz. What is the wavelength of the radio waves?
a. 280 m b. 324 m c. 400 m d. 444 m
14. Which of the following is a characteristic of image formed by plane mirror?
a. Inverted b. Real c. Upright d. Magnified
15. Images which cannot be seen on the screen are called
a. Diminished images b. Real images c. Virtual images d. Inverted images
16. The sky looks blue at noon. This caused by
a. The scattering of blue light by the particles in the atmosphere.
b. The reflection of blue light from the ocean
c. The reflection of blue light from the surface of the earth
d. The absorption of blue light by the particles in the atmosphere
17. Which color of light is scattered the least?
a. Red b. Green c. Blue d. Orange
18. If a light ray strikes a flat mirror at an angle of 27° from the normal, the reflected ray will be
a. 27° from the mirror’s surface. b. 90° from the mirror’s surface. c. 27° from the normal. d. 63° from the normal.
19. When a light ray moves from air into glass at an angle of 45°, its path is
a. bent toward the normal. b. bent away from the normal. c. parallel to the normal. d. not bent.
20. Which of the following describes what will happen to a light ray incident on a glass- to-air boundary at greater than the critical angle?
a. total internal reflection b. partial reflection, partial transmission c. total transmission d. partial reflection, total transmission
21. What kind of wave does not even require a medium to transfer energy?
a. sound waves b. water waves c. light waves d. a child’ jump rope
22. Part of a pencil that is placed in a glass of water appears bent in relation to the part of the pencil that extends out of the water. What is this phenomenon called?
a. interference b. refraction c. diffraction d. reflection
23. In a vacuum, electromagnetic radiation of short wavelengths
a. travels as fast as radiation of long wavelengths.
b. travels slower than radiation of long wavelengths.
c. travels faster than radiation of long wavelengths.
d. can travel both faster and slower than radiation of long wavelengths.
24. When red light is compared with violet light in a vacuum,
a. both have the same frequency.
b. both have the same wavelength.
c. red light has a higher frequency.
d. red light has a higher wavelength.
25. Which of the following is NOT an electromagnetic wave?
a. radio wave b. visible light c. sound waves d. gamma rays
26. Which of the following electromagnetic waves has the highest energy?
a. radio wave b. microwaves c. visible light d. gamma rays
27. A prism is used to spread sunlight into its spectrum of colors and a second prism (and lens) is used to combine these colors. What is the resultant light when
all colors are added?
a. a double rainbow b. white light c. black light d. ultraviolet light
28. Arrange the following regions of electromagnetic waves from lowest frequency to highest frequency
I. Ultraviolet rays II. Visible Light III. Gamma Ray IV. Radio Waves
a. IV, II, I, III b. IV, I, II, III c. IV, III, I, II d. IV, II, III, I
29. Which of the following has the smallest wavelength?
a. Radio Waves b. Visible Light c. Gamma Rays d. Ultraviolet Rays
30. No matter what its source, EM radiation travels in vacuum at the same speed. As we knew the speed of light in vacuum is defined to be,
a. 2.700x107m/s b. 3.0x108m/s c. 2.9x107m/s d. 3.1x108m/s
31. When light is transmitted from one material to another, the frequency of the light is
a. changed, but the wavelength and wave speed can change.
b. unchanged and the wavelength and wave speed can’t change.
c. changed and the wavelength and wave speed can’t change.
d. unchanged, but the wavelength and wave speed can change.
32. How much larger will your classroom seem to appear if the entire two adjacent walls of your classroom consist of plane mirrors?
a. 2x larger b. 3x larger c. 4x larger d. can’t be determined
33. Where is the image located if an object is 30 cm in front of convex mirror with a focal length of 20 cm?
a. Between F and V b. Between C and F c. In front of the mirror d. Can’t be determined
34. What is the distance of your image from you if you stand 1.5m in front of a plane mirror?
a. 1.5 m b. 2.0 m c. 3.0 m d. 4.5 m
35. Zed stands 1.5-m tall in front of a plane mirror. What is the height of his image?
a. 4.5 m b. 3.0 m c. 2.0 m d. 1.5 m
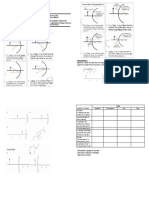
36. Given the figure at the right determine the image location, orientation, size and type.
a. Behind the mirror, inverted, reduced and virtual
b. In front of the mirror, inverted, enlarged and real
c. Behind the mirror, upright, enlarged and virtual
d. In front of the mirror, upright, reduced and real
37. Given the figure at the right determine the image location, orientation, size and type.
a. Behind the mirror, upright, reduced and virtual
b. In front of the mirror, upright, enlarged and real
c. Behind the mirror, inverted, enlarged and virtual
d. In front of the mirror, inverted, reduced and real
38. A light ray traveling obliquely to a convex mirror’s axis, goes directly to the mirror’s center of curvature before striking the mirror’s surface. What is the direction
of the reflected ray after hitting the mirror?
a. It travels parallel to the mirror’s axis
b. It passes through the mirror’s focal point
c. It travels at right angles to the mirror’s axis
d. It travels back through the mirror’s center of curvature.
39. Why is it easier to read a newspaper than a glossy magazine?
a. Because incident rays of light on a newspaper reflect in different directions while incident rays of light on a glossy magazine reflect in only one direction.
b. Because incident rays of light on a newspaper reflect in only one direction
while incident rays of light on a glossy magazine reflect in different directions.
c. Because incident rays of light on a glossy magazine converge at the focus.
d. Because incident rays of light on a newspaper converge at the focus.
40. What kind of mirror is used by department stores to give a wider area and smaller image of the shoppers/buyers?
a. Plane mirror b. Convex mirror c. Concave mirror d. None of the choices
41. An object is placed between a concave mirror and its focal point. What is the type and orientation of the image formed?
a. virtual and inverted b. virtual and erect c. real and inverted d. real and erect
42. A known Physicist who contributed in developing equations showing the relationship of electricity magnetism.
a. Andrei Marie Ampere b. James Clerk Maxwell c. Michael Faraday d. Christian Has Oersted
43. Cell phones and satellites uses what type of EM waves?
a. Radio Waves b. Microwaves c. Gamma Rays d. Visible Light
44. What are EM waves with wavelengths between 1mm & 750 billionths of a meter that is used daily in remote controls, to read CD-ROMs?
a. Radio Waves b. X-ray c. Gamma Rays d. Infrared
45. It is important for our bones to absorb Vitamin B. Which of the following EM waves helps body make vitamin D for healthy bones and teeth and is also used to
sterilize medical supplies & equipment?
a. UV Waves b. X-ray c. Gamma Rays d. Radio Waves
46. Which of the following devices uses visible light?
a. Endoscope b. MRI c. Cellphones d. Linear Accelerator
47. Both of these EM waves can cause cancer in a short exposure of time, which of these pair?
a. Gamma Rays and Visible Light b. Radio Waves and Infrared c. Visible Light and Infrared d. UVA and UVB
48. If some EM waves can cause skin diseases, which of the following EM waves can treat skin discoloration using Photodynamic Therapy?
a. Radio Waves b. Microwaves c. Gamma Rays d. Visible Light
49. X-ray and other radiation can damage the DNA and kills them, how does Radiotherapy works?
a. kills the rapidly-dividing cancer cells
b. bombards radiation to cancer cells thereby letting them grow in number
c. kills healthy cells through radiation
d. heats the body to kill the cells
50. Which of the following EM waves are used by ophthalmologist in scanning laser ophthalmoscope?
a. Radio Waves b. Microwaves c. Gamma Rays d. Visible Light
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishJoram Ray Obiedo100% (8)
- Simulating Fraunhofer Diffraction of Waves Using Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet PDFDocument12 pagesSimulating Fraunhofer Diffraction of Waves Using Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet PDFGlenn Araya VillalobosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocean Wave Hydrodynamics Tutorial ProblemsDocument6 pagesOcean Wave Hydrodynamics Tutorial Problemsramakrishnan saravananPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL 2ND PERIODICAL EXAM SCIENCE 10 2K23 A4 SizeDocument10 pagesFINAL 2ND PERIODICAL EXAM SCIENCE 10 2K23 A4 Sizemaverick arquilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Cfc-Mer1 Talk6 - FinalDocument36 pagesCfc-Mer1 Talk6 - FinalJoram Ray Obiedo100% (4)
- MER1-Participants ManualDocument17 pagesMER1-Participants ManualJoram Ray Obiedo100% (5)
- Questions & Answers On Transmission LinesDocument43 pagesQuestions & Answers On Transmission Lineskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Optical Fiber Characterization: Apparatus AvailableDocument5 pagesOptical Fiber Characterization: Apparatus AvailablearpitPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 ReviewDocument3 pagesScience 10 ReviewMarl Rina EsperanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Quarter Exam 22-23Document7 pagesSecond Quarter Exam 22-23Marife GuadalupePas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 Second Summative Test With Tos 2021 2022Document9 pagesScience 10 Second Summative Test With Tos 2021 2022Angelita MenesesPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Exam in Science 10Document5 pagesSummative Exam in Science 10Maren PendonPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Periodical Examination Science Grade 10Document6 pagesSecond Periodical Examination Science Grade 10Walter Orpilla100% (1)
- Summative Assessment in Grade 10 ScienceDocument5 pagesSummative Assessment in Grade 10 ScienceLianne Marie Cabangin0% (1)
- 10 With AnsDocument5 pages10 With AnsElma Ortega CamionPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci10 q2 Second Summative TestDocument2 pagesSci10 q2 Second Summative TestAilyn Carlos-Dizon100% (1)
- Science ExamDocument2 pagesScience ExamMary Jane Aguilar100% (2)
- 2ND Periodical Test in Science 10Document6 pages2ND Periodical Test in Science 10Aple RigorPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Written Test in Science 9 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022Document5 pagesSecond Written Test in Science 9 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022joan marie PeliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Science SUMMATIVE TEST 3Document2 pagesGrade 10 Science SUMMATIVE TEST 3Vannie MonderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 2nd GRADING ExamDocument3 pagesScience 10 2nd GRADING ExamBeaulah Yliel BaliongPas encore d'évaluation
- Science10 q4 Mod9 Chemicalreactionrates v5Document29 pagesScience10 q4 Mod9 Chemicalreactionrates v5Vicente SazilPas encore d'évaluation
- Third Quarter Test in Grade 10 ScienceDocument8 pagesThird Quarter Test in Grade 10 ScienceFroilan AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Magnetic Reversal ExamDocument1 pageGrade 10 Magnetic Reversal Examirene299Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Development of Electromagnetic Wave TheoryDocument20 pagesThe Development of Electromagnetic Wave TheoryJUDHEL BEQUILLOPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Periodic Test Grade10Document5 pagesSecond Periodic Test Grade10Marl Rina EsperanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 2nd Quarter Lesson SummaryDocument3 pagesScience 10 2nd Quarter Lesson SummaryAbigail CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Q3 Test10 Dapadap-V2.0Document5 pagesQ3 Test10 Dapadap-V2.0Alyssa F. DapadapPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Document8 pagesEnergy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Venice Gwyn ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Q2Document6 pages1st SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Q2Sabnahis Batongbuhay ExtensionPas encore d'évaluation
- q3 w3 Science 10 Learning Guide2021 2022Document14 pagesq3 w3 Science 10 Learning Guide2021 2022Arianne Jewel Contrillas100% (1)
- SCIENCE 10 4th TMTDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 10 4th TMTkaycin Duzon100% (1)
- ACTIVITY NO Amazing Waves!Document10 pagesACTIVITY NO Amazing Waves!Merlyn Mendoza100% (2)
- Long Test Science 10 2nd QuarterDocument29 pagesLong Test Science 10 2nd QuarterAple RigorPas encore d'évaluation
- g10 2nd Periodical TestDocument2 pagesg10 2nd Periodical TestSHIELLA MALANOGPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Assessment Test (Refraction in Lenses and Mirrors)Document21 pagesPre Assessment Test (Refraction in Lenses and Mirrors)Kenneth Roy Matuguina100% (1)
- 2nd Periodical ExamDocument2 pages2nd Periodical ExamAbegail FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Week 5 & 6Document4 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Week 5 & 6Esther Mae Ann TrugilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Banban National High School Science 10Document4 pagesBanban National High School Science 10robert valdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 - Q2 - LP4 Answer SheetDocument9 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - LP4 Answer SheetKeifer Lee0% (1)
- Week 2 3 Mirror 21 22.pptx 1Document90 pagesWeek 2 3 Mirror 21 22.pptx 1clairearabelle iloyPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Periodical Test in Science 10Document2 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 10tolisPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Quarter Exam Science 10Document2 pages1st Quarter Exam Science 10mj Canilang100% (1)
- Development Team of The Learners' Activity SheetsDocument7 pagesDevelopment Team of The Learners' Activity SheetsKevn KvenPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Answers Q2 M 1Document4 pagesScience Answers Q2 M 1Krisha RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 - Q2 - M9Document12 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - M9John Edmund PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 2ND Summative TestDocument2 pagesScience 10 2ND Summative TestEmerlyn Joseph100% (1)
- Science 10 Summative Test 3RD QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 10 Summative Test 3RD QuarterEsther Mae Ann TrugilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Unified Summative Test in Science 9 Quarter 2Document7 pagesUnified Summative Test in Science 9 Quarter 2RaquelPas encore d'évaluation
- 1ST Quarter Exam Science 10Document8 pages1ST Quarter Exam Science 10Bryan de VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Torio, John Carl T. Science 10 q2 Week 6Document12 pagesTorio, John Carl T. Science 10 q2 Week 6carl twqePas encore d'évaluation
- Lets Mark The BoundariesDocument18 pagesLets Mark The BoundariesndramonedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci10 SLM Q2 M4Document29 pagesSci10 SLM Q2 M4Jairos Marata BrasileñoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd QUARTER EXAM SCIENCE 10Document13 pages2nd QUARTER EXAM SCIENCE 10Manuela Kassandra Soriao Tribiana0% (1)
- SCIENCE 10 Q2 2nd Summative TestDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q2 2nd Summative TestpabsPas encore d'évaluation
- Quarter 2 - Module 2 Practical Applications and Effects of EM WavesDocument42 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 2 Practical Applications and Effects of EM WavesRex Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd TOS PTDocument2 pages3rd TOS PTAnne BongatPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 - Week 16Document6 pagesScience 10 - Week 16Mira VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci10Q2W5 - EFFECTS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES - EditedDocument14 pagesSci10Q2W5 - EFFECTS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES - EditedArchie CabaPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerZelle Miyazaki100% (1)
- Science 10 - Learning ModuleDocument16 pagesScience 10 - Learning Modulemn Kim100% (1)
- Grade 10 Diagnostic TestDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Diagnostic TestJr Capanang100% (1)
- Work Sheet: Four Principal Rays in Curved MirrorsDocument2 pagesWork Sheet: Four Principal Rays in Curved MirrorsGenesis LidanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science10 Chemistry Module3 2023-2024Document17 pagesScience10 Chemistry Module3 2023-2024mjmabini047100% (1)
- Science 9 Failed 2nd QuarterDocument34 pagesScience 9 Failed 2nd Quarterjoy100% (1)
- S10 - Q2 - Summative Test 1Document5 pagesS10 - Q2 - Summative Test 1Letsirk Saluta Ramos100% (1)
- 2nd Departmental TestDocument5 pages2nd Departmental TestMelody Delleva BarcialPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Midterm Exam Science 9Document4 pages2nd Midterm Exam Science 9Joram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Final - LAS ESP 10 - 3rd Quarter-Week 6 Edited - For PrintingDocument5 pagesFinal - LAS ESP 10 - 3rd Quarter-Week 6 Edited - For PrintingJoram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- LAC Certificate 2019Document1 pageLAC Certificate 2019Joram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Career GuidanceDocument3 pagesCareer GuidanceJoram Ray Obiedo100% (1)
- Mercury I.D.Document1 pageMercury I.D.Joram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- CLP Talk 9Document4 pagesCLP Talk 9Joram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- New American BibleDocument2 pagesNew American BibleJoram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- CLP Talk - 08Document5 pagesCLP Talk - 08Joram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Blessing & Lighting of Advent Wreath: (After The Greetings and Before The Penitential Rite)Document2 pagesBlessing & Lighting of Advent Wreath: (After The Greetings and Before The Penitential Rite)Joram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro AdventDocument1 pageIntro AdventJoram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fsuu HistoryDocument3 pagesFsuu HistoryJoram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Father Saturnino Urios University: Graduate Studies Butuan CityDocument2 pagesFather Saturnino Urios University: Graduate Studies Butuan CityJoram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Talk 6 HealingDocument6 pagesTalk 6 HealingJoram Ray ObiedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentos de Fisica Hoolliday Parcial SolucionarioDocument5 pagesFundamentos de Fisica Hoolliday Parcial SolucionarioAlejandro Zambrano ValbuenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave GuideThe first structure for guiding waves was proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1893, and was first experimentally tested by Oliver Lodge in 1894. The first mathematical analysis of electromagnetic waves in a metal cylinder was performed by Lord Rayleigh in 1897.[3] For sound waves, Lord Rayleigh published a full mathematical analysis of propagation modes in his seminal work, “The Theory of Sound”.[4] The study of dielectric waveguides (such as optical fibers, see below) began as early as the 1920s, by several people, most famous of which are Rayleigh, Sommerfeld and Debye.[5] Optical fiber began to receive special attention in the 1960s due to its importance to the communications industry.Document1 pageWave GuideThe first structure for guiding waves was proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1893, and was first experimentally tested by Oliver Lodge in 1894. The first mathematical analysis of electromagnetic waves in a metal cylinder was performed by Lord Rayleigh in 1897.[3] For sound waves, Lord Rayleigh published a full mathematical analysis of propagation modes in his seminal work, “The Theory of Sound”.[4] The study of dielectric waveguides (such as optical fibers, see below) began as early as the 1920s, by several people, most famous of which are Rayleigh, Sommerfeld and Debye.[5] Optical fiber began to receive special attention in the 1960s due to its importance to the communications industry.JonatanVignattiPas encore d'évaluation
- ISS Minimalist AntennaDocument7 pagesISS Minimalist AntennaBoed SPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1.part1Document71 pagesTopic 1.part1Apek OwePas encore d'évaluation
- Mynotes NobookDocument554 pagesMynotes Nobookgeopaok165Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diffraction and Interference of Light: PurposeDocument14 pagesDiffraction and Interference of Light: PurposeCassia MontiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sonar For Practising Engineers, 3rd EditionDocument323 pagesSonar For Practising Engineers, 3rd Editionvladimirmota1086% (7)
- Tomasi Chapter 14 - Electromagnetic Wave PropagationDocument4 pagesTomasi Chapter 14 - Electromagnetic Wave PropagationJohn DelrosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- EQ Cheat Sheet v1Document1 pageEQ Cheat Sheet v1notbuggedPas encore d'évaluation
- Aq6375 Optical Spectrum Analyzer For Long Wavelength Band: MORI Tohru ISHIHARA Gentarou KANEKO Tsutomu HORIGUCHI AtsushiDocument4 pagesAq6375 Optical Spectrum Analyzer For Long Wavelength Band: MORI Tohru ISHIHARA Gentarou KANEKO Tsutomu HORIGUCHI AtsushiGhallab AlsadehPas encore d'évaluation
- Fresnel and Fraunhoffer Diffraction: Doshi Siddharth KalpeshDocument29 pagesFresnel and Fraunhoffer Diffraction: Doshi Siddharth KalpeshRanjith R MenonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Measurement of A Transverse Profile of Laser Beam by Knife Edge MethodDocument6 pagesThe Measurement of A Transverse Profile of Laser Beam by Knife Edge Method陳宜粲Pas encore d'évaluation
- Light 7 QPDocument8 pagesLight 7 QPHabibullah AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- F5C1 (Tutorial1 6)Document3 pagesF5C1 (Tutorial1 6)ChewLee TanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3DS Max Lighting IntroductionDocument2 pages3DS Max Lighting IntroductionAnonymous ga7hz9xYPas encore d'évaluation
- Chptr10 PDFDocument111 pagesChptr10 PDFEddy VinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Amplitude and Phase ErrorDocument10 pagesAmplitude and Phase ErrorkainPas encore d'évaluation
- Work JournalDocument3 pagesWork JournalJamsheed YazdaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Data: PULSE Acoustic Material Testing in A Tube Type 7758Document4 pagesProduct Data: PULSE Acoustic Material Testing in A Tube Type 7758Joe Boby SoegiartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Chapter 2 - AnsDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 2 - AnsMohd Äwiw Vießar AvondrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Mechanism of The Ultrasound On The Bosnian Pyramid of The SunDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic Mechanism of The Ultrasound On The Bosnian Pyramid of The SunRiccardo GardanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-4 OkDocument20 pagesUnit-4 Oksaahasitha 14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Wireless Communications 3rd Edition Olenewa Test BankDocument8 pagesGuide To Wireless Communications 3rd Edition Olenewa Test BankJohnDeckerfrgam100% (16)
- PCS VR 17 10506 2DDocument2 pagesPCS VR 17 10506 2Dshaker76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activities Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Unit 1 - Task 1 - Electromagnetic Waves in Open MediaDocument8 pagesActivities Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Unit 1 - Task 1 - Electromagnetic Waves in Open MediaMargarita Diaz NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Research ArticleDocument12 pagesResearch ArticleSyed BukhariPas encore d'évaluation
















































































![Wave GuideThe first structure for guiding waves was proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1893, and was first experimentally tested by Oliver Lodge in 1894. The first mathematical analysis of electromagnetic waves in a metal cylinder was performed by Lord Rayleigh in 1897.[3] For sound waves, Lord Rayleigh published a full mathematical analysis of propagation modes in his seminal work, “The Theory of Sound”.[4] The study of dielectric waveguides (such as optical fibers, see below) began as early as the 1920s, by several people, most famous of which are Rayleigh, Sommerfeld and Debye.[5] Optical fiber began to receive special attention in the 1960s due to its importance to the communications industry.](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/271246987/149x198/5216e5a1f9/1436622029?v=1)























