Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Gas 12 2nd Quarter
Transféré par
Roldan Ormilla0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
49 vues2 pagesscie
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentscie
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
49 vues2 pagesGas 12 2nd Quarter
Transféré par
Roldan Ormillascie
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
_____1.
In the absence of a net force, a moving object will
a. slow down and eventually stop
b. turn right
c. stop immediately
d. move with constant velocity
_____2.When the engines on a rocket ship in deep space, far from any other objects, are turned off, it will
a. slow down and eventually stop
b. stop immediately
c. turn right
d. move with constant velocity
_____3.In order for a rocket ship in deep space, far from any other objects, to move in a straight line with
constant speed it must exert a net force that is
a. proportional to its mass
b. proportional to its weight
c. proportional to its velocity
d. zero
_____4.If a book on the dashboard of your car suddenly flies towards you, the forward velocity of the car
must have
a. decreased
b. increased
c. changed direction to the right
d. become zero
_____5.Which Newton’s law can explain the following statement that we often see on the highway
display: “Buckle up –it’s the State Law”?
a. First Newton’s Law
b. Third Newton’s Law
c. Second Newton’s Law
d. None from the above
_____6.The acceleration of an object is proportional to
a. the net force acting on it
b. its velocity
c. its position
d. its mass
_____7.The acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to
a. the net force acting on it
b. its velocity
c. its position
d. its mass
_____8.When a baseball is struck by a bat, the force of the bat on the ball is equal and opposite to the
force of the ball on the bat. This is an example of
a. Newton's first law
b. Newton's second law
c. Newton's third law
d. Newton's law of gravitation
_____9. If you exert a force F on an object which has a much greater mass than you do, the force which
the object exerts on you will
a. be of magnitude F and in the same direction
b. be of magnitude F and in the opposite direction
c. be of much greater magnitude than F
d. be zero
_____10. Newton’s third law refers to “action-reaction forces”. These forces always occur in pairs and
a. sometimes act on the same object
b. always act on the same object
c. never act on the same object
d. always act at right angles
_____11. Action-reaction forces are
a. equal in magnitude and point in the same direction
b. equal in magnitude and point in opposite directions
c. unequal in magnitude but point in the same direction
d. unequal in magnitude and point in opposite directions
_____12. A car traveling at 40 m/s strikes a mosquito. Which of the following is the true statement?
a. The force on the mosquito is greater than the force on the car
b. The force on the mosquito is equal to the force on the car
c. The force on the mosquito is smaller than the force on the car
d. The damage to the mosquito is equal to the damage to the car
e. None from the above
_____13. If a baseball and cannon ball are dropped from the same height at the same time in a vacuum,
which ball will hit the ground first?
a. The cannonball
b. The baseball
c. The balls land at the same time
d. The ball with the larger volume
_____14. According to newton’s first law of motion, a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced
force will
a. Remain in motion
b. Eventually come to a stop
c. Change its momentum
d. Accelerates
_____15. If an action force is a cue ball (white) hitting a billiard ball (various color) when playing pool
then the reaction force is
a. Exerted on the table
b. Exerted on all the other billiard balls
c. Not present
d. Exerted by the billiard ball on the cue ball
_____16. A sled sliding on a flat icy surface with a constant velocity is best described by
a. Newton’s first law of motion for objects at rest
b. Newton’s first law of motion for objects in motion
c. Newton’s second law of motion
d. Newton’s third law of motion
Adddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddd
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Yes o Tree Planting ProposalDocument4 pagesYes o Tree Planting ProposalRoldan Ormilla91% (23)
- 4th Grading - Grade 9 Basic PhysicsDocument3 pages4th Grading - Grade 9 Basic PhysicsDiane Marr N. Dencio100% (1)
- Worksheet - Newton's First Law of MotionDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Newton's First Law of MotionCARYS BROWN100% (1)
- Summative Test 1 For Quarter 1Document2 pagesSummative Test 1 For Quarter 1Apple Jean Yecyec Alag100% (2)
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 GRADE 12 Q1 Summative Test 1 4Document3 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 1 GRADE 12 Q1 Summative Test 1 4Monica Solomon100% (1)
- DRRR Module 11 & 12Document16 pagesDRRR Module 11 & 12Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- End Plate Design As Per-Ec3Document18 pagesEnd Plate Design As Per-Ec36j7100% (1)
- Homeworks Newton's Laws of MotionDocument4 pagesHomeworks Newton's Laws of MotionNipuna LaksithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument8 pagesMultiple Choice: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionMona Mohamed SafwatPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8Document3 pagesScience 8Juan AnthonioPas encore d'évaluation
- General ZoologyDocument19 pagesGeneral ZoologySittie Fatmah Hayamirah SinalPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 - 1st Monthly TestDocument3 pagesScience 8 - 1st Monthly TestMaria Jocosa100% (1)
- Summative Test: Newton'S Law of MotionDocument2 pagesSummative Test: Newton'S Law of MotionOchia Justine100% (2)
- Q1 Science 8 Second Summative Test Sy 2022-2023Document1 pageQ1 Science 8 Second Summative Test Sy 2022-2023Maria Theresa BongatPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8: Reviewer For The Monthly ExamDocument4 pagesScience 8: Reviewer For The Monthly Examtwinckel mae bienesPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 1st Quiz 1 Newton's Law of MotionDocument2 pagesScience 8 1st Quiz 1 Newton's Law of MotionRyan BersaminPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Pop Quiz 1Document4 pagesScience Pop Quiz 1api-372548146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Is P - 3 Laws ReviewDocument5 pagesIs P - 3 Laws Reviewapi-308247166Pas encore d'évaluation
- Joseph and Mary Academy: Multiple ChoicesDocument3 pagesJoseph and Mary Academy: Multiple ChoicesAlyssa Mae DapadapPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions in Physics ScienceDocument21 pagesPractice Questions in Physics ScienceYaj CruzadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesPhysical Scienceynid wagePas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8: Quarter 1 - Module 1: of MotionDocument35 pagesScience 8: Quarter 1 - Module 1: of MotionirahmaePas encore d'évaluation
- Cons of Momentum Gravity Torque Study GuideDocument5 pagesCons of Momentum Gravity Torque Study GuideKenneth SienaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics Practice TestDocument10 pagesDynamics Practice Testyiyin97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Your Answer Sheet.: San Juan National High School Summative Test IDocument4 pagesYour Answer Sheet.: San Juan National High School Summative Test IJhaypee SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 1: Frames of Reference, Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Frames of Reference, Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionJacko LenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam PhysicsDocument2 pagesExam PhysicsAnalyn LampaPas encore d'évaluation
- Action ReactionDocument32 pagesAction ReactionglaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Newton's First Law of Motion For Objects at MotionDocument2 pagesB. Newton's First Law of Motion For Objects at MotionRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- WS - Physics - GR - 9 Part1Document12 pagesWS - Physics - GR - 9 Part1Abdelrhman AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 Science 8 First Summative Test Sy 2022-2023Document1 pageQ1 Science 8 First Summative Test Sy 2022-2023Maria Theresa BongatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Test FORCEDocument5 pagesChapter Test FORCEArnulfo Villasfer SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Unit 2 Practice Test Newton3Document4 pagesPhysics Unit 2 Practice Test Newton3Alejandro Bon50% (2)
- Newton SummativeDocument5 pagesNewton SummativeJulia Geonzon LabajoPas encore d'évaluation
- SCI8 Q1 M2 Newtons Laws of MotionDocument28 pagesSCI8 Q1 M2 Newtons Laws of MotionScribd User83% (6)
- Quiz No. 1 - 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesQuiz No. 1 - 1st QuarterRency ReynonPas encore d'évaluation
- 12u Newtons Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pages12u Newtons Multiple ChoiceTariq ZaitounPas encore d'évaluation
- EnrichmentDocument2 pagesEnrichmentChristine Joy Togonon AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Unit Test in ScienceDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Unit Test in ScienceKarl John Del CarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 ExamDocument5 pagesScience 8 Examangge21100% (1)
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 8Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 8Mary Apostol100% (1)
- PHYSICS 101 Test Bank 2Document24 pagesPHYSICS 101 Test Bank 2Leenie Anne Ang-AngcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phyc121 Week 5 9Document26 pagesPhyc121 Week 5 9Leycoline Almren100% (1)
- Phy C 1 ReviewerDocument21 pagesPhy C 1 ReviewerLeycoline Almren100% (1)
- Module 10 Force and MotionDocument48 pagesModule 10 Force and MotionJudy Panguito Aralar0% (1)
- Physics Chapter 4 - Test A: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesPhysics Chapter 4 - Test A: Multiple ChoiceCamdrn WrightPas encore d'évaluation
- SCI9 TQ 4thquarterDocument4 pagesSCI9 TQ 4thquarterAilen Rose SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1-Science 8Document7 pagesQ1-Science 8Reynalyn CalwitPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 10 Force and MotionDocument42 pagesModule 10 Force and MotionAcza Jaimee C. KalawPas encore d'évaluation
- CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDING TEST FinalDocument6 pagesCONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDING TEST FinalJanine Faye TagardaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Reviewer - Force and MotionDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Reviewer - Force and MotionMom Gie100% (2)
- Physical Science Leomar ExamDocument16 pagesPhysical Science Leomar ExamXtine Rivera - ParungaoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 8Document2 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 8Erwin Mercado100% (1)
- Guided Practice InertiaDocument2 pagesGuided Practice InertiaAdibah KamarPas encore d'évaluation
- InertiaDocument5 pagesInertiaHanie Balmedina-RazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument5 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questiontwinckel mae bienes100% (1)
- Class 9th Chapter Force and Laws of Motion Assertions - ReasonDocument6 pagesClass 9th Chapter Force and Laws of Motion Assertions - ReasonGarvitPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Quarter Summative Test No.1Document1 page3rd Quarter Summative Test No.1Marilou KimayongPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 8Document3 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 8Irish Jhaizel Kaye FuentesPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Grade 8 Science q1 Wk2Document18 pagesModule 2 Grade 8 Science q1 Wk2canizaresajPas encore d'évaluation
- I Like To Move It! Physical Science Book for Kids - Newton's Laws of Motion | Children's Physics BookD'EverandI Like To Move It! Physical Science Book for Kids - Newton's Laws of Motion | Children's Physics BookPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 2 Module 11Document8 pagesPhysics 2 Module 11Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 11 & 12 Physical Science 2nd SemDocument10 pagesWEEK 11 & 12 Physical Science 2nd SemRoldan Ormilla0% (1)
- Physics 2 Module 12Document10 pagesPhysics 2 Module 12Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Module in General Physics 1: First Semester Quarter 2Document1 pageLearning Module in General Physics 1: First Semester Quarter 2Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cover Physical ScienceDocument1 pageCover Physical ScienceRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves: Module 7 & 8Document12 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: Module 7 & 8Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Snells Law Problem Set 1Document1 pageSnells Law Problem Set 1Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- StemDocument1 pageStemRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Volcanic Hazard: Module 9 & 10Document16 pagesVolcanic Hazard: Module 9 & 10Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaining Comfort in All Our Tribulations: Pannakaliwliwa Kadagiti Amin A Pakarigatan TayoDocument5 pagesGaining Comfort in All Our Tribulations: Pannakaliwliwa Kadagiti Amin A Pakarigatan TayoRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media6656714696549685537Document1 pageLocal Media6656714696549685537Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthquakes and Types of Waves: Science 10Document14 pagesEarthquakes and Types of Waves: Science 10Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Torque QuizDocument1 pagePhysics Torque QuizRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document8 pages1Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Newton's First Law of Motion For Objects at MotionDocument2 pagesB. Newton's First Law of Motion For Objects at MotionRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Score: - Grade and Section: - DateDocument1 pageName: - Score: - Grade and Section: - DateRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10Document2 pagesScience 10Roldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
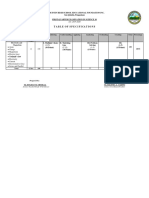
- Table of SpecificationsDocument2 pagesTable of SpecificationsRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- San Quintin High School Educational Foundation Inc. San Quintin, PangasinanDocument2 pagesSan Quintin High School Educational Foundation Inc. San Quintin, PangasinanRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Application LDocument8 pagesApplication LRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMDocument2 pagesCHEMRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- San Quintin High School Educational Foundation Inc. San Quintin, PangasinanDocument1 pageSan Quintin High School Educational Foundation Inc. San Quintin, PangasinanRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- San Quintin High School Educational Foundation Inc. San Quintin, PangasinanDocument3 pagesSan Quintin High School Educational Foundation Inc. San Quintin, PangasinanRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- LP Acid BAseDocument3 pagesLP Acid BAseRoldan OrmillaPas encore d'évaluation
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceRoldan Ormilla100% (3)
- COLOUMBDocument2 pagesCOLOUMBRoldan Ormilla0% (2)
- Circular Motion and GravitationDocument25 pagesCircular Motion and GravitationTypeNamePas encore d'évaluation
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology 2.006 Thermal-Fluids Engineering IIDocument5 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology 2.006 Thermal-Fluids Engineering IIMH MerhiPas encore d'évaluation
- CH10 Wave OpticsDocument105 pagesCH10 Wave OpticsAryan PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- CENG 5503: Design of Steel & Timber StructuresDocument37 pagesCENG 5503: Design of Steel & Timber StructuresBern Moses DuachPas encore d'évaluation
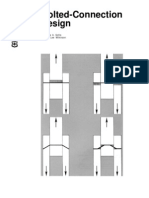
- Bolted-Connection Design: Forest ServiceDocument25 pagesBolted-Connection Design: Forest ServiceamarggPas encore d'évaluation
- STRUKTUR GABLE FRAME BAJA OKDocument26 pagesSTRUKTUR GABLE FRAME BAJA OKpriyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Note C01 - Chapter 3 5 - Load and Stress Analysis Failures Resulting From Static LoadingDocument31 pagesLecture Note C01 - Chapter 3 5 - Load and Stress Analysis Failures Resulting From Static LoadingHenry HongPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Charges and Fields MCQ Class 12 Physics Chapter 1Document8 pagesElectric Charges and Fields MCQ Class 12 Physics Chapter 1suousPas encore d'évaluation
- As OCR Mechanics QuestionsDocument167 pagesAs OCR Mechanics Questionszeeshan khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Expt#3, FinalDocument3 pagesExpt#3, Finalakhtar140Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metallurgical Thermodynamics Notes 1Document16 pagesMetallurgical Thermodynamics Notes 1Nigel FaranandoPas encore d'évaluation
- GR Endsem Spring 2022Document2 pagesGR Endsem Spring 2022Tarak Ram AlapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Point-to-Point Trajectory Generation Under Joint Constraints For Industrial RobotsDocument9 pagesPoint-to-Point Trajectory Generation Under Joint Constraints For Industrial RobotsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Punching Shear PDFDocument13 pagesPunching Shear PDFmohamedadel100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture1460085501 2Document526 pagesLecture1460085501 2Smruti Ranjan Pattanayak100% (1)
- Needle Roller BearingsDocument11 pagesNeedle Roller BearingsReyben RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Transom Output ForcesDocument6 pagesTransom Output ForcesAnonymous 0JQGC2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Open Channel FlowDocument19 pagesOpen Channel FlowRisci TaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Bin DesignDocument14 pagesBin DesignHogar Belo HorizontePas encore d'évaluation
- Slurry HandlingDocument15 pagesSlurry HandlingRodrigo GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- SFD & BMD PDFDocument1 pageSFD & BMD PDFRakesh SapkotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtons Laws: By: Armaan NooraniDocument10 pagesNewtons Laws: By: Armaan NooraniArmaan NooraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Loads and Forces Acting On Retaining Wall and Their CalculationsDocument7 pagesLoads and Forces Acting On Retaining Wall and Their CalculationsswapnilPas encore d'évaluation
- The Stability and Control of MotorcyclesDocument14 pagesThe Stability and Control of Motorcyclesyunde shiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reducer Catalog: Speed Reducers For Precision Motion ControlDocument51 pagesReducer Catalog: Speed Reducers For Precision Motion ControlJose Luis SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- M (V) - 22 Expansion JointDocument22 pagesM (V) - 22 Expansion Jointerkan aksoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete BasementsDocument184 pagesConcrete BasementsMohan BhalmePas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 Quarter 1 Learning Activity Sheet 01 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2Document7 pagesScience 8 Quarter 1 Learning Activity Sheet 01 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2shawnmiguel065Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slope ND DeflectionDocument19 pagesSlope ND DeflectionprashantbaraskarPas encore d'évaluation